
OSMOHALE POWDER FOR INHALATION (HARD CAPSULES)

How to use OSMOHALE POWDER FOR INHALATION (HARD CAPSULES)
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Osmohale Powder for Inhalation (Hard Capsules)
mannitol
Read this package leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this package leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What Osmohale is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you take Osmohale
- How to take Osmohale
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Osmohale
- Package Contents and Further Information
1. What Osmohale is and what it is used for
Osmohale is a testto check if you have sensitivity in the airways or not.
Osmohale contains the active substance mannitol.
Sensitivity in the airways can be caused by inflammation of the airways, which can sometimes make breathing difficult. People with sensitivity in the airways are often very susceptible to environmental factors such as exercise, dust, smoke, and other irritants.
Your doctor or another healthcare professional specifically trained will ask you to breathe in Osmohale using a small inhaler.
- In people who actuallyhave sensitivity in the airways, these will narrow, and it may become more difficult to breathe.
- People who do nothave sensitivity in the airwayswill not experience such narrowing of the airways when breathing in Osmohale and will be able to continue breathing normally.
As part of the test, you will be asked to blow into a tube that measures the effect of Osmohale on your lungs.
This medicine is used exclusively to check if you have sensitivity in the airways.
2. What you need to know before you take Osmohale
Do not take Osmohale
- if you are allergic(hypersensitive) to mannitol or any of the other ingredients;
- if your lung capacityis severely reduced(this will be measured before the test);
- if you currently have or have had a dilated or weakened blood vessel around the heart or brain (aneurysm);
- if you have uncontrolled high blood pressure;
- if you have had a heart attackin the last 6 months;
- if you have had a strokein the last 6 months.
Warnings and Precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking Osmohale.
- if your lung capacityis reduced(this will be measured before the test);
- if you have previously experienced difficulty breathing, or have had wheezingor coughingduring a spirometry test (a study where you blow into a measuring instrument);
- if you cough up blood;
- if you have air in the pleural space between the chest wall and the lungs, which causes chest pain and shortness of breath (pneumothorax);
- if you have recently undergone eye, stomach, or chestsurgery;
- if you experience chest pain(angina pectoris);
- if you have problems performing spirometry(the person performing it will inform you);
- if you have had a respiratory tract infectionin the last 2 weeks.
If you experience shortness of breath, wheezing, and/or coughing during the spirometry test, you may be given a medicine to keep your airways open, and the test will be stopped.
Do not engage in strenuous exerciseon the day of the test, especially before taking it, as it may affect the results.
Do not smokefor at least 6 hours before the test, as it may affect the results.
Do not take Osmohale on your own. Osmohale should only be administered in a clinic or laboratory, by trained professionals familiar with the use of similar tests and their possible effects, under the supervision of an experienced doctor.
Children and Adolescents
Osmohale should not be administered to children under 6 years of age.
Osmohale is not recommended in patients from 6 to 18 years of age due to limited information available on the use of the medicine in this population.
Other Medicines and Osmohale
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
If you are using other medicines for the treatment of asthma or allergies, you may need to stop them before the test. These medicines may affect your body's reaction to Osmohale. Your doctor will tell you which medicine(s) to stop and for how long (usually between 6 hours and 4 days before the test).
Using Osmohale with Food and Drinks
On the day of the test, do not drink coffee, tea, or cola, or eat chocolate or other foods that contain caffeine.
Pregnancy, Breast-feeding, and Fertility
Do not undergo the test with Osmohale if you are pregnant.
You can use Osmohale during breast-feeding.
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Driving and Using Machines
No effects have been observed.
3. How to Take Osmohale
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as told by your doctor or pharmacist. If you are unsure, ask your doctor or pharmacist again.
Adults
A doctor or another healthcare professional specifically trained will administer Osmohale using an inhaler and will accompany you during the test. You will not be left alone.
Do not put the Osmohale capsules in your mouth or swallow them.
Conducting the Test
- You will be asked to sit comfortably in a chair.
- Initially, you will be asked to blow forcefully into a tube (spirometry).
- A nasal clip will be placed on you so that you can only inhale and exhale through your mouth.
- After exhaling all the air, you will be asked to inhale the Osmohale medicine deeply using a special inhaler.
- You will then be asked to hold your breath for five seconds before exhaling.
- The nasal clip will be removed, and you will be asked to breathe normally.
- Then, you will be asked to blow forcefully into the tube again. This test measures the effect of Osmohale on your lungs.
- Steps 3 to 7 may be repeated up to 9 times, with more Osmohale depending on the effect on your lungs (as measured in step 7), until the test is completed.
- Once the study is finished, you may be given a medicine to help you breathe.
If you are unsure about any part of the test or have any questions about the medicine, talk to the doctor or healthcare professional specifically trained who is conducting the test.
If you take more Osmohale than you should
If you think you may have been given too much of the medicine, tell the doctor or healthcare professional conducting the test immediately. If you have taken too much Osmohale, you may feel that you cannot breathe, experience wheezing, or cough. The doctor may give you oxygen or medicine to help you breathe.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
List of Side Effects
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Asthma
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
- Cough
- Feeling sick
- Headache
- Nose and throat pain, discomfort when swallowing
- Runny nose
- Vomiting
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Cold extremities
- Diarrhea
- Dizziness
- Nervousness
- Thirst
- Tiredness
- Redness and sweating
- Hoarseness
- Itching and skin rash
- Itching in the eyes
- Reduced oxygen in the blood
- Mouth ulcers
- Nosebleeds (epistaxis)
- Stomach pain
- Muscle and joint pain
Reporting of Side Effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this package leaflet. You can also report side effects directly via the national reporting system listed in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Osmohale
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the carton after EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Do not store above 25°C.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Osmohale Composition
The active ingredient is mannitol.
The inhalation capsules contain mannitol powder. One capsule contains 0 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, or 40 mg of mannitol.
Product Appearance and Container Contents
The powder is white or almost white.
The empty capsule is transparent with two white printed bands
The 5 mg capsule is half white and half transparent, with the inscription 5 mg.
The 10 mg capsule is half yellow and half transparent, with the inscription 10 mg.
The 20 mg capsule is half pink and half transparent, with the inscription 20 mg.
The 40 mg capsules are half red and half transparent, with the inscription 40 mg.
The capsules are presented in blisters. A diagnostic kit, packaged in a box, consists of:
- 1 empty capsule
- 1 capsule of 5 mg
- 1 capsule of 10 mg
- 1 capsule of 20 mg
- 15 capsules of 40 mg
- 1 inhaler
Marketing Authorization Holder
Pharmaxis Europe Limited
108 Q House Furze Road,
Sandyford, Dublin 18,
D18AY29, Ireland
Manufacturer
MIAS Pharma Limited
Suite 1 Stafford House
Strand Road, Portmarnock
Co. Dublin, D13 WC83
Ireland
Arvato Supply Chain Solutions SE
Gottlieb-Daimler Straße 1
33428 Harsewinkel
North Rhine-Westphalia
Germany
If you have any questions about this medication, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Laboratorio Aldo-Unión, S.L.
Baronesa de Maldá, 73
08950 Esplugues de LL.
Barcelona
Spain
Tel: +34 93 372 71 11
Fax: +34 93 371 61 98
This medication is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Aridol: Finland, Germany, Norway, Sweden
Osmohale: Denmark, Ireland, Netherlands, Spain, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland)
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:06/2022
Detailed and updated information on this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
INFORMATION FOR HEALTHCARE PROFESSIONALS
This information is intended solely for healthcare professionals:
Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to mannitol or any of the capsule components.
Osmohale should not be administered to patients with severe respiratory limitation (expected FEV1 <50% or <1.0 l), or conditions that may be compromised by the induction of bronchospasms or the repetition of blowing maneuvers. These include: cerebral or aortic aneurysm, uncontrolled hypertension, myocardial infarction or a cerebrovascular accident in the previous six months.
Special Warnings and Precautions for Use
Osmohale should be administered exclusively by inhalation. Mannitol inhalation causes bronchoconstriction. The Osmohale inhalation test should only be performed in clinics or laboratories, by a doctor or other healthcare professional properly trained to perform bronchial provocation tests and to manage acute bronchospasms, and under the supervision of an experienced doctor. The responsible doctor, with the proper training to treat acute bronchospasms, including the proper use of resuscitation equipment, should be close enough to respond quickly in case of an emergency. A stethoscope, sphygmomanometer, and pulse oximeter should be available. Once Osmohale administration has begun, the patient should not be left unattended during the procedure.
In the test area, there should be medications for the treatment of severe bronchospasms, including adrenaline for subcutaneous injection, and salbutamol or other beta agonists in graduated dose inhalers. Oxygen should be available. A small volume nebulizer should be available for the administration of bronchodilators.
General precautions for spirometry and bronchial provocation tests should be observed, including additional precautions in patients with the following conditions: respiratory failure (basal FEV1 less than 70% of expected normal values or an absolute value of 1.5 l or less in adults), bronchoconstriction induced by spirometry, hemoptysis of unknown origin, pneumothorax, recent abdominal or thoracic surgery, recent intraocular surgery, unstable angina, inability to perform acceptable quality spirometry, or lower or upper respiratory tract infection in the previous 2 weeks.
If the patient presents with spirometry-induced asthma, or the FEV1 drop is greater than 10% after continuous administration after the 0 mg capsule, a standard dose of bronchodilator should be applied and the Osmohale provocation should be suspended.
Exercises: Vigorous physical exercise should be completely avoided on the day of the test, as it may affect the results.
Smoking: As smoking may affect the test results, it is recommended that patients abstain from smoking for at least 6 hours prior to the study.
The Osmohale test should not be used in patients under 6 years of age, due to their inability to provide reproducible spirometric measurements.
Information on the use of Osmohale in patients from 6 to 18 years of age is limited; consequently, the use of Osmohale is not recommended in this population.
The effects of repeated tests with Osmohale over a short period have not been investigated; consequently, special consideration should be given to the repeated use of Osmohale.
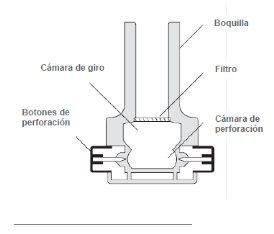
Instructions for the Inhaler Device
These instructions show how to use the inhaler
- Removing the cap: With both hands, hold the inhaler in a vertical position and remove the cap.

- Opening: Hold the base of the inhaler firmly with one hand, and open the device by turning the mouthpiece in the direction of the arrow, as shown in the image.

- Loading: Make sure your hands are dry; remove a capsule from the inhaler box and place it in the inhaler as shown in the illustration.
It does not matter which side the capsule is inserted into the chamber.

- Closing: While holding the device in a vertical position, turn the mouthpiece to the closed position, until you hear a "click".

- Piercing the capsule: Hold the inhaler in a vertical position and press the two piercing buttons located on the sides of the device simultaneously.
Do this only once, as piercing the capsule more than once could cause it to break or fragment. Piercing opens holes in the capsule, allowing the powder to come out during inhalation.

- Preparing for inhalation: Tilt the inhaler so that the mouthpiece is slightly downward at a 45-degree angle, as shown in the following figure, until the capsule falls into the rotating chamber. Keep the device tilted in this way and instruct the patient to exhale completely (outside the inhaler).

- Inhalation: The patient should tilt their head slightly back, and holding the inhaler at 45 degrees, bring it to their mouth and adjust their lips to the mouthpiece. Instruct the patient to inspire rapidly and deeply to fill their lungs. Then the patient should hold their breath for five seconds.

Note: During a correct inhalation, a "rattle" sound should be heard as the capsule rotates inside the inhaler.
- Exhalation: Remove the inhaler from the patient's mouth, and let them exhale and resume normal breathing.

- Verification: To empty, the Osmohale capsule must rotate inside the inhaler. If after inhalation the capsule has not emptied, a second inhalation may be required (with the same capsule). Check the capsule after each inhalation.

Note:
The inhaler is designed for SINGLE USE (one device per provocation test), and should not be cleaned during the test.
Discard the inhaler after each Osmohale provocation. The inhaler should not be sterilized or reused, as this could compromise the integrity of the following test results.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
READ THE COMPLETE PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS SUMMARY BEFORE PERFORMING THIS PROVOCATION TEST.
Marketing Authorization Holder:
Pharmaxis Europe Limited
108 Q House Furze Road,
Sandyford, Dublin 18,
D18AY29, Ireland
Local Representative:
Laboratorio Aldo-Unión, S.L.
Baronesa de Maldá, 73
08950 Esplugues de LL.
Barcelona
Spain
Tel: +34 93 372 71 11
Fax: +34 93 371 61 98
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
{Logo}
Osmohale Provocation Test Instructions
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Osmohale Provocation Test
Inhaler

Provocation Test Results
Positive Result of the Osmohale Provocation Test
A positive response with Osmohale is obtained in two ways:
a drop of ≥ 15% of the FEV1 with respect to the basal value (using the FEV1 value after administration of 0 mg as a comparator)
a drop of ≥ 10% of the FEV1 (between consecutive doses of Osmohale)
Negative Result of the Osmohale Provocation Test
The Osmohale provocation test is considered negative when the patient has been administered a cumulative dose of 635 mg of Osmohale and their FEV1 does not decrease by a percentage ≥ 15% with respect to the basal value.
Equipment
Osmohale Equipment(contains Osmohale capsules, inhaler, and instructions leaflet)
Spirometer and Mouthpiece
Nasal Clip
Timer(that can be set to 60 seconds)
Calculator
Bronchodilator(e.g., salbutamol)
Oxygen and other emergency equipment should be available, according to standard protocols for bronchial provocation tests.
Important Points to Consider
- The inhaler is for SINGLE USE (one device per provocation test), and should not be cleaned during the test. Discard the inhaler after each Osmohale provocation. The inhaler should not be sterilized or reused, as this could compromise the integrity of the following test results.
- When the patient exhales during the Osmohale provocation test, ensure that they do so AWAY FROM THE INHALER, to minimize humidity inside the device.
- When piercing the capsule, do so only once (by pressing both buttons simultaneously), as a new piercing could cause the capsule to break or fragment.
- The use of rubber gloves during the administration of the test and handling of the Osmohale capsules may increase static and inhibit the movement of the capsules inside the inhaler.
- If you suspect a static problem, or notice that the capsule noise is not heard during Osmohale inhalation, tap the base of the inhaler firmly with one hand while holding the inhaler with the other (with the mouthpiece oriented downward at a 45° angle). This will ensure that the capsule "unsticks" from the piercing chamber and enters the rotating chamber.

- Osmohale inhalation may cause coughing and/or throat dryness. This is a routine adverse effect of the bronchial provocation test.
You can offer the patient a glass of water after completing the test.
- In this provocation test, time is crucial, and it requires establishing and maintaining an osmotic gradient. Prolonged intervals between doses may affect the validity of the results and should be avoided.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Procedure Guidelines
STEP 1:Verify that the patient has withheld the following medications (see the table below).
Recommended withdrawal periods for medications.
Failure to withhold medications may affect the results of the Osmohale provocation test.
The recommended periods for medication withdrawal are generally based on the duration of their action.
Withdrawal Time | Medication |
6-8 hours | INHALED NON-STEROIDAL ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AGENTS for example sodium cromoglycate, sodium nedocromil |
8 hours | SHORT-ACTING BETA2 AGONISTS for example salbutamol, terbutaline |
12 hours | INHALED CORTICOSTEROIDS for example beclometasone, budesonide, fluticasone |
12 hours | IPRATROPIUM BROMIDE |
24 hours | INHALED CORTICOSTEROIDS PLUS LONG-ACTING BETA2 AGONISTS for example fluticasone and salmeterol, budesonide and eformoterol |
24 hours | LONG-ACTING BETA2 AGONISTS for example salmeterol, formoterol |
24 hours | THEOPHYLLINE |
72 hours | TIOTROPIUM BROMIDE |
72 hours | ANTIHISTAMINES for example cetirizine, fexofenadine, loratadine |
4 days | LEUKOTRIENE RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS for example montelukast |
Food:The intake of significant amounts of coffee, tea, cola drinks, chocolate, or other foods containing caffeine may decrease bronchial reactivity and should be completely avoided on the day of the study.
Other factors that may affect the results:On the day of the test, the patient should not smoke or engage in vigorous physical exercise, as this may affect the results.
STEP 2:For the test, the patient should be seated. Explain the procedure; include the requirements for a CVF maneuver and FEV1 measurement, and the type of inspiratory flow required for the inhaler. Provide a demonstration if required.
STEP 3:Enter the patient's data into the spirometer (age, height, race, date of birth, sex, etc.).
STEP 4:Determine the pre-test FEV1. Ask the patient to perform a CVF maneuver according to the ATS/ERS guidelines, perform three acceptable maneuvers, of which two are reproducible. Use the highest value as the pre-test FEV1. The patient's FEV1 should be ≥ 70% of the expected value.
Extreme caution should be exercised with patients with an FEV1 of less than 70% of the expected value.
STEP 5:Calculate the basal FEV1 (0 mg)
- Remove the 0 mg Osmohale capsule from the blister, open the inhaler (by turning as indicated by the arrow on the device), insert the capsule, and close the device.
- Pierce the capsule once, by pressing the colored buttons on both sides of the inhaler.
- Ask the patient to put on the nasal clip and breathe through their mouth.
- Tilt the inhaler to 45° (with the mouthpiece downward). Verify that the capsule has moved from the piercing chamber to the rotating chamber, closer to the mouthpiece.
Often, the capsule can be heard falling forward or seen through the holes on either side of the device. Hand the inhaler to the patient, ensuring they keep it at the same angle.
- Verify that the patient is sitting upright. Ask the patient to exhale (outside the inhaler), adjust their lips around the inhaler mouthpiece, and take a rapid and deep inspiration to fill their lungs. During a correct inhalation, a "rattle" sound should be heard as the capsule rotates inside the device.
- At the end of the patient's inhalation, start a 60-second timer and ask the patient to hold their breath for 5 seconds. After the 5 seconds, instruct the patient to exhale through their mouth (away from the inhaler), remove the nasal clip, and breathe normally.
- When the timer sounds at 60 seconds, immediately ask the patient to perform two acceptable FEV1 measurements. These measurements should be
- Within a variability of 0.15 l (150 ml). If the variability between readings is higher than 0.15 l, indicate to the patient to perform another FEV1 measurement. Record the highest reading as the baseline FEV1 value. If the highest FEV1 value is ≥ 10% lower than the pre-test FEV1, do not continue with the test.
- Calculate the target FEV1
A positive result for the Osmohale provocation test is obtained when the patient's FEV1 falls ≥ 15% with respect to the baseline value. To calculate the target FEV1, multiply the baseline value (the highest reading obtained with 0 mg) previously obtained by 0.85. Record this value.
STEP 6:5 mg capsule
- Insert the 5 mg capsule into the inhaler and perforate it as indicated in Step 5.
- Repeat the previous steps 5c – f.
- After inhalation, remove the capsule from the inhaler and verify that it has been completely emptied; otherwise, a second inhalation should be performed immediately.
- Load the 10 mg capsule in preparation for the next dose.
- 60 seconds after inhalation, immediately measure the patient's FEV1 twice (acceptability criteria must be met). Use the higher of these two values to calculate the FEV1 variation.
- Compare the FEV1 value with this dose to the target FEV1. If the FEV1 value is lower or equal to the target value, or if an incremental drop ≥ 10% has occurred since the previous dose, the provocation test is positive and complete. If not, continue immediately with the next dosing stage.
STEP 7:10 mg, 20 mg, and 40 mg capsules
Administer the 10 mg, 20 mg, and 40 mg doses according to the previous instructions (in Step 6) for the 5 mg dose.
STEP 8:80 mg dose (2 capsules of 40 mg)
- Insert and perforate the first 40 mg capsule that makes up the 80 mg dose.
- The patient should inhale the dose in the same way as the previous ones, hold their breath for 5 seconds, and exhale.
- Remove the first 40 mg capsule from the device and verify that it has been completely emptied; otherwise, a second inhalation should be performed immediately. Do this after the administration of each capsule.
- After inhalation, load the second 40 mg capsule and offer it to the patient immediately after exhalation.
- Indicate to the patient that they should inhale the second capsule immediately to ensure that the osmotic effect of Osmohale is cumulative.
- Activate the timer at the end of the inhalation of the second capsule.
- Indicate to the patient that they should hold their breath for 5 seconds before exhaling.
- 60 seconds after the inhalation of the second capsule, immediately measure the patient's FEV1 twice (acceptability criteria must be met). Use the higher of these two values to calculate the FEV1 variation.
- Compare the FEV1 value with this dose to the target FEV1. If the FEV1 value is lower or equal to the target value, or if an incremental drop ≥ 10% has occurred, the provocation test is positive and complete. If not, continue immediately with the next dosing stage.
STEP 9:First 160 mg dose (4 capsules of 40 mg)
- Insert and perforate the first 40 mg capsule that makes up the 160 mg dose.
- The patient should inhale the dose in the same way as the previous ones, hold their breath for 5 seconds, and exhale.
- Remove the capsule from the device and verify that it has been completely emptied; otherwise, a second inhalation should be performed immediately. Do this after the administration of each capsule.
- After inhalation, load the second 40 mg capsule and offer it to the patient immediately after exhalation.
- The patient should inhale the contents of the second capsule, hold their breath for 5 seconds, and exhale.
5 seconds and exhale.
- After inhalation, load the third 40 mg capsule and offer it to the patient immediately after exhalation.
- The patient should inhale the contents of the third capsule, hold their breath for 5 seconds, and exhale.
- After inhalation, load the fourth 40 mg capsule and offer it to the patient immediately after exhalation.
- Indicate to the patient that they should inhale the fourth capsule immediately to ensure that the osmotic effect of Osmohale is cumulative.
- Activate the timer at the end of the inhalation of the fourth capsule.
- Indicate to the patient that they should hold their breath for 5 seconds before exhaling.
- 60 seconds after the inhalation of the fourth capsule, immediately measure the patient's FEV1 twice (acceptability criteria must be met). Use the higher of these two values to calculate the FEV1 variation.
- Compare the FEV1 value with this dose to the target FEV1. If the FEV1 value is lower or equal to the target value, or if an incremental drop ≥ 10% has occurred since the previous dose, the provocation test is positive and complete. If not, continue immediately with the next dosing stage.
STEP 10:Second 160 mg dose (4 capsules of 40 mg)
Administer the second 160 mg dose according to the instructions in the previous Step 9.
STEP 11:Third 160 mg dose (4 capsules of 40 mg)
Administer the third 160 mg dose according to the instructions in the previous Step 9.
After completing this dose, a total of 635 mg will have been administered. If a positive response has not been obtained, the provocation test should be considered complete and negative.
STEP 12:After completing the provocation test, a bronchodilator should be administered to the patient, and they should be monitored for 15 minutes to ensure that their FEV1 has returned to a value within 5% of the pre-test level. (In the case of a negative result, the administration of the bronchodilator is optional).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to OSMOHALE POWDER FOR INHALATION (HARD CAPSULES)Dosage form: INJECTABLE, 25 mg edrophonium bromide/2 mlActive substance: edrophoniumManufacturer: Mana Pharma S.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 0.3%/0.3%/0.3% mol/molActive substance: Other diagnostic agentsManufacturer: Sociedad Española De Carburos Metalicos S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 0.28%/9.5% mol/molActive substance: Other diagnostic agentsManufacturer: Sociedad Española De Carburos Metalicos S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for OSMOHALE POWDER FOR INHALATION (HARD CAPSULES)
Discuss questions about OSMOHALE POWDER FOR INHALATION (HARD CAPSULES), including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















