NORVIR 100mg POWDER FOR ORAL SUSPENSION

How to use NORVIR 100mg POWDER FOR ORAL SUSPENSION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Norvir 100 mg powder for oral suspension
ritonavir
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start taking this medicine because it contains important information for you or your child.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack and other information:
- What is Norvir and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you or your child takes Norvir
- How to take Norvir
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Norvir
- Contents of the pack and further information
1. What is Norvir and what is it used for
Norvir contains the active substance ritonavir. Norvir is a protease inhibitor used to control HIV infection. Norvir is used in combination with other anti-HIV medicines (antiretrovirals) to control HIV infection. Your doctor will discuss with you which combination of medicines is best for you.
Norvir is used in children from 2 years of age, adolescents and adults infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS.
2. What you need to know before you or your child takes Norvir
Do not take Norvir
- if you are allergic to ritonavir or any of the other ingredients of Norvir (see section 6).
- if you have severe liver disease.
- if you are currently taking any of the following medicines:
- astemizole or terfenadine (usually used to treat allergy symptoms – these medicines can be bought without a prescription);
- amiodarone, bepridil, dronedarone, encainide, flecainide, propafenone, quinidine (used to correct irregular heartbeats);
- dihydroergotamine, ergotamine (used to treat migraine headaches);
- ergonovine, methylergonovine (used to stop bleeding that may occur after childbirth or abortion);
- chlorazepate, diazepam, estazolam, flurazepam, triazolam or oral midazolam (taken by mouth) (used to help you sleep and/or relieve anxiety);
- clozapine, pimozide, (used to treat abnormal thoughts or feelings);
- quetiapine (used to treat schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder);
- lurasidone (used to treat depression);
- ranolazine (used to treat chronic chest pain [angina]);
- petidine, piroxicam, propoxyphene (used to relieve pain);
- cisapride (used to relieve certain stomach pains);
- rifabutin (used to prevent/treat certain infections)*;
- voriconazole (used to treat fungal infections)*;
- simvastatin, lovastatin (used to lower blood cholesterol);
- neratinib (used to treat breast cancer);
- lomitapide (used to lower blood cholesterol);
- alfuzosin (used to treat enlarged prostate);
- fusidic acid (used to treat bacterial infections);
- sildenafil if you have a lung disease called pulmonary arterial hypertension that makes it difficult to breathe. Patients without this disease may use sildenafil for impotence (erectile dysfunction) under the supervision of their doctor (see section Using Norvir with other medicines);
- avanafil or vardenafil (used to treat impotence);
- colchicine (used to treat gout) if you have liver and/or kidney problems (see section Using Norvir with other medicines);
- products containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) as it may cause Norvir to stop working properly. St. John's Wort is often used in herbal medicines that you can buy yourself.
*Your doctor may decide that you can take rifabutin and/or voriconazole with a booster dose (lower dose) of Norvir but a full dose of Norvir must not be taken with these two medicines.
If you are currently taking any of these medicines, ask your doctor if you could change the medicine while taking Norvir.
For the use of other medicines that require special care, see the list included in the section “Taking Norvir with other medicines”
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor before you start taking Norvir.
Important information
- If you take Norvir with other antiretroviral medicines, it is important that you read the package leaflets of these other medicines carefully. In these package leaflets you can find more important information about situations where you should avoid taking Norvir. If you have any further questions about Norvir (ritonavir) or any other medicines that you have been prescribed, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- Norvir does not cure HIV infection or AIDS
- People taking Norvir may still develop infections or other illnesses related to HIV infection or AIDS. It is therefore important that you remain under the supervision of your doctor while taking Norvir.
- Although effective antiretroviral treatment reduces the risk of transmission, while taking this medicine you can still transmit HIV to others. Consult your doctor about the precautions needed to avoid infecting other people.
Tell your doctor if you have or have had:
- Liver disease.
- Hepatitis B or Cand are being treated with a combination of antiretroviral medicines, as you have a greater risk of serious and potentially life-threatening side effects due to the effect on the liver. You may need to have blood tests to check your liver function.
- Haemophilia, as there have been reports of patients with haemophilia treated with this type of medicine (protease inhibitors) with increased bleeding. The reason for this is not known. You may need to be given additional medication to help your blood clot (factor VIII), to control any bleeding.
- Erectile dysfunction, as medicines used to treat erectile dysfunction can cause low blood pressure and prolonged erection.
- Diabetes, as there have been reports of worsening or development of diabetes (diabetes mellitus) in some patients taking protease inhibitors.
- Kidney disease (renal disease), as your doctor may need to check the dose of other medicines you are taking (such as protease inhibitors).
Tell your doctor if you experience:
- Diarrhoea or vomitingthat does not improve (persistent), as this can reduce the effectiveness of the medicines you are taking.
- Nausea, vomitingor stomach pain, as these can be signs of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). Some patients taking Norvir may develop pancreas problems. Tell your doctor as soon as possible if this is the case.
- Signs of infection– tell your doctor immediately. Some patients with advanced HIV infection (AIDS) who start anti-HIV treatment may develop signs of infection that they have had in the past even if they did not know they had it. This is believed to occur because the body's immune response improves and helps the body fight off these infections.
In addition to opportunistic infections, you may also develop autoimmune disorders (a condition that occurs when the immune system attacks the body's healthy tissue) after you start taking medicines for the treatment of your HIV infection. Autoimmune disorders may occur several months after starting treatment. If you notice any signs of infection or other signs such as muscle weakness, weakness that starts in the hands and feet and moves up towards the trunk, palpitations, tremor or hyperactivity, please inform your doctor immediately to seek the necessary treatment.
- Joint stiffness, discomfort and pain(especially of hip, knee and shoulder) and difficulty moving, tell your doctor, as this may be a sign of a problem that can destroy bone (osteonecrosis). Some patients taking antiretroviral medicines may develop this disease.
- Muscle pain, discomfort or weakness, particularly in combination with antiretroviral therapy including protease inhibitors and nucleoside analogues. In rare cases, these muscle disorders have been serious (see section 4. Possible side effects).
- Dizziness, drowsiness, fainting or abnormal heartbeat.Some patients taking Norvir may experience changes in their electrocardiogram (ECG). Tell your doctor if you have any heart problems or problems with the electrical conduction of the heart.
- If you have other health problems, consult your doctor as soon as possible.
Children and adolescents
Norvir is not recommended for use in children under 2 years of age.
Using Norvir with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking, have recently taken or might take any other medicines, including those bought without a prescription. There are some medicines that you cannot use if you are taking Norvir. These medicines are listed in section 2, under the heading “Do not take Norvir”. There are some medicines that can only be taken under certain circumstances as described below.
The following precautions will be taken when using Norvir at full doses. However, these precautions may also be necessary when taking Norvir at low doses (boosting doses) with other medicines.
Tell your doctor if you are taking any of the medicines listed below, as special precautions may be necessary.
- Sildenafil or tadalafilfor impotence (erectile dysfunction). You should reduce the dose and/or frequency of use of these medicines to avoid low blood pressure and prolonged erection. You must not take Norvir with sildenafil if you have pulmonary arterial hypertension (see section 2. What you need to know before you or your child takes Norvir). Tell your doctor if you are taking tadalafil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
- Colchicine(for gout) as Norvir can increase the levels of this medicine in the blood. You must not take Norvir with colchicine if you have liver and/or kidney problems (see also “Do not take Norvir” above).
- Digoxin(heart medicine). To prevent heart problems, your doctor may need to adjust the dose of digoxin and monitor you while you are taking digoxin and Norvir.
- Hormonal contraceptivesthat contain ethinyl estradiol, as Norvir can reduce the effectiveness of these medicines. It is recommended that you use a condom or other non-hormonal contraceptive method instead. You may also experience irregular vaginal bleeding if you take this type of hormonal contraceptive with Norvir.
- Atorvastatin or rosuvastatin(for high cholesterol) as Norvir can increase the levels of these medicines in the blood. Tell your doctor before taking cholesterol-lowering medicines with Norvir (see “Do not take Norvir” above).
- Corticosteroids(e.g. dexamethasone, fluticasone propionate, prednisolone, triamcinolone), as Norvir can increase the levels of these medicines in the blood, which can lead to Cushing's syndrome (development of a rounded face) and reduced production of the hormone cortisol. Your doctor may want to reduce the dose of corticosteroids or monitor their side effects more closely.
- Trazodone(depression medicine) as unwanted effects such as nausea, dizziness, low blood pressure and fainting can occur when taken with Norvir.
- Rifampicin and saquinavir(used for tuberculosis and HIV respectively) as they can cause serious liver damage when taken with Norvir.
- Bosentan, riociguat(used for pulmonary arterial hypertension), as the amount of this medicine in the blood may increase when taken with Norvir.
There are medicines that must not be mixed with Norvir because their effects may increase or decrease when taken together. In some cases, your doctor may need to perform certain tests, change the dose or monitor you regularly. For this reason, you must tell your doctor if you are taking any medicine, including those bought without a prescription or herbal products, but especially the following:
- amphetamines or amphetamine derivatives;
- antibiotics (e.g. erythromycin, clarithromycin);
- cancer treatments (e.g. abemaciclib, afatinib, apalutamide, ceritinib, encorafenib, dasatinib, ibrutinib, nilotinib, venetoclax, vincristine, vinblastine);
- anticoagulants (e.g. rivaroxaban, vorapaxar, warfarin);
- antidepressants (e.g. amitriptyline, desipramine, fluoxetine, imipramine, nefazodone, nortriptyline, paroxetine, sertraline, trazodone);
- antifungals (e.g. ketoconazole, itraconazole);
- antihistamines (e.g. loratadine, fexofenadine);
- antiretroviral medicines including HIV protease inhibitors (amprenavir, atazanavir, darunavir, fosamprenavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, saquinavir, tipranavir), and non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) (delavirdine, efavirenz, nevirapine) and others (didanosine, maraviroc, raltegravir, zidovudine);
- medicines for tuberculosis (bedaquiline and delamanid);
- antiviral medicines used to treat chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in adults (e.g. glecaprevir/pibrentasvir and simeprevir);
- medicines for anxiety, buspirone;
- medicines for asthma, theophylline, salmeterol;
- atovaquone, a medicine used to treat certain types of pneumonia and malaria;
- buprenorphine, a medicine used to treat chronic pain;
- bupropion, a medicine used to help you stop smoking;
- medicines for epilepsy (e.g. carbamazepine, divalproex, lamotrigine, phenytoin);
- medicines for the heart (e.g. digoxin, disopyramide, mexiletine and calcium channel blockers such as amlodipine, diltiazem and nifedipine);
- medicines that affect the immune system (e.g. cyclosporin, tacrolimus, everolimus);
- levothyroxine (used to treat thyroid problems);
- morphine and morphine derivatives used to treat severe pain (methadone, fentanyl);
- sleeping pills (e.g. alprazolam, zolpidem) and also midazolam given by injection;
- tranquillisers (e.g. haloperidol, risperidone, thioridazine);
- colchicine, a treatment for gout.
There are some medicines that you cannot take with Norvir. These are listed earlier in section 2. “Do not take Norvir”.
Taking Norvir with food and drink
See section 3.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
It is very important that you consult your doctor if you think you are pregnant or are planning to become pregnant.
There is a lot of information on the use of ritonavir (the active substance of Norvir) during pregnancy. In general, pregnant women received low doses (boosting doses) of ritonavir together with other protease inhibitors after the first three months of pregnancy. Norvir does not appear to increase the risk of developing birth defects compared to the general population.
Norvir can pass into breast milk. To prevent transmission of the infection, mothers with HIV should not breast-feed their babies.
Driving and using machines
Norvir can cause dizziness. If you experience these effects, do not drive or use machines.
3. How to Take Norvir
Follow your doctor's or pharmacist's instructions exactly for taking this medication. If you have any questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist. Take this medication once or twice a day, every day with food.
For doses that are exact amounts of 100 mg (100, 200, 300, 400, 500, or 600 mg), mix the contents of each packet with soft food (applesauce or vanilla pudding) or mix with a small amount of liquid (water, chocolate milk, or infant formula) and consume the entire mixture.
For doses less than 100 mg, or doses that are between 100 mg amounts, you must mix the entire contents of the packet with liquid, and then administer the appropriate volume in ml using the oral dosing syringe as indicated by your doctor.
To administer through a feeding tube, follow the instructions in the section "How do I prepare the correct dose of Norvir powder for oral suspension mixed with liquids?"
Use water to mix this medicationand follow the feeding tube instructions to administer the medication.
The recommended doses of Norvir are:
- If Norvir is used to boost the effect of other anti-HIV medications, the usual dose for adults is 1 to 2 packets once or twice a day. For more information on dosage recommendations, including those for children, read the package insert of the anti-HIV medications taken in combination with Norvir.
- If your doctor prescribes a full dose, adults can start with a dose of 3 packets in the morning and 3 packets 12 hours later, which will be gradually increased over a period of up to 14 days to reach the full dose of 6 packets twice a day. Children (2-12 years) will start with a lower dose and continue until the maximum allowed dose for their height.
Your doctor will tell you the right dose for you to take.
You must take Norvir every day to control HIV, regardless of whether you feel better. If you experience any side effects that prevent you from taking Norvir as directed, inform your doctor immediately. During episodes of diarrhea, your doctor may decide that you need additional monitoring.
Always have a sufficient supply of Norvir on hand so that you do not run out. When traveling or needing to stay in the hospital, check that you have enough Norvir until you can get more.
Norvir oral powder for suspension has an aftertaste that takes time to disappear. You can help clarify this taste by taking peanut butter, chocolate cream, and hazelnuts or blackcurrant syrup immediately after administering the dose.
Prepare only one dose at a time using the correct number of packets. When mixing the powder with food or liquids, make sure to take the full dose within 2 hours of preparation. Do not mix Norvir with anything else without asking your doctor or pharmacist first.
How do I prepare the correct dose of Norvir powder for oral suspension mixed with food (complete packet)?
Follow the instructions below:
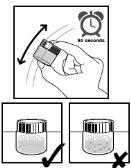
Figure 1 | Step 1. Before preparing the Norvir dose, gather the necessary utensils (see Figure 1). Step 2. Check your prescription for the number of packets you need for your dose or consult your doctor or pharmacist. |
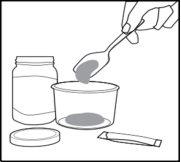
Figure 2 | Step 3. Put a small spoonful of soft food (applesauce or vanilla pudding) into a glass (see Figure 2). |
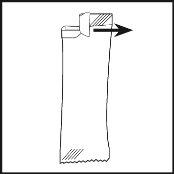
Figure 3 | Step 4. Open the packet by tearing the top (see Figure 3). |
Figure 4 | Step 5. Pour ALL the powder from the packet onto the food (see Figure 4). |
Figure 5 | Step 6. Mix well (see Figure 5). |
Step 7. Serve the food to the patient. | |
Figure 6 | Step 8. The patient must take all the food that has been served (see Figure 6). If there are powder residuesin the glass, add more spoonfuls of food and serve them to the patient. Use within 2 hours. |
Figure 7 | Step 9. Throw away the empty packet. Clean and dry the dose preparation surface. Wash the spoon and glass immediately with water and dish soap. Rinse and let air dry (see Figure 7). |
How do I prepare the correct dose of Norvir powder for oral suspension mixed with liquids?
Follow the instructions below:
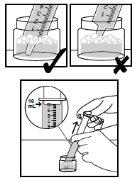
Figure 1 | What do you need? Before mixing the Norvir dose, gather the utensils shown in Figure 1. You may need to use more than one packet for each dose. Check your dose on the prescription label or consult your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure. If you need more than one packet for your dose, repeat all the steps for each packet. |
| Using the syringe Reading the scale
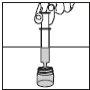
Check the syringe before each use A new syringe will be needed if:
|
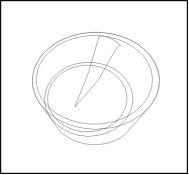
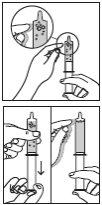
Figure 2 | Step 1. Fill the syringe
|
Figure 3 | Step 2. Move the bubbles to the tip of the syringe
|
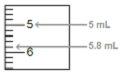
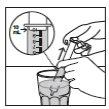
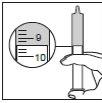
Figure 4 | Step 3. Measure the liquid
|
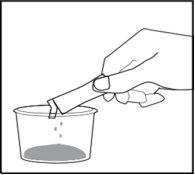
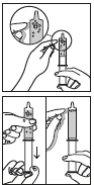
Figure 5 | Step 4. Empty the syringe a. Slowly push the plunger to empty the liquid from the syringe into the mixing cup (see Figure 5). |
Figure 6 | Step 5. Pour the powder into the mixing cup
Be careful not to spill powder outside the mixing cup (see Figure 6). |
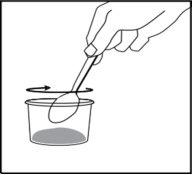
Figure 7 | Step 6. Mix the powder with the liquid
|
Figure 8 | Step 7. Fill the syringe
|
Figure 9 | Step 8. Move the bubbles to the tip of the syringe
|
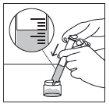
Figure 10 | Step 9. Measure the dose
|
Figure 11 | Step 10. Administer the dose to the patient
|
Step 11. (If necessary) If you need to use more than one packet, repeat the process from the beginning. | |
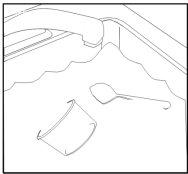
Step 12. After finishing
|
If you take more Norvir than you should
If you take too much Norvir, you may experience numbness, tingling, or a sensation of pins and needles. If you realize you have taken more Norvir than you should, contact your doctor or the Emergency Department of the nearest hospital immediately.
If you forget to take Norvir
If you have forgotten to take a dose, take it as soon as possible. If the time for the next dose is near, take only one dose. Do not take a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
If you stop taking Norvir
Even if you feel better, do not stop taking Norvir without consulting your doctor. If you take Norvir as directed, you will have a better chance of delaying the development of resistance to this medication.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
During HIV treatment, there may be an increase in weight and levels of glucose and lipids in the blood. This may be partly related to the recovery of health and lifestyle, and in the case of blood lipids, sometimes to HIV medications themselves. Your doctor will monitor these changes.
Like all medications, Norvir can produce adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them. When Norvir is used with other antiretroviral medications, the adverse effects also depend on those other medications. Therefore, it is very important that you carefully read the section on adverse reactions in the prospectus of these medications.
Very Common:can affect more than 1 in 10 people
|
|
Common:can affect up to 1 in 10 people
|
|
Uncommon:can affect up to 1 in 100 people
|
|
Rare:can affect up to 1 in 1000 people
|
|
Inform your doctor if you feel dizzy (nausea), are vomiting, or have stomach pain, as these can be symptoms of pancreatitis. Also, inform your doctor if you experience joint stiffness, discomfort, and pain (especially in the hip, knee, and shoulder) and difficulty moving, as this may be a sign of osteonecrosis. See section 2. What you need to know before you or your child takes Norvir.
There have been cases of increased bleeding in patients with hemophilia A and B during treatment with this or another protease inhibitor. If this happens to you, consult your doctor immediately.
It has been reported that patients taking Norvir have presented with alterations in liver function tests, hepatitis (liver inflammation), and rarely, jaundice. Some people had other diseases or were taking other medications. Some people with liver disease or hepatitis may have worsened.
There have been reports of muscle pain, discomfort, or weakness, particularly when taking cholesterol-reducing medications in combination with combined antiretroviral therapy, including protease inhibitors and nucleoside analogs. In rare cases, these muscle disorders were severe (rhabdomyolysis). In the case of muscle pain of unknown cause or continuous, stop taking the medication, contact your doctor as soon as possible, or go to the Emergency Department of the nearest hospital.
Inform your doctor immediately if after taking Norvir you experience any symptoms that may suggest an allergic reaction, such as skin rash, hives, or difficulty breathing.
If you consider that any of the adverse effects you suffer is serious or if you notice any adverse effect not mentioned in this prospectus, inform your doctor or pharmacist, go to the emergency department, or, if it is urgent, seek immediate medical attention.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect that does not appear in this prospectus. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medication.
5. Conservation of Norvir
Keep this medication out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use Norvir oral powder for suspension after the expiration date that appears on the envelope and packaging. The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Norvir oral powder for suspension solution should be stored below 30°C.
Medications should not be thrown down the drain.
Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of packaging and medications that you no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package Contents and Additional Information
Composition of Norvir
- The active ingredient is ritonavir. Each Norvir envelope contains 100 mg of ritonavir.
- The other components are: copovidone, sorbitan laurate, anhydrous colloidal silica.
Appearance of the Product and Package Contents
Norvir oral powder for solution is presented in individual envelopes containing 100 mg of ritonavir. Each package contains 30 envelopes, 1 mixing cup, and 2 oral dosing syringes.
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
Norvir is also presented as film-coated tablets containing 100 mg of ritonavir.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG, Knollstrasse, 67061 Ludwigshafen, Germany
Manufacturer
AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG
Knollstrasse
67061 Ludwigshafen,
Germany
AbbVie Logistics B.V.,
Zuiderzeelaan 53,
8017 JV Zwolle,
Netherlands
You can request more information about this medication by contacting the local representative of the marketing authorization holder.
België/Belgique/Belgien AbbVie SA Tél/Tel: +32 10 477811 | Lietuva AbbVie UAB Tel: +370 5 205 3023 |
България AbbVie Bulgaria EOOD Тел: +359 2 90 30 430 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg AbbVie SA Belgique/Belgien Tél/Tel: +32 10 477811 |
Ceská republika AbbVie s.r.o. Tel: +420 233 098 111 | Magyarország AbbVie Kft. Tel.: +36 1 455 8600 |
Danmark AbbVie A/S Tlf: +45 72 30-20-28 | Malta V.J.Salomone Pharma Limited Tel: +356 22983201 |
Deutschland AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG Tel: 00800 222843 33 (gebührenfrei) Tel: +49 (0) 611 / 1720-0 | Nederland AbbVie B.V. Tel: +31 (0)88 322 2843 |
Eesti AbbVie Biopharmaceuticals GmbH Eesti filiaal Tel: +372 623 1011 | Norge AbbVie AS Tlf: +47 67 81 80 00 |
Ελλάδα AbbVie ΦΑΡΜΑΚΕΥΤΙΚΗ Α.Ε. Τηλ: +30 214 4165 555 | Österreich AbbVie GmbH Tel: +43 1 20589-0 |
España AbbVie Spain, S.L.U. Tel: +34 91 384 09 10 | Polska AbbVie Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel.: +48 22 372 78 00 |
France AbbVie Tél: +33 (0)1 45 60 13 00 | Portugal AbbVie, Lda. Tel: +351 (0)21 1908400 |
Hrvatska AbbVie d.o.o. Tel: +385 (0)1 5625 501 | România AbbVie S.R.L. Tel: +40 21 529 30 35 |
Ireland AbbVie Limited Tel: +353 (0)1 4287900 | Slovenija AbbVie Biofarmacevtska družba d.o.o. Tel: +386 (1)32 08 060 |
Ísland Vistor hf. Tel: +354 535 7000 | Slovenská republika AbbVie s.r.o. Tel: +421 2 5050 0777 |
Italia AbbVie S.r.l. Tel: +39 06 928921 | Suomi/Finland AbbVie Oy Puh/Tel: +358 (0) 10 2411 200 |
Κύπρος Lifepharma (Z.A.M.) Ltd Τηλ: +357 22 34 74 40 | Sverige AbbVie AB Tel: +46 (0)8 684 44 600 |
Latvija AbbVie SIA Tel: +371 67605000 | United Kingdom AbbVie Ltd Tel: +44 (0)1628 561090 |
This prospectus has been revised in
Detailed information about this medication is available on the European Medicines Agency website http://www.ema.europa.eu
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to NORVIR 100mg POWDER FOR ORAL SUSPENSIONDosage form: TABLET, 100 mgActive substance: ritonavirManufacturer: Abbvie Deutschland Gmbh & Co. KgPrescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 100 mgActive substance: ritonavirManufacturer: Accord Healthcare S.L.U.Prescription requiredDosage form: CAPSULE, 250 mgActive substance: tipranavirManufacturer: Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbhPrescription required
Online doctors for NORVIR 100mg POWDER FOR ORAL SUSPENSION
Discuss questions about NORVIR 100mg POWDER FOR ORAL SUSPENSION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions