
Prolastin
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Prolastin

How to use Prolastin
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
Prolastin
1000 mg, powder and solvent for solution for infusion
alpha-1-Proteinase inhibitor, human
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Prolastin and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Prolastin
- 3. How to use Prolastin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Prolastin
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Prolastin and what is it used for
Prolastin belongs to a group of proteinase inhibitors.
Alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor (alpha-PI) is produced by the body to inhibit the action of substances called elastases, which damage lung tissue. Hereditary deficiency of alpha-PI leads to an imbalance between alpha-PI and elastases. This can lead to progressive lung tissue damage and the development of pulmonary emphysema. Pulmonary emphysema is an abnormal dilation of the lungs, accompanied by destruction of lung tissue. Prolastin is used to restore the balance between alpha-PI and elastases in the lungs, thereby preventing further deterioration of pulmonary emphysema.
Prolastin is used for long-term supportive treatment in patients with alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor deficiency, in whom the doctor has prescribed this form of treatment.
2. Important information before using Prolastin
When not to use Prolastin:
- if you are allergic (hypersensitive) to the active substance alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor or any of the other ingredients of Prolastin (listed in section 6);
- if you have a deficiency of a specific class of immunoglobulins (IgA), as there is a risk of severe allergic reactions, including anaphylactic shock.
Warnings and precautions
- Before starting treatment with Prolastin, discuss it with your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- Tell your doctor if you have severe heart failure. Particular caution is required, as Prolastin may cause a transient increase in blood volume.
Allergic reactions (hypersensitivity)
In rare cases, allergic reactions to Prolastin may occur, even if you have previously tolerated alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor well.
Your doctor will inform you about the symptoms of allergic reactions and what to do if they occur (see also section 4).
If you experience any symptoms of an allergic reaction during infusion of Prolastin, tell your doctor or nurse immediately.
Information on safety with regard to infection risk
When a medicine is produced from human blood or plasma, appropriate measures are taken to prevent the transmission of infections to the patient.
These measures include:
- proper selection of blood and plasma donors to exclude the possibility of transmission of infection,
- testing of individual donations and plasma pools for viruses/infections,
- inclusion of virus inactivation or removal steps in the manufacturing process.
Despite this, it is not possible to completely eliminate the risk of transmission of infection when using medicines prepared from human blood or plasma. This also applies to previously unknown or newly emerging viruses and other types of infections.
Current preventive measures are considered effective in preventing infections with enveloped viruses such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B and C.
However, they may have limited effectiveness in preventing infections with non-enveloped viruses, such as hepatitis A and parvovirus B19.
Parvovirus B19 infection can have harmful consequences for pregnant women (fetal infection) and for patients with immune disorders or certain types of anemia (e.g. sickle cell anemia, hemolytic anemia).
If proteinase inhibitors obtained from human plasma are regularly or repeatedly used, your doctor may recommend vaccinations against viral hepatitis A and B.
It is particularly recommended that during each administration of Prolastin, the name and batch number of the medicine be recorded, so that it can be determined which patient received the medicine from which batch.
Smoking
Due to the fact that smoking reduces the effectiveness of Prolastin, patients should be strongly advised to quit smoking.
Children and adolescents
So far, there is no experience with the use of Prolastin in children and adolescents under the age of 18.
Prolastin and other medicines
So far, no interactions between Prolastin and other medicines are known.
However, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking, including those that are available without a prescription.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Before using any medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
There are no clinical data on the use of Prolastin during pregnancy. You should inform your doctor about pregnancy or planning it. It is not known whether Prolastin passes into breast milk. Breastfeeding women should consult their doctor.
Driving and using machines
There are no data on the effect of Prolastin on the ability to drive and use machines.
Prolastin contains sodium
Prolastin contains approximately 110.4 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) in each vial.
In the case of a patient with a body weight of 75 kg, this corresponds to 24.84% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults. Patients controlling their sodium intake should contact their doctor or pharmacist.
3. How to use Prolastin
After reconstitution in the solvent contained in the packaging, Prolastin is administered by intravenous infusion. The first infusions of Prolastin should be supervised by a doctor with experience in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Treatment at home
After the first infusions of Prolastin, it can also be administered by another person belonging to the medical staff, but only after undergoing appropriate training. The attending physician will decide whether the patient qualifies for home treatment and ensure that the medical staff member receives instructions on the following matters:
- how to prepare and administer the prepared infusion solution (see the illustrated instructions at the end of this leaflet);
- how to maintain the medicine in a sterile state (rules for performing infusions in aseptic conditions);
- how to keep a treatment diary;
- how to recognize side effects, including symptoms of allergic reactions, and what measures to take in case of their occurrence (see also section 4).
Dose
The dose of Prolastin received by the patient depends on their body weight. Usually, administration once a week of a dose of 60 mg of active substance per kilogram of body weight (which corresponds to 180 ml of the ready-to-use solution containing 25 mg/ml of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor in the case of a patient weighing 75 kg) is sufficient to maintain alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor concentrations in the serum that protect against further progression of pulmonary emphysema.
The treatment period is determined by the attending physician. There are no recommendations for the maximum treatment period.
If you feel that the effect of Prolastin is too strong or too weak, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Using a higher dose of Prolastin than recommended
The effects of overdose are not yet known.
- If you think you have taken a higher dose of Prolastin than recommended, inform your doctor or another medical professional, who will take appropriate action.
Missing a dose of Prolastin
- Talk to your doctor to decide whether to administer the missed dose.
- Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed infusion.
Stopping treatment with Prolastin
If treatment with Prolastin is interrupted, the disease may worsen. Consult your doctor if you want to make a decision to stop treatment with Prolastin.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Prolastin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If side effects occur during infusion of Prolastin, depending on their type and severity, the infusion should be stopped or terminated.
Possible serious side effects
Rarely (in up to 1 in 1000 patients) allergic reactions may occur, and in very rare cases (in up to 1 in 10,000 patients) these reactions may be anaphylactic in nature, even if no symptoms of allergy have occurred during previous infusions.
You should immediately inform your doctor or nurse if you observe any of the following symptoms:
- rash, hives, itching;
- difficulty swallowing;
- swelling of the face or lips;
- sudden flushing of the skin;
- difficulty breathing (dyspnea);
- low blood pressure;
- change in heart rate;
- chills. Your doctor or another medical professional may, depending on the needs, decide to reduce the infusion rate or stop the infusion and administer appropriate treatment. In the case of home treatment, you should immediately stop the infusion and contact your doctor or another medical professional
The following side effects have occurred during treatment with Prolastin:
Not very common (may occur in up to 1 in 100 patients):
- chills, fever, flu-like symptoms, chest pain
- hives
- dizziness, fainting, headaches
- difficulty breathing (dyspnea)
- rash
- nausea
- joint pain
Rare (may occur in up to 1 in 1000 patients):
- allergic reactions
- -rapid heartbeat (tachycardia)
- low blood pressure (hypotension)
- high blood pressure (hypertension)
- back pain
Very rare (may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 patients):
- anaphylactic shock
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, PL-02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309,
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can be reported directly to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Prolastin
Do not store above 25°C.
Do not freeze.
The prepared solution should not be stored in the refrigerator, it should be used within 3 hours of preparation. Any unused product or waste material should be disposed of.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use Prolastin after the expiry date stated on the label and carton.
Do not use Prolastin if the prepared solution is not clear.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist what to do with medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Prolastin contains
- The active substance is human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor (derived from human blood or plasma).
- The other ingredients are: sodium chloride, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, water for injections (solvent/diluent).
What Prolastin looks like and contents of the pack
Alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor in the form of a powder, white to beige in color.
The prepared solution is clear.
1 ml of the prepared solution contains 25 mg of alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor
The carton contains:
- 1 vial of powder containing 1000 mg of human alpha-1-proteinase inhibitor
- 1 vial containing 40 ml of solvent (water for injections).
- 1 Mix2Vial connector for mixing and preparing the solution.
The packaging includes:
- 4 packs of Prolastin 1000 mg
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder:
Grifols Deutschland GmbH
Colmarer Straße 22
60528 Frankfurt
Germany
Tel.: +49 69/660 593 100
Manufacturer:
Instituto Grifols, S.A.
Can Guasc, 2 – Parets del Vallès
08150 Barcelona
Spain.
To obtain more detailed information, please contact
Grifols Polska Sp. z.o.o.
ul. Grzybowska 87
00-844 Warsaw
Poland
tel. (22) 378 85 60
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
| Austria | Prolastin |
| France Greece Netherlands Ireland Germany Poland Portugal Italy | |
| Denmark Finland Spain Norway Sweden | Prolastina |
| Belgium | Pulmolast |
Date of last revision of the leaflet:September 2021
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals and patients eligible for home treatment:
Preparation of the ready-to-use solution for infusion
- 1. Aseptic technique (cleanliness and hygiene) should be followed to maintain sterility. Preparation of the ready-to-use solution should be done on a flat surface.
- 2. Ensure that the vials of Prolastin and solvent (sterile water for injections) are at room temperature (between 20°C and 25°C).
- 3. Remove the cap from the vial of Prolastin and disinfect the rubber stopper using a sterile swab with alcohol. Let the rubber stopper dry.
- 4. Repeat this step with the vial of water for injections – solvent (Solvent).
- 5. Tear off the cover of the Mix2Vial packaging (Fig. 1). Do not remove the Mix2Vial connector from the packaging.
- 6. Place the Mix2Vial connector on a flat surface. Holding the vial of solvent securely, push the blue end of the Mix2Vial connector straight down until the needle pierces the stopper (Fig. 2)
- 7. Remove and discard the transparent part of the Mix2Vial packaging (Fig. 3)
- 8. Place the vial of Prolastin in an upright position on a flat surface and invert the vial of solvent with the attached Mix2Vial connector.
- 9. Holding the vial of Prolastin securely, push the transparent end of the Mix2Vial connector straight down until the needle pierces the stopper (Fig. 4). Under the influence of vacuum, the solvent will automatically flow into the vial of Prolastin. Note: If the Mix2Vial connector is connected at an angle, it may cause the vacuum to be removed from the vial of Prolastin and the solvent will not flow into the vial. In the event that there is no longer a vacuum in the vial, use a sterile syringe and needle to draw the water for injections from the vial of solvent and inject it into the vial of Prolastin, directing the stream towards the inner wall of the vial.
- 10. Gently rotate the connected vials of solvent and Prolastin (Fig. 5) until the powder is completely dissolved. Do not shake to avoid foaming the solution. The prepared solution should be clear. Do not use the solution if it has changed color or contains solid particles.
- 11. If it is necessary to use more than one vial of Prolastin to prepare the required dose, use an additional Mix2Vial packaging and repeat the above steps. Do not reuse the same Mix2Vial connector.
- 12. Disconnect the Mix2Vial connector (Fig. 6) and then administer the product aseptically.
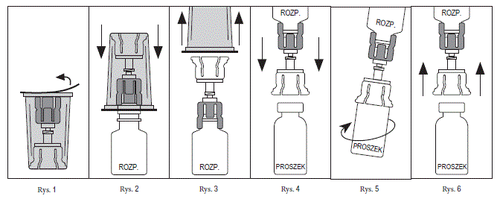
Complete dissolution should occur within 5 minutes.
Only a clear solution is suitable for use. Prolastin should not be mixed with other infusion solutions.
The prepared solution must be used within 3 hours of preparation.
The prepared solution should be administered by slow intravenous infusion using an appropriate infusion set (not included in the packaging). The infusion rate should not exceed 0.08 ml per kilogram of body weight (which corresponds to 6 ml for a patient weighing 75 kg) per minute.
- Country of registration
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterInstituto Grifols, S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to ProlastinDosage form: Powder, 500 mgActive substance: alfa1 antitrypsinManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AGPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 1000 mgActive substance: alfa1 antitrypsinManufacturer: Takeda Manufacturing Austria AGPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 277.8 Ph. Eur. units (500,000 KIU)Active substance: aprotininPrescription not required
Alternatives to Prolastin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Prolastin in Ukraine
Alternative to Prolastin in Spain
Online doctors for Prolastin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Prolastin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














