
INHIXA 4.000 UI (40 MG)/0,4 ML SOLUCION INYECTABLE

Cómo usar INHIXA 4.000 UI (40 MG)/0,4 ML SOLUCION INYECTABLE
Traducción generada por IA
Este contenido ha sido traducido automáticamente y se ofrece solo con fines informativos. No sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
Ver originalContenido del prospecto
Introducción
Prospecto: información para el usuario
Inhixa 2.000 UI (20 mg)/0,2 ml solución inyectable
Inhixa 4.000 UI (40 mg)/0,4 ml solución inyectable
Inhixa 6.000 UI (60 mg)/0,6 ml solución inyectable
Inhixa 8.000 UI (80 mg)/0,8 ml solución inyectable
Inhixa 10.000 UI (100 mg)/1 ml solución inyectable
Enoxaparina sódica
Lea todo el prospecto detenidamente antes de empezar a usar este medicamento, porque contiene información importante para usted.
- Conserve este prospecto, ya que puede tener que volver a leerlo.
- Si tiene alguna duda, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero.
- Este medicamento se le ha recetado solamente a usted, y no debe dárselo a otras personas aunque tengan los mismos síntomas que usted, ya que puede perjudicarles.
- Si experimenta efectos adversos, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero, incluso si se trata de efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. Ver sección 4.
Contenido del prospecto
- Qué es Inhixa y para qué se utiliza
- Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a usar Inhixa
- Cómo usar Inhixa
- Posibles efectos adversos
- Conservación de Inhixa
- Contenido del envase e información adicional
1. Qué es Inhixa y para qué se utiliza
Inhixa contiene un principio activo denominado enoxaparina sódica, que es una heparina de bajo peso molecular (HBPM).
Inhixa actúa de dos formas:
- Impidiendo que los coágulos de sangre ya existentes se hagan más grandes. Esto ayuda a su organismo a romperlos y que no sigan haciéndole daño.
- Interrumpiendo la formación de coágulos en la sangre.
Se puede usar Inhixa para:
- tratar los coágulos que hay en sangre
- evitar la formación de coágulos en sangre en las siguientes situaciones:
- antes y después de una operación quirúrgica
- cuando tiene una enfermedad aguda y tiene que afrontar un período de movilidad reducida
- si ha sufrido la formación de coágulos en sangre debido al cáncer, para evitar la formación de nuevos coágulos.
- cuando tiene angina inestable (una enfermedad en la que no llega suficiente cantidad de sangre al corazón)
- después de un ataque al corazón
- evitar la formación de coágulos de sangre en los tubos del aparato de diálisis (que se emplea en personas que padecen problemas graves de riñón).
2. Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a usar Inhixa
No use Inhixa
- Si es alérgico a enoxaparina sódica o a alguno de los demás componentes de este medicamento (incluidos en la sección 6). Los signos de una reacción alérgica incluyen: erupción, problemas para tragar o respirar, hinchazón de labios, cara, garganta o lengua.
- Si es alérgico a la heparina o a otras heparinas de bajo peso molecular como nadroparina, tinzaparina o dalteparina.
- Si ha tenido una reacción a la heparina que causó una disminución grave en el número de las células que intervienen en la coagulación (plaquetas) – esta reacción se denomina trombocitopenia inducida por heparina – en los últimos 100 días o si tiene en sangre anticuerpos frente a la enoxaparina.
- Si está sangrando abundantemente o padece enfermedades de alto riesgo de sangrado (como úlcera de estómago, intervención reciente de ojos o cerebro), incluyendo accidente cerebrovascular (ictus) hemorrágico reciente.
- Si está usando Inhixa para tratar coágulos en la sangre, y va a recibir anestesia espinal o anestesia epidural o punción lumbar en 24 horas.
Advertencias y precauciones
Inhixa no se debe intercambiar con otros medicamentos que pertenezcan al grupo de heparinas de bajo peso molecular. Esto es porque no son exactamente iguales y no tienen la misma actividad ni las mismas instrucciones de uso.
Consulte con su médico o farmacéutico antes de empezar a usar Inhixa si:
- alguna vez ha tenido una reacción a la heparina que causó una disminución grave en el número de las plaquetas
- va a recibir anestesia espinal/lumbar o punción lumbar (ver “Operaciones quirúrgicas y anestesia”): se debe respetar un retraso entre Inhixa y el uso de este procedimiento
- le han implantado una válvula cardiaca
- tiene endocarditis (una infección del revestimiento interior del corazón)
- tiene antecedentes de úlcera gástrica
- ha tenido recientemente un ictus (accidente cerebrovascular)
- tiene alta la presión sanguínea
- tiene diabetes o problemas en los vasos sanguíneos de los ojos causados por la diabetes (denominado retinopatía diabética)
- ha sido operado recientemente de ojos o cerebro
- es usted una persona de edad avanzada (por encima de los 65 años) y especialmente si es mayor de 75 años
- tiene problemas de riñón
- tiene problemas de hígado
- presenta un peso muy bajo o tiene sobrepeso
- tiene alto los niveles de potasio en sangre (que podría comprobarse con un análisis de sangre)
- actualmente está usando medicamentos que afectan al sangrado (ver a continuación - Uso de Inhixa con otros medicamentos)
Podría tener que realizarse un análisis de sangre antes de empezar a utilizar este medicamento, y mientras lo esté usando; esto es para comprobar el nivel de las células que intervienen en la coagulación (plaquetas) y los niveles de potasio en sangre.
Niños y adolescentes
No se ha evaluado en niños o adolescentes la seguridad y eficacia de Inhixa.
Uso de Inhixa con otros medicamentos
Informe a su médico o farmacéutico si está utilizando, ha utilizado recientemente o podría tener que utilizar cualquier otro medicamento.
- Warfarina – otro medicamento anticoagulante empleado para reducir la coagulación de la sangre
- Ácido acetil salicílico (también conocido como aspirina o AAS), clopidogrel u otros medicamentos usados para interrumpir la formación de coágulos en la sangre (ver también sección 3, “Cambio de tratamiento de anticoagulante”)
- Inyección de dextrano – usado como sustitutivo de la sangre
- Ibuprofeno, diclofenaco, ketorolaco y otros medicamentos conocidos como antiinflamatorios no esteroideos utilizados para tratar el dolor y la inflamación en artritis y otras enfermedades
- Prednisolona, dexametasona y otros medicamentos utilizados para tratar el asma, la artritis reumatoide y otras enfermedades
- Medicamentos que aumentan el nivel de potasio en sangre como sales de potasio, medicamentos para eliminar líquidos (diuréticos), y algunos medicamentos para tratar problemas de corazón.
Operaciones quirúrgicas y anestesia
En caso de que le vayan a realizar una punción lumbar o vaya a someterse a una operación quirúrgica donde se vaya a utilizar una anestesia espinal o epidural, informe a su médico que está usando Inhixa. Ver “Uso de Inhixa con otros medicamentos”. También, informe a su médico si tiene cualquier problema con su columna o si se ha sometido alguna vez a una cirugía de columna.
Embarazo y lactancia
Si está embarazada, cree que podría estar embarazada o tiene intención de quedarse embarazada, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de utilizar este medicamento.
Si está embarazada y tiene implantada una válvula cardiaca mecánica, podría tener un riesgo mayor de que se formen coágulos en sangre. Su médico hablará con usted de este tema.
Si está en período de lactancia o planea dar la lactancia, debe consultar a su médico antes de utilizar este medicamento.
Conducción y uso de máquinas
Inhixa no afecta la capacidad para conducir y usar máquinas.
Trazabilidad
Mantener un registro del número de lote de su Inhixa es imporante. Por lo tanto, cada vez que reciba un nuevo envase de Inhixa, anote la fecha y el número de lote (que está en el envase después de Lote) y guarde esta información en un lugar seguro.
Inhixa contiene sodio
Este medicamento contiene menos de 1 mmol de sodio (23 mg) por dosis; esto es, esencialmente «exento de sodio».
3. Cómo usar Inhixa
Siga exactamente las instrucciones de administración de este medicamento indicadas por su médico o farmacéutico. En caso de duda, consulte de nuevo a su médico o farmacéutico.
Uso del medicamento
- Normalmente su médico o enfermera le administrará Inhixa. Esto es porque se tiene que administrar mediante una inyección.
- Cuando regrese a casa, es posible que necesite seguir usando Inhixa y se lo tenga que administrar usted mismo (consulte las instrucciones sobre cómo hacerlo).
- Inhixa generalmente se administra por inyección debajo de la piel (vía subcutánea).
- Inhixa se puede administrar por inyección en sus venas (vía intravenosa) después de ciertos tipos de ataques al corazón y operaciones quirúrgicas.
- Inhixa se puede añadir al tubo que sale del cuerpo (línea arterial) al comienzo de la sesión de diálisis.
No administre Inhixa en músculo (vía intramuscular).
Qué cantidad se le administrará
- Su médico decidirá la cantidad de Inhixa que se le administrará. La dosis dependerá del motivo por el que se vaya a usar.
- Si tiene algún problema de riñón puede que se le administre una cantidad menor de Inhixa.
1)Tratamiento de la formación de coágulos en sangre:
- La dosis habitual es 150 UI (1,5 mg) por kilogramo de peso corporal una vez al día o 100 UI (1 mg) por kilogramo de peso corporal dos veces al día.
- Su médico decidirá cuánto tiempo recibirá Inhixa.
- Interrupción de la formación de coágulos en sangre en las siguientes situaciones:
- Operaciones o períodos de movilidad limitada por una enfermedad
- La dosis dependerá de la probabilidad que usted tenga de desarrollar un coágulo. Se le administrará 2.000 UI (20 mg) o 4.000 UI (40 mg) de Inhixa al día.
- Si le van a operar, le administrarán generalmente la primera inyección 2 o 12 horas antes de la operación.
- Si tiene movilidad reducida por una enfermedad, le administrarán generalmente 4.000 UI (40 mg) de Inhixa al día.
- Su médico decidirá cuánto tiempo recibirá Inhixa.
- Después de que haya tenido un ataque al corazón
Se puede usar Inhixa en 2 tipos diferentes de ataques al corazón, denominados IAMCEST (infarto de miocardio con elevación del segmento ST) o no IAMCEST (IAMSEST). La cantidad de Inhixa que se le administre dependerá de la edad y del tipo de ataque al corazón que haya tenido.
Ataque de corazón tipo IAMSEST:
- La dosis habitual es de 100 UI (1 mg) por kilogramo de peso corporal cada 12 horas.
- Por lo general, su médico le dirá que también tome ácido acetilsalicílico (aspirina).
- Su médico decidirá cuánto tiempo recibirá Inhixa.
Ataque de corazón tipo IAMCEST si es menor de 75 años:
- Se le administrará una inyección inicial intravenosa de 3.000 UI (30 mg) de Inhixa.
- A la vez se le administrará una inyección de Inhixa debajo de la piel (inyección subcutánea). La dosis habitual es de 100 UI (1 mg) por kilogramo de peso corporal, cada 12 horas.
- Por lo general, su médico le dirá que también tome ácido acetilsalicílico (aspirina).
- Su médico decidirá cuánto tiempo recibirá Inhixa.
Ataque de corazón tipo IAMCEST si tiene 75 años o más:
- La dosis habitual es de 75 UI (0,75 mg) por kilogramo de peso corporal, cada 12 horas.
- La cantidad máxima de Inhixa administrada en las dos primeras inyecciones es de 7.500 UI (75 mg).
- Su médico decidirá cuánto tiempo recibirá Inhixa.
Para pacientes sometidos a una intervención coronaria percutánea (ICP):
Dependiendo de cuando se le administró la última inyección de Inhixa, su médico podría decidir administrarle una dosis adicional de Inhixa antes de una intervención ICP. Sería por inyección en vena.
- Interrupción de la formación de coágulos sanguíneos en los tubos del aparato de diálisis
- La dosis habitual es de 100 UI (1 mg) por kilogramo de peso corporal.
- Inhixa se añade al tubo que sale del cuerpo (línea arterial) al comienzo de la sesión de diálisis. Esta cantidad suele ser suficiente para una sesión de 4 horas. Sin embargo, es posible que su médico practique una nueva inyección de 50 UI a 100 UI/kg (de 0,5 a 1 mg/kg) por kilogramo de peso corporal, si fuera necesario.
Autoadministración de una inyección de Inhixa con una jeringa precargada sin protector de aguja
Si puede administrarse usted mismo este medicamento, su médico o enfermero le mostrarán cómo hacerlo. No intente inyectarse usted mismo si no le han enseñado a hacerlo. Si no sabe qué ha de hacer, consulte a su médico o enfermero de inmediato.
Antes de inyectarse Inhixa
- Compruebe la fecha de caducidad del medicamento. Si ha caducado, no lo utilice.
- Compruebe si la jeringa no está dañada y el líquido del interior es transparente. En caso contrario, use otra jeringa.
- No utilice este medicamento si observa algún cambio en su aspecto.
- Compruebe la cantidad que se va a inyectar.
- Revise si la última inyección le provocó enrojecimiento, cambio del color de la piel, hinchazón, supuración o le sigue doliendo. Si es así, hable con su médico o enfermero.
- Decida la zona en la que se va a inyectar el medicamento. Alterne, cada vez que se inyecte, el lado derecho del abdomen (vientre) con el izquierdo. Este medicamento se debe inyectar justo por debajo de la piel del abdomen, pero no muy cerca del ombligo ni de ninguna cicatriz (al menos a 5 cm de distancia de ellos).
- La jeringa precargada es para un solo uso.
Instrucciones para que usted mismo se inyecte Inhixa
- Lávese las manos y la zona de inyección con agua y jabón. Séquelas.
- Siéntese o túmbese en una posición cómoda y relajada. Compruebe que puede ver la zona en la que se va a inyectar. Lo más adecuado es en un diván, un sillón reclinable o en una cama con cojines para apoyarse.
- Escoja una zona en el lado derecho o izquierdo de la barriga. Debe estar a más de 5 cm del ombligo y hacia los costados.
Recuerde.No se inyecte en los 5 cm alrededor del ombligo ni de las cicatrices o los hematomas que pueda haber. Inyéctese en la zona contraria a la que se inyectó la vez anterior (alternando el lado derecho de la barriga con el izquierdo).
- Saque de la caja el blister de plástico que contiene la jeringa precargada. Abra el blíster y extraiga la jeringa precargada.
- Retire con cuidado el capuchón de la aguja de la jeringa, tirando de él. La jeringa está precargada y lista para su uso.
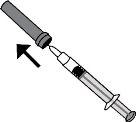
Nopresione el émbolo antes de inyectarse. Una vez que haya retirado el capuchón, no toque nada con la aguja. De este modo se asegurará de que la aguja siga estando limpia (estéril).
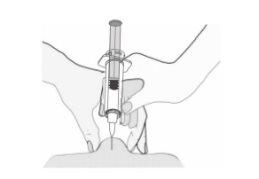
- Sostenga la jeringa con la mano con la que escribe (como si fuera un lápiz) y, con la otra mano, pellizque suavemente la zona del abdomen entre el índice y el pulgar para formar un pliegue de piel.
Asegúrese de sostener el pliegue de piel durante toda la inyección.
- Sostenga la jeringa de manera que la aguja apunte hacia abajo (verticalmente con un ángulo de 90º). Introduzca toda la aguja en el pliegue de piel.
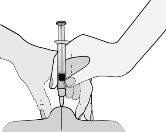
- Presione el émbolo con el pulgar. De este modo inyectará el medicamento en el tejido graso del abdomen. Asegúrese de sostener el pliegue de piel durante toda la inyección.
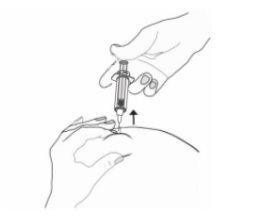
- Retire la aguja, tirando recto de ella.
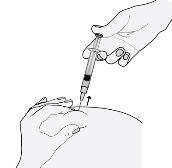
Para evitar que le salga un hematoma, no frote la zona de inyección después de que se haya inyectado.
- Deposite la jeringa usada en el contenedor para objetos punzantes. Cierre bien la tapa del contenedor y colóquelo fuera del alcance de los niños.
Cuando el contenedor esté lleno, elimínelo tal como su médico o farmacéutico le haya indicado. No lo tire al cubo de la basura.
Autoadministración de una inyección de Inhixa con una jeringa precargada con protector de aguja
Su jeringa precargada incluye un protector de aguja para protegerle de una herida por pinchazo de la aguja.
Si puede administrarse usted mismo este medicamento, su médico o enfermero le mostrarán cómo hacerlo. No intente inyectarse usted mismo si no le han enseñado a hacerlo. Si no sabe qué ha de hacer, consulte a su médico o enfermero de inmediato.
Antes de inyectarse Inhixa
- Compruebe la fecha de caducidad del medicamento. Si ha caducado, no lo utilice.
- Compruebe si la jeringa no está dañada y el líquido del interior es transparente. En caso contrario, use otra jeringa.
- No utilice este medicamento si observa algún cambio en su aspecto.
- Compruebe la cantidad que se va a inyectar.
- Revise si la última inyección le provocó enrojecimiento, cambio del color de la piel, hinchazón, supuración o le sigue doliendo. Si es así, hable con su médico o enfermero.
- Decida la zona en la que se va a inyectar el medicamento. Alterne, cada vez que se inyecte, el lado derecho del abdomen (vientre) con el izquierdo. Este medicamento se debe inyectar justo por debajo de la piel del abdomen, pero no muy cerca del ombligo ni de ninguna cicatriz (al menos a 5 cm de distancia de ellos).
- La jeringa precargada es para un solo uso.
Instrucciones para que usted mismo se inyecte Inhixa
- Lávese las manos y la zona de inyección con agua y jabón. Séquelas.
- Siéntese o túmbese en una posición cómoda y relajada. Compruebe que puede ver la zona en la que se va a inyectar. Lo más adecuado es en un diván, un sillón reclinable o en una cama con cojines para apoyarse.
- Escoja una zona en el lado derecho o izquierdo de la barriga. Debe estar a más de 5 cm del ombligo y hacia los costados.
Recuerde.No se inyecte en los 5 cm alrededor del ombligo ni de las cicatrices o los hematomas que pueda haber. Inyéctese en la zona contraria a la que se inyectó la vez anterior (alternando el lado derecho de la barriga con el izquierdo).
- Saque de la caja el blister de plástico que contiene la jeringa precargada. Abra el blíster y extraiga la jeringa precargada.
- Retire con cuidado el capuchón de la aguja de la jeringa, tirando de él. La jeringa está precargada y lista para su uso.

Nopresione el émbolo antes de inyectarse. Una vez que haya retirado el capuchón, no toque nada con la aguja. De este modo se asegurará de que la aguja siga estando limpia (estéril).
- Sostenga la jeringa con la mano con la que escribe (como si fuera un lápiz) y, con la otra mano, pellizque suavemente la zona del abdomen entre el índice y el pulgar para formar un pliegue de piel.
Asegúrese de sostener el pliegue de piel durante toda la inyección.
- Sostenga la jeringa de manera que la aguja apunte hacia abajo (verticalmente con un ángulo de 90º). Introduzca toda la aguja en el pliegue de piel.
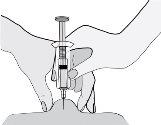
- Presione el émbolo con el pulgar. De este modo inyectará el medicamento en el tejido graso del abdomen. Asegúrese de sostener el pliegue de piel durante toda la inyección.
- Retire la aguja, tirando recto de ella. ¡No deje de presionar el émbolo!
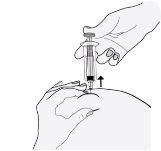
Para evitar que le salga un hematoma, no frote la zona de inyección después de que se haya inyectado.
- Suelte el émbolo y permita a la jeringa que se mueva hacia arriba hasta que toda la aguja esté guardada y bloqueada en su sitio.

- Deposite la jeringa usada en el contenedor para objetos punzantes. Cierre bien la tapa del contenedor y colóquelo fuera del alcance de los niños.
Cuando el contenedor esté lleno, elimínelo tal como su médico o farmacéutico le haya indicado. No lo tire al cubo de la basura.
Autoadministración de una inyección de Inhixa con una jeringa precargada con un Ultrasafe Passive protector de aguja
Su jeringa precargada incluye un Ultrasafe Passive protector de aguja para protegerle de una herida por pinchazo de la aguja.
Si puede administrarse usted mismo este medicamento, su médico o enfermero le mostrarán cómo hacerlo. No intente inyectarse usted mismo si no le han enseñado a hacerlo. Si no sabe qué ha de hacer, consulte a su médico o enfermero de inmediato.
Antes de inyectarse Inhixa
- Compruebe la fecha de caducidad del medicamento. Si ha caducado, no lo utilice.
- Compruebe si la jeringa no está dañada y el líquido del interior es transparente. En caso contrario, use otra jeringa.
No utilice este medicamento si observa algún cambio en su aspecto.
- Compruebe la cantidad que se va a inyectar.
- Revise si la última inyección le provocó enrojecimiento, cambio del color de la piel, hinchazón, supuración o le sigue doliendo. Si es así, hable con su médico o enfermero.
- Decida la zona en la que se va a inyectar el medicamento. Alterne, cada vez que se inyecte, el lado derecho del abdomen (vientre) con el izquierdo. Este medicamento se debe inyectar justo por debajo de la piel del abdomen, pero no muy cerca del ombligo ni de ninguna cicatriz (al menos a 5 cm de distancia de ellos).
- La jeringa precargada es para un solo uso.
Instrucciones para que usted mismo se inyecte Inhixa
- Lávese las manos y la zona de inyección con agua y jabón. Séquelas.
- Siéntese o túmbese en una posición cómoda y relajada. Compruebe que puede ver la zona en la que se va a inyectar. Lo más adecuado es en un diván, un sillón reclinable o en una cama con cojines para apoyarse.
- Escoja una zona en el lado derecho o izquierdo de la barriga. Debe estar a más de 5 cm del ombligo y hacia los costados.
Recuerde.No se inyecte en los 5 cm alrededor del ombligo ni de las cicatrices o los hematomas que pueda haber. Inyéctese en la zona contraria a la que se inyectó la vez anterior (alternando el lado derecho de la barriga con el izquierdo).
- Saque de la caja el blister de plástico que contiene la jeringa precargada. Abra el blíster y extraiga la jeringa precargada.
- Retire con cuidado el capuchón de la aguja de la jeringa, tirando de él. La jeringa está precargada y lista para su uso.

Nopresione el émbolo antes de inyectarse. Una vez que haya retirado el capuchón, no toque nada con la aguja. De este modo se asegurará de que la aguja siga estando limpia (estéril).
- Sostenga la jeringa con la mano con la que escribe (como si fuera un lápiz) y, con la otra mano, pellizque suavemente la zona del abdomen entre el índice y el pulgar para formar un pliegue de piel.
Asegúrese de sostener el pliegue de piel durante toda la inyección.
- Sostenga la jeringa de manera que la aguja apunte hacia abajo (verticalmente con un ángulo de 90º). Introduzca toda la aguja en el pliegue de piel.
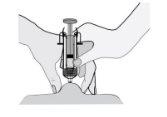
- Presione el émbolo con el pulgar. De este modo inyectará el medicamento en el tejido graso del abdomen. Asegúrese de sostener el pliegue de piel durante toda la inyección.
- Retire la aguja, tirando recto de ella. ¡No deje de presionar el émbolo!
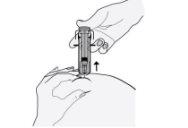
Para evitar que le salga un hematoma, no frote la zona de inyección después de que se haya inyectado.
- Suelte el émbolo y permita a la jeringa que se mueva hacia arriba hasta que toda la aguja esté guardada y bloqueada en su sitio..

- Deposite la jeringa usada en el contenedor para objetos punzantes. Cierre bien la tapa del contenedor y colóquelo fuera del alcance de los niños.
Cuando el contenedor esté lleno, elimínelo tal como su médico o farmacéutico le haya indicado. No lo tire al cubo de la basura.
Autoadministración de una inyección de Inhixa con una aguja precargada con un protector de aguja activado manualmente
Su jeringa precargada incluye un protector de aguja activado manualmente para protegerle de una herida por pinchazo de la aguja.
Si puede administrarse usted mismo este medicamento, su médico o enfermero le mostrarán cómo hacerlo. No intente inyectarse usted mismo si no le han enseñado a hacerlo. Si no sabe qué ha de hacer, consulte a su médico o enfermero de inmediato.
Antes de inyectarse Inhixa
- Compruebe la fecha de caducidad del medicamento. Si ha caducado, no lo utilice. - Compruebe si la jeringa no está dañada y el líquido del interior es transparente. En caso contrario, use otra jeringa.
- No utilice este medicamento si observa algún cambio en su aspecto.
- Compruebe la cantidad que se va a inyectar.
- Revísese el abdomen por si la última inyección le provocó enrojecimiento, cambio del color de la piel, hinchazón, supuración o le sigue doliendo. Si es así, hable con su médico o enfermero.
- Decida la zona en la que se va a inyectar el medicamento. Alterne, cada vez que se inyecte, el lado derecho del abdomen (vientre) con el izquierdo. Este medicamento se debe inyectar justo por debajo de la piel del abdomen, pero no muy cerca del ombligo ni de ninguna cicatriz (al menos a 5 cm de distancia de ellos).
- La jeringa precargada es para un solo uso.
Instrucciones para que usted mismo se inyecte Inhixa
- Lávese las manos y la zona de inyección con agua y jabón. Séquelas
- Siéntese o túmbese en una posición cómoda y relajada. Compruebe que puede ver la zona en la que se va a inyectar. Lo más adecuado es en un diván, un sillón reclinable o en una cama con cojines para apoyarse.
- Escoja una zona en el lado derecho o izquierdo de la barriga. Debe estar a más de 5 cm del ombligo y hacia los costados. Recuerde. No se inyecte en los 5 cm alrededor del ombligo ni de las cicatrices o los hematomas que pueda haber. Inyéctese en la zona contraria a la que se inyectó la vez anterior (alternando el lado derecho de la barriga con el izquierdo).
- Saque de la caja el blister de plástico que contiene la jeringa precargada. Abra el blíster y extraiga la jeringa precargada.
- Retire con cuidado el capuchón de la aguja de la jeringa, tirando de él. La jeringa está precargada y lista para su uso.

Nopresione el émbolo antes de inyectarse. Una vez que haya retirado el capuchón, no toque nada con la aguja. De este modo se asegurará de que la aguja siga estando limpia (estéril).
- Sostenga la jeringa con la mano con la que escribe (como si fuera un lápiz) y, con la otra mano, pellizque suavemente la zona del abdomen entre el índice y el pulgar para formar un pliegue de piel.
Asegúrese de sostener el pliegue de piel durante toda la inyección.
- Sostenga la jeringa de manera que la aguja apunte hacia abajo (verticalmente con un ángulo de 90º). Introduzca toda la aguja en el pliegue de piel.
- Presione el émbolo con el pulgar. De este modo inyectará el medicamento en el tejido graso del abdomen. Asegúrese de sostener el pliegue de piel durante toda la inyección.
- Retire la aguja, tirando recto de ella. ¡No deje de presionar el émbolo
Para evitar que le salga un hematoma, no frote la zona de inyección después de que se haya inyectado.
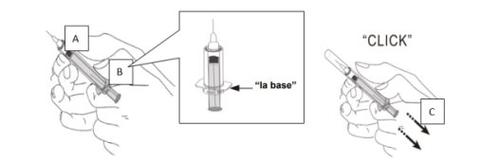
- Sostenga firmemente el cuerpo de la jeringa con una mano (A). Con la otra mano sostenga la base por las “alas” de la jeringa (B), y tire de la base hasta que escuche un clic (C). Ahora la aguja usada está completamente protegida.
- Deposite la jeringa usada en el contenedor para objetos punzantes. Cierre bien la tapa del contenedor y colóquelo fuera del alcance de los niños.
Cuando el contenedor esté lleno, elimínelo tal como su médico o farmacéutico le haya indicado. No lo tire al cubo de la basura.
Cambio de tratamiento de anticoagulante
- Cambio de Inhixa a medicamentos para reducir la coagulación de la sangre denominados antagonistas de la vitamina k (p. ej. warfarina)
Su médico solicitará la determinación en sangre de un parámetro denominado INR y le dirá cuándo debe interrumpir, por lo tanto, el tratamiento con Inhixa.
- Cambio de medicamentos para reducir la coagulación de la sangre denominados antagonistas de la vitamina k (p. ej. warfarina) a Inhixa
Interrumpa el uso del antagonista de la vitamina K. Su médico solicitará la determinación en sangre de un parámetro denominado INR y le dirá cuándo empezar a utilizar, por lo tanto, Inhixa.
- Cambio de Inhixa a tratamiento con anticoagulantes orales directos (por ejemplo apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, rivaroxabán)
Interrumpa el uso de Inhixa. Empiece a tomar el anticoagulante oral directo 0-2 horas antes de cuando le hubiera tocado la siguiente inyección de Inhixa, y después continúe como habitualmente lo hace.
- Cambio de tratamiento con anticoagulante oral directo a Inhixa
Deje de tomar el anticoagulante oral directo. No inicie el tratamiento con Inhixa hasta pasadas 12 horas desde la última dosis del anticoagulante oral directo.
Si usa más Inhixa del que debe
Si considera que ha usado demasiada cantidad o demasiado poco Inhixa, informe inmediatamente a su médico, enfermera o farmacéutico, incluso si no presenta signos de que esté padeciendo algún problema. Si un niño se inyecta o traga Inhixa accidentalmente, llévelo inmediatamente al servicio de urgencias de un hospital.
Si olvidó utilizar Inhixa
Si olvidó administrarse una dosis, hágalo tan pronto como lo recuerde. No use una dosis doble en el mismo día para compensar las dosis olvidadas. Para asegurarse que no olvida ninguna dosis, puede serle de utilidad el uso de un diario.
Si interrumpe el tratamiento con Inhixa
Si tiene cualquier otra duda sobre el uso de este medicamento, pregunte a su médico o farmacéutico o enfermera. Es importante que usted siga recibiendo Inhixa hasta que su médico decida interrumpir el tratamiento. Si deja de usarlo, se podría formar un coágulo de sangre, lo que puede ser muy peligroso.
4. Posibles efectos adversos
Al igual que todos los medicamentos, este medicamento puede causar efectos secundarios, aunque no todos los sufren.
Al igual que otros medicamentos anticoagulantes (medicamentos para reducir los coágulos en sangre), Inhixa podría causar sangrado lo que podría potencialmente poner en peligro su vida. En algunos casos el sangrado podría no ser evidente.
Si aprecia cualquier episodio de sangrado que no para por sí mismo o si nota signos de sangrado excesivo (debilidad fuera de lo normal, cansancio, palidez, mareo, dolor de cabeza o hinchazón inexplicable) consulte inmediatamente con su médico.
Su médico podría decidir mantenerle bajo estricta observación o cambiar su medicación.
Interrumpa el tratamiento con Inhixa e informe inmediatamente a su médico o enfermera si experimenta cualquier signo de reacción alérgica grave (como dificultad para respirar, hinchazón de labios, boca, garganta u ojos).
Interrumpa el tratamiento con enoxaparina e informe inmediatamente a su médico o enfermera si experimenta alguno de los siguientes síntomas:
- Una erupción generalizada, roja y escamosa, con protuberancias bajo la piel y ampollas, acompañada de fiebre. Los síntomas suelen aparecer al inicio del tratamiento (pustulosis exantemática generalizada aguda).
Debe informar inmediatamente a su médico
- Si presenta cualquier signo de bloqueo de un vaso sanguíneo por un coágulo de sangre como:
- dolor tipo calambre, enrojecimiento, calor, o hinchazón en una de sus piernas – que son síntomas de trombosis venosa profunda
- dificultad para respirar, dolor en el pecho, desmayo o tos con sangre – que son síntomas de embolismo pulmonar
- Si tiene erupción cutánea dolorosa con puntos de color rojo oscuro bajo la piel que no desaparecen al presionarlos.
Su médico podría solicitar que le hagan un análisis de sangre para comprobar el número de plaquetas.
Lista general de posibles efectos adversos:
Muy frecuentes (pueden afectar a más de 1 de cada 10 personas)
- Sangrado.
- Aumento de las enzimas hepáticas.
Frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 10 personas)
- Si aparecen hematomas con mayor frecuencia de lo habitual. Esto podría deberse a un problema de la sangre debido a un número bajo de plaquetas.
- Placas rosadas en la piel. Aparecen con mayor frecuencia en la zona en la que le han inyectado Inhixa.
- Erupción en la piel (habones, urticaria).
- Enrojecimiento y picor en la piel.
- Moratón o dolor en el lugar de inyección.
- Disminución del número de células rojas en sangre.
- Aumento del número de plaquetas en sangre.
- Dolor de cabeza.
Poco frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 personas)
- Dolor de cabeza grave repentino. Esto podría ser un signo de hemorragia en el cerebro.
- Sensación de sensibilidad a la palpación e hinchazón del estómago. Podría ser indicativo de una hemorragia gástrica.
- Marcas rojas y grandes en la piel, de forma irregular con o sin ampollas.
- Irritación en la piel (irritación local).
- Amarilleamiento de la piel u ojos, y oscurecimiento del color de la orina. Estso podrían ser signos de un problema de hígado.
Raros (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas)
- Reacción alérgica grave. Los signos de esta reacción podrían incluir: erupción en la piel, problemas para tragar o respirar, hinchazón en los labios, cara, garganta o lengua.
- Aumento del potasio en sangre. Esto es más probable que suceda en personas con problemas de riñón o diabetes. Su médico podrá comprobarlo realizando un análisis de sangre.
- Aumento del número de glóbulos blancos llamados eosinófilos en sangre. Su médico podrá comprobarlo realizando un análisis de sangre.
- Pérdida de pelo.
- Osteoporosis (una enfermedad en la que los huesos se pueden fracturar con mayor probabilidad).
- Hormigueo, entumecimiento y debilidad en los músculos (especialmente en la parte inferior del cuerpo) cuando le han practicado una punción lumbar o una anestesia espinal.
- Pérdida de control de la vejiga o el intestino (de modo que no puede controlar sus necesidades).
- Endurecimiento o nódulo en el lugar de inyección.
Comunicación de efectos adversos
Si experimenta cualquier tipo de efecto adverso, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de posibles efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. También puede comunicarlos directamente a través del sistema nacional de notificación incluido en el Apéndice V. Mediante la comunicación de efectos adversos usted puede contribuir a proporcionar más información sobre la seguridad de este medicamento.
5. Conservación de Inhixa
Mantener este medicamento fuera de la vista y del alcance de los niños.
No utilice este medicamento después de la fecha de caducidad que aparece en la etiqueta y la caja. La fecha de caducidad es el último día del mes que se indica.
Conservar por debajo de 25 ºC. No congelar.
La solución debe usarse en el plazo de 8 horas después de su dilución.
No utilice este medicamento si observa algún cambio visible en el aspecto de la solución.
Las jeringas precargadas de Inhixa son únicamente para un solo uso. Deseche el contenido no utilizado del medicamento.
Los medicamentos no se deben tirar por los desagües ni a la basura. Pregunte a su farmacéutico cómo deshacerse de los envases y de los medicamentos que ya no necesita. De esta forma, ayudará a proteger el medio ambiente.
6. Contenido del envase e información adicional
Composición de Inhixa
- El principio activo es enoxaparina sódica.
Cada mililitro contiene 10 000 UI (100 mg) de enoxaparina sódica.
Cada jeringa precargada de 0,2 ml contiene 2.000 UI (20 mg) de enoxaparina sódica.
Cada jeringa precargada de 0,4 ml contiene 4.000 UI (40 mg) de enoxaparina sódica.
Cada jeringa precargada de 0,6 ml contiene 6000 UI (60 mg) de enoxaparina sódica.
Cada jeringa precargada de 0,8 ml contiene 8000 UI (80 mg) de enoxaparina sódica.
Cada jeringa precargada de 1 ml contiene 10 000 UI (100 mg) de enoxaparina sódica.
- Los demás componentes son agua para preparaciones inyectables.
Aspecto del producto y contenido del envase
Inhixa 2.000 UI (20 mg)/0,2 ml es 0,2 ml de solución contenida en:
- una jeringa de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de polipropileno de color púrpura. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un protector de aguja o un protector de aguja manual; o
- una jeringa de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de policarbonato blanco. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un Ultrasafe Passive protector de aguja.
Este medicamento se presenta en envases de:
- 1, 2, 6, 10, 20 y 50 jeringa(s) precargada(s)
- 2, 6, 10, 20, 50 y 90 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja
- 6, 10 y 20 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja manual
- 2 y 6 jeringas precargadas con UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja
Inhixa 4.000 UI (40 mg)/0,4 ml solución inyectable es 0,4 ml de solución contenida en:
- una jeringa de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de polipropileno de color amarillo. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un protector de aguja o un protector de aguja manual; o
- una jeringa de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de policarbonato blanco. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja.
Este medicamento se presenta en envases de:
- 2, 5, 6, 10, 20, 30 y 50 jeringas precargadas
- 2, 5, 6, 10, 20, 30, 50 y 90 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja
- 2, 6,10, 20 y 50 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja manual
- 2 y 6 jeringas precargadas con UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja
Inhixa 6.000 UI (60 mg)/0,6 ml solución inyectable es 0,6 ml de solución contenida en:
- una jeringa graduada de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de polipropileno de color naranja. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un protector de aguja o un protector de aguja manual; o
- una jeringa graduada de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de policarbonato blanco. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja.
Este medicamento se presenta en envases de:
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30 y 50 jeringas precargadas
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30 y 50 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja
- 6, 10, 12, 20 , 24 y 50 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja manual
- 2 y 10 jeringas precargadas con UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja
Inhixa 8.000 UI (80 mg)/0,8 ml solución inyectable es 0,8 ml de solución contenida en:
- una jeringa graduada de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de polipropileno de color rojo. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un protector de aguja o un protector de aguja manual; o
- una jeringa graduada de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de policarbonato blanco. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja.
Este medicamento se presenta en envases de:
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30 y 50 jeringas precargadas
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30 y 50 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja
- 6, 10, 12, 20, 24 y 50 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja manual
- 2 y 10 jeringas precargadas con UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja
Inhixa 10.000 UI (100 mg)/1 ml solución inyectable es 1 ml de solución contenida en:
- una jeringa graduada de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de polipropileno de color negro. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un protector de aguja o un protector de aguja manual; o
- una jeringa graduda de vidrio transparente, incoloro, neutro y de tipo I, con aguja fija y protector de la aguja cerrado con tapón de goma de clorobutilo y émbolo de policarbonato blanco. La jeringa se puede equipar de forma adicional con un UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja.
Este medicamento se presenta en envases de:
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30, 50 y 90 jeringas precargadas
- 2, 6, 10, 12, 20, 24, 30 y 50 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja
- 6, 10, 12, 20, 24 y 50 jeringas precargadas con protector de aguja manual
- 2 y 10 jeringas precargadas con UltraSafe Passive protector de aguja
Puede que solamente estén comercializados algunos tamaños de envases.
Titular de la autorización de comercialización y responsable de fabricación
Titular de la autorización de comercialización
Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V.
Strawinskylaan 1143, Toren C-11
1077XX Amsterdam
Países Bajos
Responsable de la fabricación
SciencePharma spólka z ograniczona odpowiedzialnoscia
Chelmska 30/34
00-725 Varsovia
Polonia
Pueden solicitar más información respecto a este medicamento dirigiéndose al representante local del titular de la autorización de comercialización:
België/Belgique/Belgien Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V.+31 (0)76 531 5388 | Lietuva Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +37125892152 |
| Luxembourg/Luxemburg Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 |
Ceská republika Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +420255790502 | Magyarország Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +3618001930 |
Danmark Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +4578774377 | Malta Mint Health Ltd +441483928995 |
Deutschland Mitvertrieb: Techdow Pharma Germany GmbH Potsdamer Platz 1, 10785 Berlin +49 (0)30 98 321 31 00 | Nederland Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +31208081112 |
Eesti Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +37125892152 | Norge Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +4721569855 |
Ελλáδα Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 | Österreich Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +43720230772 |
España TECHDOW PHARMA SPAIN, S.L. Tel: +34 91 123 21 16 | Polska Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 |
France Viatris Santé +33 4 37 25 75 00 | Portugal Laboratórios Atral, S.A. +351308801067 |
Hrvatska Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +385 17776255 Ireland Techdow Pharma England Ltd +441483928995 | România Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 Slovenija Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 |
Ísland Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +49 (0)30 220 13 6906 | Slovenská republika Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +421233331071 |
Italia Techdow Pharma Italy S.R.L. Tel: +39 0256569157 | Suomi/Finland Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +358942733040 |
Κúπρος MA Pharmaceuticals Trading Ltd +357 25 587112 | Sverige Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +46184445720 |
Latvija Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V. +37125892152 | United Kingdom(Northern Ireland) Techdow Pharma Netherlands B.V + 44 28 9279 2030 |
Fecha de la última revisión de este prospecto:
Otras fuentes de información
La información detallada de este medicamento está disponible en la página web de la Agencia Europea de Medicamentos: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
- País de registro
- Precio medio en farmacia38.29 EUR
- Principio activo
- Requiere recetaSí
- Fabricante
- Esta información es de carácter general y no sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
- Alternativas a INHIXA 4.000 UI (40 MG)/0,4 ML SOLUCION INYECTABLEForma farmacéutica: INYECTABLE, 100 mg (10000 UI) enoxaparina sodica/mlPrincipio activo: enoxaparinFabricante: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Requiere recetaForma farmacéutica: INYECTABLE, 120 mg (12000 UI) /0,8 mlPrincipio activo: enoxaparinFabricante: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Requiere recetaForma farmacéutica: INYECTABLE, 150 mg (15000 UI) /1 mlPrincipio activo: enoxaparinFabricante: Sanofi Aventis S.A.Requiere receta
Médicos online para INHIXA 4.000 UI (40 MG)/0,4 ML SOLUCION INYECTABLE
Comenta la dosis, los posibles efectos secundarios, interacciones, contraindicaciones o la revisión de receta de INHIXA 4.000 UI (40 MG)/0,4 ML SOLUCION INYECTABLE, sujeto a valoración médica y a la normativa local.
Preguntas frecuentes
















