HUMIRA 20 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE

How to use HUMIRA 20 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Humira 20mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
adalimumab
Read all of this leaflet carefully before your child starts using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again. Your doctor will give you a patient information card, which contains important safety information that you need to know before and during your child's treatment with Humira. You or your child should keep this patient information card.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for your child only and should not be given to others, even if they have the same symptoms as your child, as it may harm them.
- If your child experiences side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Humira and what is it used for
- What you need to know before your child starts using Humira
- How to use Humira
- Possible side effects
- Storing Humira
- Package contents and further information
- How to inject Humira
1. What is Humira and what is it used for
Humira contains the active substance adalimumab
Humira is indicated for the treatment of the following inflammatory diseases:
- Juvenile idiopathic polyarticular arthritis
- Arthritis associated with enthesitis
- Pediatric plaque psoriasis
- Pediatric Crohn's disease
- Pediatric uveitis
The active substance in Humira, adalimumab, is a human monoclonal antibody. Monoclonal antibodies are proteins that target a specific target.
The target of adalimumab is a protein called tumor necrosis factor (TNFα), which is involved in the immune system (defense) and is found in high levels in the inflammatory diseases described above. By targeting TNFα, Humira reduces the inflammation process in these diseases.
Juvenile idiopathic polyarticular arthritis
Juvenile idiopathic polyarticular arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints that usually appears for the first time in childhood.
Humira is used to treat juvenile idiopathic polyarticular arthritis in patients from 2 years of age. Your child may have first received other disease-modifying drugs, such as methotrexate. If these medications do not respond well enough, your child will receive Humira to treat their juvenile idiopathic polyarticular arthritis.
Your doctor will decide whether Humira should be used with methotrexate or alone.
Arthritis associated with enthesitis
Arthritis associated with enthesitis is an inflammatory disease of the joints and areas where tendons attach to bones.
Humira is used to treat arthritis associated with enthesitis in patients from 6 years of age. Your child may have first received other disease-modifying drugs, such as methotrexate. If these medications do not respond well enough, your child will receive Humira to treat their arthritis associated with enthesitis.
Pediatric plaque psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is a skin disease that causes red, scaly, crusty areas covered with silver scales. Plaque psoriasis can also affect the nails, causing them to deteriorate, thicken, and lift off the nail bed, which can be painful. It is believed that psoriasis is caused by a defect in the body's immune system that leads to an increase in skin cell production.
Humira is used to treat severe chronic plaque psoriasis in children and adolescents between 4 and 17 years of age who have not responded or are not suitable candidates for topical therapy and phototherapy.
Pediatric Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is an inflammatory disease of the digestive tract.
Humira is used to treat moderate to severe Crohn's disease in children and adolescents between 6 and 17 years of age.
Your child may have first received other medications. If these medications do not respond well enough, your child will receive Humira to reduce the signs and symptoms of their disease.
Pediatric uveitis
Non-infectious uveitis is an inflammatory disease that affects certain parts of the eye.
Humira is used to treat children with chronic non-infectious uveitis from 2 years of age with inflammation that affects the front part of the eye.
This inflammation can lead to decreased vision and/or the presence of floaters in the eye (black dots or thin lines that move along the field of vision). Humira works by reducing this inflammation.
Your child may have first received other medications. If these medications do not respond well enough, your child will receive Humira to reduce the signs and symptoms of their disease.
2. What you need to know before your child starts using Humira
Do not use Humira:
- If your child is allergic to adalimumab or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If your child has active tuberculosis or other severe infection (see "Warnings and precautions"). If your child has symptoms of infection, such as fever, wounds, fatigue, dental problems, it is important that you inform your doctor.
- If your child has moderate or severe heart failure. It is important that you tell your doctor if your child has had or has any serious heart problems (see "Warnings and precautions").
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before starting treatment with Humira.
Allergic reactions
- If you notice in your child an allergic reaction with symptoms such as chest tightness, difficulty breathing, dizziness, swelling, or rash, discontinue the administration of Humira and contact your doctor immediately, as these reactions can be life-threatening.
Infections
- If your child has an infection, including chronic or localized infections (e.g., a leg ulcer), consult your doctor before starting treatment with Humira. If you are not sure, contact your doctor.
- With Humira treatment, your child may be more likely to get infections. This risk may be greater if they have damaged lungs. These infections can be serious and include:
- tuberculosis
- infections caused by viruses, fungi, parasites, or bacteria
- severe blood infection (sepsis)
In rare cases, these infections can be life-threatening. For this reason, it is essential that if your child has symptoms such as fever, wounds, fatigue, or dental problems, you inform your doctor. Your doctor may recommend temporarily discontinuing treatment with Humira.
- Tell your doctor if your child lives or travels to areas where fungal infections (e.g., histoplasmosis, coccidioidomycosis, or blastomycosis) are common.
- Tell your doctor if your child has had recurrent infections or other factors that increase the risk of infections.
- Your child and their doctor should pay special attention to signs of infection while your child is being treated with Humira. It is essential that if your child has symptoms such as fever, wounds, fatigue, or dental problems, you inform your doctor.
Tuberculosis
- As cases of tuberculosis have been reported in patients treated with Humira, before starting treatment with Humira, your doctor will check for signs and symptoms of tuberculosis in your child. This will include a thorough medical evaluation, including your child's medical history and appropriate screening tests (e.g., chest X-ray and tuberculin test). The behavior and results of these tests should be recorded on your child's patient information card.
- It is crucial that you tell your doctor if your child has ever had tuberculosis or if your child has been in contact with someone who has had tuberculosis. If your child has active tuberculosis, do not use Humira.
- Tuberculosis can develop during treatment, even if your child has received treatment for tuberculosis prevention.
- Tell your doctor immediately if symptoms of tuberculosis (e.g., persistent cough, weight loss, lack of energy, mild fever) or any other infection that appears during or after treatment.
Hepatitis B
- Tell your doctor if your child is a carrier of the hepatitis B virus (HBV), has had active HBV infection, or thinks they may be at risk of getting HBV.
- Your doctor should perform an HBV test. Humira may cause the reactivation of the virus in HBV carriers.
- In rare cases, especially if your child is taking other medications that suppress the immune system, HBV reactivation can be life-threatening.
Surgery or dental procedure
- If your child is going to have surgery or a dental procedure, please inform your doctor that they are taking Humira. Your doctor may recommend temporarily discontinuing treatment with Humira.
Demyelinating disease
- If your child has or develops a demyelinating disease (a disease that affects the insulation layer around nerves, such as multiple sclerosis), their doctor will decide whether they should be treated or continue treatment with Humira. Tell your doctor immediately if your child experiences symptoms such as changes in vision, weakness in arms or legs, or numbness or tingling in any part of the body.
Vaccines
- Certain vaccines may cause infections and should not be given if your child is being treated with Humira.
- Consult your doctor before your child receives any vaccine.
- If possible, it is recommended that children receive scheduled vaccines for their age before starting treatment with Humira.
- If your daughter received Humira during pregnancy, her baby may have a higher risk of getting infections during the first five months after the last dose of Humira received during pregnancy. It is essential that you inform the pediatrician and other healthcare professionals about your daughter's use of Humira during pregnancy so they can decide whether the baby should receive any vaccine.
Heart failure
- If your child has mild heart failure and is being treated with Humira, they may be closely monitored by their doctor. It is essential that you tell your doctor if your child has had or has any serious heart problems. If your child develops new symptoms or worsens their symptoms (difficulty breathing, or swelling of their feet), they should contact their doctor immediately. Their doctor will decide whether they should continue taking Humira.
Fever, bruising, bleeding, or pale appearance
- In some patients, the body may be unable to produce a sufficient number of the type of blood cells that help the body fight infections or stop bleeding. Your doctor may decide to discontinue treatment. If your child develops persistent fever, easy bruising, or bleeding, or looks pale, call their doctor immediately.
Cancer
- In very rare cases, certain types of cancer have been reported in children and adults treated with Humira or other TNF blockers.
- People with more severe rheumatoid arthritis and who have had the disease for a long time may have a higher-than-average risk of developing lymphoma (a cancer that affects the lymphatic system) and leukemia (a cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow).
- If your child is being treated with Humira, the risk of developing lymphoma, leukemia, and other types of cancer may increase. A rare and severe type of lymphoma has been observed in patients treated with Humira. Some of these patients were also receiving treatment with azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine.
- Tell your doctor if your child is taking azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine with Humira.
- Cases of non-melanoma skin cancer have been observed in patients using Humira.
- Tell your doctor if new skin lesions appear or if existing lesions change in appearance during or after treatment.
- Cancers other than lymphoma have been reported in patients with a certain lung disease, called Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), treated with another TNF blocker. If your child has COPD or is a heavy smoker, they should consult their doctor to determine whether treatment with a TNF blocker is suitable for them.
Autoimmune disease
- In rare cases, treatment with Humira may lead to a lupus-like syndrome. Contact your doctor if you have symptoms such as unexplained persistent rash, fever, joint pain, or fatigue.
Using Humira with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if your child is taking, has recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Your child should not take Humira with other medicines that contain the following active substances due to an increased risk of severe infections:
- anakinra
- abatacept
Humira can be taken with:
- methotrexate
- certain disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (e.g., sulfasalazine, hydroxychloroquine, leflunomide, and injectable gold salts)
- corticosteroids or pain medications, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
If you have any doubts, please consult your doctor.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Your daughter should consider using adequate contraceptive methods to avoid becoming pregnant and continue using them for at least 5 months after the last treatment with Humira.
- If your daughter is pregnant, thinks she may be pregnant, or plans to have a baby, she should ask her doctor for advice on using this medicine.
- Humira should be used during pregnancy only if necessary.
- According to a pregnancy study, there was no increased risk of congenital defects when the mother had received treatment with Humira during pregnancy compared to mothers with the same disease who did not receive treatment with Humira.
- Humira can be used during breastfeeding.
- If your daughter used Humira during pregnancy, her baby may have a higher risk of getting infections.
- It is essential that you inform the pediatrician and other healthcare professionals about your daughter's use of Humira during pregnancy before the baby receives any vaccine. For more information on vaccines, see the "Warnings and precautions" section.
Driving and using machines
Humira has a minor influence on your child's ability to drive, ride a bicycle, or use machines. Dizziness and vision disturbances may occur after using Humira.
3. How to use Humira
Follow the administration instructions for this medication exactly as indicated by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
The recommended doses of Humira for each of the approved uses are shown in the following table. Your doctor may prescribe a different dose of Humira if your child needs a different dose.
Juvenile Idiopathic Polyarticular Arthritis | ||
Age or Body Weight | How Much and How Often to Take | Notes |
Children, adolescents, and adults from 2 years of age with a weight of 30 kg or more | 40 mg every other week | Not applicable |
Children and adolescents from 2 years of age with a weight of 10 kg to 30 kg | 20 mg every other week | Not applicable |
Arthritis Associated with Entesis | ||
Age or Body Weight | How Much and How Often to Take | Notes |
Children, adolescents, and adults from 6 years of age with a weight of 30 kg or more | 40 mg every other week | Not applicable |
Children and adolescents from 6 years of age with a weight of 15 kg to 30 kg | 20 mg every other week | Not applicable |
Pediatric Plaque Psoriasis | ||
Age or Body Weight | How Much and How Often to Take | Notes |
Children and adolescents from 4 to 17 years of age with a weight of 30 kg or more | The initial dose is 40 mg, followed by 40 mg one week later. After that, the usual dose is 40 mg every other week. | Not applicable |
Children and adolescents from 4 to 17 years of age with a weight of 15 kg to 30 kg | The initial dose is 20 mg, followed by 20 mg one week later. After that, the usual dose is 20 mg every other week. | Not applicable |
Pediatric Crohn's Disease | ||
Age or Body Weight | How Much and How Often to Take | Notes |
Children and adolescents from 6 to 17 years of age with a weight of 40 kg or more | The initial dose is 80 mg, followed by 40 mg two weeks later. If a faster response is needed, your pediatrician may prescribe an initial dose of 160 mg, followed by 80 mg two weeks later. After that, the usual dose is 40 mg every other week. | Your pediatrician may increase the dose to 40 mg every week or 80 mg every two weeks. |
Children and adolescents from 6 to 17 years of age with a weight of less than 40 kg | The initial dose is 40 mg, followed by 20 mg two weeks later. If a faster response is needed, the doctor may prescribe an initial dose of 80 mg, followed by 40 mg two weeks later. After that, the usual dose is 20 mg every other week. | Your pediatrician may increase the frequency of the dose to 20 mg every week. |
Pediatric Uveitis | ||
Age or Body Weight | How Much and How Often to Take | Notes |
Children and adolescents from 2 years of age with a weight of less than 30 kg | 20 mg every other week | Your doctor may prescribe an initial dose of 40 mg that can be administered one week before starting the usual schedule of 20 mg every other week. It is recommended to use Humira in combination with methotrexate. |
Children and adolescents from 2 years of age with a weight of 30 kg or more | 40 mg every other week | Your doctor may prescribe an initial dose of 80 mg that can be administered one week before starting the usual schedule of 40 mg every other week. It is recommended to use Humira in combination with methotrexate. |
Form and Route of Administration
Humira is injected under the skin (by subcutaneous injection).
In the section 7 "How to inject Humira" you will find the instructions for the administration of a Humira injection.
If you use more Humira than you should
If you accidentally inject Humira more frequently than scheduled by your doctor or pharmacist, you should call your doctor or pharmacist and tell them that your child has used more. Always carry the medicine box with you, even if it's empty.
If you forget to use Humira
If you forget to give your child an injection, you should inject the next dose of Humira as soon as you remember. Then, give your child the next dose as usual, as if you had not forgotten a dose.
If you stop treatment with Humira
The decision to stop using Humira should be discussed with your doctor. Your child's symptoms may return after stopping treatment.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Side Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Most side effects are mild to moderate. However, some can be serious and require treatment. Side effects may appear up to 4 months after the last injection of Humira.
Contact your doctor immediately if you notice any of the following effects
- severe rash, hives, or other signs of allergic reaction
- swelling of the face, hands, feet
- difficulty breathing, swallowing
- shortness of breath when exercising or lying down, swelling of feet
Contact your doctor as soon as possible if you notice any of the following effects
- signs of infection such as fever, nausea, wounds, dental problems, burning sensation when urinating
- feeling of weakness or fatigue
- cough
- tingling
- numbness
- double vision
- weakness in arms or legs
- a lump or an open wound that does not heal
- signs and symptoms of blood disorders such as persistent fever, bruising, bleeding, and paleness
The symptoms described above may be signs of the following side effects, which have been observed with Humira.
Very Common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- reactions at the injection site (including pain, swelling, redness, or itching)
- lower respiratory tract infections (including cold, runny nose, sinusitis, pneumonia)
- headache
- abdominal pain
- nausea and vomiting
- rash
- muscle pain
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- serious infections (including sepsis and flu)
- intestinal infections (including gastroenteritis)
- skin infections (including cellulitis and herpes)
- ear infection
- oral infections (including dental infection and cold sore)
- infections of the reproductive system
- urinary tract infections
- fungal infections
- joint infections
- benign tumors
- skin cancer
- allergic reactions (including seasonal allergy)
- dehydration
- mood changes (including depression)
- anxiety
- difficulty sleeping
- sensory disturbances such as tingling, itching, or numbness
- migraine
- nerve root compression (including lower back pain and leg pain)
- visual disturbances
- eye inflammation
- eyelid inflammation and eye swelling
- vertigo (feeling of dizziness or spinning)
- feeling of rapid heartbeat
- high blood pressure
- flushing
- bruising (accumulation of blood outside blood vessels)
- cough
- asthma
- difficulty breathing
- gastrointestinal bleeding
- indigestion (indigestion, bloating, and heartburn)
- acid reflux
- dry eye syndrome (including dryness in eyes and mouth)
- itching
- itchy rash
- bruising
- skin inflammation (such as eczema)
- breaking of fingernails and toenails
- increased sweating
- hair loss
- new or worsening psoriasis
- muscle spasms
- blood in urine
- kidney problems
- chest pain
- edema (swelling)
- fever
- decrease in platelet count in blood, which increases the risk of bleeding or bruising
- wound healing problems
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- opportunistic infections (including tuberculosis and other infections that occur when resistance to disease decreases)
- neurological infections (including viral meningitis)
- eye infections
- bacterial infections
- diverticulitis (inflammation and infection of the large intestine)
- cancer
- cancer affecting the lymphatic system
- melanoma
- immune system disorders that can affect the lungs, skin, and lymph nodes (the most common presentation is sarcoidosis)
- vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels)
- tremor (feeling shaky)
- neuropathy (nerve disorder)
- stroke
- hearing loss, tinnitus
- feeling of irregular heartbeat like skips
- heart problems that can cause difficulty breathing or swelling of ankles
- heart attack
- aneurysm (ballooning of a major artery), inflammation, and clotting in a vein, blockage of a blood vessel
- lung diseases that can cause difficulty breathing (including inflammation)
- pulmonary embolism (blockage of a pulmonary artery)
- pleural effusion (abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space)
- pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas that causes severe abdominal and back pain)
- difficulty swallowing
- facial edema (swelling of the face)
- gallbladder inflammation, gallstones
- fatty liver
- night sweats
- scars
- abnormal muscle crisis
- systemic lupus erythematosus (including skin inflammation, heart, lung, joint, and other organ inflammation)
- sleep disturbances
- impotence
- inflammations
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1000 people)
- leukemia (cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow)
- severe allergic reaction with shock
- multiple sclerosis
- nerve disorders (such as optic neuritis and Guillain-Barré syndrome that can cause muscle weakness, abnormal sensations, tingling in the arms and upper body)
- cardiac arrest
- pulmonary fibrosis (scarring in the lung)
- intestinal perforation
- hepatitis
- reactivation of hepatitis B virus
- autoimmune hepatitis (inflammation of the liver caused by the body's own immune system)
- cutaneous vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels in the skin)
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (early symptoms include discomfort, fever, headache, and rash)
- facial edema (inflammation of the face) associated with allergic reactions
- erythema multiforme (inflammatory rash on the skin)
- lupus-like syndrome
- angioedema (localized inflammation of the skin)
- lichenoid reaction on the skin (purple-red rash with itching)
Frequency Not Known(cannot be estimated from the available data)
- hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (a rare and often fatal blood cancer)
- Merkel cell carcinoma (a type of skin cancer)
- Kaposi's sarcoma, a rare cancer related to human herpesvirus 8 infection. Kaposi's sarcoma usually occurs more frequently as purple-colored skin lesions
- liver failure
- worsening of a disease called dermatomyositis (seen as skin rash accompanied by muscle weakness)
- weight gain (for most patients, weight gain was reduced)
Some side effects observed in clinical trials do not have symptoms and can only be identified by a blood test. These include:
Very Common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
- low white blood cell count
- low red blood cell count
- increased lipids in blood
- increased liver enzymes
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- high white blood cell count
- low platelet count
- increased uric acid in blood
- abnormal sodium levels in blood
- low calcium levels in blood
- low phosphate levels in blood
- high blood sugar
- high lactate dehydrogenase levels in blood
- presence of autoantibodies in blood
- low potassium levels in blood
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people)
- elevated bilirubin levels (liver function test)
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1000 people)
- low counts in blood for white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets
Reporting of Side Effects
If your child experiences any type of side effect, consult with your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible side effect that is not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the national reporting system included in Appendix V. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Humira
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date that appears on the label/blister/packaging after "EXP".
Store in a refrigerator (between 2°C and 8°C). Do not freeze.
Store the pre-filled syringe in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
Alternative storage:
When necessary (e.g., when traveling), you can store a single Humira pre-filled syringe at room temperature (up to 25°C) for a maximum period of 14 days - make sure to protect it from light. Once you have removed the syringe from the refrigerator to store it at room temperature, you must use it within the next 14 days or discard it, even if you put it back in the refrigerator.
You should write down the date when you removed the syringe from the refrigerator and the date after which you must discard the syringe.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your doctor or pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and additional information
Composition of Humira
The active substance is adalimumab.
The other components are mannitol, polysorbate 80, and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance and pack contents of the product
Humira 20 mg solution for injection in pre-filled syringe for pediatric use is supplied as a sterile solution of 20 mg of adalimumab dissolved in 0.2 ml of solution.
The Humira pre-filled syringe is a glass syringe that contains an adalimumab solution.
The Humira pre-filled syringe is available in a pack that contains 2 pre-filled syringes with 2 alcohol swabs.
Humira is also available in vial, pre-filled syringe, and/or pre-filled pen.
Marketing authorization holder
AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG
Knollstrasse
67061 Ludwigshafen
Germany
Manufacturer
AbbVie Biotechnology GmbH
Knollstrasse
67061 Ludwigshafen
Germany
You can request more information about this medicinal product by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder.
Belgium/Belgique/Belgien AbbVie SA Tel: +32 10 477811 | Lithuania AbbVie UAB Tel: +370 5 205 3023 |
Bulgaria AbbVie Bulgaria EOOD Tel: +359 2 90 30 430 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg AbbVie SA Belgique/Belgien Tel: +32 10 477811 |
Czech Republic AbbVie s.r.o. Tel: +420 233 098 111 | Hungary AbbVie Kft. Tel: +36 1 455 8600 |
Denmark AbbVie A/S Tel: +45 72 30-20-28 | Malta V.J.Salomone Pharma Limited Tel: +356 21220174 |
Germany AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG Tel: 00800 222843 33 (free of charge) Tel: +49 (0) 611 / 1720-0 | Netherlands AbbVie B.V. Tel: +31 (0)88 322 2843 |
Estonia AbbVie OÜ Tel: +372 623 1011 | Norway AbbVie AS Tel: +47 67 81 80 00 |
Greece AbbVie ΦΑΡΜΑΚΕΥΤΙΚΗ Α.Ε. Tel: +30 214 4165 555 | Austria AbbVie GmbH Tel: +43 1 20589-0 |
Spain AbbVie Spain, S.L.U. Tel: +34 91 384 09 10 | Poland AbbVie Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel: +48 22 372 78 00 |
France AbbVie Tel: +33 (0) 1 45 60 13 00 | Portugal AbbVie, Lda. Tel: +351 (0)21 1908400 |
Croatia AbbVie d.o.o. Tel: +385 (0)1 5625 501 | Romania AbbVie S.R.L. Tel: +40 21 529 30 35 |
Ireland AbbVie Limited Tel: +353 (0)1 4287900 | Slovenia AbbVie Biofarmacevtska družba d.o.o. Tel: +386 (1)32 08 060 |
Iceland Vistor hf. Tel: +354 535 7000 | Slovak Republic AbbVie s.r.o. Tel: +421 2 5050 0777 |
Italy AbbVie S.r.l. Tel: +39 06 928921 | Finland AbbVie Oy Tel: +358 (0) 10 2411 200 |
Cyprus Lifepharma (Z.A.M.) Ltd Tel: +357 22 34 74 40 | Sweden AbbVie AB Tel: +46 (0)8 684 44 600 |
Latvia AbbVie SIA Tel: +371 67605000 |
Date of last revision of this leaflet
Detailed information on this medicinal product is available on the European Medicines Agency website: http://www.ema.europa.eu.
To listen to or request a copy of this leaflet inbraille, large print, or listen to it in audio, contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder.
- How to inject Humira
- The following instructions explain how to inject Humira subcutaneously using the pre-filled syringe. Read all the instructions carefully first and then follow them step by step.
- Your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist will show you the injection technique.
- Do not attempt to give your child the injection until you are sure you understand how to prepare and administer the injection.
- After you have been properly trained, your child or another person, such as a family member or friend, can give the injection.
- Use each pre-filled syringe for one injection only.
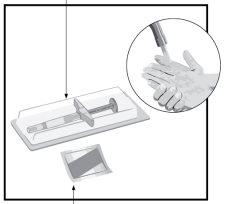
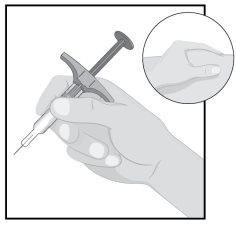
Humira Pre-filled Syringe
PlungerWingsNeedle Cap
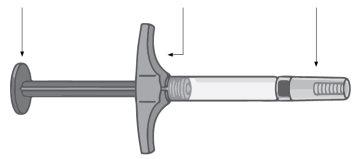
Do not use the pre-filled syringe and call your doctor or pharmacist if
- the liquid is cloudy, discolored, or contains flakes or particles
- the expiration date (EXP) has passed
- the liquid has been frozen or exposed to direct sunlight
- the pre-filled syringe has been dropped or crushed
Do not remove the needle cap until just before injection. Keep Humira out of sight and reach of children.
STEP1 Take Humira out of the refrigerator. Let Humira come to room temperature for 15 to 30minutesbefore injection.
| |
STEP2 Syringe
Alcohol Swab | Check the expiration date (EXP). Do notuse the pre-filled syringe if the expiration date (EXP) has passed. On a flat and clean surface, place
Wash your hands and dry them. |
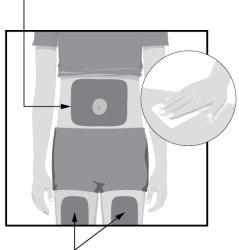
STEP3 Injectable Areas
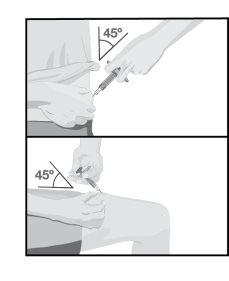
Injectable Areas | Choose an injection site on your body:
Clean the injection site with the alcohol swab in a circular motion.
|
STEP4
| Hold the pre-filled syringe with one hand. Check the liquid in the pre-filled syringe.
Carefully remove the needle cap with the other hand. Dispose of the needle cap and do not reuse it.
|
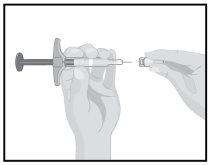
STEP5
| Hold the pre-filled syringe with the needle pointing upwards.
Slowly push the plunger to remove the air through the needle
|
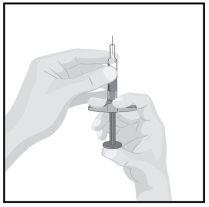
STEP6
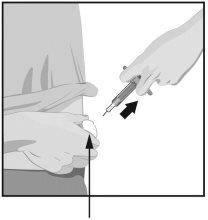
| Hold the body of the pre-filled syringe with one hand between the thumb and index finger, as if holding a pen. Pinch the skin at the injection site with the other hand to make it rise and hold it firmly. |
STEP7
| Insert the needle into the skin at an approximate 45-degree angle, with a short and quick motion.
Slowly push the plunger until it reaches the end, until all the liquid has been injected and the pre-filled syringe is empty. |
STEP8
Cotton Ball | When the injection is complete, slowly pull the needle out of the skin, keeping the pre-filled syringe at the same angle. After completing the injection, place a cotton ball or gauze over the skin at the injection site.
|
STEP9 Dispose of the pre-filled syringe in a special waste container as instructed by your doctor, nurse, or pharmacist. Neverput the needle cap back on a used needle.
The needle cap, alcohol swab, cotton ball or gauze, blister pack, and packaging can be disposed of in household waste. |
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to HUMIRA 20 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGEDosage form: INJECTABLE, 20 mgActive substance: adalimumabManufacturer: Amgen Europe B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 20 mgActive substance: adalimumabManufacturer: Amgen Europe B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 40 mgActive substance: adalimumabManufacturer: Amgen Europe B.V.Prescription required
Online doctors for HUMIRA 20 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE
Discuss questions about HUMIRA 20 mg SOLUTION FOR INJECTION IN PRE-FILLED SYRINGE, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions