
Trimesolphar

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Trimesolphar

How to use Trimesolphar
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Trimesolphar, (80 mg + 16 mg)/ml, concentrate for solution for infusion
Sulfamethoxazole + Trimethoprim
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any further questions, you should ask your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What Trimesolphar is and what it is used for
- 2. Important information before using Trimesolphar
- 3. How to use Trimesolphar
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Trimesolphar
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What Trimesolphar is and what it is used for
Trimesolphar is an antibacterial medicine containing two active substances – sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim (co-trimoxazole). It is intended for intravenous administration, after prior dilution, for patients who cannot take the medicine orally.
Trimesolphar is used:
- to treat severe uncomplicated urinary tract infections;
- to treat and prevent pneumonia caused by the microorganism Pneumocystis jirovecii;
- to treat and prevent the occurrence of toxoplasmosis (a disease caused by microorganisms, characterized by changes in the eyes, nervous system, and also in the developing fetus, if the mother is infected);
- to treat nocardiosis (a disease caused by microorganisms, characterized by changes in the skin or organs, e.g. in the lungs). Trimesolphar is intended for use in adults, adolescents, children, and infants over 6 weeks of age.
Trimesolphar is always administered by medical personnel.
2. Important information before using Trimesolphar
When not to use Trimesolphar:
- if the patient is allergic to sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, sulfonamide medicines, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has severe liver tissue damage;
- if the patient has severe kidney failure;
- if the patient has ever had a disorder called thrombocytopenia, causing bruising or bleeding, especially after taking sulfonamide medicines;
- if the patient has been diagnosed with porphyria - a rare disease that can affect the skin or nervous system. Co-trimoxazole should not be given to infants in the first 6 weeks of life.
Trimesolphar is not intended for the treatment of throat infections caused by bacteria called beta-hemolytic streptococci group A.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Trimesolphar, you should discuss it with your doctor.
After using co-trimoxazole, life-threatening skin reactions have been reported (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis [Lyell's syndrome]). These reactions initially have the form of red dots or round spots on the torso, often with blisters in their center.
Additional symptoms to look for are ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and conjunctiva (red and swollen eyes). In the course of these potentially life-threatening skin rashes, flu-like symptoms often occur.
The rash may transform into widespread blisters on the skin or peeling of the skin.
The highest risk of serious skin reactions occurs within the first few weeks of treatment.
If it is found that the patient has Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis [Lyell's syndrome] after using Trimesolphar, the patient should never be given Trimesolphar again.
If a rash or the above-mentioned skin symptoms occur, you should immediately tell your doctor.
The doctor will exercise special caution when using Trimesolphar and take appropriate action:
- in patients with folate deficiency (e.g. in the elderly, alcoholics, patients taking antiepileptic drugs, with malabsorption syndrome), with a deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- in people with severe atopy or asthma;
- in patients with cardiovascular and respiratory diseases; if the patient experiences worsening cough and shortness of breath, they should immediately tell their doctor.
- in patients with kidney and/or liver function disorders;
- in elderly patients;
- in malnourished patients; in patients with blood disorders - if the patient has a blood disorder, such as a low number of red blood cells (anemia), a low number of white blood cells (leukopenia), or a low number of platelets that can cause bleeding and bruising (thrombocytopenia);
- in case of a need for longer use of the medicine than recommended;
- in patients with diagnosed or suspected porphyria (disorders of heme production - a red pigment that is part of some enzymes);
- in patients with phenylketonuria (a congenital metabolic disease) who do not follow a diet suitable for this condition;
- in case of increased potassium and decreased sodium levels in the blood. Concurrent use of co-trimoxazole with certain medicines, potassium supplements, and foods high in potassium may lead to severe hyperkalemia (elevated potassium levels in the blood). Symptoms of severe hyperkalemia may include muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, diarrhea, nausea, dizziness, or headache.
During the entire treatment period, the doctor should monitor whether the patient is excreting the proper amount of urine.
In rare cases, crystals may occur in the urine. In malnourished patients, this risk is increased.
Severe, life-threatening side effects have been reported, such as acute liver failure, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, and other blood and hematopoietic system disorders, as well as respiratory hypersensitivity reactions - see section 4.
A link has been reported between the use of co-trimoxazole and the occurrence of metabolic acidosis, characterized by very deep and rapid breathing, consciousness disorders, heart rhythm and blood pressure disorders.
Trimesolphar contains two active substances. The doctor should only administer this medicine after considering the possibility of using a single antibacterial medicine.
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
Very rare cases of severe immune reactions have occurred, resulting from uncontrolled activation of white blood cells, leading to inflammatory conditions (hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis). They can be life-threatening if not diagnosed and treated early. If multiple symptoms occur simultaneously or with a slight delay, such as fever, lymph node swelling, weakness, dizziness, shortness of breath, bruising, or skin rash, you should immediately contact your doctor.
Additionally, co-trimoxazole should be avoided in infants under 8 weeks of age due to their tendency to hyperbilirubinemia (elevated bilirubin levels in the blood).
Effect on laboratory tests
Trimethoprim may change the values of creatinine concentrations in serum (blood plasma) determined using picric acid.
Trimesolphar and other medicines
You should tell your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take. This is especially important for the following medicines:
- diuretics, e.g. hydrochlorothiazide;
- pyrimethamine - an antimalarial medicine; in people taking Trimesolphar and pyrimethamine in doses greater than 25 mg per week, cases of megaloblastic anemia have been reported - these medicines should not be taken at the same time;
- anticoagulant medicines, e.g. warfarin;
- phenytoin - an antiepileptic medicine;
- oral hypoglycemic medicines, such as sulfonylurea derivatives, e.g. glibenclamide, glipizide, tolbutamide (sulfonylurea derivatives), repaglinide;
- digoxin - a heart medicine;
- cyclosporine - a medicine given after transplantation, e.g. kidney;
- azathioprine - a medicine used to prevent transplant rejection and to treat autoimmune diseases;
- methotrexate - a medicine used in cancer; patients receiving methotrexate and Trimesolphar should receive folic acid salts;
- lamivudine - an antiviral medicine used in HIV infection;
- procainamide - an antiarrhythmic medicine;
- amantadine, zidovudine - antiviral medicines;
- rifampicin - an antibacterial medicine;
- medicines that increase potassium levels in the blood, such as diuretics that help increase the amount of urine produced (e.g. spironolactone), ACE inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers. Symptoms of high potassium levels in the blood (severe hyperkalemia) may include muscle cramps, irregular heartbeat, diarrhea, nausea, dizziness, or headache.
- potassium folinate.
Trimesolphar with food and drink
Food and drink do not affect the action of Trimesolphar. Patients taking this medicine should drink plenty of fluids to avoid the formation of drug crystals in the urine.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
You should tell your doctor if you:
- are pregnant;
- suspect you are pregnant;
- plan to become pregnant;
- are breastfeeding. The decision to use Trimesolphar will be made by your doctor. See also the section below: "Trimesolphar contains propylene glycol, ethanol, and sodium".
Effect on fertility
There is no available data on the effect on fertility.
Driving and using machines
It has not been determined how Trimesolphar affects the ability to drive and use machines.
Trimesolphar contains propylene glycol, ethanol, and sodium
The medicine contains 420 mg of propylene glycol in each 1 ml, which corresponds to 2100 mg/5 ml.
Before administering the medicine to a child under 5 years of age, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist, especially if the child is taking other medicines containing propylene glycol or alcohol.
Patients with liver or kidney function disorders, as well as pregnant or breastfeeding women, should not take this medicine without their doctor's recommendation. The doctor may decide to perform additional tests on such patients.
This medicine contains 500 mg of alcohol (96% ethanol) in each 5 ml of solution, which is equivalent to 12 ml of beer or 5 ml of wine.
The amount of alcohol in this medicine is unlikely to have an effect on adults and adolescents, and its effect on children is likely to be negligible. However, it may cause some effect in younger children, such as drowsiness. The alcohol in this medicine may alter the effect of other medicines.
You should consult your doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine if you are taking other medicines, are addicted to alcohol, or if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
The medicine contains 34.5 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in 5 ml, which corresponds to 1.73% of the maximum recommended daily sodium intake in the diet for adults.
The medicine is administered only after dilution - see the section "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals" at the end of the leaflet. The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, you should consult the product characteristics of the diluent used.
3. How to use Trimesolphar
This medicine should always be used as directed by your doctor. If you are unsure, you should ask your doctor.
Trimesolphar is always administered by medical personnel.
- The medicine is administered after prior dilution, slowly, in a so-called intravenous infusion, or drip (using appropriate equipment, with a controlled rate of administration).
- The dose of the medicine is determined by the doctor. The administered dose depends on the indication and the patient's age, weight, and overall health. Detailed dosing and administration - see "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals" at the end of the leaflet.
Using a higher dose of Trimesolphar than recommended
- Trimesolphar is administered by medical personnel, and it is unlikely that the patient will receive more medicine than they should. However, if the patient thinks they have received too much medicine, they should tell their doctor or nurse.
- After using a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, confusion (disorders of consciousness); in severe overdose - inhibition of bone marrow function may occur. The medical personnel will take appropriate action.
Missing a dose of Trimesolphar
Trimesolphar is administered by medical personnel, and it is unlikely that a dose of the medicine will be missed. However, if the patient thinks that a dose of the medicine has been missed, they should tell their doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Trimesolphar can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
You should immediately tell your doctor or nurse if you experience:
- the first symptoms of an allergic reaction (e.g. swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, causing difficulty breathing or swallowing) or severe skin reactions with blistering or peeling of the skin- see section "Warnings and precautions". Such symptoms have occurred very rarely after administration of the medicine.
- painful, bulging skin lesions, purple in color, appearing on the limbs, and sometimes on the face and neck, with accompanying fever (Sweet's syndrome). Such symptoms have occurred with an unknown frequency (the frequency cannot be determined based on available data). The doctor will decide on further action.
Very common (more than 1 in 10 patients):
- increased potassium levels in the blood (manifested by weakness, drowsiness, fatigue, heart rhythm disorders).
Common (less than 1 in 10 patients):
- fungal infections of the mucous membranes of the mouth, vagina, skin, and nails;
- headache;
- nausea, diarrhea;
- rash.
Uncommon (less than 1 in 100 patients):
- vomiting.
Rare (less than 1 in 1,000 patients):
- pseudomembranous colitis (manifested by diarrhea, acute or persistent);
- disorders of the number of different types of blood cells, including those manifested by fever and frequent infections;
- methemoglobinemia;
- thrombocytopenia;
- hemolysis in patients with a deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase;
- syndrome of serum sickness (a systemic allergic reaction that can occur, for example, after intravenous administration of the medicine, manifested by fever, muscle pain, abdominal pain, joint swelling), anaphylactic reactions (a type of allergic reaction with a rapid course), angioedema (see symptoms listed at the beginning of section 4), allergic myocarditis, drug fever, allergic vasculitis, nodular vasculitis, systemic lupus erythematosus (immune system disorders leading to inflammation of many internal organs);
- low blood sugar (glucose) and/or sodium levels;
- metabolic acidosis - see section "Warnings and precautions";
- depression, hallucinations;
- aseptic meningitis (symptoms: sudden severe headache, neck stiffness with accompanying high fever; it subsides quickly after discontinuation of the medicine, but in many cases, it occurred after re-administration of co-trimoxazole or trimethoprim alone), seizures, peripheral neuropathy, ataxia;
- uveitis (inflammation of the middle layer of the eye wall);
- dizziness, tinnitus;
- cough, shortness of breath, lung infiltrates (may be early symptoms of respiratory hypersensitivity, which can very rarely be fatal);
- glossitis, stomatitis;
- pancreatitis (manifested by severe abdominal pain);
- jaundice due to bile stasis, liver necrosis (can be fatal);
- increased transaminase (enzyme) levels in serum, increased bilirubin levels;
- photosensitivity, exfoliative dermatitis, angioedema, persistent drug rash, erythema multiforme, potentially life-threatening severe skin reactions (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis [Lyell's syndrome])- see symptoms listed at the beginning of section 4 and in section "Warnings and precautions";
- arthralgia, myalgia;
- kidney function disorders, kidney diseases: tubulointerstitial nephritis and uveitis, renal tubular acidosis.
Unknown (the frequency cannot be determined based on available data):
- psychotic disorder (a mental state in which one can lose contact with reality).
Unwanted effects related to the treatment of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia
Very rare:
- severe hypersensitivity reactions related to Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, urticaria, drug fever, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, increased liver enzyme levels, high potassium levels, low sodium levels, muscle breakdown (rhabdomyolysis - manifested by very severe muscle pain, kidney function disorders); muscle breakdown has also been reported in patients with a positive HIV status, receiving co-trimoxazole prophylactically or for the treatment of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Trimesolphar
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature below 25°C.
Store the ampoules in the original packaging to protect them from light.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the ampoule and carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Trimesolphar contains
- The active substances of the medicine are sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Each 1 ml of concentrate contains 80 mg of sulfamethoxazole and 16 mg of trimethoprim. Each 5 ml ampoule of concentrate contains 400 mg of sulfamethoxazole and 80 mg of trimethoprim, i.e. 480 mg of co-trimoxazole.
- The other ingredients are: propylene glycol, 96% ethanol, ethanoloamine, sodium hydroxide, 10% sodium hydroxide (to adjust pH), water for injections.
What Trimesolphar looks like and what the packaging contains
Trimesolphar is a colorless or slightly yellowish liquid in ampoules.
The carton contains 10 ampoules made of colorless glass, containing 5 ml of concentrate.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
tel. +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:December 2024
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
You should consult the current Summary of Product Characteristics of Trimesolphar.
Trimesolphar, (80 mg + 16 mg)/ml, concentrate for solution for infusion
Sulfamethoxazolum + Trimethoprimum
Method of preparation of Trimesolphar for administration and method of administration
Trimesolphar concentrate for solution for infusion is intended exclusively for intravenous administration and should be diluted before administration.
Trimesolphar should only be used during the period when the patient cannot take medicines orally, when immediate treatment is necessary, or when the patient is already receiving intravenous fluids and concurrent administration of the medicine is convenient. Although intravenous administration of co-trimoxazole is useful in critically ill patients, it may not provide greater therapeutic benefits than oral forms.
Trimesolphar should be diluted immediately before use. After adding Trimesolphar to the infusion solution, the resulting mixture should be shaken vigorously to ensure thorough mixing. If precipitates or crystals are found before or during mixing or infusion, the mixture should be discarded and a new one prepared.
The following dilution scheme for Trimesolphar is recommended:
1 ampoule (5 ml) of Trimesolphar in 125 ml of infusion solution
2 ampoules (10 ml) of Trimesolphar in 250 ml of infusion solution
3 ampoules (15 ml) of Trimesolphar in 500 ml of infusion solution
The following infusion solutions can be used to dilute Trimesolphar:
- 5% and 10% glucose solution,
- 0.9% NaCl solution,
- Ringer's solution,
- 0.45% NaCl solution with 2.5% glucose solution. The prepared Trimesolphar infusion solution should not be mixed with other medicines or other infusion solutions than those listed above.
After dilution, the chemical and physical stability of the medicine has been demonstrated for 6 hours at 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the diluted medicine should be used immediately. If it is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the storage conditions and storage time.
The infusion should be administered over a period of approximately 60 to 90 minutes; the duration of the infusion depends on the patient's hydration status.
If the patient cannot receive large amounts of fluid, a higher concentration of co-trimoxazole can be used - 5 ml in 75 ml of 5% glucose. The prepared solution should be administered by infusion over a period not exceeding 1 hour.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, you should make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down.
A colored dot has been placed on each ampoule (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the location of the break point below it.
- To open the ampoule, you should hold it vertically, in both hands, with the colored dot facing you - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
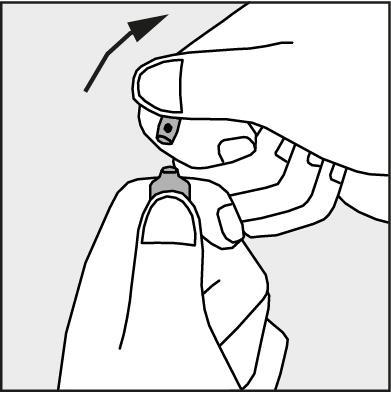
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused medicine should be disposed of in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1.
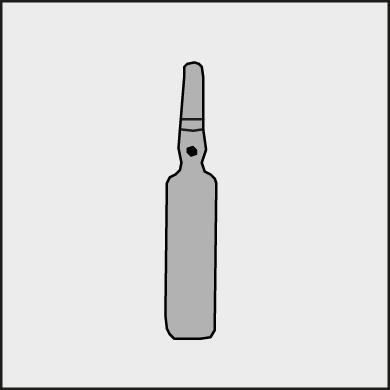
Figure 2.
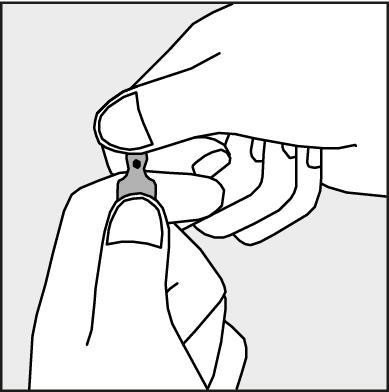
Figure 3.
Dosage
Recommendations for usual dosing in acute infections
Adults and adolescents over 12 years of age
2 ampoules (10 ml) every 12 hours.
Children under 12 years of age
The recommended dosage is approximately 30 mg of sulfamethoxazole and 6 mg of trimethoprim per kg of body weight per day, administered in 2 equal doses divided.
The following dosing schedule for Trimesolphar is provided, taking into account the child's age - before administration, the medicine should be diluted (see "Method of preparation of Trimesolphar for administration and method of administration").
From 6 weeks to 5 months of age: 1.25 ml every 12 hours.
From 6 months to 5 years of age: 2.5 ml every 12 hours.
From 6 to 12 years of age: 5 ml every 12 hours.
See also section 2 of the patient leaflet.
In the treatment of particularly severe infections in all age groups, the dose can be increased by 50%.
Treatment should be continued for 2 days after the symptoms of the disease have subsided, and in most cases, treatment should be continued for at least 5 days.
Elderly patients
In elderly patients, it is recommended to regularly perform monthly laboratory blood tests. Additionally, special caution should be exercised in these patients, as this group is more susceptible to side effects and more likely to experience severe side effects, especially if other diseases are present, such as kidney or liver function disorders, and/or if they are taking other medicines.
Patients with liver function disorders
There is no data on dosing in patients with liver function disorders. See also section 2 of the patient leaflet.
Special dosing recommendations
(If not otherwise specified, the usual dose should be used.)
Patients with kidney function disorders
In adults and adolescents over 12 years of age (there is no data for children under 12 years of age) with kidney failure, the dose of Trimesolphar should be modified depending on the creatinine clearance.
It is recommended to determine the sulfamethoxazole concentration in serum every 2-3 days in samples taken 12 hours after administration of Trimesolphar. If the total sulfamethoxazole concentration exceeds 150 micrograms/ml, treatment should be discontinued until the concentration decreases to below 120 micrograms/ml.
See also section 2 of the patient leaflet.
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia
Treatment
100 mg of sulfamethoxazole and 20 mg of trimethoprim per kg of body weight per day in 2 or more divided doses. As soon as possible, the patient should be given the oral form of the medicine and treatment should be continued for a total of 14 days. The goal is to achieve a maximum trimethoprim concentration in serum or plasma of 5 micrograms/ml or higher (this is checked in the patient after administration of the medicine in infusion within 1 hour).
Prevention
Usual dosing throughout the entire period of exposure to the risk.
Nocardiosis
Standard dosing for the treatment or prevention of nocardiosis has not been established. In adults, doses of 6 to 8 tablets per day have been used for up to 3 months (one tablet contains 400 mg of sulfamethoxazole and 80 mg of trimethoprim).
Toxoplasmosis
Appropriate dosing for the treatment or prevention of toxoplasmosis has not been established. The decision should be made based on clinical experience. In prevention, the dosing may be the same as for the prevention of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
| Creatinine clearance [ml/min] | Recommended dosage |
| Above 30 | usual dose |
| From 15 to 30 | ½ usual dose |
| Below 15 | use not recommended |
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to TrimesolpharDosage form: Tablets, 800 mg + 160 mgActive substance: sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprimPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 800 mg + 160 mgActive substance: sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprimPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 800 mg + 160 mgActive substance: sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprimPrescription required
Alternatives to Trimesolphar in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Trimesolphar in Ukraina
Alternative to Trimesolphar in Hiszpania
Online doctors for Trimesolphar
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Trimesolphar – subject to medical assessment and local rules.















