
DEXAMETHASONE KALCEKS 4 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION AND PERFUSION SOLUTION


How to use DEXAMETHASONE KALCEKS 4 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION AND PERFUSION SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/ml Solution for Injection and Infusion EFG
dexamethasone phosphate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What Dexamethasone Kalceks is and what it is used for
- What you need to know before you are given Dexamethasone Kalceks
- How Dexamethasone Kalceks is given
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Dexamethasone Kalceks
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Dexamethasone Kalceks is and what it is used for
This medicine contains the active substance dexamethasone phosphate (also known as dexamethasone). Dexamethasone is a synthetic glucocorticoid (adrenocortical hormone). It reduces the symptoms of inflammation and intervenes in essential metabolic processes.
Systemic use (affects the whole body)
This medicine is often used after emergency treatment has been started with high doses:
- Treatment and prophylaxis of cerebral edema (swelling of the brain) in brain tumors (after surgical intervention and X-ray radiation) and after spinal cord trauma.
- Shock due to an allergic reaction called "anaphylactic shock" (e.g. due to a reaction to a contrast medium).
- Shock states after severe injuries, prevention of acute respiratory distress syndrome.
- Severe persistent symptoms of an asthma attack.
- Initial treatment of some extensive, acute, and severe skin disorders, such as pemphigus vulgaris or erythroderma.
- Severe blood diseases (e.g. acute thrombocytopenic purpura or hemolytic anemia, as part of the treatment of leukemia).
- As a second-line treatment in patients with reduced or absent adrenocortical activity (adrenocortical insufficiency, Addisonian crisis).
This medicine is used as a treatment for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in adult and adolescent patients (from 12 years of age, with a body weight of at least 40 kg) with breathing difficulties and need for oxygen therapy.
Local use (affects a limited part of the body)
- Injection near the joints (periarticular) and infiltrative treatment, e.g. for shoulder joint inflammation (periarthritis of the shoulder), elbow joint inflammation (epicondylitis), joint cushion inflammation (bursitis), tendon sheath inflammation (tendovaginitis), and wrist inflammation (styloiditis).
- Injection into a joint (intraarticular), e.g. in rheumatoid arthritis, if individual joints are affected or do not respond adequately to systemic treatment, accompanying inflammatory reactions in degenerative joint disease (rheumatoid arthritis).
2. What you need to know before you are given Dexamethasone Kalceks
Dexamethasone Kalceks must not be given to you
- If you are allergic to dexamethasone or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have a systemic infection, including fungal infections (e.g. candidiasis) that are not being treated with antibiotics.
- Injection into a joint must not be given in the following cases: infections within or near the joint to be treated; bacterial joint inflammation (bacterial arthritis); instability of the joint to be treated; tendency to bleeding (spontaneous or due to anticoagulants); calcium deposits near the joint (periarticular calcification); localized death of bone tissue, especially in the head of the humerus and femur (avascular necrosis of the bone); tendon rupture; joint disease due to syphilis (Charcot's joint).
- Infiltration without additional treatment of the cause is contraindicated in the presence of infections within the administration area.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before you start using this medicine, as special care is required if:
- You have an acute or chronic bacterial infection.
- You have had tuberculosis.
- You have a fungal infection that affects the internal organs.
- You have a parasitic disease (e.g. amoebic infection, worm infection).
- You have an acute viral infection (hepatitis B, herpes infection, chickenpox).
- You (or your child) have been or are to be vaccinated (see "Other medicines and Dexamethasone Kalceks"). Inform your doctor especially if you have not had measles or chickenpox or if your child's immune system is weakened.
- You have stomach or intestinal ulcers.
- You have osteoporosis (breakdown of bone tissue). Your doctor may want to determine your bone density before starting long-term treatment. Your doctor may prescribe calcium, vitamin D, and/or medications to reduce bone density loss if necessary. In patients with advanced osteoporosis, this medicine will only be used in life-threatening situations or for short periods.
- You have high blood pressure that is difficult to control.
- You have diabetes.
- You have a history of mental illness, including the risk of suicide.
- You have increased pressure inside the eye (glaucoma, open and closed angle), corneal injuries, or eye ulcers (as close monitoring and treatment by an ophthalmologist are necessary).
- You have heart or kidney disorders.
- You have severe myasthenia (a muscle disease), as symptoms may worsen initially after administration of dexamethasone; the initial dose should be selected with caution.
- You have an adrenal gland tumor (pheochromocytoma).
If you are not sure if the above applies to you, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice.
Tell your doctor if you notice any of the following symptoms while being treated with this medicine:
- Muscle cramps, muscle weakness, confusion, vision loss, or difficulty breathing, in case you have blood cancer. These may be symptoms of tumor lysis syndrome.
- Blurred vision or other visual disturbances.
Concomitant use of corticosteroids
Do not stop taking any other corticosteroid medicine unless your doctor has told you to.
General precautions for the use of corticosteroids in specific diseases, masking of infections, concomitant medications, etc. should be adjusted according to current recommendations.
Severe allergic reactions
Severe allergic reactions and even anaphylaxis (a potentially life-threatening reaction) may occur with symptoms such as irregular heartbeat, constriction of the respiratory muscles, decrease or increase in blood pressure, circulatory failure, or cardiac arrest.
Adrenocortical insufficiency
Sudden discontinuation of treatment after more than 10 days may lead to the onset of acute adrenocortical insufficiency. Therefore, the dose should be gradually reduced if discontinuation is planned. Depending on the dose and duration of treatment, adrenocortical insufficiency caused by glucocorticoid treatment may persist for several months and, in individual cases, for more than a year after treatment has been discontinued.
If specific physical stress situations occur during treatment, such as a febrile illness, an accident, or surgery, your doctor or emergency doctor should be informed immediately about the ongoing treatment with dexamethasone. It may be necessary to temporarily increase the daily dose of dexamethasone. The administration of glucocorticoids may also be necessary in situations of physical stress if adrenocortical insufficiency persists after the end of treatment.
Risk of infection
Dexamethasone in doses higher than those required for maintenance treatment is associated with an increased risk of infection, possible worsening of a pre-existing infection, and possible activation of a latent infection. The anti-inflammatory effect may mask the symptoms of infection until it has reached a higher level.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Due to the risk of intestinal wall perforation with peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum), this medicine will be used if there are compelling medical reasons, along with adequate monitoring, in the following cases:
- severe colon inflammation (ulcerative colitis) with imminent perforation;
- abscesses or purulent infections (filled with pus);
- diverticulitis (inflammation of bulges [known as diverticula] in the colon wall);
- after certain types of intestinal surgery (intestinal anastomosis) immediately after the intervention.
Patients receiving high doses of glucocorticoids may not have signs of peritoneal irritation after stomach or intestinal ulcer perforation.
Prolonged treatment
During prolonged treatment, regular medical check-ups (including ophthalmological check-ups every three months) are indicated; at comparatively high doses, care should be taken to ensure adequate potassium intake (e.g. with vegetables or bananas) and to restrict sodium (salt) intake, and potassium levels in the blood should be monitored. Close monitoring is also indicated in patients with severe heart failure (inability of the heart to provide the necessary amount of blood expelled for metabolism, during exertion or even at rest).
Warnings related to specific administration methods
- The medicine will be injected slowly (2-3 minutes) into a vein, as too rapid an injection can cause temporary, unpleasant tingling or abnormal skin sensations that can last up to 3 minutes. These effects are harmless in themselves.
- Administration of glucocorticoids into a joint increases the risk of joint infections. Prolonged and repeated use of glucocorticoids in weight-bearing joints can lead to worsening of degenerative changes within the joint. A possible cause is overloading of the affected joint after regression of pain or other symptoms.
Other warnings
- At high doses, a decrease in heart rate may occur.
- The risk of tendon disorders, inflammation, and rupture increases when fluoroquinolones (antibiotics) are used at the same time as dexamethasone.
- In principle, vaccination with inactivated (killed) vaccines is possible. However, it should be remembered that higher doses may compromise the immune response and thus the success of vaccination.
- In elderly patients, the doctor will carefully weigh the benefits and risks and pay attention to side effects, such as osteoporosis (breakdown of bone tissue).
- If dexamethasone is administered to a premature infant, it is necessary to monitor the function and structure of the heart.
Children and adolescents
Dexamethasone should not be used routinely in premature infants with respiratory problems.
In children and adolescents, treatment should only be given if there are compelling medical reasons, due to the risk of growth retardation. Whenever possible, intermittent therapy should be sought during long-term treatment.
Other medicines and Dexamethasone Kalceks
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or might use any other medicines.
Some medicines may increase the effects of dexamethasone, and your doctor may want to monitor you closely if you are using these medicines (including HIV medicines: ritonavir, cobicistat).
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking any of the following medicines:
- medicines for treating heart failure or asthma (cardiac glycosides);
- medicines used to increase urine production;
- medicines for reducing blood sugar levels (antidiabetics);
- medicines for preventing blood clots/anticoagulants (coumarin derivatives);
- ephedrine (used for asthma and poor circulation);
- rifampicin (used to treat tuberculosis);
- medicines for treating seizures and epilepsy (phenytoin, carbamazepine, primidone);
- barbiturates (medicines to help you sleep);
- ketoconazole, itraconazole (used to treat fungal infections);
- medicines for treating infections (macrolide antibiotics, such as erythromycin, or fluoroquinolones, such as ciprofloxacin);
- analgesics and anti-inflammatory/anti-rheumatic medicines (e.g. salicylates and indomethacin);
- estrogen-containing contraceptives;
- a medicine for treating intestinal parasite infestation (praziquantel);
- medicines for treating high blood pressure and certain heart diseases (ACE inhibitors or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors);
- antimalarials (chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, mefloquine);
- somatropin (a growth hormone);
- laxatives;
- atropine and other anticholinergics (medicines that block the action of a certain brain neurotransmitter);
- muscle relaxants;
- medicines that weaken the immune system (cyclosporin);
- bupropion (a smoking cessation aid).
Effect on test methods: Skin reactions to allergy tests may be suppressed. Interactions with a medicine used in thyroid function tests (protirelin: the increase in TSH that occurs when protirelin is administered may be reduced).
If treatment with dexamethasone is carried out 8 weeks before and up to 2 weeks after an active preventive vaccination, it can be expected that the effectiveness of such vaccination will be reduced or abolished.
Pregnancy, breast-feeding, and fertility
Pregnancy
If you are pregnant or breast-feeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
Dexamethasone crosses the placental barrier. During pregnancy, especially in the first three months, it should only be used after careful evaluation of the benefits/risks. Therefore, women should inform their doctor if they are or become pregnant. During long-term treatment in pregnancy, fetal growth disorders cannot be excluded. If glucocorticoids are administered at the end of pregnancy, there is a risk of hypoadrenocorticism in the newborn, which may require gradual substitute treatment in the neonate, which will be slowly reduced. Newborn babies of mothers who received Dexamethasone Kalceks near the end of pregnancy may have low blood sugar levels after birth.
Breast-feeding
Glucocorticoids are excreted in human milk. To date, no harm has been reported in breast-fed infants. However, they should only be used when strictly indicated during breast-feeding. If higher doses are required, breast-feeding should be discontinued.
Fertility
No fertility studies have been conducted.
Driving and using machines
No studies on the effects on the ability to drive and use machines have been performed.
Dexamethasone Kalceks contains sodium
This medicine contains approximately 3 mg of sodium (the main component of table/cooking salt) in each ml of solution. This is equivalent to 0.15% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake for an adult.
3. How Dexametasona Kalceks will be administered to you
This medicine should only be used as your doctor has prescribed. Your doctor will decide how long you should use dexamethasone. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist again.
This medicine can be administered into a vein, into a muscle or into a joint, as well as by infiltration into soft tissues.
The dose depends on the indication, the intensity of the symptoms, the individual patient's response, and in the case of injection into a joint, the size of the joint.
Glucocorticoids should only be used for as long as and at the lowest dose absolutely necessary to achieve and maintain the desired effect. The duration of use is governed by the indication. Prolonged use of dexamethasone should not be stopped abruptly, but the dose should be gradually reduced, according to the doctor's instructions.
For the treatment of COVID-19
Adult patientsare recommended to be administered 6 mg into a vein, once a day, for a maximum of 10 days.
Use in adolescents:It is recommended that pediatric patients (adolescents from 12 years old with a body weight of at least 40 kg) be administered 6 mg into a vein, once a day, for a maximum of 10 days.
Renal insufficiency
No dose adjustment is necessary.
Hepatic insufficiency
In patients with severe liver disease, a dose adjustment may be necessary.
Children and adolescents
In children up to 14 years of age, during long-term treatment, a 4-day treatment-free interval should be introduced after each 3-day treatment period due to the risk of growth disturbances.
If you have been administered more Dexametasona Kalceks than you should
Acute intoxication with dexamethasone is not known. In case of overdose, an increase in side effects can be expected. If you think you have been administered too much of this medicine, inform your doctor immediately.
If you stop treatment with Dexametasona Kalceks
Treatment should not be stopped or discontinued abruptly, unless indicated by a doctor. If you nonetheless decide to stop treatment on your own, for example, due to side effects that occur or because you feel better, you will not only jeopardize the success of your treatment, but you will also expose yourself to significant risks. In particular, after a prolonged treatment period, you should never stop this medicine on your own. You should always consult your doctor first.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
In short-term treatment with dexamethasone, the risk of side effects is low. The following side effects may appear:
- stomach or duodenal ulcers;
- reduction of the body's defenses against infections;
- increase in blood sugar levels (decrease in glucose tolerance).
The following side effects may occur, which largely depend on the dose and duration of treatment, and whose frequency is therefore unknown (cannot be estimated from the available data):
Infections and infestations
Masking of infections, fungal, viral, and other (opportunistic) infections that favor development or worsening, activation of worms (see section 2, "Warnings and precautions").
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Alterations in the blood count (moderate leukocytosis, lymphocytopenia, eosinopenia, polycythemia).
Immune system disorders
Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., exanthema), weakening of the immune system, allergic reactions, and even anaphylaxis (potentially life-threatening allergic reaction), with symptoms such as irregular heartbeat, constriction of the respiratory muscles, decrease or increase in blood pressure, circulatory failure, or cardiac arrest.
Endocrine disorders
Cushing's syndrome (e.g., moon face, obesity in the upper body), adrenal cortical insufficiency or atrophy.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders
Sodium retention in the body with water accumulation in tissues, increased potassium excretion (caution: possible cardiac rhythm disorders), weight gain, increased blood sugar levels (decrease in glucose tolerance), diabetes, increased fat levels in the blood (cholesterol and triglycerides), increased appetite.
Psychiatric disorders
Psychosis, depression, irritability, euphoria (excessive joy), sleep disorders, instability, anxiety, mania, hallucinations, suicidal thoughts.
Nervous system disorders
Pseudotumor cerebri ("false" brain tumor), first appearance of epilepsy promoted in patients with latent epilepsy (previously "inactive") and increased susceptibility to seizures in pre-existing epilepsy (attacks).
Eye disorders
Glaucoma, cataracts, worsening of corneal ulcer symptoms, promotion of eye inflammation due to viruses, fungi, and bacteria; worsening of bacterial corneal inflammation, drooping eyelid (ptosis), dilated pupils, conjunctival edema, iatrogenic scleral perforation (lesion of the white part of the eye induced by the doctor), altered or lost vision, blurred vision. In rare cases, reversible protrusion of the eyeball (exophthalmos).
Cardiac disorders
Thickening of the heart muscle (hypertrophic cardiomyopathy) in premature babies, which usually returns to normal after treatment is discontinued.
Vascular disorders
Hypertension, increased risk of atherosclerosis (alteration of the blood vessel wall) and thrombosis (obstruction of blood vessels by a clot), inflammation of blood and lymphatic vessels (vasculitis, also as withdrawal syndrome after prolonged treatment), fragility of blood vessel walls (capillary fragility).
Gastrointestinal disorders
Stomach upset, gastrointestinal ulcer, digestive bleeding, inflamed pancreas, risk of intestinal perforation in ulcerative colitis (severe inflammation of the large intestine).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Stretch marks, thinning of the skin, localized small hemorrhages under the skin, bruising, steroid acne, skin inflammation around the mouth, dilation of superficial blood vessels, excessive body hair, changes in skin pigmentation.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Muscle weakness, muscle atrophy, inflammatory muscle disease, disorders, inflammation, or rupture of tendons, bone tissue breakdown (osteoporosis), growth retardation in children, aseptic bone necrosis (death of bone tissue without the presence of microbes), increased fat tissue in the spinal canal.
Reproductive system and breast disorders
Disorders of sex hormone secretion, such as absence of menstruation, excessive hair growth with a male pattern in women, impotence.
General disorders and administration site conditions
Delayed wound healing.
Local use
Local irritation and signs of intolerance (sensations of heat, prolonged pain) are possible, especially with eye use. Tissue wear cannot be ruled out if dexamethasone is not carefully injected into the joint cavity.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible side effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Medicines Agency's website: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Dexametasona Kalceks
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not store above 30°C.
Store the ampoules in the outer packaging to protect them from light.
After opening the ampoule: Once opened, the medicine should be used immediately.
Validity period after dilution
Chemical and physical stability in use has been demonstrated for 48 hours at 25°C (protected from light) and 2-8°C.
From a microbiological point of view, the diluted solution should be used immediately. If not used immediately, the storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user and should not normally exceed 24 hours at a temperature of 2 to 8°C, unless the dilution has been carried out under controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and ampoule after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine in the pharmacy's SIGRE collection point. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and additional information
Composition of Dexametasona Kalceks
- The active substance is dexamethasone phosphate.
Each 1 ml ampoule contains sodium phosphate dexamethasone, equivalent to 4 mg of dexamethasone phosphate.
- The other ingredients are: creatinine, sodium citrate, disodium edetate, sodium hydroxide, and water for injectable preparations.
Appearance of Dexametasona Kalceks and package contents
Clear and colorless solution, without visible particles.
Type I glass ampoules, transparent, colorless, 1 ml with a break point.
The ampoules are marked with a ring code of a specific color.
The ampoules are placed in trays. The trays are packaged in cardboard boxes.
Package sizes:
3, 10, 25, 50, or 100 ampoules of 1 ml.
Not all package sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
AS KALCEKS
Krustpils iela 71E,
Riga, LV-1057,
Latvia
Tel.: +371 67083320
E-mail: [email protected]
You can request more information about this medicine from the local representative of the marketing authorization holder
EVER Pharma Therapeutics Spain SL
c/ Toledo 170
28005 Madrid
Spain
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Estonia Dexamethasone Kalceks
Austria, Germany Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/ml Injektions-/Infusionslösung
Croatia Deksametazon Kalceks 4 mg/ml otopina za injekciju/infuziju
Czech Republic, Poland Dexamethasone Kalceks
Denmark, Norway Dexamethasone phosphate Kalceks
Finland Dexalcex 4 mg/ml injektio-/infuusioneste, liuos
France DEXAMETHASONE KALCEKS 4 mg/1 mL, solution injectable/pour perfusion
Hungary Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/ml oldatos injekció vagy infúzió
Ireland Dexamethasone phosphate 4 mg/ml solution for injection/infusion
Italy Desametasone Kalceks
Latvia Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/ml škidums injekcijam/infuzijam
Lithuania Dexamethasone Kalceks 4 mg/ml injekcinis ar infuzinis tirpalas
Netherlands Dexamethasonfosfaat Kalceks 4 mg/ml oplossing voor injectie/infusie
Portugal Dexametasona Kalceks
Slovenia Deksametazon Kalceks 4 mg/ml raztopina za injiciranje/infundiranje
Spain Dexametasona Kalceks 4 mg/ml solución inyectable y para perfusión EFG
Sweden Dexalcex
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:January 2022.
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) (http://www.aemps.gob.es/).
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Posology and method of administration
In case high doses are necessary for a particular treatment, the use of medicines containing dexamethasone with higher concentration/volume should be considered.
- Systemic route
For the treatment and prophylaxis of cerebral edema associated with brain tumors (postoperative and after X-ray radiation) and after spinal cord trauma
Depending on the cause and severity, the initial dose is 8-10 mg (up to 80 mg), intravenously, then 16-24 mg (up to 48 mg)/day, divided into 3-4 (6) single intravenous doses for 4-8 days. During radiation therapy and in the conservative treatment of inoperable brain tumors, long-term administration of lower doses of dexamethasone phosphate may be necessary.
In case of anaphylactic shock, first, intravenous injection of adrenaline, then injection of 40-100 mg (children 40 mg) intravenously, repeated as necessary.
Polytraumatic shock/prophylaxis of post-traumatic pulmonary shock
Initially, 40-100 mg (children 40 mg) intravenously, repetition of the dose after 12 hours, or every 6 hours 16-40 mg for 2-3 days.
For severe asthma exacerbations, 8-40 mg intravenously, as soon as possible; if necessary, repeated injections of 8 mg every 4 hours.
For severe acute dermatosisand severe blood diseases, initial treatment with 20-40 mg of dexamethasone phosphate intravenously and subsequent treatment according to the severity of the case, with the same daily dose or lower doses in the first days and change to oral therapy.
For the treatment of acute adrenal insufficiency(Addisonian crisis), start treatment with 4-8 mg of dexamethasone phosphate intravenously.
For the treatment of COVID-19
Adult patients:6 mg intravenously, once a day, for a maximum of 10 days.
Elderly patients, renal insufficiency, hepatic insufficiency [treatment at low doses (6 mg daily) and short duration]:No dose adjustment is necessary.
Pediatric population:Pediatric patients (adolescents from 12 years old with a body weight of at least 40 kg) are recommended to use 6 mg intravenously, once a day, for a maximum of 10 days.
The duration of treatment should be guided by the clinical response and individual patient requirements.
- Local route
For local infiltrative, periarticular, and intraarticular treatment, under strictly aseptic conditions, injection of 4 mg or 8 mg of dexamethasone phosphate. For injection into a small joint, 2 mg of dexamethasone phosphate is sufficient. According to the severity of the disease, no more than 3-4 infiltrations or 3-4 injections per joint should be performed. The interval between injections should not be less than 3-4 weeks.
Method of administration
Intravenous, intramuscular, intraarticular, or local (infiltration).
This medicine is usually administered intravenously slowly (2-3 minutes) in acute diseases, by injection or infusion. However, it can also be administered intramuscularly (only in exceptional cases), as local infiltration, or intraarticularly.
Instructions for use, disposal, and other manipulations
For single use.
Once the ampoule is opened, the medicine should be used immediately. Discard the remaining contents.
Inspect the ampoule visually before use. It should only be used if the solution is transparent and particle-free.
pH of the solution between 7.0-8.5
This medicine should not be mixed with others, except for those mentioned below.
This medicine should preferably be administered intravenously directly or injected into the infusion tube. However, the injectable solutions are compatible with the following infusion solutions (250 ml and 500 ml):
- sodium chloride solution 9 mg/ml (0.9%)
- glucose solution 50 mg/ml (5%)
- Ringer's solution.
When combining with infusion solutions, the information of the respective manufacturers on their infusion solutions, including compatibility data, contraindications, undesirable effects, and interactions, should be taken into account.
Instructions for opening the ampoule:
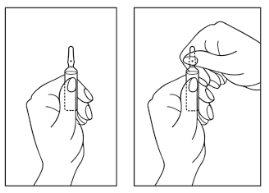
- Hold the ampoule with the colored point upwards. If some solution remains in the top part of the ampoule, gently tap with your finger to make the solution flow down to the bottom of the ampoule.
- Use both hands to open it, and while holding the bottom of the ampoule with one hand, use the other to break the top of the ampoule in the opposite direction of the colored point (see the images below).
The disposal of unused medicine and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DEXAMETHASONE KALCEKS 4 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION AND PERFUSION SOLUTIONDosage form: TABLET, 20 mgActive substance: dexamethasoneManufacturer: Mabo Farma S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 4 mgActive substance: dexamethasoneManufacturer: Mabo Farma S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: TABLET, 8 mgActive substance: dexamethasoneManufacturer: Mabo Farma S.A.Prescription required
Online doctors for DEXAMETHASONE KALCEKS 4 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION AND PERFUSION SOLUTION
Discuss questions about DEXAMETHASONE KALCEKS 4 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION AND PERFUSION SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions











