
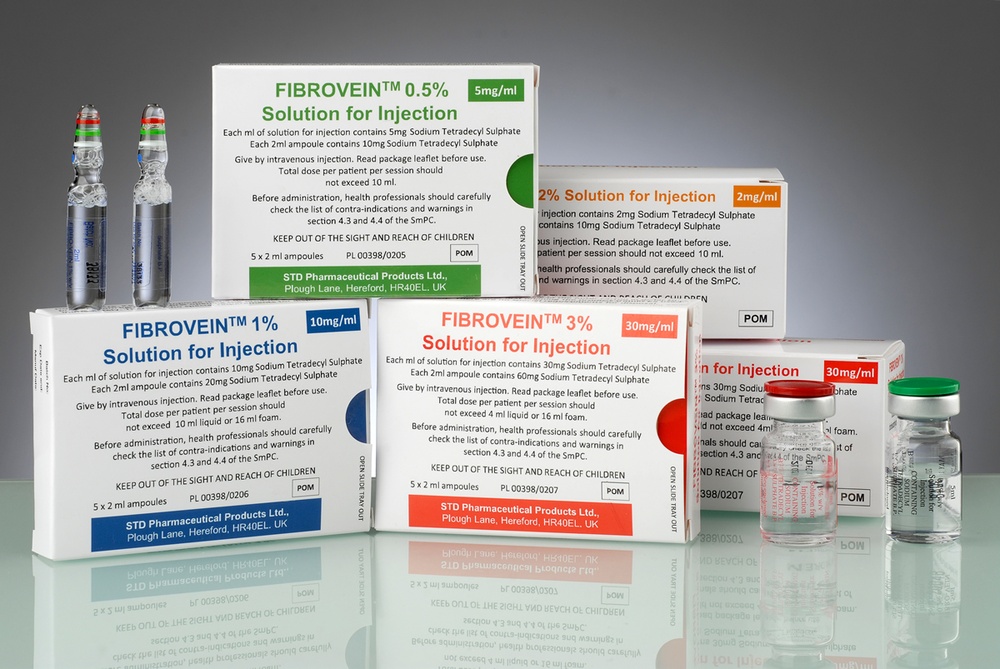
Fibrovein

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fibrovein

How to use Fibrovein
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Fibrovein, 0.2%, 0.5%, 1% and 3%, solution for injection
Sodium tetradecyl sulfate
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
In case of any doubts, you should consult a doctor or nurse.
If the patient experiences any serious side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Fibrovein and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Fibrovein
- 3. How to use Fibrovein
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Fibrovein
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Fibrovein and what is it used for
Fibrovein contains the active substance sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Fibrovein is available in different concentrations and is used to treat varicose veins, large, medium and small dilated blood vessels and spider veins.
The active substance of Fibrovein belongs to a group of so-called sclerosing agents. Sclerosing agents are chemical substances that, when injected into a diseased vein, cause the inner surface of the vein to swell and the walls to stick together. Blood flow through the vein becomes impossible and eventually the vein tissue becomes scarred. After a few weeks, the vein usually becomes invisible.
Fibrovein is intended for use only in adults.
2. Important information before using Fibrovein
When not to use Fibrovein:
- if the patient has been diagnosed with an allergy to sodium tetradecyl sulfate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6) or if the patient has an allergic disease;
- if the patient is unable to walk for any reason or is bedridden;
- if the patient is at risk of developing blood clots in the venous system due to:
- genetically determined blood disease, e.g. thrombophilia;
- use of hormonal contraceptives or hormone replacement therapy;
- severe obesity;
- smoking;
- prolonged immobilization;
- if the patient has recently experienced blood clots in superficial or deep veins or in the lungs;
- if the patient has recently undergone surgery;
- if the patient has twisted veins (varicose veins of the lower limbs) caused by tumors in the pelvic or abdominal cavity, unless the tumor has been removed;
- if the patient has an uncontrolled systemic disease such as diabetes, hyperthyroidism, asthma, blood abnormalities, blood infection or recent skin disorders or breathing difficulties;
- if the patient has swelling or redness of the skin, warmth or tenderness to the touch (connective tissue inflammation);
- if the patient has any infection;
- if the patient has a progressive tumor;
- if the patient has been diagnosed with improper closure of the deep vein valves (valve insufficiency);
- if the patient has an arterial blockage;
- if the patient has acute inflammation of the veins of the lower limbs (acute phlebitis);
- if the patient has a symptomatic hole in the heart (only in the case of using the sclerosant in the form of foam).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Fibrovein, the patient should discuss it with their doctor if:
they are allergic to any foods or medicines, or if they have any other allergy, before taking the medicine, they should consult a doctor so that they can be given a test dose 24 hours before further treatment;
they have had blood clots in superficial or deep veins or in the lungs in the past;they have a symptomatic hole in the heart (in the case of using the sclerosant in the form of foam).
they have migraines;
if the patient has vein disorders in the legs, which is associated with a long-term condition, causing swelling of body tissues (lymphedema). Fibrovein may exacerbate local pain and inflammation for several days or weeks;
if the patient has had pulmonary hypertension in the past;
if the patient has had a transient ischemic attack (TIA), stroke or serious cerebral incident;
if the patient has been diagnosed with arterial or venous disease (vascular arteriosclerosis);
if the patient has been diagnosed with blood clots and inflammation of the arteries and veins of the hands and feet (Buerger's disease);
if the patient has breathing difficulties, which are controlled with treatment (asthma).
Fibrovein should only be administered by a doctor, and if national guidelines permit, the medicine may be administered under the supervision of a doctor by appropriately qualified medical personnel who have experience in the anatomy of the venous system and are familiar with the proper injection technique.
Before performing the injection, the doctor may perform an assessment of the patient's venous valve function.
Before starting the procedure, the doctor will ask the patient a few questions about their health and provide information about potential side effects related to the procedure.
During treatment
The doctor will monitor the patient during and after the sclerotherapy procedure for signs of hypersensitivity (redness, itching, coughing) or neurological symptoms (vision disturbances, migraines, tingling or numbness).
The doctor will recommend that the patient come for a follow-up visit.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of Fibrovein in children and adolescents have not been established.
Fibrovein and other medicines
If the patient is taking hormonal contraceptives (so-called "pill") or hormone replacement therapy, they may be at risk of developing blood clots in the veins (see "When not to use Fibrovein").
The patient should tell their doctor or nurse about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take, including those available without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
The patient must tell their doctor if:
they are pregnant or think they may be pregnant;
they plan to become pregnant;
they are breastfeeding.
The safety of using Fibrovein during pregnancy has not been established. Fibrovein should not be used in pregnant women unless it is absolutely necessary. The doctor will decide whether Fibrovein is suitable for the patient.
It is not known whether Fibrovein passes into breast milk. If the patient is breastfeeding, the doctor will decide whether Fibrovein is a suitable medicine for them.
Driving and using machines
After using Fibrovein, to reduce the risk of inflammation and skin discoloration, the doctor may recommend appropriate bandaging of the legs and/or wearing compression stockings, which may affect the ability to drive vehicles.
Fibrovein contains sodium, potassium and benzyl alcohol
This medicine contains:
less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per vial/ampoule, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
less than 1 mmol (39 mg) of potassium per vial/ampoule, which means the medicine is considered "potassium-free".
40 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 2 ml ampoule or 100 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 5 ml vial, which corresponds to 20 mg/ml. Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions. In case of pregnancy, breastfeeding or liver or kidney disease, the patient should consult a doctor or pharmacist. This is because large amounts of benzyl alcohol can accumulate in the body, which can cause side effects (so-called "metabolic acidosis").
3. How to use Fibrovein
Do notattempt to self-inject Fibrovein. Treatment should always be carried out by an experienced doctor trained in the proper techniques of injection.
The treatment involves very careful and slow injection of the medicine using the smallest possible needles to the diseased veins, which allows the removal of blood from them. The medicine can be mixed manually using two syringes and a connector to create a mixture with air and produce foam, which helps to remove blood from larger veins. In this case, the medicine must be administered to the patient by a doctor trained in the proper techniques of producing and administering the medicine in the form of foam.
In the case of treating invisible varicose veins of the lower limbs and foam sclerotherapy, the procedure should be performed under ultrasound control.
The doctor will decide which concentration of Fibrovein to use and which areas to treat. Recommended doses:
Adults and the elderly
- from 0.1 ml to 2 ml of Fibrovein per injection. The doctor may inject up to 10 ml of the three lower concentrations of Fibrovein, but no more than 4 ml in the case of using the highest concentration.
Due to the limitations on the maximum daily dose of the sclerosant, it may be necessary to repeat the procedure several times.
After completing treatment with Fibrovein, the patient should follow the doctor's instructions. The doctor may recommend appropriate bandaging of the legs and/or wearing compression stockings to reduce the risk of inflammation and skin discoloration.
If the patient has any further doubts about using this medicine, they should consult a doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Fibrovein can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Serious side effects may occur. Treatment with Fibrovein should be stopped and the doctor or the emergency department of the nearest hospital should be contacted immediately if any of the following symptoms occur:
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Blood clots in deep veins (deep vein thrombosis, most likely caused by the underlying disease). Symptoms include pain, swelling and tenderness in one leg (usually in the calf), severe pain in the affected area, increased warmth of the skin in the area where the clot has formed or redness of the skin, especially in the back of the leg below the knee.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- Local tissue necrosis or, less frequently, nerve necrosis. Symptoms include pain, change in skin color (redness), swelling or fluid accumulation, blisters on the skin (which may be filled with clear fluid or blood), dark red, purple or black skin color, abnormal sensations (tingling, stinging, burning), numbness or loss of sensation
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- The most serious side effect is a severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic shock), which can cause breathing difficulties or a sudden drop in blood pressure, leading to dizziness or loss of consciousness. Anaphylactic shock is rare but can be life-threatening, so if it occurs, the patient should receive immediate treatment.
- Arterial blockage caused by a blood clot, which can lead to:
o
stroke or interruption of blood flow to the brain or eye (transient ischemic attack). Symptoms may include weakness, numbness or paralysis of the face, arm or leg, usually on one side of the body, slurred or distorted speech or difficulty understanding others, blindness in one or both eyes or double vision.
o
pulmonary embolism. Symptoms may include sudden shortness of breath, sudden, severe chest pain that worsens with deep breathing or coughing, rapid heartbeat or rapid breathing.
To protect patients from this very rare side effect, Fibrovein should not be used in patients who are at increased risk of developing blood clots in the veins and arteries (thrombosis risk).
- Circulatory failure. Symptoms may include feeling tired, dizziness, fainting, chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and rapid heartbeat.
- Tissue necrosis in case of injection into an artery. Symptoms may vary depending on the amount of medicine injected, the site of injection, and the speed of receiving medical attention. They may range from pain without long-term damage to loss of large areas of tissue, including the foot, which can lead to the need for amputation of the limb.
Other side effects that may occur include:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Superficial vein inflammation.
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
- Pain or burning (short-term at the injection site);
- Skin pigmentation;
- Expansion of subcutaneous blood vessels at the injection site (so-called "matting").
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Local allergic or non-allergic skin reactions, e.g. redness, itching, rash or swelling;
- Visual disturbances;
- Migraine.
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- Cough, shortness of breath, feeling of compression/pressure in the chest;
- Burning, tingling, stinging or itching of the skin;
- Headache, feeling of fainting;
- Disorientation, dizziness, loss of consciousness.
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- Fever, heat waves, red itchy skin (hives);
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, feeling of a swollen tongue or increased tongue volume, dry mouth;
- Vein inflammation.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181 C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: + 48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Fibrovein
The medicine should be stored in a place that is out of sight and reach of children.
There are no special storage temperature recommendations for the medicine.
- Do not freeze.
- Vials and ampoules should be stored in the outer packaging to protect them from light.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton after "Expiry date (EXP)". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
For single use only. The contents of the packaging should be used immediately after opening.
Any unused product should be disposed of.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What does Fibrovein contain
The active substance of Fibrovein is sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
For a concentration of 0.2%
Each ml of the solution for injection contains 2 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Each 5 ml vial contains 10 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
For a concentration of 0.5%
Each ml of the solution for injection contains 5 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Each 2 ml ampoule contains 10 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
For a concentration of 1%
Each ml of the solution for injection contains 10 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Each 2 ml ampoule contains 20 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
For a concentration of 3%
Each ml of the solution for injection contains 30 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Each 2 ml ampoule contains 60 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
Each 5 ml vial contains 150 mg of sodium tetradecyl sulfate.
The other ingredients of the medicine are: benzyl alcohol (20 mg/ml), disodium phosphate dodecahydrate, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, water for injections, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment). See section 2 "Fibrovein contains sodium and potassium".
What Fibrovein looks like and contents of the packaging
Fibrovein is a solution for injection contained in glass ampoules or vials. The solution is clear, colorless, sterile, and free of visible particles.
Fibrovein, 0.2%: the packaging contains 2, 5 or 10 vials of 5 ml each.
Fibrovein, 0.5%: the packaging contains 5 ampoules of 2 ml each.
Fibrovein, 1%: the packaging contains 5 ampoules of 2 ml each.
Fibrovein, 3%: the packaging contains 5 ampoules of 2 ml each or 2, 5 or 10 vials of 5 ml each.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer:
Marketing authorization holder:
STD Pharmaceutical (Ireland) Limited
Block 1, Blanchardstown Corporate Park, Ballycoolen Road, Blanchardstown, Dublin 15
D15 AKK1, Ireland
+353 1588 6916
Manufacturer:
Medipha Sante
Les Fjords-Immeuble Oslo
19 Avenue de Norvege
91953 Courtaboeuf CEDEX
France
Chemische Fabrik Kreussler & Co. GmbH
Rheingaustrasse 87-93
65203 Wiesbaden,
Germany
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Fibrovein
Bulgaria, Czech Republic, France, Germany,
Ireland, Netherlands, Poland, Romania
Austria, Spain
Veinfibro
Date of last revision of the leaflet:05/2024
Other sources of information:
Detailed information about this medicine is available on the website of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products
www.urpl.gov.pl
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Fibrovein, 0.2%, solution for injection
Fibrovein, 0.5%, solution for injection
Fibrovein, 1%, solution for injection
Fibrovein, 3%, solution for injection
Additional information about this product can be found in the Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC).
Dosage and administration
Dosage
Fibrovein is intended for intravenous administration only. Depending on the size and severity of the venous changes, different concentrations are required. Spider veins should only be treated with a 0.2% concentration, and reticular veins with a 0.5% concentration. The 1% concentration is most effective for small and medium-sized varicose veins, while the 3% concentration is most effective for larger varicose veins. The size of invisible varicose veins of the lower limbs should be determined under ultrasound control.
The sclerosant should be administered intravenously in small equal portions along the course of the diseased vein. Fibrovein at a concentration of 0.2% and 0.5% should be administered in the form of a liquid. Fibrovein at a concentration of 1% and 3% can be administered in the form of a liquid sclerosant or a mixture of sclerosant with air (foam form) in accordance with the description given in the table below. The goal of the procedure is to achieve optimal destruction of the vessel walls using the minimum effective concentration of the medicinal product necessary for effective treatment. Too high a concentration of the medicinal product can lead to tissue necrosis or other complications.
Adults
| Concentration | Standard injection dose at designated sites for the procedure | Maximum total dose to be injected per procedure | ||
| Liquid | Foam* | Liquid | Foam* | |
| Fibrovein, 0.2% and 0.5% | from 0.1 to 1.0 ml | Not applicable | 10 ml | Not applicable |
| Fibrovein, 1% | from 0.1 to 1.0 ml | from 0.5 to 2.0 ml | 10 ml | 16 ml |
| Fibrovein, 3% | from 0.5 to 2.0 ml | from 0.5 to 2.0 ml | 4 ml | 16 ml |
*Sum of liquid and air volumes
In cases where special caution is required, a sensitivity test is recommended, administering 0.25 to 0.5 ml of Fibrovein to the patient and observing them for several hours, and then administering a second or larger dose.
The procedure often requires repetition (on average, the patient needs 2 to 4 additional procedures) due to the limited dose that can be used during one procedure. To protect the patient from an allergic reaction, it is recommended to administer a small test dose of Fibrovein at the beginning of each procedure.
Fibrovein, 1% and 3% solution for injection
In the case of administering the sclerosant in the form of foam
The foam intended for the treatment of larger veins can be prepared using Fibrovein at a concentration of 1% and 3%. The foam should be prepared immediately before administration. It must be administered to the patient by a doctor who is properly trained in the proper techniques of producing and administering the medicinal product in the form of foam. It is best if the foam sclerotherapy procedure is performed under ultrasound control.
Fibrovein, 0.2% solution for injection
In the case of spider veins for injection
For the treatment of spider veins, the smallest possible needles should be used (e.g. 30 G) and the medicinal product should be injected slowly to allow the removal of blood from the treated veins. For the treatment of spider veins, a technique involving the additional administration of air, so-called air-block, can also be used.
Elderly
There are no special dosage recommendations.
Children and adolescents
The safety and efficacy of Fibrovein in children and adolescents have not been established. There are no data.
Administration
The instructions below are for the preparation of foam. The method of preparing foam presented is the Tessari technique. Other techniques can also be used (e.g. DSS, Easyfoam, Sterivein).
When preparing Fibrovein for administration, strict aseptic conditions must be maintained.
Fibrovein is intended for single use and for parenteral use only. After opening the vial or ampoule, the product should be used immediately and any unused solution should be discarded.
Before use, a visual inspection should be performed to check for the presence of particles. If the solution contains particles, it should not be used.
It is best if the foam sclerotherapy procedure is performed under ultrasound control. In this case, the product must be administered by a doctor who is properly trained in the proper techniques of producing and administering the medicinal product in the form of foam.
Incompatibilities
This medicinal product should not be mixed with heparin.
The medicinal product should not be mixed with other medicinal products, as compatibility studies have not been performed.
Special warnings and precautions
Fibrovein should only be administered by a doctor, and if national guidelines permit, the medicinal product may be administered under the supervision of a doctor by appropriately qualified medical personnel who have experience in the anatomy of the venous system, diagnosis and treatment of venous system diseases, and are familiar with the proper injection technique.
Allergic reactions, including anaphylactic shock, have also been reported, so the doctor administering the medicinal product should be prepared to administer anti-shock treatment.
During the procedure, the doctor must have direct access to emergency resuscitation equipment.
Due to special caution, the patient should be treated in a hospital.
In the event of extravasation, serious local side effects may occur, including tissue necrosis, so caution should be exercised when inserting the needle and the minimum effective dose should be injected at each injection site. The solution should be injected slowly.
Special caution should be exercised to avoid injecting the solution into an artery, as this can cause tissue necrosis, which can lead to the need for amputation of the limb.
Special caution should be exercised when performing injections in the foot and above and below the ankle (malleolus) due to the risk to one of the arteries. When treating smaller veins, compression should be applied, as the likelihood of pigmentation may be higher if blood extravasation occurs at the injection site.
Preparing foam and administration
General recommendations
The quality of the foam depends on certain conditions:
Concentration of the product: Foam can only be prepared using sodium tetradecyl sulfate at a concentration of 1% to 3%.
Liquid-to-air ratio: This ratio is usually 1 volume of liquid to 3 to 4 volumes of air.
Number of times the sclerosant/air mixture is pumped from one syringe to another: The doctor should follow the number of pumpings specified for each technique.
Macroscopic consistency of the foam: Before administration, the quality of the foam should be checked outside the syringe. The foam should be uniform, soft and consistent without visible large bubbles. If the foam contains large bubbles, it should be discarded and new foam prepared.
Total preparation time of the foam: Preparing the foam should take about 10 seconds from the first to the last pumping of the liquid from one syringe to another.
Maximum time between preparation and administration of the foam: The sclerosant foam should be used within 60 seconds of preparation. After 60 seconds, any unused foam should be discarded. If necessary, more foam can be prepared.
Preparing foam (Tessari technique)
When preparing the foam, strict aseptic conditions must be maintained.
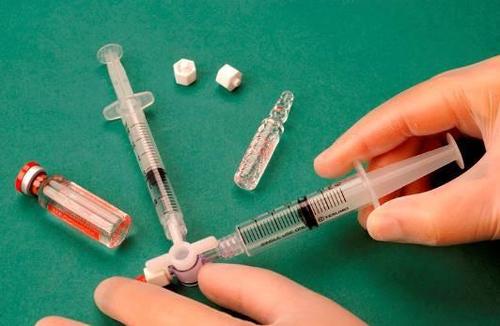
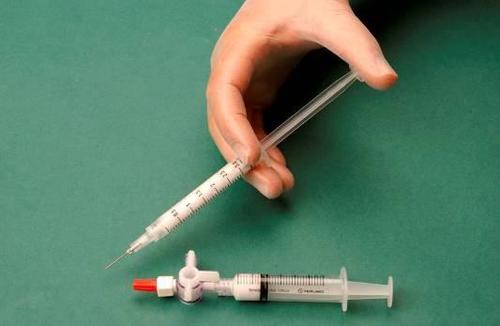
To prepare the foam, 1 ml of the liquid sclerosant is drawn into one sterile syringe and 3 ml or 4 ml of sterile air into another sterile syringe. The air is aspirated into the syringe through a 0.2 μm sterile filter, which ensures its sterility. The syringes are connected using a sterile three-way connector (Figure 1). When preparing the foam, it is recommended to use Luer Lock syringes and eye protection. Connecting a syringe with a Luer slip connector to a three-way connector under pressure may result in failure, leading to uncontrolled leakage of the product.
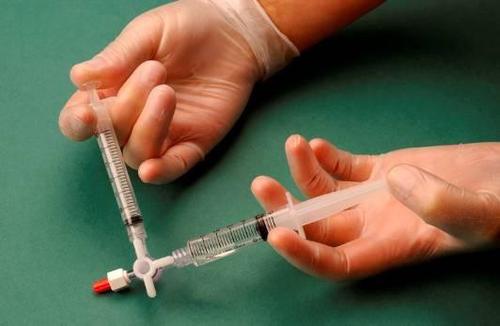
After connecting the syringes, the sclerosant/air mixture is dynamically pumped about 20 times from one syringe to another through the three-way connector until a foam with a uniform, smooth consistency is obtained (Figures 2 and 3).
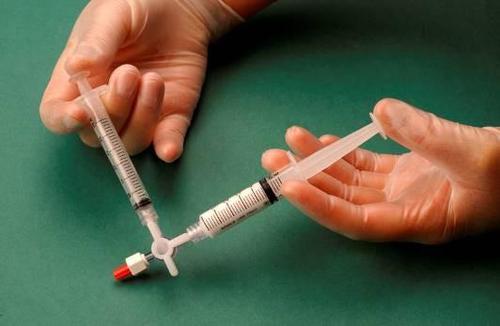
The syringe containing the foam is removed from the connector and used to immediately perform the intravenous injection, through which the foam is administered to the vessel (Figure 4).
The sclerosant foam should be used within 60 seconds of preparation. After 60 seconds, any unused foam should be discarded. If necessary, more foam can be prepared.
Before administering the foam, its quality should be checked. The foam should have a uniform consistency, be white in color and not contain visible large bubbles.
Excipients
This medicinal product contains:
less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per vial/ampoule, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
less than 1 mmol (39 mg) of potassium per vial/ampoule, which means the medicine is considered "potassium-free".
40 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 2 ml ampoule or 100 mg of benzyl alcohol in each 5 ml vial, which corresponds to 20 mg/ml. Benzyl alcohol may cause allergic reactions. It may cause metabolic acidosis in case of pregnancy, breastfeeding or liver or kidney disease.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterChemische Fabrik Kreussler Co.GmbH Medipha Sante
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FibroveinDosage form: Solution, 0.5% (5 mg/ml)Active substance: sodium tetradecyl sulfatePrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 1% (10 mg/ml)Active substance: sodium tetradecyl sulfatePrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 3% (30 mg/ml)Active substance: sodium tetradecyl sulfatePrescription not required
Alternatives to Fibrovein in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fibrovein in Espanha
Online doctors for Fibrovein
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fibrovein – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














