

Vetira

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Vetira

How to use Vetira
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Vetira, 100 mg/ml, Oral Solution
Levetiracetam
Read the package leaflet carefully before taking the medicine or giving it to a child, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet:
1
What is Vetira and what is it used for
2
Important information before taking Vetira
3
How to take Vetira
4
Possible side effects
5
How to store Vetira
6
Contents of the pack and other information
1.
WHAT IS VETIRA AND WHAT IS IT USED FOR
Vetira, 100 mg/ml, oral solution is an antiepileptic medicine (used to treat seizures in epilepsy).
Vetira is used:
as monotherapy (only Vetira) in adults and adolescents from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy, for the treatment of certain types of epilepsy. Epilepsy is a condition where patients have repeated seizures (fits). Levetiracetam is used for the treatment of a type of epilepsy where seizures initially are limited to one part of the brain but can spread to other parts of the brain (partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalization). The doctor has prescribed levetiracetam to reduce the number of seizures.
as an additional medicine alongside another antiepileptic medicine:
- in adults, adolescents, children, and infants from 1 month of age for the treatment of partial onset seizures with or without secondary generalization,
- in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy for the treatment of myoclonic seizures (short, shock-like muscle contractions),
- in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (a type of epilepsy that is likely to have a genetic basis) for the treatment of primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures (large seizures, including loss of consciousness).
2. IMPORTANT INFORMATION BEFORE TAKING VETIRA
When not to take Vetira
If you are allergic to levetiracetam, pyrrolidone derivatives, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Vetira, discuss with your doctor:
- If kidney disease has been diagnosed in the patient, Vetira should be used as directed by the doctor. The doctor may decide to adjust the dose. If any slowing of growth or unexpected premature puberty in the child is observed, contact the doctor. In some patients treated with antiepileptic medicines such as Vetira, thoughts of self-harm or suicidal thoughts have occurred. In case of symptoms of depression and/or suicidal thoughts, contact the doctor. If there is a history of irregular heart rhythm (visible on an electrocardiogram) in the patient's family or previously in the patient, or if the patient has a disease and/or is taking medicines that cause a tendency to irregular heart rhythm or electrolyte imbalance.
Tell your doctor or pharmacist if any of the following side effects worsen or last more than a few days:
Unusual thoughts, irritability, or a more aggressive reaction than usual, or if the patient or their family and friends notice significant changes in their mood or behavior.
Worsening of epilepsy
In rare cases, seizures may worsen or occur more frequently, especially in the first month after starting treatment or increasing the dose. If any of these new symptoms occur while taking Vetira, contact the doctor as soon as possible.
Children and adolescents
Vetira should not be used as monotherapy (only Vetira) in children and adolescents under 16 years of age.
Vetira and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the patient is taking or has recently taken, as well as any medicines the patient plans to take.
Do not take macrogol (a medicine used for constipation) one hour before and one hour after taking levetiracetam, as it may prevent levetiracetam from working.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine. Levetiracetam can be used during pregnancy only if the doctor considers it necessary.
Do not stop treatment without discussing it with the doctor.
The risk of birth defects cannot be completely ruled out.
Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment.
Driving and using machines
Vetira may affect the ability to drive and use tools or machines, as it can cause drowsiness. This is more likely at the start of treatment or after increasing the dose. It is not recommended to drive or operate machinery until the effect of the medicine on the patient's ability to perform these activities is known.
Vetira contains maltitol liquid (E965).
If you have been told by your doctor that you have an intolerance to some sugars, contact your doctor before taking this medicine.
Vetira contains methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218).
Methyl parahydroxybenzoate may cause an allergic reaction.
Vetira contains sodium.
Vetira 100 mg/ml, oral solution contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per 15 ml, i.e., the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. HOW TO TAKE VETIRA
This medicine should always be taken as directed by the doctor. In case of doubt, consult the doctor or pharmacist.
Vetira should be taken twice a day, in the morning and evening, at approximately the same time every day. The oral solution should be used as directed by the doctor.
Monotherapy (from 16 years)
Adults and adolescents (from 16 years)
Measure the correct dose using the 10 ml syringe provided with the packaging for patients from 4 years of age.
Usual dose:
Vetira is taken twice a day, in two divided doses; each dose is between 5 ml (500 mg) and 15 ml (1500 mg).
If the patient is taking Vetira for the first time, the doctor will initially prescribe a lower dosefor 2 weeks, and then the usual dose.
Adjunctive therapy
Dose for adults and adolescents (from 12 to 17 years) with a body weight of 50 kg or more:
Measure the correct dose using the 10 ml syringe provided with the packaging for patients from 4 years of age.
Usual dose:
Vetira should be taken twice a day, in two divided doses; each dose is between 5 ml (500 mg) and 15 ml (1500 mg).
Dose for children from 6 months, with a body weight below 50 kg:
The doctor will prescribe the most suitable form of Vetira, depending on the age, weight, and dose.
For children from 6 months to 4 years, measure the correct dose using the 3 ml syringe provided with the packaging.
For children over 4 years, measure the correct dose using the 10 ml syringe provided with the packaging.
Usual dose:
Vetira is taken twice a day, in two divided doses, each dose is between 0.1 ml (10 mg) and 0.3 ml (30 mg) per kilogram of the child's body weight (see the table below for examples of doses).
Dose for children from 6 months
Dose for infants (from 1 month to less than 6 months)
| Body weight | Initial dose: 0.1 ml/kg body weight, twice a day | Maximum dose: 0.3 ml/kg body weight, twice a day |
| 6 kg | 0.6 ml twice a day | 1.8 ml twice a day |
| 8 kg | 0.8 ml twice a day | 2.4 ml twice a day |
| 10 kg | 1 ml twice a day | 3 ml twice a day |
| 15 kg | 1.5 ml twice a day | 4.5 ml twice a day |
| 20 kg | 2 ml twice a day | 6 ml twice a day |
| 25 kg | 2.5 ml twice a day | 7.5 ml twice a day |
| from 50 kg | 5 ml twice a day | 15 ml twice a day |
For infants from 1 month to less than 6 months, measure the correct dose using the 1 ml syringe provided with the packaging.
Usual dose:
Vetira is taken twice a day, in two divided doses; each dose is between 0.07 ml (7 mg) and 0.21 ml (21 mg) per kilogram of the infant's body weight (see the table below for examples of doses).
Dose for infants (from 1 month to less than 6 months)
Method of administration:
After measuring the correct dose using the appropriate syringe, Vetira oral solution can be diluted in a glass of water or in a baby bottle. After oral administration, levetiracetam may leave a bitter taste in the mouth.
Instructions for preparing the medicine for use:
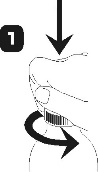
open the bottle: press the cap and turn it in the opposite direction of the arrow (figure 1)
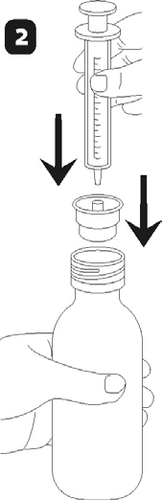
place the syringe adapter on the bottle neck (figure 2). Make sure it is well secured.
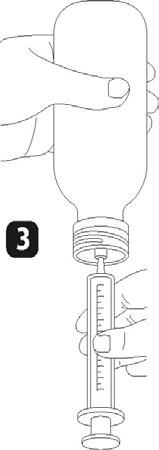
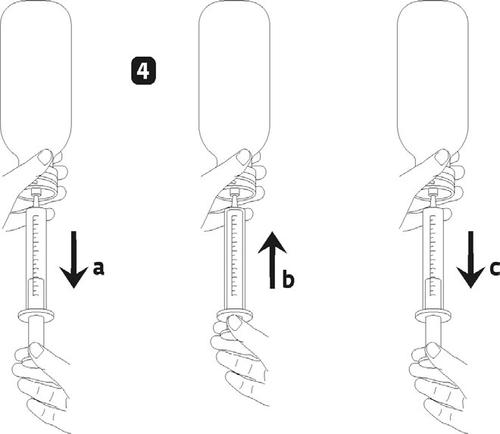
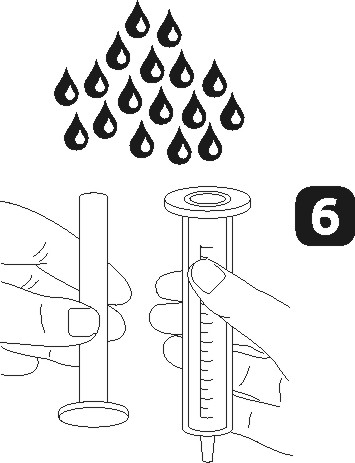
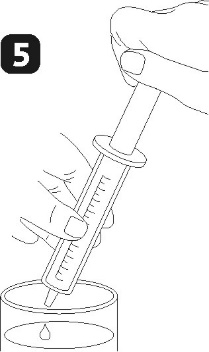
place the dosing syringe on the adapter opening. Invert the bottle (figure 3) and draw a small amount of solution into the syringe by pulling the plunger down (figure 4a), then, while pressing the plunger, remove air bubbles from the syringe (figure 4b) and pull the plunger down to the mark on the syringe corresponding to the prescribed dose in milliliters (ml) (figure 4c). Invert the bottle. Remove the syringe from the adapter. Press the plunger to empty the syringe into a glass of water or a baby bottle (figure 5). Drink the entire contents of the glass/baby bottle. Close the bottle with the plastic cap. Rinse the syringe with water (figure 6).
- 3) nabrać do strzykawki niewielką ilość roztworu przez pociągnięcie tłoczka w dół (rysunek 4 a), następnie wciskając tłoczek, usunąć pęcherzyki powietrza ze strzykawki (rysunek 4b) i pociągnąć tłoczek w dół do miejsca na podziałce odpowiadającego zaleconej przez lekarza dawce w mililitrach (ml) (rysunek 4c). odwrócić butelkę. Wyjąć strzykawkę z łącznika. wycisnąć zawartość strzykawki do szklanki wody lub butelki do karmienia dziecka naciskając tłok strzykawki (rysunek 5). wypić całą zawartość szklanki/ butelki do karmienia dziecka. zamknąć butelkę z plastikową nakrętką. wypłukać strzykawkę wodą (rysunek 6) .
| Body weight | Initial dose: 0.07 ml/kg body weight, twice a day | Maximum dose: 0.21 ml/kg body weight, twice a day |
| 4 kg | 0.3 ml twice a day | 0.85 ml twice a day |
| 5 kg | 0.35 ml twice a day | 1.05 ml twice a day |
| 6 kg | 0.45 ml twice a day | 1.25 ml twice a day |
| 7 kg | 0.5 ml twice a day | 1.5 ml twice a day |
Duration of treatment:
Vetira is used for long-term treatment. Continue taking Vetira for as long as the doctor recommends.
Do not stop treatment without consulting the doctor, as this may cause an increase in the frequency of seizures.
Overdose of Vetira
Possible side effects of overdosing on Vetira include: drowsiness, restlessness, aggression, decreased alertness, respiratory depression, and coma. If a higher dose than recommended is taken, contact a doctor or pharmacist immediately. The doctor will recommend the best possible treatment for the overdose.
Missed dose of Vetira
Contact the doctor if one or more doses of Vetira have not been taken.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping treatment with Vetira
If treatment with Vetira is to be stopped, the medicine should be discontinued gradually to avoid an increase in the frequency of epileptic seizures. If the doctor decides to stop treatment, they will also inform you how to gradually discontinue the medicine.
If you have any further questions about taking this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. POSSIBLE SIDE EFFECTS
Like all medicines, Vetira can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Immediately inform your doctor or contact the nearest hospital emergency department if you experience:
- weakness, dizziness, or difficulty breathing, as these symptoms may indicate a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis);
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat (Quincke's edema);
- flu-like symptoms and rash on the face and then on the rest of the body, accompanied by high fever, increased liver enzyme activity in blood tests, increased number of certain white blood cells (eosinophilia), and swollen lymph nodes (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms - DRESS syndrome);
- symptoms such as decreased urine output, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, confusion, and swelling of the feet, ankles, or legs, as this may be a sign of sudden worsening of kidney function;
- a skin rash that may cause blisters and looks like small targets (a dark spot surrounded by a lighter area and a dark ring around) (erythema multiforme);
- a widespread rash with blisters and peeling skin, mainly on the lips, eyes, mouth, and genitals (Stevens-Johnson syndrome);
- a more severe form of rash causing skin peeling over more than 30% of the body surface (toxic epidermal necrolysis);
- signs of serious mental changes, or if the patient shows signs of disorientation, drowsiness, memory loss (amnesia), memory disorders (forgetfulness), behavioral disorders, or other neurological symptoms, including involuntary or uncontrolled movements. These may be symptoms of encephalopathy.
The most common side effects reported are: inflammation of the nasal passages and throat, drowsiness, headache, fatigue, and dizziness. At the start of treatment or after increasing the dose, side effects such as drowsiness, fatigue, or dizziness may occur more frequently.
These effects should decrease over time.
Very common:may affect more than 1 in 10 people
- inflammation of the nasal passages and throat;
- drowsiness, headache.
Common:may affect up to 1 in 10 people
loss of appetite (anorexia);
depression, feeling hostile or aggressive, anxiety, insomnia, nervousness, or irritability;
seizures, balance disorders, dizziness (feeling of spinning), lethargy (lack of energy and enthusiasm), tremors (involuntary shaking);
dizziness (feeling of spinning);
cough;
abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia (indigestion), vomiting, nausea;
rash;
asthenia/fatigue (exhaustion).
Uncommon:may affect up to 1 in 100 people
decreased platelet count, decreased white blood cell count;
weight loss, weight gain;
suicidal thoughts and attempts, mental disorders, abnormal behavior, hallucinations, anger, disorientation, panic attacks, mood swings, excitement;
memory loss (amnesia), memory disorders (forgetfulness), ataxia (coordination disorder), paresthesia (tingling), attention disorders;
double vision, blurred vision;
abnormal liver test results;
hair loss, rash, itching;
muscle weakness, muscle pain;
injuries.
Rare:may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people
infection;
decreased count of all types of blood cells;
severe allergic reactions: drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms - DRESS syndrome, Quincke's edema (swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat);
decreased sodium levels in the blood;
suicide, personality disorders (behavioral disorders), thinking disorders (slow thinking, inability to concentrate);
delirium;
encephalopathy (detailed description of symptoms, see "Immediately inform your doctor");
seizures may worsen or occur more frequently;
involuntary muscle contractions of the head, trunk, and limbs, difficulty controlling movements, hyperkinesia (hyperactivity);
change in heart rhythm (electrocardiogram);
pancreatitis;
liver dysfunction, hepatitis;
sudden worsening of kidney function;
a skin rash that may cause blisters and looks like small targets (a dark spot surrounded by a lighter area and a dark ring around) (erythema multiforme), widespread rash with blisters and peeling skin, mainly on the lips, eyes, mouth, and genitals (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), and a more severe form of rash causing skin peeling over more than 30% of the body surface (toxic epidermal necrolysis);
rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of striated muscle) and associated increased creatine phosphokinase activity in the blood. The incidence is significantly higher in Japanese patients compared to other patients (non-Japanese);
stuttering or difficulty walking.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including those not listed in this leaflet, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49-21-301, fax: +48 22 49-21-309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl .
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
5. HOW TO STORE VETIRA
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use Vetira after the expiry date stated on the carton and bottle after:
Expiry date (EXP). The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Do not use after 4 months from the first opening of the bottle.
Store in the original bottle to protect from light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. CONTENTS OF THE PACK AND OTHER INFORMATION
What Vetira contains
The active substance is levetiracetam. Each 1 ml of solution contains 100 mg of levetiracetam.
The other ingredients are: sodium citrate (to adjust pH), anhydrous citric acid (to adjust pH), methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218), glycerol (E422), acesulfame potassium (E950), maltitol liquid (E965), raspberry flavor, purified water.
What Vetira looks like and contents of the pack
Vetira 100 mg/ml oral solution is a colorless liquid.
A glass bottle containing 300 ml of Vetira 100 mg/ml oral solution ( for children from 4 years, adolescents, and adults) is placed in a cardboard box, containing a 10 ml dosing syringe (with a scale every 0.25 ml) and a syringe adapter.
A glass bottle containing 150 ml of Vetira 100 mg/ml oral solution ( for infants and children from 6 months to 4 years) is placed in a cardboard box, containing a 3 ml dosing syringe (with a scale every 0.1 ml) and a syringe adapter.
A glass bottle containing 150 ml of Vetira 100 mg/ml oral solution ( for infants from 1 month to less than 6 months) is placed in a cardboard box, containing a 1 ml dosing syringe (with a scale every 0.05 ml) and a syringe adapter.
On the outer packaging and labels, a graphical distinction of the available packaging is provided to avoid confusion when measuring Vetira for different age groups.
For each age group, a different dosing syringe is provided (1 ml or 3 ml, 10 ml), and it is also recommended to pay special attention when using Vetira in a given age group.
After using Vetira and when the bottle is empty, dispose of the dosing syringe provided with the packaging, as each packaging contains a different dosing syringe.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
Adamed Pharma S.A.
Pieńków, ul. M. Adamkiewicza 6A
05-152 Czosnów
Manufacturer
Remedica Ltd
Aharnon Street
Limassol Industrial Estate,
3056 Limassol
Cyprus
Galenica Pharmaceutical Industry S.A.
3rd Km Old National Road Chalkida Athens
Chalcis, 341 00
Greece
Adamed Pharma S.A.
ul. Marszałka Józefa Piłsudskiego 5
95-200 Pabianice
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
{Poland}
{Vetira}
Date of approval of the leaflet:11.2023
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAdamed Pharma S.A. Galenica Pharmaceutical Industry S.A. Remedica Ltd
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to VetiraDosage form: Tablets, 250 mgActive substance: levetiracetamPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 500 mgActive substance: levetiracetamPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 750 mgActive substance: levetiracetamPrescription required
Alternatives to Vetira in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Vetira in Spain
Alternative to Vetira in Ukraine
Online doctors for Vetira
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Vetira – subject to medical assessment and local rules.







