
CETRORELIX EDEST 0.25 mg POWDER FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION


How to use CETRORELIX EDEST 0.25 mg POWDER FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
- Introduction
- What is Cetrorelix Edest and what is it used for
- What is Cetrorelix Edest
- What is Cetrorelix Edest used for
- How Cetrorelix Edest works
- What you need to know before you use Cetrorelix Edest
- Warnings and precautions
- Allergies
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
- Use of Cetrorelix Edest for more than one cycle
- Liver disease
- Kidney disease
- How to use Cetrorelix Edest
- Possible side effects
- Allergic reactions
- Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
- Other side effects
- Reporting of side effects
- Storage of Cetrorelix Edest
- Contents of the pack and other information
- Composition of Cetrorelix Edest
- Before you start
- Mixing the powder and water to prepare your medicine
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Cetrorelix Edest 0.25 mg Powder for Solution for Injection
cetrorelix
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the Package Leaflet
- What is Cetrorelix Edest and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Cetrorelix Edest
- How to use Cetrorelix Edest
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Cetrorelix Edest
- Contents of the pack and other information
How to mix and inject Cetrorelix Edest
1. What is Cetrorelix Edest and what is it used for
What is Cetrorelix Edest
This medicine contains a substance called ‘cetrorelix acetate’. This substance prevents your body from releasing an egg from the ovary (ovulation) during your menstrual cycle. This medicine belongs to a group of medicines known as ‘gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists’.
What is Cetrorelix Edest used for
This medicine is one of the medicines used during ‘assisted reproduction techniques’ to help you get pregnant. It works by immediately stopping the release of eggs. This is because if eggs are released too early (premature ovulation), your doctor may not be able to collect them.
How Cetrorelix Edest works
Cetrorelix blocks a natural hormone in your body, called LHRH (‘luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone’).
- LHRH controls another hormone, called LH (‘luteinizing hormone’).
- LH stimulates ovulation during the menstrual cycle.
This means that this medicine stops the chain of events that leads to the release of an egg from the ovary. When your eggs are ready to be collected, you will be given another medicine that will release them (induction of ovulation).
2. What you need to know before you use Cetrorelix Edest
Do not use Cetrorelix Edest
- if you are allergic to cetrorelix acetate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- if you are allergic to medicines similar to this medicine (any other peptide hormone).
- if you are pregnant or breast-feeding.
- if you have severe kidney disease.
Do not use this medicine if any of the above applies to you. If you are in doubt, consult your doctor or nurse before using this medicine.
Warnings and precautions
Allergies
Consult your doctor before starting treatment with Cetrorelix Edest if you have an active allergic problem or have had allergies in the past.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
This medicine is used together with other medicines that stimulate your ovaries to develop more eggs ready to be released. During or after receiving these medicines, you may suffer from Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS). This happens when your follicles develop too much and become large cysts.
To learn about the possible signs to look out for and what to do if they occur, see section 4 ‘Possible side effects’.
Use of Cetrorelix Edest for more than one cycle
Experience with the use of Cetrorelix for more than one cycle is limited. Your doctor will carefully assess the benefits and risks for you if you need to use this medicine for more than one cycle.
Liver disease
Tell your doctor before starting treatment with Cetrorelix Edest if you have any liver disease. Cetrorelix has not been studied in patients with liver disease.
Kidney disease
Tell your doctor before starting treatment with Cetrorelix Edest if you have any kidney disease. Cetrorelix has not been studied in patients with kidney disease.
Children and adolescents
Cetrorelix Edest is not indicated for use in children and adolescents.
Other medicines and Cetrorelix Edest
Tell your doctor if you are taking, have recently taken, or might take any other medicines.
Pregnancy and breast-feeding
Do not use Cetrorelix Edest if you are pregnant, think you may be pregnant, or are breast-feeding.
Driving and using machines
Cetrorelix Edest is not expected to affect your ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to use Cetrorelix Edest
Follow the instructions for administration of this medicine exactly as prescribed by your doctor. If you are in doubt, consult your doctor again.
Use of this medicine
This medicine is for subcutaneous injection only, i.e. just under the skin of your abdomen. To reduce skin irritation, choose a different area of your abdomen each day.
- Your doctor should supervise the first injection. Your doctor or nurse will teach you how to prepare and inject the medicine.
- You can give yourself the following injections, provided your doctor has informed you about the symptoms that may indicate an allergy and the possible serious or life-threatening consequences that would require immediate treatment (see section 4 ‘Possible side effects’).
- Read and carefully follow the instructions at the end of this leaflet, entitled ‘How to mix and inject Cetrorelix Edest 0.25 mg powder for solution for injection’.
- You will start using another medicine on day 1 of your treatment cycle. You will then start using Cetrorelix Edest a few days later. (See the next section ‘How much to use’.)
How much to use
Inject the contents of one vial (0.25 mg of Cetrorelix Edest) once a day. It is best to use the medicine at the same time each day, leaving 24 hours between each dose.
You can choose to inject the medicine either every morning or every evening.
- If you inject the medicine every morning: Start your injections on the fifth or sixth day of your treatment cycle. Depending on your ovarian response, your doctor may decide to start treatment on another day. Your doctor will tell you the exact date and time. You will continue using this medicine until the morning of egg collection, including that morning (induction of ovulation).
or
- If you inject the medicine every evening: Start your injections on the fifth day of your treatment cycle. Depending on your ovarian response, your doctor may decide to start treatment on another day. Your doctor will tell you the exact date and time. You will continue using this medicine until the night before egg collection, including that night (induction of ovulation).
If you use more Cetrorelix Edest than you should
No adverse effects are expected if more medicine is injected accidentally than should be. The effect of the medicine will be longer. In general, no specific measures are necessary. In case of overdose or accidental ingestion, consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately or call the Toxicology Information Service, phone: 91 562 04 20, stating the medicine and the amount taken.
If you forget to use Cetrorelix Edest
- If you forget a dose, inject it as soon as you remember and consult your doctor.
- Do not inject a double dose to make up for forgotten doses.
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Allergic reactions
- Redness and feeling of heat in the skin, itching (often in the groin or armpits), red, swollen, and itchy areas (hives), runny nose, rapid or irregular heartbeat, swelling of the tongue and throat, sneezing, whistling sound while breathing (wheezing), severe difficulty breathing or dizziness. You may be experiencing a possible serious allergic reaction to the medicine. This is uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 women).
If you notice any of the above side effects, stop using Cetrorelix acetate Edest and consult your doctor immediately.
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS)
This can occur due to the other medicines you are using to stimulate your ovaries.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, along with feeling sick or vomiting, can be symptoms of Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS). This may indicate that your ovaries have overreacted to treatment and developed large ovarian cysts. This effect is common (may affect up to 1 in 10 women).
- OHSS can become severe, with clearly enlarged ovaries, decreased urine production, weight gain, difficulty breathing, or fluid accumulation in the stomach or chest. This effect is uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 women).
If you notice any of the above side effects, consult your doctor immediately.
Other side effects
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 women):
- Mild and short-lasting skin reactions may occur at the injection site, such as redness, itching, or swelling.
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 women):
- Feeling sick.
- Headache.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly to the Spanish Medicines Agency (AEMPS) at www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Cetrorelix Edest
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the vial after EXP. The expiry date is the last day of the month shown.
Store in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C). Do not freeze or place near the freezer compartment of the refrigerator or next to a cold accumulator.
Store in the original package to protect from light.
The unopened product can be stored at room temperature (not above 30°C) for a maximum of three months.
The solution should be used immediately after preparation.
Do not use this medicine if you notice that the white sediment in the vial has changed appearance. Do not use it if the prepared solution in the vial is no longer clear and colorless or contains particles.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Place the packaging and any unused medicine in the SIGRE collection point at your pharmacy. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the packaging and any unused medicine. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
Composition of Cetrorelix Edest
- The active substance is cetrorelix. Each vial contains 0.25 mg of cetrorelix (as acetate).
- The other ingredient is mannitol.
Appearance of the product and pack contents
Cetrorelix Edest is a compact powder or powder for solution for injection, white, in a glass vial with a rubber stopper and an aluminum flip-off cap.
It is available in packs of one vial or seven vials (not all pack sizes may be marketed).
Marketing Authorisation Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorisation Holder
Intas Third Party Sales 2005, S.L. World Trade Center Calle Moll de Barcelona S/N Edificio Este, 6ª Planta 08039 Barcelona, Spain
Manufacturer
Accord Healthcare Polska Sp.z o.o. ul. Lutomierska 50, 95-200 Pabianice Poland
or
Laboratori Fundació Dau C/ C, 12-14 Pol. Ind. Zona Franca, Barcelona, 08040, Spain
This medicine is authorised in the Member States of the EEA under the following names:
Member State | Marketing Authorisation Holder |
Croatia | Cetrorelix acetate Edest 0.25 mg powder for solution for injection |
Slovenia | Cetrorelix Edest 0.25 mg powder for solution for injection |
Portugal | Cetrorrelix Edest |
Spain | Cetrorelix Edest 0.25 mg powder for solution for injection |
Date of last revision of this leaflet:October 2020
Detailed information on this medicine is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.es/.
HOW TO MIX AND INJECT CETRORELIX EDEST 0.25 MG POWDER FOR SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
- In this section, it is explained how to mix the powder and the water (solvent) and then how to inject the medicine.
- Before you start using this medicine, read these instructions completely.
- This medicine is for you only; do not let anyone else use it.
- Use each needle, vial, and syringe only once.
Before you start
- This medicine must be at room temperature before injection. Remove it from the refrigerator approximately 30 minutes before use.
- Wash your hands
- It is important that your hands and the objects you use are as clean as possible.
3.Place everything you need on a clean surface:
- a vial of powder
- 1 ml of sterile water for injections (solvent)
- a syringe and needle (yellow mark) to withdraw the prepared medicine from the vial
- a needle (grey mark) to inject the medicine into your abdomen
- two alcohol swabs.
Mixing the powder and water to prepare your medicine
1.Remove the cap from the vial
- You will find a rubber stopper underneath; leave it in the vial.
- Clean the rubber stopper and the metal ring with the first alcohol swab.
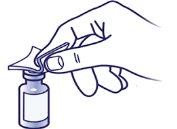
2.Filling the syringe with sterile water
- Remove the needle cover with the yellow mark (figure a).
- Attach the needle to the syringe. Remove the needle cover (figure b).
- Fill the syringe with sterile water for injections (figure c).
- b. c.
- Add the water from the pre-filled syringe to the powder in the vial Push the needle through the center of the rubber stopper of the vial.
- Slowly push the plunger of the syringe to inject the water into the vial. Do not use any other type of water.
- Leave the syringe in the rubber stopper.
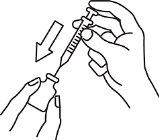
4.Mix the powder and water in the vial
- While carefully holding the syringe and vial, gently move it to mix the powder and water. Once mixed, the solution will have a clear and particle-free appearance.
- Do not shake the vial, as this will create bubbles in the medicine.
5.Refill the syringe with the medicine from the vial
- Place the vial upside down. Then, gently pull the plunger to withdraw the medicine from the vial into the syringe. Be careful not to completely separate the plunger from the plunger cap. If the plunger cap has been separated from the plunger by mistake, make sure to discard the dose, as sterility will be lost, and prepare a new dose (start again from step 1).
- If medicine remains in the vial, pull the yellow needle until the tip of the needle is just inside the rubber stopper. If you look sideways through the empty space in the rubber stopper, you can control the movement of the needle and the liquid.
- Make sure to withdraw all the medicine from the vial.
- Put the needle cover back on the needle. Remove the needle from the syringe and set the syringe aside.
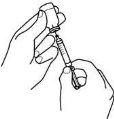
Preparing the injection site and injecting the medicine
1.Removing air bubbles
- Remove the cover from the needle with the grey mark. Attach the needle to the syringe and remove the needle cover.
- Hold the syringe with the needle pointing upwards and check that there are no air bubbles.
- To remove air bubbles, gently tap the syringe until the air accumulates at the top. Then, slowly push the plunger until the bubbles disappear.
- Do not touch the needle or allow the needle to touch any surface.
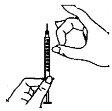
2.Clean the injection site
- Choose an injection site on your stomach. The area around the navel is best.
To reduce skin irritation, select a different part of your stomach each day.
- Clean the skin of the chosen injection site with the second alcohol swab, using a circular motion.
3.Puncture the skin
- Hold the syringe with one hand, as if it were a pencil.
- Gently take a fold of skin around the injection site and hold it firmly with your other hand.
- Slowly insert the gray needle completely into the skin at an angle of approximately 45 to 90 degrees. Then, release the skin.
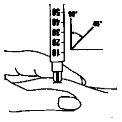
4.Medication injection
- Gently pull back on the syringe plunger. If blood appears, continue as indicated in step 5.
- If no blood appears, push the plunger gentlyto inject the medication.
- When the syringe is empty, slowly withdraw the needle at the same angle.
- Use the second alcohol swab to apply gentle pressure to the injection site.
- If blood appears:
- slowly withdraw the needle at the same angle
- use the second alcohol swab to apply gentle pressure to the skin puncture site
- discard the medication in a sink and continue as indicated in step 6 below
- wash your hands and start again with a new pre-filled vial and syringe.
6.Disposal
- Use each needle, vial, and syringe only once.
- Put the caps back on the needles so they can be disposed of safely.
- Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of the used needles, vial, and syringe.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to CETRORELIX EDEST 0.25 mg POWDER FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, UnknownActive substance: cetrorelixManufacturer: Merck Europe B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, UnknownActive substance: cetrorelixManufacturer: Merck Europe B.V.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.25 mgActive substance: cetrorelixManufacturer: Sun Pharmaceutical Industries (Europe) B.V.Prescription required
Online doctors for CETRORELIX EDEST 0.25 mg POWDER FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about CETRORELIX EDEST 0.25 mg POWDER FOR INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






