
ENTONOX 50%/50% MEDICINAL GAS COMPRESSED
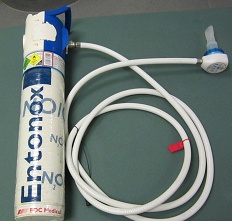

How to use ENTONOX 50%/50% MEDICINAL GAS COMPRESSED
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Entonox 50%/50% Medical Gas, Compressed
Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Entonox and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Entonox
- How to use Entonox
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Entonox
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Entonox and what is it used for
Entonox contains a prepared mixture of nitrous oxide (medical "laughing gas", N2O) and oxygen (medical oxygen, O2), 50% of each, and should be used by inhaling the gas mixture.
The effects of Entonox:
Nitrous oxide makes up 50% of the gas mixture. Nitrous oxide has an analgesic effect, reduces the sensation of pain, and increases the pain threshold. Nitrous oxide also has a relaxing and slightly calming effect. These effects occur due to the action of nitrous oxide on the substances that send signals in your nervous system.
The concentration of 50 percent oxygen, about twice that in ambient air, ensures a safe oxygen content in the inhaled gas.
What Entonox is used for
Entonox should be used when an analgesic effect and a quick remedy for moderate-intensity and limited-duration ailments are desired. Entonox produces an analgesic effect after a few inhalations and this effect stops within minutes of stopping use. Entonox can be used in adults and children from 1 month of age.
2. What you need to know before you use Entonox
Do not use Entonox:
Before using Entonox, you should inform your doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Gases or gas bubbles in cavities: if you suspect you have air in your pleural cavities outside the lungs, or gas bubbles in the blood, or in any other organ (for example, if you have been diving with diving equipment and may have gas bubbles in the blood; or if you have received an intraocular gas injection, for example, for a retinal detachment, or similar) these gas bubbles can expand and cause damage.
- Heart disease: if you have heart failure or poor heart function, as the mild relaxing effect of nitrous oxide on the heart muscle can worsen its function.
- Central nervous system injury: if you have high pressure in the brain, for example, as a result of a tumor or cerebral hemorrhage, nitrous oxide can increase brain pressure further with potential risk of damage.
- Vitamin deficiency: If you have a diagnosed but untreated vitamin B12 deficiency, or folic acid deficiency, the use of nitrous oxide can worsen the symptoms caused by vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency.
- Pseudo-obstruction of the intestine (ileus or intestinal obstruction): if you have severe abdominal discomfort: if there are symptoms that may indicate ileus, Entonox can increase intestinal dilation further.
- Facial or jaw injuries, when the use of a face mask may present difficulties or risks.
Warnings and precautions
Also, consult your doctor if you have any of the following signs or symptoms:
- Decreased level of consciousness or signs of persistent confusion: Inform your doctor if you do not feel well or feel that due to trauma or illness you are not fully awake. This is important due to the sedative effects of nitrous oxide contained in Entonox. There is a risk of greater sedation that can affect your natural protective reflexes.
- Ear discomfort: e.g., ear inflammation, as Entonox can increase pressure in the middle ear.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), as oxygen can cause respiratory depression.
- If you have or have had drug abuse because there is a high risk of dependence on nitrous oxide if you take it repeatedly. Your doctor will decide if treatment with nitrous oxide is possible in your case.
- Vitamin deficiency: if you suspect you have a vitamin B12 deficiency or folic acid deficiency, as the use of nitrous oxide can worsen the symptoms caused by vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency.
Your doctor will decide if it is convenient to use Entonox.
Prolonged or repeated use of nitrous oxide can increase the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency, which can cause damage to the bone marrow or nervous system. Your doctor may require blood tests before and after treatment to evaluate the consequences of a possible vitamin B12 deficiency.
Using Entonox with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
- Methotrexate for the treatment of arthritis. The combined administration of Entonox with methotrexate may have an effect on the blood cell count.
If you are taking other medicines that affect the brain or brain function, e.g., benzodiazepines (tranquilizers) or morphine, you should inform your doctor. Entonox can increase the effects of these medicines. Entonox, taken together with other sedatives or medicines that affect the central nervous system, increases the risk of side effects.
- Bleomycin (for cancer treatment) or amiodarone (to treat an irregular heartbeat), before taking Entonox, as there is a possibility of toxic effects on the lungs due to high oxygen concentration.
- Nitrofurantoin or similar antibiotics (to treat infections).
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or nurse before using this medicine.
Entonox can be used during pregnancy if your doctor considers it clinically necessary. It can also be used during childbirth. If used near childbirth, your baby should be monitored for respiratory difficulties (respiratory depression) and other side effects.
Entonox can be used during breastfeeding, but it should not be used while breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines:
It should be noted that after administration of Entonox, recovery is necessary. The nitrous oxide contained in Entonox disappears from the body quickly with brief inhalations. The effects on cognitive abilities (consciousness) can last for several hours. For safety reasons, you should avoid driving, operating machines, or performing complex tasks until you have fully recovered (at least 30 minutes).
Make sure the healthcare professional informs you if it is safe for you to drive.
3. How to use Entonox
Entonox should always be administered in the presence of personnel familiar with this type of medicine. During the period you use Entonox, both you and the administration of the medicine should be monitored to ensure safe administration. After finishing treatment, you should be monitored by competent personnel until you have recovered.
Follow exactly the administration instructions of this medicine indicated by your doctor. In case of doubt, consult your doctor again. Your doctor or nurse should explain how to use Entonox, how Entonox works, and what effects derive from its use.
Normally, Entonox is inhaled through a mask attached to a special valve, having full control of the gas flow through your own breathing. The valve is open only during inhalation. Entonox can also be administered with a nasal mask. Regardless of which mask is used, you should breathe normally.
Use in children
In children who are not able to understand and follow instructions, Entonox should be administered under the supervision of competent medical personnel who can help them keep the mask in place and actively monitor administration. In these cases, Entonox can be administered with a continuous gas flow.
After stopping the use of Entonox, you should rest and recover until you feel mentally recovered.
Safety measures:
- Smoking and the presence of flames are strictly prohibited in the room where the treatment with Entonox takes place.
- Entonox is exclusively for medical use.
Please also review the handling and storage instructions for Entonox (5. Storage of Entonox).
If you use more Entonox than you should:
It is unlikely that you will receive too much gas, as you control the application of gas and the gas mixture is fixed (with 50% nitrous oxide and 50% oxygen).
If you breathe faster than normal, receiving more nitrous oxide than with normal breathing, you may feel noticeably tired and lose contact with your surroundings to some extent. In such a case, you should immediately inform the medical personnel and interrupt its use.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult the Toxicological Information Service. Telephone 91 562 04 20.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Frequent(may affect up to 1 in 10 users):
Dizziness, drowsiness, euphoria, nausea, and vomiting.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 users):
Severe fatigue. Feeling of pressure in the middle ear, if Entonox is used for a prolonged period. This is because Entonox increases pressure in the middle ear. Abdominal bloating, because Entonox slowly increases the volume of intestinal gases.
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from the available data):
Effects on nervous system function, feeling of numbness and weakness, usually in the legs.
Effects on the bone marrow, which can cause anemia (low red blood cell count) and leukopenia (low white blood cell count).
You may also experience headache and confusion after finishing administration.
Psychiatric effects, such as psychosis, confusion, and anxiety, have been reported in extremely rare cases. Respiratory depression.
Addiction.
Generalized seizures.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if it is possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Medicines and Healthcare Products Agency's website: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Entonox
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
Do not store below -5°C.
If you suspect that Entonox has been stored in conditions that are too cold, the cylinders should be placed in a horizontal position at a temperature above +10°C for at least 48 hours before use.
Store the cylinder in a storage area reserved for medical gases.
It should be kept away from combustible materials. It should only be used in well-ventilated areas.
Do not smoke or expose to strong heat near the cylinder.
If there is a risk of fire, the Entonox cylinder should be moved to a safe place.
Keep the cylinder clean, dry, and free of oil and grease.
Make sure the cylinder has not been impacted or dropped.
It should be stored and transported with the valves closed.
The vapor can cause drowsiness and dizziness.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Entonox
- The active substances are:
Nitrous oxide 50% = medical "laughing gas" (chemical term: N2O) and
Oxygen 50% = medical oxygen (chemical term: O2)
- Entonox does not contain any other ingredients.
Appearance of the product and pack contents
Entonox is a colorless, odorless, tasteless gas, supplied in a cylinder with a valve to control the gas flow.
Pharmaceutical form: medical gas, compressed.
The top of the cylinder is marked in white and blue (oxygen/nitrous oxide). The body of the cylinder is white (medical gas).
Package size in liters | 2 | 5 | 10 |
Not all pack sizes are marketed.
Marketing authorization holder:
Linde Sverige AB
Rättarvägen 3
169 68 Solna
Sweden
Manufacturers:
AGA Gas AB
Rotevägen 2
SE- 192 78 Sollentuna (Rotebro site)
Sweden
Linde Gas AB
Baltzar von Platens gata 4-6
SE-74521 Enköping
Sweden
Linde France
16 avenue de la Saudrune
Zone industrielle du Bois Vert
31 120 Portet sur Garonne
France
Linde Gaz Polska Sp. Z o.o.
ul. Zwirowa 4
33-100 Tarnów
Poland
LINDE GAZ POLSKA Sp. Z o. o.
Oddzial w Tarnów
Poland
Information provided by:
LINDE GAS ESPAÑA, SA.U.
C/ Camino de Liria, s/n, apartado de correos nº 25,
46530 Puzol, Valencia, Spain
Tel: 902 426 462
This medicinal product is authorized in the EEA Member States under the following names:
Austria LIVOPAN
Belgium RELIVOPAN
Czech Republic ENTONOX
Cyprus ENTONOX
Denmark LIVOPAN
Estonia ENTONOX
Finland LIVOPAN
Germany LIVOPAN
Greece ENTONOX
Hungary ENTONOX
Iceland LIVOPAN
Italy LIVOPAN
Latvia ENTONOX
Lithuania ENTONOX
Luxembourg RELIVOPAN
Netherlands RELIVOPAN
Norway LIVOPAN
Poland ENTONOX
Portugal LIVOPAN
Romania ENTONOX
Spain ENTONOX
Slovakia ENTONOX
Sweden LIVOPAN
Date of last revision of this leaflet:May 2019
Other sources of information
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Healthcare Products: www.aemps.es
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Safety instructions
No risk of adverse fetal effects has been observed in women exposed occupationally to chronic inhalation of nitrous oxide during pregnancy when an adequate ventilation and air renewal system is available. For more information, see the technical data sheet. Special precautions should be taken when working with nitrous oxide. Nitrous oxide should be administered according to local guidelines.
Entonox should only be used in well-ventilated areas and where there is special equipment to extract excess gas. Using an extraction system and ensuring good ventilation, high atmospheric concentrations of laughing gas in the air can be avoided. High concentrations of laughing gas in the air can cause adverse health effects on personnel and people in the surrounding area. There are national values for the concentration of nitrous oxide in the air that should not exceed the so-called "health limit values", often expressed as: TWA (time-weighted average), which is the average value during a working day, and STEL (short-term exposure limit), which is the average value during a shorter exposure.
These values should not be exceeded to ensure that personnel are not exposed to risks.
Repeated administration or exposure to nitrous oxide can lead to addiction. Caution should be exercised in healthcare professionals with occupational exposure to nitrous oxide.
- The valve should be opened slowly and carefully.
- Turn off the equipment in case of fire or if it is not working.
- During use of the cylinder, it should be fixed with a suitable support.
- The cylinder should be replaced when the pressure has dropped to a point where the valve indicator is within the yellow field.
- When a small amount of gas remains in the cylinder, the valve should be closed. It is important to leave some pressure in the cylinder to avoid the entry of contaminants.
- After use, the cylinder valve should be closed firmly. Depressurize the regulator or connection.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ENTONOX 50%/50% MEDICINAL GAS COMPRESSEDDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 50% / 50% v/vActive substance: nitrous oxide, combinationsManufacturer: Sociedad Española De Carburos Metalicos S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 50%/50% (V/V)Active substance: nitrous oxide, combinationsManufacturer: Sol France Sucursal En EspanaPrescription requiredDosage form: PULMONARY INHALATION, 50% nitrous oxide; 50% oxygenActive substance: nitrous oxide, combinationsManufacturer: Air Liquide Sante InternationalPrescription required
Online doctors for ENTONOX 50%/50% MEDICINAL GAS COMPRESSED
Discuss questions about ENTONOX 50%/50% MEDICINAL GAS COMPRESSED, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















