
AMGLIDIA 6 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION

How to use AMGLIDIA 6 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
AMGLIDIA 6mg/ml oral suspension
glibenclamide
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as your child's.
- If your child gets any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Amglidia and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you start giving Amglidia
- How to give Amglidia
- Possible side effects
- Storing Amglidia
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is AMGLIDIA and what is it used for
Amglidia contains the active substance called glibenclamide, which belongs to a group of medicines called sulfonylureas, used to reduce blood sugar levels (blood glucose or glycemia).
Amglidia is used in newborns, infants, and children to treat diabetes that occurs at birth (known as neonatal diabetes mellitus). Neonatal diabetes is a disease in which the child's body does not release enough insulin to control blood sugar levels; Amglidia is used only in patients who maintain some ability to produce insulin.
It has been shown that sulfonylureas such as glibenclamide are effective in certain genetic mutations responsible for the origin of neonatal diabetes.
This medicine is an oral suspension that is administered in the mouth, making it a more comfortable treatment for newborns and children than regular insulin injections.
You should consult a doctor if your child worsens or does not improve after a few days.
2. What you need to know before you start giving AMGLIDIA
Do not give AMGLIDIA
- if your child is allergic to glibenclamide or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- if your child has ketoacidosis (high levels of acidic substances called ketone bodies in the blood),
- if your child has porphyria (inability to break down chemical substances in the body called porphyrins),
- if your child is receiving treatment with bosentan, a medicine used to treat blood circulation problems,
- if your child has severe kidney failure,
- if your child has severe liver failure.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor before starting to give Amglidia to your child.
Your child's blood sugar levels may become very low (hypoglycemia) after taking Amglidia. Inform the doctor if your child presents paleness, sweating, or an irregular heartbeat, if they seem disoriented or confused, or do not respond. See section 4 also. Low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia).
Ask your doctor how often you should measure your child's capillary blood sugar.
G6PD is an enzyme involved in sugar metabolism. If your child has a G6PD deficiency, they may experience abnormal red blood cell breakdown (acute hemolytic anemia) after taking Amglidia.
Inform the doctor if you know your child has a G6PD deficiency and contact them if you notice your child is pale compared to their usual color.
Inform your doctor if your child has kidney or liver disorders.
Your child may experience diarrhea when increasing the dose of glibenclamide in suspension, but it will be transient if the dose is maintained.
Your child may experience nausea. If your child is able to take glibenclamide in suspension, do not interrupt treatment.
Talk to your doctor if your child has experienced vomiting; in case of severe vomiting, the doctor may decide to treat your child with insulin until the vomiting stops.
In case of mild vomiting, the doctor may also decide to treat your child with an anti-vomiting medicine. In this case, Amglidia will be continued.
Children and adolescents
Amglidia is indicated for use in newborns, infants, and children.
Other medicines and AMGLIDIA
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if your child is taking, has recently taken, or might take any other medicines, as taking some medicines while taking Amglidia may result in more side effects or affect how Amglidia works.
It is especially important to inform your child's doctor or pharmacist about the following:
These medicines may decrease blood sugar levels when taken with Amglidia:
- ACE inhibitors (such as captopril and enalapril), used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).
- Anabolic steroids and male sex hormones (such as testosterone enanthate), used to treat low testosterone levels (testosterone deficiency).
- Biguanides (such as metformin), used to treat diabetes mellitus.
- Chloramphenicol (in case of oral administration), an antibiotic used to treat infections.
- Clarithromycin, an antibiotic used to treat certain infections.
- Cyclophosphamides, used to treat different types of cancer.
- Disopyramide, used to treat an irregular heartbeat.
- Fibrates (such as bezafibrate, fenofibrate, and gemfibrozil), used to reduce fat levels.
- Fluoxetine, used to treat depression and anxiety disorders.
- Heparin, used to reduce blood clotting.
- Ifosfamide, used to treat different types of cancer.
- Insulin, used to reduce blood sugar levels.
- MAO inhibitors (such as iproniazid), used to treat depression.
- Miconazole, used to treat fungal infections.
- Other oral antidiabetics (such as metformin), used to reduce blood sugar levels (blood glucose level).
- Oxypentifylline, used to improve blood flow in the limbs (peripheral blood flow).
- Probenecid, used to treat gout and gouty arthritis.
- Quinolone antibiotics (such as nalidixic acid and ciprofloxacin), used to treat infections.
- Sulfamethoxazole with trimethoprim (cotrimoxazole), used to treat infections.
- Salicylates (such as aminosalicylic acid and para-aminosalicylic acid), used for tuberculosis.
- Tetracycline antibiotics (such as doxycycline and minocycline), used to treat infections.
These medicines may increase blood sugar levels when taken with Amglidia:
- Acetazolamide, used to treat eye nerve disorders (glaucoma).
- Adrenaline (epinephrine and other sympathomimetic drugs), used to treat severe allergic reactions, cardiac arrest, and asthma.
- Barbiturates (such as phenobarbital), used to treat epilepsy.
- Calcium channel blockers (such as nifedipine), used to treat high blood pressure.
- Cimetidine, used to relieve symptoms of gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
- Corticosteroids (such as prednisone and prednisolone), used for various indications such as inflammation and asthma.
- Diazoxide, used to treat low blood sugar levels.
- Diuretics (such as furosemide and hydrochlorothiazide), used to treat high blood pressure in the arteries (arterial hypertension).
- Glucagon, used to treat high blood sugar levels (elevated blood glucose level).
- Isoniazid, used to treat tuberculosis.
- High doses of laxatives (such as macrogol).
- Nicotinic acid (in high doses), used to reduce high cholesterol and triglyceride levels, which are fatty substances in the blood.
- Estrogens (such as 17-β-estradiol), used for hormonal treatment.
- Phenothiazine derivatives (such as chlorpromazine), used to treat schizophrenia and other psychoses.
- Phenytoin, used to treat epilepsy.
- Progestogens (such as desogestrel and dydrogesterone), used for hormonal treatment.
- Rifampicin, used to treat infections such as tuberculosis.
- Thyroid hormones (such as L-thyroxine), used for hormonal treatment.
These medicines may decrease blood sugar levels or may mask low blood sugar levels when taken with Amglidia:
- Betablockers (such as propranolol), used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension), control irregular or rapid heart rhythms, and help prevent a new heart attack.
These medicines may affect blood sugar levels (may increase and/or decrease them) and/or blood sugar control when taken with Amglidia:
- Bosentan, used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension) in the blood vessels between the heart and lungs.
- Clonidine, used to treat high blood pressure in the arteries (arterial hypertension).
- Coumarin derivatives (such as dicumarol and acenocoumarol), used to reduce blood clotting.
- Colesevelam, used to reduce cholesterol.
- Coumarin derivatives (such as dicumarol and acenocoumarol), used to reduce blood clotting.
- Guanethidine, used to treat high blood pressure (hypertension).
- H2 receptor antagonists, used to reduce stomach acid (such as ranitidine) to relieve symptoms of gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome.
Cyclosporin, used to prevent organ rejection after transplantation.
- Increased risk of cyclosporin toxicity.
Alcohol.
- Alcohol may affect blood sugar levels.
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if your child is taking, has recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Using AMGLIDIA with alcohol
Both acute and chronic alcohol consumption may reduce the hypoglycemic effect of glibenclamide or potentiate it in a dangerous way by delaying its degradation in the body. After concomitant use of alcohol and glibenclamide, symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, flushing, dizziness, headache, chest and abdominal discomfort, and general symptoms similar to those of a hangover have occurred. Concomitant use of alcohol and glibenclamide should be avoided.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
This medicine is only used to treat neonatal diabetes in newborns, infants, and children.
This medicine is not indicated for use in pregnant women, and patients who intend to become pregnant should inform their doctor. It is recommended that these patients switch to insulin treatment.
Breastfeeding appears to be compatible, but as a precautionary measure, it is recommended to monitor the blood sugar levels of children who are exclusively breastfed.
Talk to your doctor to find out the best way to control blood sugar levels in case of pregnancy.
Driving and using machines
Glibenclamide may increase the risk of hypoglycemia and, therefore, may have a moderate influence on the ability to drive, cycle, or use machines.
You or your child should avoid activities that require balance (such as cycling or using a scooter) and driving or using machines if you or your child feel dizzy, tired, or unwell.
AMGLIDIA contains sodium
This medicine contains 2.80 mg of sodium per milliliter, equivalent to 0.1% of the maximum daily intake recommended by the WHO of 2 g of sodium for an adult, which should be taken into account in patients who have been advised to follow a low-salt diet (sodium).
AMGLIDIA contains sodium benzoate
This medicine contains 5 mg of sodium benzoate per milliliter of oral suspension. Sodium benzoate may increase the risk of jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) in newborns (up to 4 weeks of age).
3. How to Administer AMGLIDIA
Follow the administration instructions for this medication exactly as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
Dosage
Treatment with glibenclamida should be initiated by a doctor with experience in treating patients with very early-onset diabetes.
The dose of Amglidia depends on your child's body weight, and the doctor will calculate it as a volume (in milliliters) of oral suspension to be measured with the oral syringe (1 ml or 5 ml syringe) provided with the medication. Your doctor will prescribe the specific package size and concentration, including the specific syringe you should use. Do not use any other syringe to administer Amglidia.
It is essential that you do not adjust the doses of Amglidia or insulin yourself unless your child's doctor has specifically instructed you to do so.
Make sure to use the correct concentration of the medication and the appropriate oral syringe prescribed by your doctor to avoid accidental administration of too high or too low amounts. |
The initial dose of Amglidia is 0.2 mg of glibenclamida per kilogram (kg) of body weight per day, divided into two doses of 0.1 mg/kg. As the dose is increased, it is usually possible to reduce the dose of insulin the patient is already receiving and subsequently discontinue its administration.
If necessary, higher doses of Amglidia can be administered, and they can be administered up to four times a day, based on blood glucose control, according to the dosage adjustment recommendations indicated by the patient's doctor.
In case of mild vomiting, your doctor will prescribe an antiemetic medication, and treatment with Amglidia can continue.
As usually recommended in these situations, if vomiting occurs less than 30 minutes after administration of Amglidia, a new dose can be administered. If vomiting occurs more than 30 minutes after administration of AMGLIDIA, no new dose should be administered. Always consult your child's doctor in these circumstances.
The treating doctor should carefully monitor the situation in case of severe vomiting, ketonemia, and ketonuria. The doctor may restart insulin treatment if it is determined that ketonemia or ketonuria are responsible for the severe vomiting. In case of inability to ingest food or drinks, the child should be taken to an emergency service to receive a glucose and insulin infusion until the vomiting disappears.
Method of Administration
Always administer the medication before meals.
The medication should be administered at the same time every day.
In case of feeding with milk, it is recommended to administer the suspension 15 minutes before milk feeding.
This medication is a ready-to-use oral suspension that is administered with a graduated oral syringe. Only the oral syringe included in the box should be used.
The 1 ml syringe is thin and short and is graduated in 0.05 ml increments. The 5 ml syringe is thick and long and is graduated in 0.1 ml increments.
Instructions for Use
The dose is measured by pulling the syringe plunger until it reaches the mark corresponding to the dose prescribed by the doctor for your child. The dose in ml per administration and the number of administrations per day must strictly follow the medical prescription.
With the child awake, place them in a semi-sitting position in the crook of your arm, with the child's head resting on your arm.
Insert the first centimeter of the syringe into the child's mouth and apply it against the inner cheek. Let the child suck. If the child does not suck, slowly press the syringe plunger so that the suspension drips into the mouth.
Do not lay the child down immediately after administration. It is recommended to wait until the child has swallowed the medication before placing them back in a lying position.
For the First Use
- Open the bottle by unscrewing the child-resistant cap while pressing down.
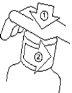
- Insert the adapter firmly into the bottle while holding the bottle in a vertical position.
- Replace the screw cap on the bottle with the adapter.
- Tighten the screw cap to introduce the adapter well into the bottle.
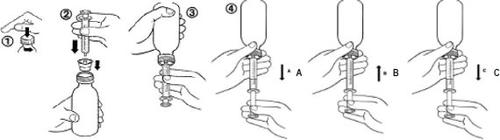
For Each Administration
- No need to shake the bottle before administration. The medication is administered as a ready-to-use oral suspension using a specific graduated syringe.
- Open the bottle by unscrewing the child-resistant cap while pressing down (figure 1).
- While holding the bottle in a vertical position, insert the syringe firmly into the adapter attached to the bottle (figure 2).
- Invert the bottle with the syringe (figure 3).
- Pull the plunger to obtain the desired volume (figure 4A). Then, push the plunger to eliminate as many air bubbles as possible from the syringe (figure 4B). Finally, pull the plunger until it reaches the mark corresponding to the prescribed dose in milliliters (figure 4C).
Note: If air enters the syringe, empty the syringe into the bottle and start the procedure again.
- Turn the bottle with the syringe to its vertical position.
- Remove the syringe from the adapter. Insert the syringe into the child's mouth and push the plunger to administer the medication slowly into the mouth.
- Close the bottle by tightening the screw cap well over the top of the adapter.
- The bottle should be closed after each use and stored for a maximum of 30 days.
- After each use, the syringe should be rinsed well with water, dried with a cloth, and placed back in the medication box. The oral syringe included in the box should only be used with this medication.
If You Administer More AMGLIDIA to Your Child Than You Should
Consult your doctor, nurse, or hospital pharmacist immediately.
There is a risk of hypoglycemia. You should measure your child's capillary blood glucose level and follow the instructions described in section 4.
If You Forget to Administer AMGLIDIA
If you forget to administer Amglidia, there is a risk of hyperglycemia.
You should measure your child's blood glucose level (capillary blood glucose) and administer Amglidia as soon as you realize you have forgotten to administer it. If your child's capillary blood glucose level is above 3 g/l (or 300 mg/dl or 16.5 mmol/l), check for ketonuria by performing a blood test obtained through a finger prick or a urine test using a test strip according to your child's doctor's recommendations. If ketonuria is detected, you should inject insulin into your child immediately according to the procedure defined in advance with your child's doctor and contact them or their team for advice.
Do not administer a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
If You Interrupt Treatment with AMGLIDIA
There is a risk of high blood sugar levels.
You should measure your child's blood glucose level (capillary blood glucose). The symptoms of diabetes may reappear and cause a severe disruption of the body's metabolism with high levels of ketone bodies in the blood (ketoacidosis), dehydration, and disruption of the body's acid balance. Therefore, you should never interrupt treatment with the medication without consulting your child's doctor first. Consult your doctor.
You will be asked to bring the remaining amount of Amglidia oral suspension to each consultation.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, consult your child's doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medications, this medication can cause side effects, although not everyone will experience them.
Serious Side Effects
Low Blood Sugar Level (Hypoglycemia)(very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
If you take Amglidia, there is a risk of having a low blood sugar level (hypoglycemia). The signs of a low blood sugar level can be:
- trembling, sweating, intense anxiety or confusion, rapid heartbeat
- excessive hunger, headache
If your child starts to show paleness, sweating, or an irregular heartbeat, seems disoriented or confused, or does not respond, these can be signs that your child's blood sugar level is too low; first, you should resolve the situation as explained below, and then you should consult your child's doctor to adjust the dose of Amglidia.
The risk of low blood sugar increases if the medication is not taken with a meal, is taken with alcohol, or is combined with certain medications (see section 2. Other medications and Amglidia). This low blood sugar should be treated by taking sugar orally followed by a snack or a meal. If a very low blood sugar level occurs that affects consciousness, you should call the emergency services and administer an intravenous glucose injection. After a severe episode of hypoglycemia, the child and their family should visit the child's doctor to check the suitability of the glibenclamida dose in suspension.
Eye Disorders(common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Blurred vision in case of high blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia)
Gastrointestinal Disorders(very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Transient diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Vomiting
- Stomach pain (dyspepsia)
Dental Problems(common: may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Change in tooth color
Skin Disorders(very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Rash
Abnormal Blood Test Results(very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
Clinical blood tests may show changes in blood cells (decrease in the number of white blood cells: neutropenia) and effects on liver function (brief elevation of certain enzymes called transaminases).
Other Side Effects:
Other side effects have been observed in adults treated with other medications containing glibenclamida. The following side effects have not been observed with Amglidia.
- Allergic reactions: can be severe in isolated cases and include difficulty breathing, low blood pressure, and shock. If your child experiences any of these symptoms, you should immediately go to the nearest emergency service.
- Rash: itching, hives (urticaria), skin allergic reaction, blistering of the skin, skin inflammation.
- Increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight.
- Transient visual disturbances.
- Other changes in clinical blood tests: elevated levels of a type of white blood cell called eosinophils (hypereosinophilia) and mild to moderate decrease in blood components called platelets (thrombocytopenia) that can lead to subcutaneous bleeding (purpura).
Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you notice any of these side effects.
Reporting Side Effects
If you observe any side effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a side effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Storage of AMGLIDIA
Keep this medication out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medication after the expiration date stated on the carton and bottle after EXP. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store the bottle in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
After the first opening, use within 30 days. Keep the bottle tightly closed.
Medications should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and medications you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of AMGLIDIA
- The active ingredient is glibenclamida. Each milliliter contains 6 mg of glibenclamida.
- The other ingredients are: xanthan gum, hydroxyethyl cellulose, lactic acid, purified water, sodium citrate, and sodium benzoate (E211) (see section 2 "AMGLIDIA contains sodium and sodium benzoate").
Appearance and Package Contents
Amglidia is a white, odorless oral suspension. Each carton contains:
- 1 bottle containing 30 ml of oral suspension.
- 1 oral syringe of 1 ml (thin and short) or 1 oral syringe of 5 ml (thick and long) depending on the prescribed dose and volume to be administered. The syringe is packaged in a transparent bag.
- 1 syringe adapter.
Marketing Authorization Holder
AMMTek
8 rue Campagne Première
75014 Paris
France
Manufacturer
Euromed Pharma France1 Rue de la Chaudanne
69290 Grézieu-la-Varenne
France
Unither Développement Bordeaux
ZA Tech-Espace, Avenue Toussaint-Catros
33185 Le Haillan
France
Centre Spécialités Pharmaceutiques
76-78 Avenue du midi
63800 Cournon d’Auvergne
France
You can request more information about this medication by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
België/Belgique/Belgien Bioprojet Benelux NV Tél/Tel: + 31 (0)63 75 59 353 | Lietuva Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
| Luxembourg/Luxemburg Bioprojet Benelux NV Tél/Tel: + 31 (0)63 75 59 353 |
Ceská republika Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Magyarország Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Danmark Bioprojet Pharma Tlf: +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Malta Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Deutschland Bioprojet Deutschland GmbH Tel: +49(0)30 3465 5460-0 | Nederland Bioprojet Benelux NV Tel: + 31 (0)63 75 59 353 |
Eesti Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Norge Bioprojet Pharma Tlf: +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Ελλáδα Bioprojet Pharma Τηλ: +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Österreich Bioprojet Deutschland GmbH Tel: +49(0)30 3465 5460-0 |
España Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Polska Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 [email protected] |
France Bioprojet Pharma Tél : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Portugal Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Hrvatska Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | România Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Ireland Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Slovenija Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Ísland Bioprojet Pharma Sími: +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Slovenská republika Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Italia Bioprojet Italia s.r.l. Tel: +39 (0)2.84254830 | Suomi/Finland Bioprojet Pharma Puh/Tel: +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Κúπρος Bioprojet Pharma Τηλ: +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | Sverige Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Latvija Bioprojet Pharma Tel: +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 | United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) Bioprojet Pharma Tel : +33 (0) 1 47 03 66 33 |
Date of the Last Revision of this Leaflet:
Other Sources of Information
Detailed information about this medication is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu. There are also links to other websites about rare diseases and orphan medications.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to AMGLIDIA 6 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSIONDosage form: ORAL SOLUTION/SUSPENSION, 0.6 mg/mlActive substance: glibenclamideManufacturer: AmmtekPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 5 mgActive substance: glibenclamideManufacturer: Laboratorio Generfarma S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 2 mgActive substance: glimepirideManufacturer: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for AMGLIDIA 6 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION
Discuss questions about AMGLIDIA 6 mg/ml ORAL SUSPENSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions












