VEINFIBRO 1% INJECTABLE SOLUTION


How to use VEINFIBRO 1% INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Leaflet: Information for the user
Veinfibro 1% injectable solution
Sodium tetradecyl sulfate
Read this leaflet carefully before starting to use this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only and you should not give it to others, even if they have the same symptoms as you, as it may harm them.
- If you experience side effects, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the leaflet:
- What is Veinfibro and what is it used for
- What you need to know before using Veinfibro
- How to use Veinfibro
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Veinfibro
- Package contents and additional information
1. What is Veinfibro and what is it used for
Veinfibro is a medicine that contains sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Veinfibro is used to treat varicose veins, large, medium, or small venules, and spider veins.
Veinfibro belongs to a group of medicines called sclerosing agents. Sclerosing agents are chemical agents that, when injected into the affected vein, cause the vein wall to become inflamed and the walls to stick together. This stops the blood flow and the vein becomes scar tissue. Within a few weeks, the vein should disappear.
Veinfibro is for use in adults only.
2. What you need to know before using Veinfibro
Do not use Veinfibro if you:
- are allergic to sodium tetradecyl sulfate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6) or have an allergic disease.
- cannot walk for any reason or are bedridden.
- are at risk of developing blood clots in the veins due to:
- inherited blood disorders such as thrombophilia
- hormonal contraceptive or replacement therapy.
- significant overweight
- being a smoker
- prolonged immobilization
- have recently had blood clots in the superficial or deep veins or lungs
- have recently undergone surgery
- have varicose veins (varices) caused by pelvic or abdominal tumors, unless the tumor has been removed
- have uncontrolled diseases such as diabetes, hyperthyroidism, asthma, blood abnormalities, blood infection, or recent respiratory or skin problems
- have swelling or a red area of the skin that is hot or sensitive (cellulitis)
- have any type of infection
- have a progressing cancer
- if you have been told that you have problems with the closure of the valves of the deep veins (valvular incompetence)
- have a blocked artery
- Have a severe inflammation of the veins in the legs (acute phlebitis)
- have symptoms of a congenital heart disease (only if the sclerosant is used as foam)
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor or nurse before starting to use Veinfibro if:
- you are allergic to any food or medicine or have other allergies. You should inform your doctor, as it is necessary to administer a test dose 24 hours before administering a larger dose later.
- you have a history of blood clots in superficial or deep veins or lungs
- you have an asymptomatic hole in the heart (if the sclerosant is used as foam)
- you have a symptomatic or asymptomatic hole in the heart (if the sclerosant is used as liquid)
- you suffer from migraines
- you have problems with the veins in your legs associated with a prolonged disease that causes inflammation of the body tissues (lymphedema). Veinfibro may worsen local pain and inflammation for a few days or weeks.
- you have a history of pulmonary hypertension
- you have a history of a transient ischemic attack (TIA), stroke, or severe cerebral attack
- you have been told that you have any disease in the arteries or veins (arteriosclerosis)
- you have severe inflammation and blood clots in the arteries and veins that affect your hands and feet (Buerger's disease)
- you have any breathing difficulties (controlled asthma)
Veinfibro should be administered by a doctor when national guidelines allow it. Veinfibro may be administered by properly qualified healthcare professionals with experience in vein anatomy and familiar with the appropriate injection technique under the supervision of a doctor. Before using this injection, you may need to undergo tests to check if you have any problems with the closure of the valves in your veins.
Your doctor will ask you questions about your health and inform you about the possible side effects of this procedure.
During treatment
Your doctor will monitor you during and after sclerotherapy for signs of hypersensitivity (redness, itching, cough) or neurological symptoms (visual disturbances, migraines, tingling, numbness).
They will ask you to return for a follow-up visit.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of Veinfibro in children and adolescents have not been established.
Other medicines and Veinfibro
If you are taking hormonal contraceptives (the pill) or hormone replacement therapy, you may be at risk of developing blood clots in the veins (see "Do not use Veinfibro if you"). You should inform your doctor or nurse.
Tell your doctor or nurse if you are taking or have recently taken any other medicine, including those obtained without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
You should inform your doctor if:
- you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant
- you plan to become pregnant
- you are breastfeeding
There is no adequate information on the use of Veinfibro in pregnant women. Veinfibro should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary. Your doctor will decide if this treatment is suitable for you or not.
It is not known if Veinfibro is excreted in breast milk. If you are breastfeeding, your doctor will decide if Veinfibro can be used.
Driving and using machines
After treatment with this injection, you may be advised to wear a bandage and/or compression stockings to help reduce inflammation and skin pigmentation, which could affect your ability to drive.
Veinfibro contains sodium, potassium, and benzyl alcohol
This medicine contains:
- less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per vial or ampoule, i.e., essentially "sodium-free".
- less than 1 mmol of potassium (39 mg) per vial or ampoule, i.e., essentially "potassium-free".
- 40 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 2 ml ampoule or 100 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 5 ml vial, which is equivalent to 20 mg/ml. Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or have liver or kidney disease. This is because large amounts of benzyl alcohol can accumulate in your body and cause side effects (metabolic acidosis).
3. How to use Veinfibro
Do not attemptto inject Veinfibro yourself. You should always be treated by an experienced doctor familiar with the injection technique.
The therapy involves injecting the medicine into the affected vein using the smallest possible needles and should be injected slowly and with extreme care to expel the contents of these veins. The medicine can be manually mixed with air using two syringes and a connector to create foam that helps expel blood from larger veins. In this case, it should be administered by a doctor trained in the correct generation and administration of the foam.
Your doctor should be guided by ultrasound technique in the treatment of non-visible varicose veins to administer the sclerosant in foam.
Your doctor will decide on the areas to be treated and the correct dose for you. The recommended doses are as follows:
Adults and elderly
The dose varies between 0.1 and 2 ml for each injection. A maximum of 10 ml of the three injections of the lowest concentration can be used; however, no more than 4 ml is used when the highest concentration injection is used.
Due to the limited volume of sclerosant authorized, repeated sessions of sclerotherapy may be necessary.
After being treated with Veinfibro, you should follow your doctor's advice. They may advise you to wear a bandage or compression stockings to help reduce inflammation and skin pigmentation.
If you have any doubts about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
You may experience serious side effects. Stop treatment with Veinfibro and consult your doctor or go to a hospital emergency department immediately if you have:
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients):
- Blood clots in deep veins (deep vein thrombosis possibly due to an underlying disease). Symptoms may include pain, inflammation, sensitivity in one leg (usually the calf), intense pain in the affected area, hot skin in the area of the clot, or red skin, especially on the back of the leg below the knee.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients):
- Local tissue death (necrosis) of the skin and, less commonly, nerves. Symptoms include pain, skin discoloration (redness), inflammation, or fluid accumulation, blisters (which may be filled with clear fluid or blood), the skin turns dark red, purple, or black, abnormal sensation (tingling, stinging, burning), numbness, or loss of sensation.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 patients):
- A very severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock), which can cause difficulty breathing or a sudden drop in blood pressure, making you feel dizzy or faint. It is very rare but should be treated immediately as it can be fatal.
- Blockage of an artery due to a clot, which can cause:
- a stroke or interruption of blood supply to the brain or eye (transient ischemic attack). Symptoms may include weakness, numbness, paralysis in the face, arm, or leg, usually on one side of the body, slurred or unintelligible speech, or difficulty understanding others, blindness in one or both eyes, or double vision.
- a clot in the lungs. Symptoms may include sudden difficulty breathing, sharp and sudden chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing, rapid heartbeat, or rapid breathing.
To avoid this serious and very rare event, this medicine should not be administered to patients at high risk of forming clots in veins and arteries (thrombosis risk).
- Circulatory failure. Symptoms may include fatigue, loss of consciousness, fainting, chest pain, difficulty breathing, weakness, dizziness, vomiting, and palpitations.
- Tissue death after intra-arterial injection. Symptoms may vary depending on the amount of medicine injected and how quickly medical attention is received. Symptoms may range from pain without long-term damage to loss of large areas of tissue, including the foot, resulting in amputation.
Other side effects that you may experience are:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 patients):
- Superficial inflammation of the vein
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 patients):
- Pain or burning (short-term at the injection site),
- Skin discoloration
- Growth of very fine spider veins in the treated area (capillarization)
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients):
- Local allergic and non-allergic skin reactions such as redness, itching, rash, skin inflammation.
- Visual disturbances
- Migraines
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients):
- Cough, difficulty breathing, feeling of pressure, chest tightness
- Burning, tingling, numbness, or itching of the skin
- Headache and feeling of fainting
- Confusion, dizziness, and loss of consciousness
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 patients):
- Fever, hot flashes, itching, and skin redness (urticaria)
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, sensation of inflammation in the tongue, dry mouth
- Inflammation of blood vessels.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse, even if they are not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines Monitoring System for Human Use: https://www.notificaram.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Veinfibro
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
- This medicine does not require any special storage temperature
- Do not freeze.
- Keep the container in the outer packaging to protect it from light
- Do not use this medicine after the expiration date shown on the label or carton. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
For single use. Once the container is opened, the contents should be used immediately. Discard any unused portion of the product.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Deposit the containers and medicines you no longer need at the pharmacy's SIGRE point. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the containers of medicines you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container contents and additional information
Composition of Veinfibro
The active ingredient is sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Each ml of injectable solution contains 10 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Each 2 ml ampoule contains 20 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
The other components are: benzyl alcohol (20 mg/ml), disodium phosphate dodecahydrate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, water for injectable preparations, sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH). See section 2, "Veinfibro contains sodium and potassium".
Appearance of Veinfibro and container contents
This medicine is presented as an injectable solution in transparent glass vials or ampoules.
The solution is transparent, colorless, sterile, and free of visible particles.
Packaging of 5 ampoules of 2 ml.
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
STD Pharmaceutical (Ireland) Limited,
Block 1, Blanchardstown Corporate Park,
Ballycoolen Road, Blanchardstown,
Dublin 15, D15 AKK1,
Ireland
Manufacturer
Medipha Sante
Les Fjords-Immeuble Oslo
19 Avenue de Norvege
91953 Courtaboeuf CEDEX
France
O
Chemische Fabrik Kreussler & Co. GmbH
Rheingaustrasse 87-93
65203 Wiesbaden,
Germany
You can request more information about this medicine by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Local representative:
Logsa Endomedical S.L.
C/ Escritora Carmen Martín Gaite, 2,
Local 2, 29196 Málaga. Spain
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of theEconomic European Areaunder the following names:
Germany, Bulgaria, France, Ireland, Netherlands, Poland, Czech Republic, Romania Fibrovein
Austria, Spain Veinfibro
Date of the last revision of this prospectus: 05/2024
The following information is intended only for healthcare professionals
Veinfibro 1% injectable solution
For more information, see the Technical Sheet
Posology and method of administration
Posology
Veinfibro should be administered only by the intravenous route. The necessary concentration will depend on the size and degree of varicosity. Vascular spiders should be treated with the 0.2% solution and reticular veins with the 0.5% solution. The 1% solution is more useful for small or medium varices and the 3% solution for large varices. The size of non-visible varices should be measured by ultrasound.
The sclerosant should be administered intravenously in small aliquots at multiple points along the vein to be treated. Veinfibro 0.2% and 0.5% should be administered in liquid form. Veinfibro 1% and 3% solutions can be administered either as a liquid or as a sclerosant/air mixture (foam) as detailed in the table below. The goal is to achieve optimal destruction of the vessel wall with the minimum concentration of sclerosant necessary for a clinical result. If the concentration is too high, necrosis or other adverse sequelae may occur.
Adults
Concentration | Normal volume injected intravenously at the appropriate site per session | Maximum total volume injected per session | ||
Liquid | Foam* | Liquid | Foam* | |
Veinfibro 1% | 0.1 to 1.0 ml | 0.5 to 2.0 ml | 10 ml | 16 ml |
- The volume is the sum of the liquid and air components.
When special caution is required, it is recommended to administer a test dose of 0.25 to 0.5 ml of Veinfibro and observe the patient for several hours before administering a second dose or a larger dose.
Since the volume to be injected is limited per session, repeated sessions (2 to 4 on average) are often necessary. To prevent a possible allergic reaction, it is recommended to give a small test dose of Veinfibro at the beginning of each session.
When the sclerosant is administered as foam.
Veinfibro 1% and 3% can be converted into foam for use in the treatment of larger veins. The foam should be prepared just before use and administered by a doctor trained in the correct preparation and administration of the foam. Ideally, it should be administered under ultrasound guidance.
Elderly population
No specific dose recommendation is applicable.
Pediatric population
The safety and efficacy of Veinfibro in children and adolescents have not been established. No data are available.
Method of administration
See the instructions for preparing the foam below. The Tessari method for preparing the foam is described. Other techniques (e.g., DSS, Easyfoam, Sterivein) may be used.
To see the method of preparing the foam, consult the end of this section. Other techniques (e.g., DSS, Easyfoam, Sterivein) may be used.
A strictly aseptic technique should be maintained when handling Veinfibro. Veinfibro is a single-use parenteral medicine. Once the container is opened, it should be used immediately and any unused portion discarded.
Visually inspect before use to ensure there are no visible particles. Solutions containing visible particles should not be used.
When the sclerosant is administered as foam, it should ideally be administered under ultrasound guidance. It should be administered by a doctor trained in the correct generation and administration of foam.
Incompatibilities
This medicine is incompatible with heparin.
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicine should not be mixed with other medicines.
Special warnings and precautions
Veinfibro should only be administered by a doctor when national guidelines permit it. Veinfibro may be administered by qualified healthcare professionals with experience in venous anatomy and in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases affecting the venous system and who are familiar with the correct injection technique under the supervision of a doctor.
Allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported, and the doctor should be prepared to treat them properly. An emergency resuscitation team should be available. As a precaution, the patient should be treated in the hospital.
Severe local adverse effects, including tissue necrosis, may occur after extravasation; therefore, extreme care should be taken in the intravenous placement of the needle, and the effective minimum volume should be used at each injection site. The solution should be injected slowly.
Caution should be exercised not to inject the solution into an artery, as this could cause tissue death (necrosis) and could lead to the death of the limb.
Caution should be exercised when injecting into the foot and the area above and below the ankle (malleolar area) due to the risk to one of the arteries. Compression should be applied when treating small veins, as pigmentation may occur if blood is expelled into the injection site area.
Preparation and handling
General indications
The quality of the foam depends on specific criteria:
- The product concentration: the foam can only be prepared with concentrations of 1 and 3% of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
- The liquid-to-air ratio: this ratio is often 1 volume of liquid to 3 or 4 volumes of air.
- Number of forward and backward steps: the doctor should precisely follow the defined number of movements for each technique.
- The macroscopic consistency of the foam: the quality of the foam should be checked outside the syringe before administration. The foam should be homogeneous, smooth, and cohesive without visible large bubbles. If large bubbles are visible, the foam should be discarded and a new foam prepared.
- The total foam preparation time: the preparation should take about 10 seconds from the first to the last transfer movement.
- The maximum time between preparation and injection: the sclerosant foam should be used within sixty seconds of being produced. After sixty seconds, any remaining foam should be discarded. More foam should be prepared if necessary.
Prepare the foam (Tessari technique)
A strictly aseptic technique should be maintained during foam preparation.
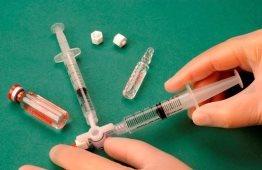
To make the foam, 1 ml of sclerosant liquid is drawn into a sterile syringe and 3 ml or 4 ml of sterile air is drawn into another sterile syringe. The air is drawn through a 0.2-micron filter to ensure its sterility. The syringes are then connected using a sterile three-way valve (Figure 1). The use of Luer Lock syringes and eye protection when preparing the foam is recommended. The connection with the three-way valve may fail under pressure with Luer Slip syringes, causing the product to exit uncontrolled.
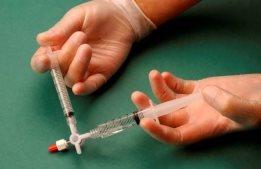
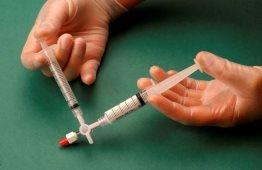
The air and sclerosant mixture is then forced to pass from one syringe to the other through the three-way valve at least 20 times to produce a smooth and consistent foam (Figures 2 and 3).
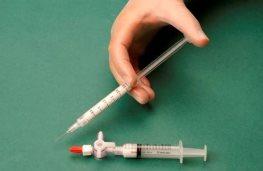
The syringe containing the foam is then removed and injected into the vein immediately (Figure 4).
The sclerosant foam should be used within sixty seconds of being produced. After sixty seconds, any remaining foam should be discarded. More foam should be prepared if necessary.
The quality of the foam should be checked before administration. It should have a homogeneous appearance, white color, and no visible large bubbles.
Figure 1 |
Figure 2 |
Figure 3 |
Figure 4 |
Excipients
This medicine contains:
- Less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per vial/ampoule, i.e., essentially "sodium-free".
- Less than 1 mmol of potassium (39 mg) per vial/ampoule, i.e., essentially "potassium-free".
- 40 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 2 ml ampoule or 100 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 5 ml vial, which is equivalent to 20 mg/ml. Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions. It may cause metabolic acidosis in pregnant patients, during lactation, or in patients with liver or kidney disease.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to VEINFIBRO 1% INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.5%Active substance: sodium tetradecyl sulfateManufacturer: Std Pharmaceutical (Ireland) LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 3%Active substance: sodium tetradecyl sulfateManufacturer: Std Pharmaceutical (Ireland) LimitedPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution for injection, 2 mgActive substance: sodium tetradecyl sulfateManufacturer: Std Pharmaceutical (Ireland) LimitedPrescription required
Online doctors for VEINFIBRO 1% INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about VEINFIBRO 1% INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions