
BERTANEL 10 mg/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION

How to use BERTANEL 10 mg/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Bertanel 7.5 mg/0.75 ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
Bertanel 10 mg/1 ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
Bertanel 15 mg/1.5 ml solution for injection in pre-filled syringe
methotrexate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- Keep this leaflet, as you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack
- What is Bertanel and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Bertanel
- How to use Bertanel
- Possible side effects
- Storing Bertanel
- Package contents and further information
1. What is Bertanel and what is it used for
Bertanel is a medicine that contains methotrexate. Methotrexate is a substance with the following properties:
- interferes with the growth of certain rapidly multiplying body cells (antitumour agent)
- reduces unwanted reactions of the body's own defence mechanism (immunosuppressant)
and
- has anti-inflammatory effects.
Bertanel is used in patients with:
- active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) in adult patients
- polyarticular forms (when five or more joints are involved) of active and severe juvenile idiopathic arthritis (children over 3 years) when the response to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) has been inadequate
- severe recalcitrant psoriasis that is disabling and unresponsive to other forms of treatment such as phototherapy, PUVA, and retinoids, and severe psoriasis that affects the joints (psoriatic arthritis) in adult patients.
.
2. What you need to know before using Bertanel
Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions before using Bertanel.
Do not use Bertanel
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to methotrexate or any of the other components of this medicine (included in section 6)
- if you have any existing or severe infection
- if you have inflammation of the mouth or active digestive ulcers
- if you have any significant kidney disease (your doctor decides the severity of the disease)
- if you have any significant liver disease (your doctor decides the severity of the disease)
- if you have disorders of the system that forms blood components (your doctor decides the severity of the disease)
- if you have increased alcohol consumption (if you have liver disease caused by alcohol or other chronic liver disease)
- if you have an altered immune system (e.g., AIDS)
- if you are pregnant or breastfeeding (see section "Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility").
Warnings and precautions
Important warning regarding methotrexate dosing:
Methotrexate for the treatment of rheumatic or skin diseases should only be used once a week.
Always use Bertanel exactly as your doctor has indicated.
Incorrect dosing of methotrexate can cause serious adverse effects, including fatal consequences. Read section 3 of this prospectus carefully.
Talk to your doctor before using Bertanel.
Especially in elderly people, deaths have been reported after accidental daily use of the weekly dose.
Methotrexate should only be prescribed by doctors who have sufficient experience in treating the disease with methotrexate.
Your doctor will inform you about the possible benefits and risks (including the first signs and symptoms of toxicity) of methotrexate therapy.
You need to be closely monitored during therapy so that signs of possible toxic effects or adverse reactions can be detected with minimal delay.
If you notice symptoms of poisoning (please consult section 4 "Possible adverse effects"), contact your doctor immediately. Your doctor will decide if it is necessary to monitor and treat the symptoms of poisoning and will inform you of additional measures.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using Bertanel if you:
- have diabetes mellitus treated with insulin
- have chronic inactive infections (e.g., tuberculosis, hepatitis B or C, herpes (herpes zoster)), as these diseases could reactivate
- have or have had any liver or kidney disease
- have or have had problems with lung function
- are obese
- have abnormal fluid accumulation in the abdomen or in the cavity between the lungs and the thoracic wall (ascites, pleural effusion)
Liver function
Methotrexate can damage the liver; during treatment with Bertanel, you should avoid drinking alcohol and taking other medications that can damage the liver. Before and during treatment with Bertanel, your doctor must perform blood tests to monitor liver function. Please also consult the sections "Other medicines and Bertanel" and "Bertanel with food and alcohol" and section 4.
Kidney function
Bertanel can damage the kidneys. Your doctor must perform blood tests before and during treatment to monitor your kidney function. If you are dehydrated or have a condition that can cause dehydration (vomiting, diarrhea, stomatitis), the toxicity of methotrexate could increase. Your doctor may suspend therapy with Bertanel. Please also consult section 4.
Blood formation system and immune system
Treatment with Bertanel could damage your bone marrow (bone marrow depression). This can cause serious infections and/or bleeding and anemia.
Your doctor will perform blood tests so that they can be treated as soon as possible.
Contact your doctor if you experience fever, sore throat, mouth ulcers, flu-like symptoms, fatigue, bruising, or bleeding.
Methotrexate can influence the effectiveness of vaccines or immune reaction tests due to its effect on the immune system.
Nervous system
Certain brain disorders (encephalitis/encephalopathy), which can be fatal, have been reported with methotrexate administered intravenously. There have been reports of leukoencephalopathy in patients treated with oral methotrexate. If you, your partner, or your caregiver notice the appearance or worsening of neurological symptoms, such as general muscle weakness, vision changes, changes in thinking, memory, and orientation that cause confusion and changes in personality, contact your doctor immediately because these can be symptoms of a rare and serious brain infection called progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).
Skin
Methotrexate can make your skin sensitive to sunlight, so you should avoid prolonged sun exposure.
You should not visit a tanning salon without consulting your doctor first.
Methotrexate can make your skin more sensitive to sunlight. Avoid intense sun and do not use tanning beds or ultraviolet lamps without medical advice. To protect your skin from intense sun, wear suitable clothing or use a sunscreen with a high protection factor.
Changes in the skin caused by psoriasis can worsen during treatment with Bertanel if UV radiation exposure occurs at the same time.
If you have experienced skin problems after radiation therapy (radiation-induced dermatitis) and sunburn, these diseases may recur under methotrexate therapy (memory effect).
There have been reports of serious skin reactions, sometimes fatal, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell syndrome) after single or continuous use of methotrexate (please consult section 4).
Gastrointestinal system
Treatment with methotrexate can lead to serious complications in your gastrointestinal system. In this case, treatment with methotrexate should be discontinued.
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any problems in your gastrointestinal system (please consult section 4).
Infections
Treatment with methotrexate can lead to infections, which can be fatal in some cases.
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience signs of infection (please consult section 4).
Lung function
Treatment with methotrexate can lead to serious lung complications. In this case, treatment with methotrexate should be discontinued.
Contact your doctor immediately if you experience any respiratory problems or problems with your lungs (please consult section 4).
Acute lung hemorrhage has been reported with methotrexate in patients with underlying rheumatologic disease. If you experience symptoms of coughing or spitting blood, you should contact your doctor immediately.
Tumors
A rare cancer in the lymph nodes (malignant lymphoma) can occur in patients receiving low doses of methotrexate, which in some cases improved after discontinuing treatment; therefore, no cytotoxic treatment was required. If lymphoma occurs, therapy with methotrexate should be discontinued; and only if the lymphoma does not disappear, appropriate treatment with cytostatics should be initiated.
Methotrexate temporarily affects sperm and egg production, which is reversible in most cases.
Methotrexate can cause abortions and serious birth defects. If you are a woman, you should avoid becoming pregnant while using methotrexate and for at least six months after discontinuing treatment. If you are a man, you should avoid fathering a child if you are being administered methotrexate at that time and for at least 3 months after finishing your treatment. See also the section "Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility".
Recommended follow-up investigations and precautions:
Although Bertanel is administered at low doses, serious adverse effects can occur. To diagnose them as soon as possible, your doctor must perform follow-up reviews and laboratory tests.
Before starting treatment:
Before starting treatment, you will have a blood test to check if you have enough blood cells. Your liver function and hepatitis will also be checked in your blood. Additionally, serum albumin (a blood protein), hepatitis status (liver infection), and kidney function will be checked. Your doctor may decide to perform other liver tests, some of which may involve images of your liver and others that may require a small tissue sample from your liver to examine it more closely. Your doctor may also check if you have tuberculosis and may perform a chest X-ray or lung function test.
During treatment:
Your doctor may perform the following tests:
- examination of the oral cavity and pharynx to detect changes in the mucous membrane, such as inflammation or ulcers
- blood test/blood count, with blood cell count and measurement of serum methotrexate levels
- blood test to monitor liver function
- imaging tests to monitor liver function
- taking a small tissue sample from the liver to examine it more closely
- blood test to monitor kidney function
- monitoring of the respiratory tract and, if necessary, lung function test
It is very important that you attend these scheduled tests.
If the results of any of these tests are remarkable, your doctor will adjust the treatment accordingly.
Do not miss your appointments for any of these tests.
If the results of any of these analyses are not normal, your doctor will take the appropriate measures.
Elderly patients
Elderly patients treated with methotrexate should be under close medical supervision, so that possible adverse effects can be detected as soon as possible. The deterioration of liver and kidney function associated with age, as well as having low folate reserves at an advanced age, require the administration of a relatively low dose of methotrexate.
Children and adolescents
The use of methotrexate is not recommended in children under 3 years of age, due to the lack of experience in this age group.
Children treated with methotrexate should be kept under particularly close medical supervision by specialists in this area, in order to identify possible side effects as soon as possible.
Other medicines and Bertanel
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you are using, have recently used, or may need to use other medicines, including non-prescription medicines, such as herbal remedies or vitamins.
It is especially important that you inform your doctor if you are using:
- medicines that can damage the liver, such as:
- azathioprine (used to prevent organ rejection after a transplant)
- leflunomide (for rheumatoid arthritis)
- retinoids (used to treat psoriasis and other skin disorders)
- sulfasalazine (used for rheumatoid arthritis and ulcerative colitis)
- other treatments for rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis, such as gold, penicillamine, hydroxychloroquine, sulfasalazine, azathioprine, and cyclosporine (to suppress the immune system)
- medicines for pain and/or inflammation (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or salicylates, such as ibuprofen, indomethacin, phenylbutazone, aminopyrine derivatives, and acetylsalicylic acid, including salicylic acid). This also applies to medicines available without a prescription
- certain cancer treatments (cytotoxics such as doxorubicin, mercaptopurine, procarbazine, cisplatin, L-asparaginase, vincristine, cytarabine, and 5-fluorouracil)
- antibiotics (e.g., penicillin, sulfonamides, trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, tetracyclines, ciprofloxacin, pristinamycin, chloramphenicol)
- metamizole (synonyms novaminsulfon and dipyrone) (medicine for severe pain and/or fever)
- penicillins may reduce the excretion of methotrexate, causing a potential increase in adverse effects
- tranquilizers (e.g., benzodiazepines, such as lorazepam, alprazolam)
- medicines for high blood sugar levels (tolbutamide, glipizide, glimepiride)
- para-aminobenzoic acid (treatment for skin problems)
- oral contraceptives
- triamterene (treatment for high blood pressure)
- anticonvulsant medicines, such as phenytoin, levetiracetam (prevent seizures) and barbiturates (also used as injections for sleeping)
- probenecid (for gout)
- hippuric acid (substance to check kidney function)
- pyrimethamine (used to prevent and treat malaria)
- medicines used to treat severe stomach acid or ulcers (e.g., proton pump inhibitors, such as omeprazol, pantoprazol, lansoprazol)
- theophylline (used to treat asthma and other lung diseases)
- amiodarone (for heart rhythm disorders)
- anesthesia based on nitrous oxide (talk to your doctor if you have a planned operation)
- vitamin preparations containing folic acid, folinic acid, or any derivative
You should not receive simultaneous vaccination with live vaccines during treatment with methotrexate. If you are unsure, consult your doctor.
There have been reports of skin cancer development in some patients with psoriasis who received methotrexate and PUVA treatment (treatment with ultraviolet light).
Radiation treatment during methotrexate treatment could increase the risk of necrosis (tissue damage due to cell death) in soft tissue or bone tissue.
Bertanel with food and alcohol
During treatment with Bertanel, you should avoid consuming alcohol, as this can increase toxicity (especially liver toxicity). You should also avoid excessive consumption of coffee, caffeinated beverages, and black tea.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to become pregnant, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
Do not use Bertanel during pregnancy or if you are trying to become pregnant. Methotrexate can cause birth defects, harm the fetus, or cause abortions. It is associated with malformations of the skull, face, heart, and blood vessels, brain, and limbs. Therefore, it is very important that methotrexate is not administered to pregnant patients or those planning to become pregnant. In women of childbearing age, any possibility of pregnancy should be excluded with appropriate measures, such as a pregnancy test before starting treatment. You should avoid becoming pregnant while taking methotrexate and for at least 6 months after discontinuing treatment, using reliable contraceptive methods during this entire time (see also section "Warnings and precautions").
If you become pregnant during treatment or suspect you may be pregnant, consult your doctor as soon as possible. You should be offered information about the risk of harmful effects on the child during treatment.
If you wish to become pregnant, consult your doctor, who may refer you to a specialist for information before the planned start of treatment.
Breastfeeding
You should not breastfeed your child during treatment, as methotrexate passes into breast milk. If your doctor considers treatment with methotrexate to be absolutely necessary, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Male fertility
Available data do not indicate an increased risk of malformations or abortions if the father takes a dose of methotrexate less than 30 mg/week. However, this risk cannot be completely ruled out. Methotrexate can be genotoxic, which means it can cause genetic mutations. Methotrexate can affect sperm production and cause birth defects. Therefore, you should avoid fathering a child or donating sperm while taking methotrexate and for at least 3 months after discontinuing treatment.
Driving and using machines
During treatment with Bertanel, adverse effects can occur that affect the central nervous system, such as fatigue, drowsiness, and dizziness. Therefore, in some cases, the ability to drive vehicles and/or operate machines may be impaired. If you feel tired or dizzy, do not drive or operate tools or machines. This applies even more if you consume alcohol.
Bertanel contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol of sodium (23 mg) per weekly dose; it is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Bertanel
Follow your doctor's administration instructions for Bertanel exactly. Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure.
Important warning about Bertanel (methotrexate) dosage
Use Bertanel only once a weekfor the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, polyarticular forms of juvenile idiopathic arthritis, or psoriasis. Excessive use of Bertanel (methotrexate) can be fatal. Please read section 3 of this prospectus very carefully. If you have any doubts, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
Bertanel should only be prescribed by doctors familiar with the different characteristics of the medication and its mode of action.
Bertanel is administered onlyonce a week. Along with your doctor, you can decide on a suitable day of the week, every week, to receive your injection.
Incorrect administration of Bertanel can cause serious adverse effects, including potentially fatal adverse effects.
The recommended dose is:
Dosage in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
The initial recommended dose is 7.5 mg of methotrexate once a week.
If this is not sufficient and if you tolerate the medication well, the initial dose of Bertanel can be gradually increased by 2.5 mg. Alternatively, a higher initial dose can be used. The average weekly dose is 15-20 mg. Generally, a weekly dose of 20 mg of Bertanel should not be exceeded. Once the desired therapeutic result is achieved, if possible, the dose should be gradually reduced to the lowest effective maintenance dose.
A response to treatment is expected after 4-8 weeks. After discontinuation of treatment with Bertanel, symptoms may reappear.
Use in children (over 3 years) and adolescents
Dosage in children (over 3 years) and adolescents with polyarticular forms of juvenile idiopathic arthritis
The recommended dose is 10-15 mg/m2 of body surface area per week. In cases of inadequate response, the weekly dose can be increased up to 20 mg/m2 of body surface area per week. However, more frequent monitoring should be performed.
Adults with severe forms of psoriasis vulgaris or psoriatic arthritis
Recommended initial dose (relative to an average adult weighing 70 kg): A single test dose of 2.5-5 mg is recommended to assess toxicity.
If laboratory parameters do not change, treatment can be continued with approximately 7.5 mg 1 week later. The dose is gradually increased (in increments of 5-7.5 mg per week) while laboratory parameters are analyzed, until the optimal expected result is achieved. Generally, a weekly dose of 25 mg of methotrexate should not be exceeded.
Once the desired result is achieved, the maintenance dose should be gradually reduced to the lowest effective dose in the patient, if possible.
A response to treatment usually occurs after 4-8 weeks. Thereafter, treatment is continued or discontinued according to the clinical situation and changes in laboratory parameters.
Elderly patients
A dose reduction should be considered in elderly patients due to decreased renal and hepatic function, as well as the decline in folate reserves that occurs with age.
Patients with renal insufficiency
Patients with renal insufficiency may require lower doses.
Method and duration of administration
Your doctor will determine the duration of treatment. Bertanel is injected once a week! It is recommended to specify a particular day of the week as the "injection day".
Bertanel is administered by subcutaneous, intramuscular, or intravenous injection; in children and adolescents, it should not be administered intravenously.
Treatment with Bertanel for rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriasis vulgaris, and psoriatic arthritis is long-term treatment.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Improvement of symptoms can usually be expected after 4-8 weeks of treatment. Symptoms may reappear after discontinuation of treatment with Bertanel.
Severe forms of psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis (psoriatic arthropathy)
A response to treatment can usually be expected after 4-8 weeks. Depending on the clinical situation and changes in laboratory parameters, treatment will be continued or discontinued.
At the start of treatment, Bertanel may be injected by medical personnel. However, your doctor may decide that you can learn to inject Bertanel yourself. You will receive adequate training for this. Under no circumstances should you attempt to inject yourself unless you have been taught to do so.
If you use more Bertanel than you should
Follow your doctor's administration instructions. Do not change the dose on your own.
If you suspect that you (or someone else) have administered too much Bertanel, contact your doctor or go to the nearest hospital immediately, or consult the Toxicology Information Service, phone 91 562 04 20. They will decide what measures to take based on the severity of the poisoning.
An overdose of methotrexate can cause serious toxic reactions, including a fatal outcome. Symptoms of overdose may include bleeding or bruising, unusual weakness, mouth sores, nausea, vomiting, black or bloody stools, coughing up blood or vomit resembling coffee grounds, and decreased urine production. See section 4.
Bring the medication with you if you go to the doctor or hospital.
The antidote in case of overdose is calcium folinate.
If you forget to use Bertanel
If you miss a dose, administer it within 24 hours of the specified day. If a longer delay occurs, consult your doctor first. Do not take a double dose to make up for missed doses; continue using the prescribed dose. If you have doubts, consult your doctor.
If you interrupt treatment with Bertanel
You should not interrupt treatment with Bertanel unless your doctor has indicated it. If you suspect serious adverse effects, consult your doctor immediately.
If you have any other questions about the use of this medication, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause adverse effects, although not all people suffer from them.
Adverse effects generally depend on the dose level and the duration of treatment with methotrexate.
Severe adverse effects can also occur at lower doses, which may lead to interruption or termination of therapy.
Adverse effects can appear at any time during treatment.
Most adverse effects are reversible if recognized in time. Termination of treatment does not always completely resolve all adverse effects.
However, some of the severe adverse effects mentioned below can cause sudden death in very rare cases.
Some adverse effects may occur after treatment has ended.
Please talk to your doctor.
If you develop any of the following adverse effects, contact your doctor immediately, as they could be signs of potentially fatal adverse effects that need to be treated immediately. Your doctor may decide to reduce the dose or suspend treatment.
Severe Adverse Effects
- Allergic symptoms such as rash or itching (which especially affects the whole body), swelling of the hands, feet, ankles, eyelids, face, lips, mouth, or throat (which can cause difficulty swallowing or breathing), sudden wheezing, difficulty breathing, and feeling of fainting (these can be signs of severe allergic reactions or anaphylactic shock) (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients)
- Pulmonary disorders (symptoms may be, generally, discomfort, irritating and dry cough, difficulty breathing, feeling of lack of air at rest, chest pain, or fever), these can be signs of pneumonia, interstitial pneumonitis, or alveolitis (may affect up to 1 in 10 patients)
- Coughing up or spitting blood
- Symptoms of liver failure such as yellowish color of the skin (jaundice) and the whites of the eyes, dark urine, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, pain in the right side of the abdomen, and itching (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients)
- Symptoms of kidney failure such as swelling of the hands, ankles, or feet, or changes in urination frequency or decreased or absent urine (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients)
- Symptoms of an infection such as fever, chills, pain, sore throat. Methotrexate can decrease your resistance to infections; severe infections such as a special form of pneumonia (Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia) (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 patients) or blood poisoning (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients) can occur
- Fever, sore throat, mouth ulcers, general feeling of discomfort and fatigue, nosebleeds, and small red spots on the skin can be symptoms of bone marrow damage (may affect up to 1 in 10 patients)
- Ulcers in the mouth and throat (may affect more than 1 in 10 patients)
- Pain in the stomach area, nausea, vomiting, and fever, as these can be signs of pancreatitis (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients)
- Severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, severe diarrhea, black or tarry stools, or changes in bowel habits, as these could be symptoms of gastrointestinal tract complications, such as ulcers (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients) or intestinal perforation (frequency not known)
- Severe toxic skin reactions, such as blistering and peeling of the top skin layer (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis/Lyell's syndrome). Skin reactions are associated with severe general condition disorders and fever. The skin reaction can be potentially fatal (may affect up to 1 in 100 patients)
- Symptoms of thrombosis (blood clot) such as pain or pressure in the chest, pain in the arms, back, neck, or jaw, shortness of breath, numbness or weakness in one half of the body, speech disorders, headache, or drowsiness (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients)
- Cough, chest pain, sudden shortness of breath, or coughing up blood; these can be symptoms of a pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lung) (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 patients)
The following adverse effects have also been reported:
Very common (may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- reduction in blood cell formation with decreased white blood cells and/or platelets (leukopenia, thrombocytopenia)
- headache, dizziness
- cough
- loss of appetite, nausea (feeling of discomfort), vomiting, diarrhea (particularly during the 24-48 hours following the first administration of methotrexate), abdominal pain
- inflammation and ulcers in the mouth and throat (particularly during the 24-48 hours following the first administration of methotrexate)
- increase in liver enzymes in blood tests
- hair loss
- decrease in creatinine clearance (your doctor may determine this through a blood test and it is a sign of worsening kidney function)
- feeling of weakness
Common (may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- herpes (herpes zoster)
- anemia
- decrease in the number of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, sudden drop in certain white blood cells (agranulocytosis), disorders in blood cell formation (pancytopenia)
- fatigue, drowsiness
- tingling, prickling, pinching (paresthesia)
- burning sensation on the skin, rash, redness of the skin, itching
- skin ulcers
- red eyes (conjunctivitis)
Uncommon (may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- opportunistic infections (due to the immune system not functioning properly) that can be fatal in some cases
- lymph tissue cancer (lymphoma), see also section 2
- the immune system does not function properly, leading to a higher likelihood of suffering from infections/inflammations
- diabetes
- depression
- weakness on one complete side of the body (hemiparesis)
- dizziness, confusion
- seizures
- brain damage (encephalopathy/leukoencephalopathy)
- inflammation of blood vessels (vasculitis)
- allergic vasculitis
- scarring of lung tissue (pulmonary fibrosis), fluid around the lungs
- ulcers and bleeding in the digestive tract
- inflammation of the pancreas
- liver damage, liver thickening, scarring of liver tissue (liver fibrosis), chronic liver damage (liver cirrhosis)
- decrease in serum albumin
- hives (alone), skin darkening
- increase in rheumatoid nodules
- painful psoriasis
- skin lesions similar to herpes
- reactions similar to sunburn due to increased skin sensitivity to sunlight
- muscle or joint pain
- osteoporosis (reduction in bone mass)
- inflammation and ulcers of the bladder (possibly with blood in the urine), problems emptying the bladder, absence of urination, painful or reduced urination
- fetal malformations
- inflammation and ulcers of the vagina
- fever
Rare (may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- very large red blood cells (megaloblastic anemia)
- mood swings
- temporary perception disorders
- weakness of voluntary movement in the whole body
- speech problems (aphasia/dysarthria)
- severe visual disorders (blurred or cloudy vision), blood clots in the retina
- low blood pressure
- blood clots (thromboembolic episodes)
- sore throat
- breathing interruption
- inflammation of the digestive tract, bloody stools
- inflamed gums
- acute hepatitis (liver inflammation)
- change in nail color, nail loss
- acne, red or purple spots due to bleeding from blood vessels
- erythema multiforme, red skin rash
- stress fracture
- electrolyte disorders, increase in urea, creatinine, and uric acid in the blood (azotemia)
- abortion
- defective sperm formation (men) and egg formation (women)
- menstrual cycle disorders
Very rare (may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- hepatitis caused by herpes viruses (herpes simplex hepatitis), fungal infections (histoplasmosis, cryptococcosis), bacterial infections (nocardiosis), viral infections (cytomegalovirus infections, including pneumonia)
- fever (herpes simplex)
- anemia due to inadequate red blood cell formation (aplastic anemia), increased eosinophils in the blood (eosinophilia), decreased neutrophils in the blood (neutropenia), inflammation of lymph nodes in the head, neck, armpits, and groin (partially reversible), uncontrolled proliferation of lymphocytes (partially reversible)
- immunodeficiency (hypogammaglobulinemia)
- hepatitis
- muscle and weakness pain in the limbs
- changes in taste (metallic taste)
- inflammation of the brain lining causing paralysis or vomiting
- swelling around the eyes, eyelid inflammation, tearing, increased sensitivity to light, transient blindness, vision deterioration
- inflammation of the sac around the heart (pericarditis), obstruction of cardiac filling due to pericardial effusion (cardiac tamponade), accumulation of fluid between the pericardial leaves (pericardial effusion)
- abnormal lung function test results, with difficulty breathing and coughing
- vomiting blood
- death of liver cells (liver necrosis), acute liver degeneration, liver failure
- deep infection of hair follicles (furunculosis), permanent enlargement of capillaries visible on the skin (telangiectasia), acute inflammation of the nail bed
- blood and/or protein in the urine
- fetal death
- problems with ovule formation (women) and sperm formation (men)
- menstrual cycle disorders
- loss of sexual desire
- problems having an erection
- breast enlargement in men
- vaginal discharge
- infertility
- feeling of numbness or tingling/sensitivity to stimuli less than normal
Unknown frequency (cannot be estimated from available data):
- pneumonia
- reactivation of hepatitis B infection or worsening of hepatitis C infection
- lung bleeding
- skin cancer (see also section 2)
- increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure with symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting, increased blood pressure, confusion; nerve system damage (neurotoxicity), inflammation of the brain lining (arachnoiditis), leg paralysis (paraplegia), stupor, coordination problems (ataxia), dementia
- non-inflammatory eye disorder (retinopathy)
- hypoxia (lack of oxygen in organs)
- non-infectious inflammation of the abdominal lining characterized by stomach pain and sensitivity to pressure (peritonitis)
- toxic megacolon (severe complication due to massive colon enlargement combined with intense pain), intestinal perforation
- tongue inflammation
- drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS)
- dermatitis
- bone damage in general and in the jaw (secondary to excessive white blood cell growth)
- urogenital dysfunction
- chest pain, chills, tissue destruction at the injection site
- skin redness and peeling
- swelling
When methotrexate is administered intramuscularly, local adverse effects (burning sensation) or damage (formation of sterile abscesses, destruction of fatty tissue) may occur at the injection site.
Subcutaneous administration of methotrexate is well-tolerated locally. Only mild local skin reactions were observed, decreasing during treatment.
Reporting of Adverse Effects
If you experience any type of adverse effect, consult your doctor or pharmacist, even if it is a possible adverse effect not listed in this leaflet. You can also report them directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: www.notificaRAM.es. By reporting adverse effects, you can contribute to providing more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Bertanel
Keep this medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the label of the pre-filled syringe and on the packaging after "EXP". The expiration date is the last day of the month indicated.
Store in the original packaging to protect it from light.
Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze.
The product must be used immediately after opening the packaging.
Do not use Bertanel if the solution is not transparent and contains particles.
For single use. Discard any unused solution!
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Place the packaging and any unused medicines in the pharmacy's SIGRE collection point. If in doubt, ask your pharmacist how to dispose of packaging and unused medicines. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Contents and Additional Information
Bertanel Composition
The active ingredient is methotrexate.
Each ml of injectable solution contains 10 mg of methotrexate (equivalent to 10.97 mg of methotrexate disodium).
Each pre-filled syringe with 0.75 ml of injectable solution contains 7.5 mg of methotrexate.
Each pre-filled syringe with 1 ml of injectable solution contains 10 mg of methotrexate.
Each pre-filled syringe with 1.5 ml of injectable solution contains 15 mg of methotrexate.
The other components are: sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment) and water for injectable preparations.
Product Appearance and Container Contents
Bertanel pre-filled syringes contain a clear, yellow, particle-free injectable solution.
Bertanel is available in pre-filled glass syringes (Type I according to Ph. Eur.) with a capacity of 1.25 ml, 2.25 ml or 3.00 ml, with an elastomeric stopper and elastomeric plunger.
Container size:
1 x 0.75 ml, 4 x 0.75 ml, 5 x 0.75 ml
1 x 1.0 ml, 4 x 1.0 ml, 5 x 1.0 ml
1 x 1.5 ml, 4 x 1.5 ml, 5 x 1.5 ml
1 x 2.0 ml, 4 x 2.0 ml, 5 x 2.0 ml
Single-use injection needles and alcohol swabs.
Only some container sizes may be marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder
Ebewe Pharma Ges.m.b.H. Nfg.KG,
Mondseestrasse 11,
4866 Unterach, Austria
Manufacturer
Ebewe Pharma Ges.m.b.H. Nfg.KG,
Mondseestrasse 11,
4866 Unterach, Austria
Fareva Unterach GmbH
Mondseestraße 11
4866 Unterach
Austria
Local Representative
Laboratorios Farmacéuticos ROVI, S.A.
Julián Camarillo, 35
28037 Madrid
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
AT/H/0192/01/MR
Austria | Ebetrexat 10 mg/ml Injektionslösung in einer Fertigspritze |
Spain | Bertanel 7.5 mg/0.75 ml, solution for injection in pre-filled syringe Bertanel 10 mg/ml, solution for injection in pre-filled syringe Bertanel 15 mg/1.5 ml, solution for injection in pre-filled syringe |
Netherlands | Metotrexato Sandoz 7.5 mg = 0.75 ml, oplossing voor injectie 10 mg/ml |
Date of the last revision of this leaflet:September 2024
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Instructions for use, handling, and disposal
The solution should be clear and particle-free.
Handling and disposal of the medicinal product should be carried out as with other cytotoxic preparations and in accordance with local regulations. If any female healthcare worker is pregnant, she should not handle and/or administer Bertanel.
For single use. Discard any unused solution.
Disposal of unused medicinal product or waste materials should be carried out in accordance with local regulations for cytotoxic agents.
Incompatibilities
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medicinal product should not be mixed with others.
Special Precautions for Storage
Store in the original container to protect from light.
Do not store above 25°C.
Do not freeze.
Step-by-step instructions for subcutaneous injection:
Step 1:
- Remove the inner container containing the pre-filled syringe, needle, and cannula from the box.
- Open the inner container by pulling the corner flap. Remove the pre-filled syringe.
- Twist the gray rubber cap covered with plastic on the syringe without touching the opening of the pre-filled syringe (see Figure 1).
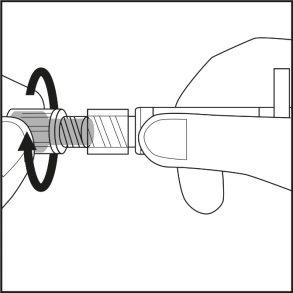
Figure 1.
Step 2:
- Place the syringe back in the inner container. The yellow solution will not spill.
- Check the label on the plastic needle container. The label should be intact (see Figure 2).
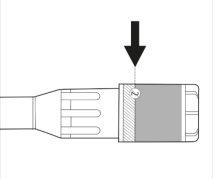
Figure 2.
Step 3:
- Remove the cap from the plastic needle container by twisting and pulling. See Figure 3.1
- Carefully twist the needle along with the plastic container onto the syringe until it reaches the end. See Figure 3.2
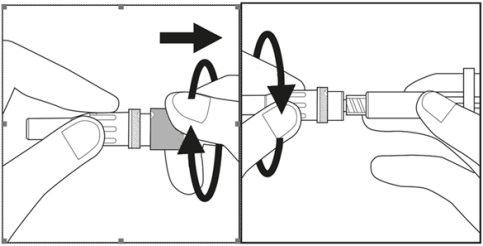
Figure 3.1 Figure 3.2
Step 4:
- Choose the injection site on the abdomen or thigh and clean it with an alcohol swab. Do not touch this area before injection (see Figures 4.1 and 4.2).
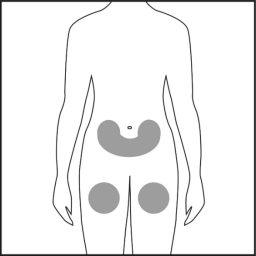
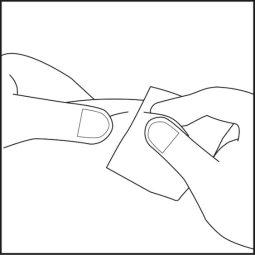
Figure 4.1 Figure 4.2
Step 5:
- Remove the cannula cover and set it aside.
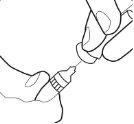
- Do not touch the sterile cannula. If this happens, ask your doctor or pharmacist about the possibility of using another cannula. With two fingers, form a fold in the skin and then insert the needle into it almost vertically.
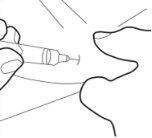
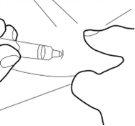
Step 6:
- Insert the cannula completely into the skin fold. Then, slowly push the plunger down and inject all the liquid under the skin.
Step 7:
- Carefully remove the cannula and pass a cotton swab over the injection site. Do not rub, as this may irritate the injection site.
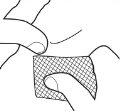
- To avoid injury, deposit the used syringe in a sharps container.
.
- Country of registration
- Average pharmacy price13.49 EUR
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BERTANEL 10 mg/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 15 mgActive substance: methotrexateManufacturer: Ebewe Pharma Ges.M.B.H. Nfg.KgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 20 mgActive substance: methotrexateManufacturer: Ebewe Pharma Ges.M.B.H. Nfg.KgPrescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 25 mgActive substance: methotrexateManufacturer: Ebewe Pharma Ges.M.B.H. Nfg.KgPrescription required
Online doctors for BERTANEL 10 mg/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION
Discuss questions about BERTANEL 10 mg/1 ml PRE-FILLED SYRINGE SOLUTION FOR INJECTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions






