
Ventolin

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Ventolin

How to use Ventolin
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Ventolin, 100 μg/dose inhalation, inhalation aerosol, suspension
Salbutamol
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Ventolin inhalation aerosol and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Ventolin inhalation aerosol
- 3. How to use Ventolin inhalation aerosol
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Ventolin inhalation aerosol
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Ventolin inhalation aerosol and what is it used for
Ventolin inhalation aerosol, suspension, contains a medicine called salbutamol. It belongs to a group of
quick-acting bronchodilators.
Bronchodilators:
- help maintain airway patency, making it easier to breathe,
- help reduce chest tightness, wheezing, and cough associated with asthma. Ventolin inhalation aerosol, suspension is used to treat breathing disorders in adults, adolescents, and children aged 4 and over, with asthma and similar conditions, as well as to prevent asthma symptoms caused by physical exertion and contact with allergens (factors that trigger shortness of breath). These include house dust, pollen, cat and dog hair, and tobacco smoke.
2. Important information before using Ventolin inhalation aerosol
When not to use Ventolin inhalation aerosol
- if the patient is allergic to salbutamol sulfate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- in the case of threatened abortion,
- to prevent premature labor.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Ventolin inhalation aerosol, the patient should consult their doctor if they:
- have poorly controlled asthma (e.g., they often experience asthma symptoms or exacerbations, or have reduced physical fitness). The doctor may recommend starting or increasing the dose of a medicine, e.g., an inhaled corticosteroid, to control the disease,
- have high blood pressure,
- have hyperthyroidism,
- have had heart problems in the past, such as irregular or rapid heartbeat or chest pain,
- have low potassium levels in the blood,
- are taking xanthine derivatives (e.g., theophylline) or steroids to treat asthma,
- are taking diuretics (sometimes used to treat high blood pressure or heart disease).
➔ If the patient is taking any of these medicines, the doctor will recommend monitoring potassium levels in the blood.
➔ The patient should consult their doctor if any of these circumstances apply to them.
The patient should consult their doctor if the duration of action of the medicine is less than 3 hours.
Ventolin and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take, including those available without a prescription.
Some medicines may affect the action of Ventolin inhalation aerosol or increase the risk of side effects. These include:
- beta-adrenergic receptor blockers, such as propranolol, used to treat high blood pressure or other heart diseases.
➔ The doctor will decide whether the patient can use Ventolin inhalation aerosol with these medicines.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Ventolin inhalation aerosol is not usually recommended for use during pregnancy.
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine. The doctor will assess whether the patient can take Ventolin during this period.
Driving and using machines
No effect on the ability to drive and use machines has been observed.
3. How to use Ventolin inhalation aerosol
Ventolin inhalation aerosol should always be used as directed by the doctor. If in doubt, the patient should consult their doctor.
Ventolin inhalation aerosol is for inhalation use only.
The dose or frequency of use should only be increased under medical supervision.
Patients who have difficulty coordinating inhalation and actuation of the inhaler may use Ventolin inhalation aerosol with a spacer.
Children under 5 years of age may use Ventolin inhalation aerosol with a Babyhaler spacer.
Ventolin inhalation aerosol should be used as needed, not regularly.
If the patient's asthma is active (e.g., they experience frequent symptoms or exacerbations, such as shortness of breath that interferes with speaking, eating, or sleeping, coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, or reduced physical fitness), they should immediately consult their doctor, who may initiate treatment or increase the dose of a medicine that helps control asthma symptoms, such as an inhaled corticosteroid.
If the patient thinks the medicine is not working as well as usual, they should consult their doctor as soon as possible (e.g., if they need higher doses to relieve breathing problems or if asthma symptoms do not improve for at least 3 hours after using the inhaler), as their asthma may be worsening and another medicine may be needed.
If the patient uses Ventolin inhalation aerosol more frequently than twice a week to relieve asthma symptoms, excluding preventive use before physical exertion, it means that their asthma is not well controlled and may increase the risk of severe asthma attacks (asthma exacerbations), which can cause serious complications and be life-threatening. The patient should consult their doctor as soon as possible to verify their asthma treatment. If the patient uses a medicine with anti-inflammatory effects in the lungs, e.g., an inhaled corticosteroid, every day, it is essential to continue using it regularly, even if they feel better.
The patient should tell their doctor if the medicine does not work as it has before, as this may be due to worsening asthma control and a change in medicine may be necessary.
Adults and adolescents over 12 years of age
- To relieve sudden bronchospasm, use one to two inhalations (100 to 200 micrograms of salbutamol).
- For preventive use before exercise or expected contact with an allergen, usually use two inhalations (2 x 100 micrograms of salbutamol) 10-15 minutes before exercise or expected contact with the allergen.
- Long-term treatment: 2 inhalations (2 x 100 micrograms of salbutamol) up to 4 times a day.
The maximum daily dose is 800 micrograms (2 inhalations no more than 4 times in 24 hours).
Children under 12 years of age
- To relieve sudden bronchospasm, use one inhalation (100 micrograms of salbutamol). If necessary, the dose can be increased to two inhalations (2 x 100 micrograms).
- For preventive use before exercise or expected contact with an allergen, usually use one inhalation (100 micrograms of salbutamol) 10-15 minutes before exercise or expected contact with the allergen. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 2 inhalations (2 x 100 micrograms).
- Long-term treatment: up to 200 micrograms 4 times a day.
The maximum daily dose is 800 micrograms (2 inhalations no more than 4 times in 24 hours).
Instructions for using the inhaler
The doctor, nurse, or pharmacist should instruct the patient on how to use the inhaler properly.
The medicine is in a pressurized container with a plastic actuator and mouthpiece.
Checking the inhaler
Before first use, check that the inhaler works. Remove the cap from the mouthpiece by gently pressing the sides of the cap with your thumb and index finger.

Figure 1
To ensure the inhaler works, shake it vigorously, point the mouthpiece away from you, and release a dose of the medicine into the air.
If the inhaler has not been used for a week or longer, remove the mouthpiece cap, shake the inhaler vigorously, and release two doses of the medicine into the air.
Using the inhaler
It is essential to start slow breathing, as slow as possible, before using the inhaler.
- 1. Inhalation should be performed standing or sitting.
- 2. Remove the cap from the mouthpiece of the inhaler (as shown in Figure 1). Check the mouthpiece outside and inside to ensure it is clean and free of foreign objects.
- 3. Shake the inhaler 4 or 5 times to ensure that any foreign objects are removed and the contents of the inhaler are evenly mixed before use.

Figure 2
It is essential not to rush the actions described in points 4-7.
- 4. Hold the inhaler upright with your fingers, with your thumb on the base of the inhaler, under the mouthpiece. Take a deep breath, as deep as possible.
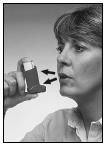
Figure 3
- 5. Put the mouthpiece in your mouth and close your lips tightly around it. Do not bite the mouthpiece.
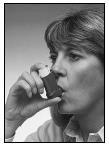
Figure 4
- 6. Immediately after starting to inhale through your mouth, press the inhaler to release the Ventolin medicine, and then continue with a slow, deep breath.

Figure 5
- 7. Hold your breath, remove the inhaler from your mouth, and remove your finger from the actuator. Hold your breath for a few seconds, or as long as is comfortable, and then breathe out slowly.

Figure 6
- 8. If the doctor has prescribed two inhalations of the medicine, wait about half a minute before repeating the actions described in points 3-7.
- 9. After inhalation, always replace the cap on the mouthpiece to prevent dust from entering it. Replace the cap by pushing it into place. If you do not hear a click when replacing the cap, remove it, turn it over, and try to replace it again. Do not use too much force.
Cleaning the inhaler
To prevent the inhaler from clogging, clean it at least once a week. To clean the inhaler:
- Remove the cap from the mouthpiece.
- Do not remove the metal canister from the plastic casing during cleaning or at any other time.
- Clean the mouthpiece inside and outside and the plastic casing outside with a dry cloth or tissue.
- Replace the cap on the mouthpiece. When the cap is properly replaced, you will hear a click. If you do not hear a click when replacing the cap, remove it, turn it over, and try to replace it again. Do not use too much force.
Do not immerse the metal canister in water.
Using a higher dose of Ventolin inhalation aerosol than recommended
If a higher dose of Ventolin than recommended is used, the patient should contact their doctor or pharmacist as soon as possible for advice. The patient should have the carton of the medicine with them to show the doctor.
The following symptoms may occur:
- faster than usual heartbeat,
- tremors,
- excessive restlessness. These symptoms usually resolve within a few hours. Additionally, the following may occur:
- decreased potassium levels in the blood (hypokalemia),
- abdominal pain, increased ventilation of the lungs (rapid breathing), shortness of breath despite decreased wheezing, cold hands and feet, irregular heartbeat, thirst (symptoms suggesting the occurrence of lactic acidosis).
Missing a dose of Ventolin inhalation aerosol
If a dose of Ventolin inhalation aerosol is missed, the patient should take it as soon as possible and then continue taking the medicine as directed by the doctor.
The patient should not take a double dose of the medicine to make up for a missed dose.
If the patient has any further doubts about using the medicine, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
If breathing worsens or wheezing increases immediately after taking this medicine, the patient should stop using it and contact their doctor immediately.
Like all medicines, Ventolin inhalation aerosol can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been observed in patients taking Ventolin inhalation aerosol.
Symptoms to watch out for
Allergic reactions:These occur very rarely (i.e., less frequently than in 1 in 10,000 patients taking the medicine). Symptoms include:
- skin rash (hives) or redness,
- swelling, mainly of the face, lips, tongue, or throat (angioedema),
- worsening of wheezing, coughing, or difficulty breathing,
- sudden feeling of weakness or dizziness (which can lead to falls or loss of consciousness).
➔ The patient should contact their doctor immediately if they experience any of these symptoms. Stop using Ventolin inhalation aerosol.
The patient should contact their doctor immediately if they experience:
- a faster or stronger than usual heartbeat (palpitations). This is usually not serious and resolves soon after taking the medicine,
- an irregular heartbeat. The patient should not stop using Ventolin inhalation aerosol unless their doctor advises them to do so.
Common side effects(i.e., occurring in less than 1 in 10 patients, but more than 1 in 100 patients taking the medicine):
- tremors,
- headache,
- rapid heartbeat.
Uncommon side effects(i.e., occurring in less than 1 in 100 patients, but more than 1 in 1,000 patients taking the medicine):
- palpitations,
- irritation of the mouth and throat mucosa,
- muscle cramps.
Rare side effects(i.e., occurring in less than 1 in 1,000 patients, but more than 1 in 10,000 patients taking the medicine):
- decreased potassium levels in the blood,
- peripheral vasodilation.
Very rare side effects(i.e., occurring in less than 1 in 10,000 patients taking the medicine):
- allergic reactions (see above),
- excessive restlessness,
- heart rhythm disorders,
- paradoxical bronchospasm. Like other inhaled medicines, paradoxical bronchospasm may occur, which is characterized by wheezing immediately after taking the medicine. In such a situation, the patient should stop using Ventolin inhalation aerosol immediately and consult their doctor. The doctor will assess the patient's condition and, if necessary, recommend alternative treatment.
Side effects of unknown frequency
- myocardial ischemia, which may be manifested by, for example, chest pain.
➔ If any side effect worsens or if any side effects not listed in the leaflet occur, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder or its representative.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Ventolin inhalation aerosol
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature not exceeding 30°C.
Do not freeze.
The container contains a pressurized suspension. Do not expose to temperatures above 50°C, protect from direct sunlight. Do not pierce, damage, burn, or throw away the container, even if it seems empty.
As with most inhaled medicines in pressurized containers, the effectiveness of the medicinal product may be reduced if the inhaler is cold.
After inhalation, always replace the cap on the mouthpiece. Do not force the cap on.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated. It is stated on the packaging after the abbreviation "EXP".
The batch number of the medicine is stated on the packaging after the abbreviation "Lot".
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines they no longer use. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Ventolin inhalation aerosol contains
- The active substance of the medicine is salbutamol in the form of salbutamol sulfate. Each dose of Ventolin inhalation aerosol contains 100 μg (micrograms) of salbutamol in the form of salbutamol sulfate.
- The other ingredient is: 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane (HFA 134a).
This medicine contains fluorinated greenhouse gases.
Each inhaler contains 18 g of HFC-134a (also known as 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane or HFA 134a), which corresponds to 0.0257 tons of CO2 equivalent (GWP = 1430).
What Ventolin looks like and contents of the packaging
An aluminum canister containing 200 doses, closed with a metering valve, equipped with a plastic actuator, in a cardboard box.
Manufacturer:
Glaxo Wellcome Production
Zone Industrielle No. 2
23, rue Lavoisier
27000 Evreux
France
Glaxo Wellcome S.A.
Avenida de Extremadura 3
09400 Aranda de Duero
Burgos,
Spain
To obtain more detailed information, the patient should contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder:
GSK Services Sp. z o.o.
ul. Rzymowskiego 53
02-697 Warsaw
tel. (22) 576-90-00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Marketing authorization holder:
GlaxoSmithKline Trading Services Limited
12 Riverwalk
Citywest Business Campus
Dublin 24
D24 YK11
Ireland
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterGlaxo Wellcome Production Glaxo Wellcome S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to VentolinDosage form: Aerosol, 100 mcg/dose inh.Active substance: salbutamolManufacturer: Laboratorio Aldo-Union S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 100 mcg/doseActive substance: salbutamolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 200 mcg/doseActive substance: salbutamolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription required
Alternatives to Ventolin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Ventolin in Spain
Alternative to Ventolin in Ukraine
Online doctors for Ventolin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Ventolin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














