
Rabipur

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Rabipur

How to use Rabipur
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Rabipur
Powder and solvent for solution for injection in a pre-filled syringe
Rabies virus, Flury LEP strain, (inactivated)
Read the leaflet carefully before using the Rabipur vaccine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This vaccine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others.
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Rabipur vaccine and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Rabipur vaccine
- 3. How to use Rabipur vaccine
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Rabipur vaccine
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Rabipur vaccine and what is it used for
What is Rabipur vaccine
Rabipur is a vaccine containing inactivated rabies virus. After administration of the vaccine, the immune system (the body's natural defense system) produces antibodies against rabies viruses. These antibodies protect against infections or diseases caused by the rabies virus. None of the vaccine components can cause rabies.
What is Rabipur vaccine used for
Rabipur vaccine can be used in people of all ages.
Rabipur vaccine can be used to prevent disease caused by rabies virus:
- before exposure to the rabies virus (pre-exposure prophylaxis) or
- after suspected or confirmed exposure to the rabies virus (post-exposure prophylaxis). Rabies is an infection that can be transmitted by being bitten, scratched, or even just licked by an infected animal, especially if the skin is damaged. Even contact with animal traps that have been licked or chewed by infected animals can cause infection in humans.
2. Important information before using Rabipur vaccine
Do not administer Rabipur vaccine before exposure to the rabies virus:
Severe allergic reactions (hypersensitivity)
If the patient is at risk of a severe allergic reaction to the vaccine or any of its components, another rabies vaccine that does not contain them can be administered. If another vaccine is not available, the doctor or nurse will assess the risk associated with vaccination and the risk of rabies infection before administering the vaccine.
Warnings and precautions
In case of an acute illness requiring treatment, vaccination is usually delayed for at least 2 weeks after recovery. A mild infection should not be a reason to delay vaccination, but this should be discussed with the doctor or nurse beforehand.
Before receiving the Rabipur vaccine as part of post-exposure prophylaxis, tell your doctor or nurse if:
- the patient has a severe allergy to chicken eggs or products containing them (symptoms are listed in section 4of this leaflet). The Rabipur vaccine contains trace amounts of chicken egg protein remaining from the manufacturing process.
- the patient has a severe allergy to antibiotics such as neomycin, chlorotetracycline, or amphotericin B. These antibiotics may be present in the vaccine in trace amounts.
- the patient has a severe allergy to polygeline. Fainting can occur during or even before any needle injection, so the doctor or nurse should be informed if the patient has fainted before during an injection. After receiving the Rabipur vaccine, very rare but serious cases of neurological disorders have been reported. See section 4. Anti-inflammatory drugs (steroids), often used to treat such disorders, may affect the efficacy of the vaccine (see below, Rabipur and other medicines). The doctor or nurse will decide on further action in such a situation. As with all vaccines, the Rabipur vaccine may not fully protect all vaccinated individuals. Vaccines should notbe administered in the buttocks, subcutaneously, or into a blood vessel.
Rabipur and other medicines
Tell your doctor or nurse about all medicines the patient is taking or has recently taken, as well as any medicines the patient plans to take, including those available without a prescription. Unless the doctor advises otherwise, continue taking all prescribed medicines as usual.
If the patient's immune system is weakened or the patient is taking medicines that reduce the body's resistance to infections, the Rabipur vaccine can be administered, but protection may not be as high as in other individuals. In such cases, the doctor may recommend a blood test after vaccination to check if the level of antibodies produced is sufficient. If necessary, additional doses of the vaccine may be given (see section 3of this leaflet).
The Rabipur vaccine can be administered simultaneously with other inactivated vaccines.
A different injection site should be used for each type of vaccine.
It may also be necessary to administer rabies immunoglobulin (called "rabies immunoglobulin")if the patient has not been fully vaccinated against rabies and there is a high risk of infection. In such cases, the rabies immunoglobulin (given only once, usually with the first dose of vaccine) and the vaccine will be injected into different siteson the body.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, or thinks she may be pregnant, or is planning to have a baby, the rabies vaccine should be administered if contact with the rabies virus has occurred or is likely to occur.
The Rabipur vaccine can also be administered to pregnant or breastfeeding women before exposure to the rabies virus if the risk of exposure is considered significant. In such cases, the doctor will assess the risk associated with vaccination and the risk of rabies infection and determine the best time to administer the Rabipur vaccine.
Driving and using machines
Some side effects mentioned in section 4of this leaflet may affect the ability to drive and use machines.
Rabipur contains:
Less than 23 mg of sodium per dose, which means that it is essentially "sodium-free".
3. How to use Rabipur vaccine
The Rabipur vaccine will be administered by a doctor or nurse trained in vaccine administration.
Means to treat very serious allergic reactions that may occur after vaccination (see section 4of this leaflet) should be available. The vaccine should be administered in a clinic or treatment room where means to treat such reactions are available.
Instructions for healthcare professionals on the reconstitution of the vaccine can be found at the end of this leaflet.
The recommended dose for adults and children of all ages is one milliliter (1 ml) per injection.
The doctor will decide how many doses to administer. The number of doses depends on whether the Rabipur vaccine is administered before or after suspected contact with the rabies virus.
The vaccine is administered by intramuscular injection (usually into the muscle of the upper arm or, in small children, into the thigh muscle).
DOSE BEFORE SUSPECTED CONTACT WITH THE VIRUS
In individuals who have not been previously vaccinated against rabies:
- initially, 3 doses of vaccine should be administered. The first dose is administered during the first visit, the second dose 7 days later, and the third dose 21 or 28 days after the first dose.
- in adults between 18 and 65 years of age, for whom rapid protection is necessary, the Rabipur vaccine can also be administered in 3 doses over 7 days. The first dose is administered during the first visit, the second dose 3 days later, and the third dose 4 days after the second dose.
- alternatively, in individuals with a normal immune response, the Rabipur vaccine can be administered in 2 doses over 7 days. The first dose is administered during the first visit, and the second dose 7 days later. If a vaccination appointment is missed, the vaccine should be administered as soon as possible after the recommended date.
The need for booster doses depends on the risk of contact with the rabies virus.
The doctor will assess the need for a booster dose after reviewing official recommendations for rabies vaccination.
In individuals at constant high riskof infection, the doctor may also recommend regular tests to measure the level of antibodies against the rabies virus in the blood, so that a booster dose can be administered as soon as possible if necessary.
Experience shows that booster doses are usually required every 2 to 5 years.
DOSE AFTER SUSPECTED OR CONFIRMED CONTACT WITH THE VIRUS
Previously vaccinated individuals
In individuals who have been fully vaccinated against rabies and/or have received booster doses, after contact with an animal infected with rabies or suspected of having rabies, usually 2 additional doses of vaccine (each 1.0 ml) should be administered. The first dose should be administered as soon as possible after contact, and the second dose 3 days later.
Unvaccinated individuals
In individuals who have not been previously vaccinated or have received inadequate primary vaccination, 4 or 5 doses (each 1.0 ml) should be administered, according to one of the following schedules:
- In the 4-dose schedule, the first 2 doses of vaccine are administered as soon as possible after contact on day 0, and the next single doses are administered 7 and 21 days after the first dose.
- An alternative 4-dose schedule can be used in healthy individuals with a known good immune response; the first dose is administered as soon as possible after contact on day 0, and the remaining doses are administered 3, 7, and 14 days after the first dose.
- In the 5-dose schedule, the first dose of vaccine is administered as soon as possible after contact on day 0, and the remaining doses are administered on days 3, 7, 14, and 28 after the first dose. After suspected contactwith the rabies virus, the doctor will assess the risk of infection based on the type of contact that occurred. For example, in individuals who have been bitten or scratched by an animal that may be infected with the virus, or who have had contact with bats, the risk of rabies infection is much higher than in individuals who have been licked by an animal but have no skin damage. Individuals with impaired immune systems (with weakened resistance to infections)
In individuals at increased riskof rabies infection due to impaired immune system function, after contact with an animal infected with rabies or suspected of having rabies, 5 or 6 doses (each 1.0 ml) of rabies vaccine should be administered. In addition to vaccination, local wound care and administration of rabies immunoglobulin are necessary. In the 6-dose schedule, the first 2 doses are administered as soon as possible after contact, and the next single doses are administered on days 3, 7, 14, and 28 after the first dose. In the 5-dose schedule, the first dose is administered as soon as possible after contact, and the remaining doses are administered on days 3, 7, 14, and 28 after the first dose. It may also be necessary to perform a blood test to assess the level of antibodies against the rabies virus and the need for additional doses of vaccine. The doctor will inform the patient what to do and when to come back for additional tests or booster doses.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this vaccine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Severe side effects affecting the whole body, sometimes with shock (dangerously low blood pressure)*, can occur after administration of the Rabipur vaccine. Appropriate treatment and supervision should always be readily available in case of rare severe allergic reactions to the vaccine. If they occur, tell your doctor immediately.
The most commonly reported side effects associated with the use of the Rabipur vaccine were pain at the injection site, mainly pain associated with the injection, or hardening of the skin at the injection site. These reactions were very common (in more than 1 in 10 people). Most injection site reactions were mild or moderate and resolved within 24 to 48 hours after vaccination.
Other side effects include:
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people)
Headache
Dizziness
Rash
General discomfort
Fatigue
Weakness
Fever
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people)
Swollen lymph nodes
Decreased appetite
Nausea
Vomiting
Diarrhea
Abdominal pain/discomfort
Hives
Muscle pain
Joint pain
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people)
Allergic reactions
Feeling of tingling, numbness
Sweating
Chills
Very rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people)
Brain inflammation, nerve damage that can cause weakness, inability to move, or loss of sensation in parts of the body*
Fainting, dizziness with lightheadedness*
Severe allergic reactions that can cause swelling of the face or throat*
*Description of side effects reported spontaneously
Additional side effects in children
It is expected that the frequency, type, and severity of side effects in children are the same as in adults.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309. Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Rabipur vaccine
Store the vaccine out of sight and reach of children.
Protect from light. Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C). Do not freeze.
Store the vial and pre-filled syringe in the outer packaging to protect from light.
Do not use this vaccine after the expiry date stated on the outer carton.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Rabipur vaccine contains
The active substance of the vaccine is inactivated rabies virus (Flury LEP strain) at least 2.5 IU, grown on purified chick embryo cells (PCEC).
Other ingredientsare: trometamol, sodium chloride, disodium edetate, potassium L-glutamine, polygeline, sucrose, and water for injection. Chicken egg proteins (e.g., egg albumin), human albumin, neomycin, chlorotetracycline, and amphotericin B are present in the vaccine as residues.
What Rabipur vaccine looks like and contents of the pack
Rabipur is a white, freeze-dried powder, intended for reconstitution using a clear, colorless solvent. The vaccine after reconstitution is clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to slightly pink.
Rabipur vaccine is supplied in packs containing 1 vial of powder, 1 pre-filled syringe with a sterile solvent, and 2 identical needles (25 G, 25 mm) – one for reconstitution and one for injection.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Bavarian Nordic A/S
Philip Heymans Alle 3
2900 Hellerup
Denmark
Manufacturer
GSK Vaccines GmbH
Emil-von-Behring-Str. 76
35041 Marburg
Germany
Bavarian Nordic A/S
Hejreskovvej 10A
3490 Kvistgaard
Denmark
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria
Rabipur
Belgium
Rabipur
Croatia
Rabipur
Denmark
Rabipur
France
Rabipur
Spain
Rabipur
Netherlands
Rabipur
Luxembourg
Rabipur
Germany
Rabipur
Norway
Rabipur
Poland
Rabipur
Portugal
Rabipur
Sweden
Rabipur
Hungary
Rabipur
Italy
Rabipur
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Other sources of information
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Instructions for using the pre-filled syringe with Rabipur vaccine
Pre-filled syringe
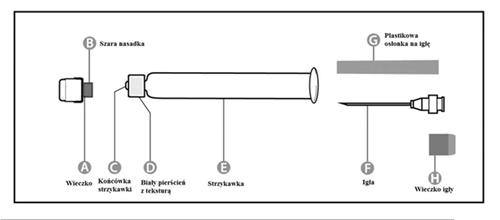
| Step 1: Hold the syringe (E) with one hand, with the cap facing up. Hold the syringe by the white ring with texture (D). | 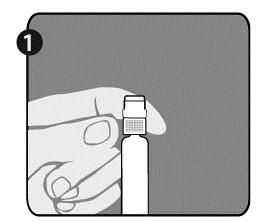 |
| Step 2: With the other hand, grasp the cap (A) and move it firmly back and forth to detach it from the ring (D). Do not twist or unscrew the cap. | 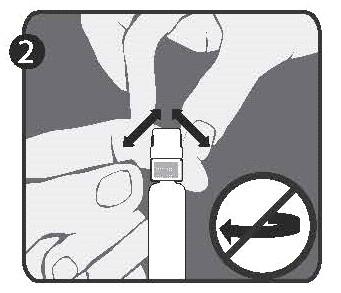 |
| Step 3: Lift the cap (A) to remove it and discard the gray nozzle (B). Be careful not to touch the sterile tip of the syringe (C). | 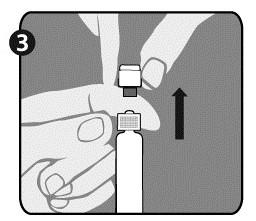 |
Attaching the needle (instructions apply to both provided needles):
| Step 1: Twist the cap (H) to remove it from one of the two identical needles. This will be the needle used for reconstitution. Do not remove the plastic shield (G). | 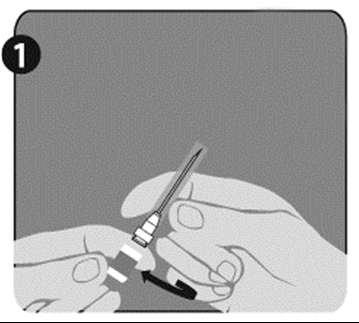 |
| Step 2: Hold the syringe (E) firmly with one hand, by the white ring with texture (D). With the other hand, attach the needle (F) and twist it clockwise until it clicks into place. After attaching the needle, remove the plastic shield (G). The syringe (E) is now ready for use. | 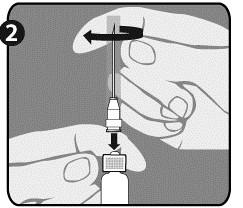 |
Instructions for reconstituting the Rabipur vaccine using the pre-filled syringe:
Both before and after reconstitution of the vaccine, visually inspect the vaccine for foreign particles and changes in appearance. The vaccine should not be used if its appearance has changed. The vaccine after reconstitution is clear to slightly opalescent and colorless to slightly pink.
The powder should be dissolved using the provided solvent to prepare the solution. The solution should be gently shaken before injection. The vaccine should be administered immediately after reconstitution.
The vial is under vacuum. After reconstitution of the vaccine, it is recommended to unscrew the syringe from the needle to remove the vacuum. After doing so, it will be easy to withdraw the vaccine from the vial. It is not recommended to generate excessive pressure, as this may cause problems with withdrawing the correct amount of vaccine.
The length of the needle does not allow it to reach the bottom of the vial, so the vial should be turned upside down and the needle withdrawn towards the stopper. This will allow the entire amount of vaccine solution to be withdrawn from the vial.
After reconstitution of the vaccine, remove the cap from the second needle (as described in step 1 for the needles), and then replace the needle used for reconstitution with the second needle, which will be used for injection.
Do not use the same needle for reconstitution and injection.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterBavarian Nordic A/S GSK Vaccines GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to RabipurDosage form: Powder, 3.25 IU of rabies virus, Wistar Rabies PM/WI38 1503-3M (inactivated)/0.5 ml; 1 dose (0.5 ml)Active substance: rabies, inactivated, whole virusPrescription requiredDosage form: Suspension, 160 ELISA antigen units of hepatitis A virus, strain GBM/0.5 ml; 1 dose (0.5 ml)Active substance: hepatitis A, inactivated, whole virusPrescription requiredDosage form: Suspension, 60 mcg HA/strain, 1 dose (0.7 ml)Active substance: influenza, inactivated, split virus or surface antigenPrescription required
Alternatives to Rabipur in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Rabipur in Espanha
Alternative to Rabipur in Ukraine
Online doctors for Rabipur
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Rabipur – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














