

Relanium

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Relanium

How to use Relanium
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
RELANIUM, 2 mg, tablets
RELANIUM, 5 mg, tablets
Diazepam
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Relanium and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Relanium
- 3. How to take Relanium
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Relanium
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Relanium and what is it used for
Relanium contains the active substance diazepam, which belongs to a group of medicines called benzodiazepine derivatives.
The medicine has anxiolytic, sedative, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant effects. It also reduces skeletal muscle tension.
Indications for use:
- Treatment of anxiety states.
- Treatment of insomnia associated with anxiety states (only in cases of severe disorders that prevent normal daily activities or cause extreme discomfort to the patient).
- Control of muscle spasms, including those associated with increased muscle tension of central origin.
- Pharmacological preparation of the patient before minor surgical procedures (premedication).
- Treatment of symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal.
2. Important information before taking Relanium
When not to take Relanium
- if the patient is allergic (hypersensitive) to the active substance, other benzodiazepines, or any of the other ingredients of the medicine (listed in section 6),
- if the patient has excessive muscle weakness (called myasthenia gravis),
- if the patient has severe respiratory failure,
- if the patient has sleep apnea syndrome (repeated pauses in breathing during sleep, leading to hypoxia),
- if the patient has severe liver failure.
2
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to take Relanium, you should discuss it with your doctor.
- Diazepam is not recommended for the treatment of chronic psychoses or states with phobias or obsessions.
- Relanium should not be taken with alcohol, sleeping pills, or sedatives, as it may enhance their effects (see section: Relanium and other medicines).
- If the patient is addicted to alcohol or drugs, they should avoid taking Relanium. This does not apply to the treatment of acute withdrawal symptoms. In such cases, the doctor will regularly monitor the patient and recommend the use of the smallest effective dose.
- If the patient has a history of alcohol or drug abuse, Relanium should be used with caution.
- If Relanium is taken for several weeks, tolerance to the medicine may develop (reduced efficacy of the medicine).
- Long-term use of Relanium, especially in high doses, may lead to physical and psychological dependence. The risk of dependence increases with the dose and duration of treatment. It is higher in patients who have previously abused alcohol or drugs and in patients with personality disorders.
- If the patient is dependent on Relanium, sudden withdrawal of the medicine may cause withdrawal symptoms, such as headaches, muscle pain, extreme anxiety, tension, agitation, confusion, irritability. In severe cases, the following symptoms may occur: loss of sense of reality, personality disorders, numbness and tingling of limbs, hallucinations, seizures.
- The occurrence of withdrawal symptoms may also be caused by switching from Relanium to benzodiazepines with a short duration of action.
- During withdrawal or after withdrawal of Relanium, a transient worsening of the symptoms of the disease for which the medicine was used may occur. To prevent this, the medicine should be withdrawn gradually, strictly according to the doctor's instructions (see section: Stopping Relanium).
- Relanium may cause anterograde amnesia (inability to learn and remember new information, see section 4: Possible side effects). To reduce the risk of anterograde amnesia, it is essential that the patient has uninterrupted sleep for 7 to 8 hours.
- In children and the elderly, there is a higher risk of adverse psychological reactions and paradoxical reactions (see section 4: Possible side effects).
- In elderly and debilitated patients, the doctor may recommend a lower dose of the medicine (see section 3: How to take Relanium). The medicine reduces muscle tension. This increases the risk of falls and consequent hip fractures in the elderly.
- If the patient has chronic respiratory failure, the doctor will use a lower dose of the medicine, as respiratory disorders may occur.
- In patients with heart failure, caution should be exercised when taking Relanium.
- In patients with epilepsy, sudden discontinuation of treatment should be avoided due to the risk of seizures.
- If the patient has severe liver failure, Relanium should not be taken due to the risk of neurological disorders (hepatic encephalopathy).
- In patients with impaired liver and/or kidney function, the doctor will decide on a dose reduction. In the case of long-term use of Relanium, the doctor may order blood tests to closely monitor the blood cell count and liver function.
- If the patient has psychotic disorders (e.g., schizophrenia), Relanium should not be taken.
- If the patient has depression or anxiety states associated with depression, Relanium should not be used as the only medicine, as it may increase the risk of suicide.
- Taking Relanium in people who are grieving (after the loss of loved ones) does not improve their well-being.
Children and adolescents
Use of Relanium in children; the doctor will determine the dose and duration of treatment (see section 3: How to take Relanium).
Relanium is not recommended for the treatment of anxiety states and insomnia in children.
The medicine should not be used in children under 6 years of age,as the safety and efficacy of the medicine have not been assessed in this age group. Only when it is impossible to use alternative medicines, the doctor may decide to administer Relanium, but under strict supervision of a specialist (paediatrician, neurologist, psychiatrist, anaesthetist, and intensive care specialist), who will determine the dose.
Relanium and other medicines
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
Particularly, you should tell your doctor about the following medicines, as they may enhance the effects of Relanium:
- atazanavir and ritonavir - used in the treatment of HIV and hepatitis C,
- cimetidine - a medicine used in the treatment of stomach and duodenal ulcers,
- ketoconazole - a medicine used in the treatment of fungal infections,
- medicines used in the treatment of depression, such as fluvoxamine, fluoxetine,
- omeprazole - a medicine that reduces stomach acid,
- cisapride - a medicine used in gastroesophageal reflux disease,
- disulfiram - a medicine used in the treatment of alcoholism,
- isoniazid - a medicine used in the treatment of tuberculosis,
- propranolol - a medicine used in the treatment of high blood pressure and irregular heartbeat,
- rifampicin - a medicine used in the treatment of bacterial infections,
- antipsychotic medicines,
- anxiolytic and sedative medicines,
- sleeping pills,
- medicines used in the treatment of epilepsy,
- medicines used for general anaesthesia,
- antihistamines with sedative effects - used in the treatment of allergies.
- opioid analgesics. Concomitant use of Relanium and opioids (strong painkillers, medicines used in substitution therapy for addiction, and some cough medicines) increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma, and can be life-threatening. Therefore, concomitant use of these medicines can only be considered when other treatment options are not possible. If the doctor has prescribed Relanium together with opioids, they should limit the dose and duration of concomitant treatment. You should inform your doctor about all opioid medicines you are taking and strictly follow the dosage instructions. It may be helpful to inform your friends or relatives so that they are aware of the above symptoms. If such symptoms occur, you should contact your doctor.
Relanium may affect the action of phenytoin used as an antiepileptic medicine.
Theophylline - a medicine used in the treatment of asthma - may weaken the action of benzodiazepines.
Concomitant use of buprenorphine with Relanium (or other benzodiazepines) should be avoided, as it may cause death due to respiratory depression.
Concomitant use of valproic acid increases the risk of psychosis.
Relanium with food, drinks, and alcohol
While taking this medicine, you should not drink any alcoholic beverages. Alcohol enhances the sedative effect of Relanium.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, you should consult your doctor before taking this medicine.
Relanium should not be taken during pregnancy, especially in the first and third trimesters.
Taking Relanium during pregnancy is only allowed when the doctor considers it absolutely necessary and will closely monitor you.
If you take Relanium in the last three months of pregnancy or during childbirth, the newborn may experience hypothermia, decreased muscle tone, irregular heartbeat, difficulty sucking, and breathing difficulties.
In children of mothers who take diazepam for a long time in late pregnancy, physical dependence may develop, and there is a risk of withdrawal symptoms after birth.
The medicine passes into breast milk, so it should not be taken during breastfeeding. If you are breastfeeding, you should consult your doctor before starting to take Relanium.
Driving and using machines
Relanium may impair your mental and physical abilities. You should not drive vehicles or operate machines while taking this medicine.
Relanium contains lactose monohydrate
If you have previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, you should consult your doctor before taking the medicine.
Relanium, 2 mg, tablets contain sodium (present in cochineal red)
Relanium, 5 mg, tablets contain sodium (present in quinoline yellow)
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per tablet, which means that the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
Relanium, 2 mg, tablets contain the dye cochineal red (E124).
Due to the presence of cochineal red, the medicine may cause allergic reactions.
Relanium, 5 mg, tablets contain the dye quinoline yellow (E104).
Due to the presence of quinoline yellow, the medicine may cause allergic reactions.
3. How to take Relanium
Relanium should always be taken according to the doctor's instructions. If you have any doubts, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Treatment with diazepam should last as short as possible and should not exceed 4 weeks in the case of insomnia or 8-12 weeks in the case of anxiety states, including the time of gradual withdrawal of the medicine. The treatment time should not be extended beyond the above periods without re-evaluation of the patient's condition by the doctor.
Dosage in adults
- anxiety states and insomnia
- anxiety states: the usual dose is 2 mg three times a day; the maximum dose used in the treatment of anxiety states is 30 mg per day in divided doses.
- insomnia associated with anxiety states: 5 mg to 15 mg per day, before sleep. The doctor will recommend the smallest dose that controls the symptoms.
- states associated with muscle spasms
- muscle spasms: 2 mg to 15 mg per day in divided doses.
- control of increased muscle tension of central origin: 2 mg to 60 mg per day in divided doses.
- preparation (premedication) for general anaesthesia
- 5 mg to 20 mg.
- treatment of symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal
- usually 10 mg, 3 to 4 times in the first 24 hours, then the doctor may reduce the dose to 5 mg, 3 to 4 times a day.
Dosage in children
- anxiety states and insomnia
- Relanium is not recommended for the treatment of anxiety states and insomnia in children.
- states associated with muscle spasms
- in the control of irritability and increased muscle tension of central origin: 5 mg to 40 mg per day in divided doses.
- children from 6 to 12 years: the initial dose is 5 mg twice a day.
- children from 12 to 18 years: the initial dose is 10 mg twice a day; the maximum dose is 40 mg per day.
- preparation (premedication) for general anaesthesia
- children from 6 to 18 years: 2 mg to 10 mg.
Dosage in children under 6 years
Diazepam tablets are not intended for children under 6 years of age.
Dosage in the elderly and debilitated
The dose should not exceed half of the usual dose used in adults.
Patients with impaired renal and/or hepatic function
In patients with impaired renal and/or hepatic function, the doctor will decide on a dose reduction.
Method of administration
- The medicine should be taken orally.
- Do not take for longer than 4 weeks in the case of insomnia or 8 to 12 weeks in the case of anxiety states (including the time of gradual withdrawal of the medicine).
Taking a higher dose of Relanium than recommended
In case of taking a higher dose of Relanium than recommended, you should immediately seek medical help or go to the nearest hospital.
Overdose of Relanium rarely poses a threat to life if the medicine was taken alone.
The following overdose symptoms may occur: drowsiness, clumsiness, weakness, slurred speech, nystagmus, areflexia, apnea, hypotension, circulatory and respiratory depression, and coma.
Coma, if it occurs, usually lasts a few hours, but may last longer and occur at regular intervals, especially in the elderly.
Missing a dose of Relanium
In case of missing a dose, you should take the medicine as soon as possible. If it is almost time for the next dose, you should skip the missed dose. The next dose should be taken according to the doctor's instructions. Do not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose.
Stopping Relanium
The medicine should be withdrawn gradually. Sudden discontinuation of Relanium may transiently worsen the symptoms of the disease for which the medicine was used. Other symptoms may also occur, such as headaches, muscle pain, extreme anxiety, tension, agitation, confusion, irritability. In severe cases, the following symptoms may occur: loss of sense of reality, personality disorders, hypersensitivity to sound, numbness and tingling of limbs, hallucinations, seizures.
You should always follow the doctor's instructions. If you have any doubts about taking the medicine, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Relanium can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The most common side effects are:
- fatigue,
- drowsiness,
- muscle weakness. These effects occur especially at the beginning of treatment and disappear after repeated administration.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from the available data):
- paradoxical reactions: anxiety, agitation, irritability, aggressive behavior, anger, rage, delusions,
- nightmares, hallucinations, psychoses,
- changes in behavior, including inadequate behavior,
- disorders of thought, disorientation regarding time, place, situation, or own person (confusion),
- apathy (emotional flattening),
- reduced alertness,
- depression,
- decreased or increased libido,
- clumsiness (difficulty maintaining balance) - may cause falls and dangerous fractures, especially in the elderly,
- slurred speech, unclear speech,
- headaches, dizziness,
- tremors,
- inability to learn and remember new information (anterograde amnesia); to prevent this, the patient should have uninterrupted sleep for 7 to 8 hours,
- double vision, blurred vision,
- heart failure, cardiac arrest, irregular heartbeat,
- hypotension, bradycardia,
- slow and shallow breathing, apnea,
- nausea, constipation, gastrointestinal disorders (e.g., bloating),
- dry mouth or excessive salivation,
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes), increased activity of liver enzymes (aminotransferases and alkaline phosphatase) in the blood,
- skin reactions,
- urinary incontinence or inability to urinate (strong urge to urinate, abdominal pain),
- blood disorders (blood dyscrasia). Long-term use (even at therapeutic doses) may lead to physical dependence; sudden withdrawal of the medicine may cause withdrawal symptoms or rebound phenomenon (see section Warnings and precautions). Psychological dependence may occur. Cases of benzodiazepine abuse have been reported.
7
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder or its representative.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Relanium
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature below 25°C. Protect from light and moisture. Store in the original packaging.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging after EXP.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
The batch number is stated on the packaging after Lot.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Relanium contains
The active substance of the medicine is diazepam.
One tablet contains 2 mg or 5 mg of diazepam.
The other ingredients are:
Relanium, 2 mg, tablets: lactose monohydrate, potato starch, talc, magnesium stearate, anhydrous colloidal silica, cochineal red (E124).
Relanium, 5 mg, tablets: lactose monohydrate, potato starch, talc, magnesium stearate, anhydrous colloidal silica, quinoline yellow (E104).
What Relanium, 2 mg, tablets look like and contents of the packaging
Relanium, 2 mg, tablets are pink, round, biconvex, with a smooth surface.
The packaging contains 20 tablets.
What Relanium, 5 mg, tablets look like and contents of the packaging
Relanium, 5 mg, tablets are yellow, round, biconvex, with a smooth surface.
The packaging contains 20 tablets.
8
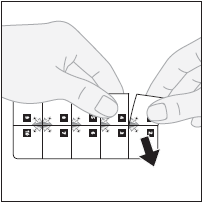
Removing a tablet from the blister pack
These tablets are provided in a special packaging with a child safety lock.
Each blister pack segment with one tablet has a number. The tablets should be taken in sequence, according to the numbering, starting from number 1.
- 1. Separating the tablet:to separate the blister pack segment with one tablet, tear the blister pack along the perforated lines.
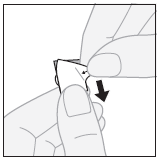
- 2. Removing the outer layer:starting from the corner, pry and tear the outer layer of the separated blister pack segment.
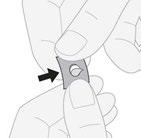
- 3. Removing the tablet:gently push the tablet through the foil.
Marketing authorization holder
GSK PSC Poland sp. z o.o.
Grunwaldzka Street 189
60-322 Poznań
Manufacturer
Delpharm Poznań Spółka Akcyjna
Grunwaldzka Street 189
60-322 Poznań
To obtain more detailed information about this medicine, you should contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder.
GSK Services Sp. z o.o.
tel. (22) 576-90-00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:June 2022
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterDelpharm Poznań S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to RelaniumDosage form: Tablets, 2 mgActive substance: diazepamManufacturer: Santa S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 10 mg/2 mlActive substance: diazepamManufacturer: AS GrindeksPrescription not required
Alternatives to Relanium in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Relanium in Spain
Alternative to Relanium in Ukraine
Online doctors for Relanium
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Relanium – subject to medical assessment and local rules.









