
Oxazepam Gsk
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Oxazepam Gsk

How to use Oxazepam Gsk
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
OXAZEPAM GSK, 10 mg, tablets
Oxazepam
Read the leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Oxazepam GSK and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Oxazepam GSK
- 3. How to take Oxazepam GSK
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Oxazepam GSK
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Oxazepam GSK and what is it used for
Oxazepam GSK is a psychotropic medicine, belonging to the group of medicines called benzodiazepines.
It contains the active substance oxazepam. The medicine has anxiolytic, sedative, hypnotic, and anticonvulsant effects.
Indications for use:
- treatment of anxiety states,
- treatment of anxiety associated with depression (as an adjunctive treatment),
- treatment of symptoms of acute alcohol withdrawal.
States of tension and anxiety associated with everyday difficulties are not an indication for the use of this medicinal product.
2. Important information before taking Oxazepam GSK
When not to take Oxazepam GSK
- if the patient is allergic to the active substance, other benzodiazepines, or any of the other ingredients of the medicine (listed in section 6),
- if the patient has severe respiratory failure,
- if the patient has excessive muscle weakness (called myasthenia),
- if the patient is dependent on drugs, alcohol, except in cases of treatment of acute withdrawal symptoms, such as seizures and anxiety in alcoholics,
- in children under 12 years of age,
- if the patient has sleep apnea. If the patient has respiratory failure (e.g., COPD - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - limiting airflow to and from the lungs) or sleep apnea (repeated pauses in breathing during sleep, causing hypoxia), the medicine may cause life-threatening respiratory depression (slowing and shallowing of breathing, apnea, and death by suffocation).
Warnings and precautions
- Taking Oxazepam GSK may lead to psychological and physical dependence. The risk of dependence increases with the dose and duration of treatment. It is higher in patients who have been dependent on alcohol or drugs and in patients with personality disorders. The possibility of dependence decreases if the dose and duration of treatment are tailored to the patient.
- During treatment with Oxazepam GSK, tolerance to the medicine may occur (decreased efficacy of the medicine).
- Sudden withdrawal of the medicine may cause withdrawal symptoms (see section: Stopping Oxazepam GSK).
- If the patient has depression, psychotic disorders (disorders of perception of reality), anxiety states, or insomnia, Oxazepam GSK should not be used as the only medicine, as it may increase the risk of suicidal behavior. Anxiety states and tension caused by everyday stress usually do not require the use of anxiolytic medicines.
- In elderly patients (over 65 years), there is a higher risk of paradoxical reactions (see section 4. Possible side effects).
- Oxazepam GSK may cause a decrease in blood pressure, so it should be used with caution in patients who may experience cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disorders due to a decrease in blood pressure. This is especially true for elderly patients.
- If Oxazepam GSK is used for a long period, liver and hematopoietic system function should be monitored.
- Oxazepam GSK should be used with caution in patients with impaired liver or kidney function.
- If the patient has severe liver failure, the medicine may cause brain damage (called encephalopathy).
Oxazepam GSK and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take.
Oxazepam GSK used concomitantly with the following medicines may cause respiratory depression and enhance their effects. You should tell your doctor if you are taking:
- barbiturates (medicines used to treat insomnia and epilepsy),
- medicines used to treat depression
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs),
- antipsychotic medicines (medicines used to treat, among other things, schizophrenia),
- sedatives,
- sleeping medicines,
- anxiolytic medicines,
- medicines used to treat epilepsy,
- first-generation antihistamines (medicines used to treat, for example, allergies),
- anesthetics,
- opioid analgesics (e.g., morphine), as euphoria (excessive joy) may occur, which increases the risk of psychological dependence. Concomitant use of Oxazepam GSK and opioids (strong painkillers, medicines used for substitution therapy for addiction, and some cough medicines) increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma, and can be life-threatening. Therefore, concomitant use can only be considered if other treatment methods are not possible. If, however, your doctor has prescribed Oxazepam GSK concomitantly with opioids, they should limit the dose and duration of concomitant treatment. You should inform your doctor about all opioid medicines you are taking and strictly follow your doctor's dosage instructions. It may be helpful to inform friends or relatives so that they are aware of the above symptoms. If such symptoms occur, you should contact your doctor.
- levodopa (a medicine used to treat Parkinson's disease),
- medicines used to treat hypertension,
- oral contraceptives.
Oxazepam GSK must not be used concomitantly with:
- probenecid (a medicine used to treat gout), as it may enhance the inhibitory effect of Oxazepam GSK on the central nervous system,
- muscle relaxants, as Oxazepam GSK may enhance their effects,
- theophylline and aminophylline (medicines used to treat asthma), as they may decrease the sedative effect of Oxazepam GSK.
Taking Oxazepam GSK with food and drink
Do not drink any alcoholic beverages while taking this medicine. Alcohol enhances the sedative effect of Oxazepam GSK.
Oxazepam GSK can be taken with or without food.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Before taking any medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Oxazepam GSK must not be used in pregnant women, as it may cause harm to the fetus.
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor before taking this medicine.
Regular use of benzodiazepines during pregnancy may cause physical dependence and withdrawal symptoms in the newborn. Benzodiazepines used during the last 3 months of pregnancy cause inhibition of central nervous system activity, hypotonia, difficulty sucking, hypothermia (body temperature below 36°C), and breathing difficulties in the newborn. Oxazepam GSK must not be used during breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
Oxazepam GSK may cause visual disturbances, drowsiness, dizziness, and balance disorders, so you should not drive or operate machinery during treatment with oxazepam.
Oxazepam GSK contains lactose
If you have been diagnosed with an intolerance to some sugars, consult your doctor before taking the medicine.
3. How to take Oxazepam GSK
Always take this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are not sure, consult your doctor.
Recommended dose
Adults:
10 to 30 mg (1 to 3 tablets) 3 to 4 times a day.
Patients over 65 years:
Initially 10 mg (1 tablet) 3 times a day.
Then the doctor may increase the dose to 15 mg (1.5 tablets) 3 or 4 times a day.
The dose will depend on the efficacy of the medicine and the severity of side effects.
Method of administration:
Oxazepam GSK should be taken orally.
The medicine should not be used for more than 8-12 weeks, including the period of gradual withdrawal of the medicine.
In some cases, treatment may last longer. This requires a specialized assessment of the patient's health.
Use in children and adolescents
The medicinal product is not recommended for use in children and adolescents.
In children and adolescents, Oxazepam GSK should not be used due to insufficient clinical data on its efficacy and safety in this population.
Use in patients with impaired renal or hepatic function
Oxazepam GSK should be used with caution in patients with impaired liver or kidney function.
Overdose of Oxazepam GSK
If you have taken more than the recommended dose of the medicine, consult your doctor immediately.
Symptoms of mild overdose:
- lack of response to stimuli while maintaining consciousness (stupor),
- disorders of consciousness (disorientation),
- paradoxical reactions,
- lethargy (a state of deep sleep, combined with apathy and lack of sensitivity to stimuli; vital processes are significantly inhibited).
Symptoms of severe overdose:
- balance disorders, unsteady gait,
- muscle weakness,
- decreased blood pressure,
- slowed heart rate,
- slowing and shallowing of breathing, apnea,
- coma (rarely),
- death (very rarely).
Missed dose of Oxazepam GSK
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as possible. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose. Take the next dose as directed by your doctor.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping Oxazepam GSK
The medicine should be withdrawn gradually. Sudden withdrawal of Oxazepam GSK may cause withdrawal symptoms, which can be life-threatening.
- Withdrawal symptoms may include, from headache, mild dysphoria, sleep disturbances/insomnia to severe side effects, which may include abdominal cramps, muscle cramps, muscle pain, vomiting, sweating, feeling of intense anxiety, tension, restlessness, irritability, tremors, and seizures. Severe, acute signs and symptoms of withdrawal, including life-threatening reactions, may include: delusions, disturbed self-perception, numbness and paresthesia of limbs, hypersensitivity to light, sound, and touch, tremors, hallucinations, depression, delirium, mania, psychosis, seizures, and suicidal behavior.
- In addition, the following symptoms may occur: disorientation, dizziness, increased muscle tone, rebound phenomenon (i.e., worsening of symptoms that were the reason for taking the medicine), mood disorders, loss of reality, personality disorders, perception disorders, involuntary movements, short-term memory loss, concentration disorders, elevated body temperature, nausea, diarrhea, loss of appetite, palpitations, and tachycardia (accelerated heart rate), excessive response to reflexes, perception disorders, and, in rare cases, delirium, panic attacks, and seizures. Seizures may occur in patients who have had them before
or in patients taking other medicines that lower the seizure threshold (e.g., antidepressants).
Withdrawal symptoms, especially severe ones, occur more frequently in patients who have taken high doses of the medicine for a long time. Withdrawal symptoms have also been reported after stopping continuous treatment with benzodiazepines at therapeutic doses. Since the risk of withdrawal symptoms and rebound effect is higher in the case of sudden discontinuation of treatment, gradual dose reduction is recommended.
The time of onset of withdrawal symptoms varies and can range from a few hours to a week or more after discontinuation of the medicine.
If withdrawal symptoms occur, consult your doctor immediately.
If you have any further doubts about taking the medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Misuse of the medicine
The risk of benzodiazepine misuse is known, and patients taking Oxazepam GSK should be monitored during its use. Benzodiazepines have the potential to be misused.
Deaths have been reported due to overdose when benzodiazepines were misused with other central nervous system depressant medicines, including opioids, other benzodiazepines, alcohol, and/or illegal substances. To obtain information on the proper storage and disposal of unused medicines, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Oxazepam GSK can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Side effects to be aware of:
If you experience any of the following symptoms, you should seek medical help immediately and
stop taking Oxazepam GSK.
Severe allergic reactions.Symptoms include:
- anaphylactic and/or anaphylactoid reactions (severe allergic reactions causing breathing difficulties, skin reactions, or dizziness).
Breathing problemsSymptoms include:
- slowing and shallowing of breathing, apnea, and even death by suffocation (respiratory depression),
- worsening of sleep apnea symptoms (see section: When not to take Oxazepam GSK),
- worsening of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease symptoms (see section: When not to take Oxazepam GSK).
Paradoxical reactions(occurring more frequently in elderly patients). Symptoms include:
- excitement,
- agitation,
- anxiety,
- hostility,
- anger,
- aggressive behavior,
- delusions (false beliefs resistant to argumentation),
- hallucinations (false sensory perceptions),
- mania (elevated or irritable mood),
- nightmares,
- psychosis,
- behavioral changes,
- lack of inhibition,
- euphoria (unnatural well-being),
- suicidal thoughts and ideas,
- suicide attempts.
If such symptoms occur, you should stop taking Oxazepam GSK and consult
your doctor.
Other side effects:
Very common side effects(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- sedation,
- fatigue,
- drowsiness.
Common side effects(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- depression,
- balance disorders, unsteady gait, muscle weakness; may cause falls and dangerous bone fractures, especially in elderly patients (over 65 years),
- lack of response to stimuli while maintaining consciousness (stupor),
- disorders of consciousness (disorientation),
- weakness.
Uncommon side effects(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- decreased or increased libido,
- impotence,
- anorgasmia (inability to achieve orgasm),
- nausea.
Side effects with unknown frequency(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- muscle stiffness, poor mimicry, slowed movement, restlessness, involuntary muscle contractions, and involuntary movements (extrapyramidal symptoms),
- speech disorders, unclear, slowed speech,
- dizziness, headaches,
- tremors,
- seizures and/or convulsions,
- coma,
- transient anterograde amnesia (inability to learn and remember new information) or memory disorders; the risk is higher with high doses of the medicine,
- vision disorders (e.g., double vision, blurred vision),
- constipation,
- jaundice (yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes) and changes in blood test results (elevated bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase levels, and increased activity of liver enzymes AST and ALT),
- skin reactions (e.g., itchy papules or blisters on the skin), hair loss,
- thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count, leading to increased risk of bleeding and bruising),
- agranulocytosis (decreased number of certain white blood cells, leading to decreased immunity),
- blood dyscrasia (disorder of blood cell production), pancytopenia (decreased number of all blood cells),
- hypersensitivity reactions (allergic reactions),
- Schwartz-Bartter syndrome (a disease caused by excessive secretion of vasopressin, characterized by: headache, irritability, nausea, vomiting, mood changes, excessive excitability, disorders of consciousness, decreased muscle tone, and weakened tendon reflexes),
- decreased sodium levels in the blood (hyponatremia),
- urinary incontinence,
- urinary retention,
- decreased blood pressure,
- decreased body temperature,
- misuse of the medicine,
- dependence,
- withdrawal symptoms.
Oxazepam GSK may cause psychological and physical dependence (see section: Warnings and precautions).
Sudden withdrawal of Oxazepam GSK may cause withdrawal symptoms (see section: Stopping Oxazepam GSK).
If you have had depression, it may recur while taking Oxazepam GSK.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Oxazepam GSK
Keep out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use Oxazepam GSK after the expiry date stated on the outer packaging after "Expiry date" and on the blister after "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Store in a temperature below 25°C. Store in the original packaging to protect from light and moisture.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Oxazepam GSK contains
The active substance is oxazepam.
One tablet contains 10 mg of oxazepam.
The other ingredients are: lactose monohydrate, potato starch, talc, magnesium stearate, anhydrous colloidal silica.
What Oxazepam GSK looks like and contents of the pack
Oxazepam GSK is a white or almost white, biconvex tablet.
The packaging contains 20 tablets.
Removing a tablet from the blister pack
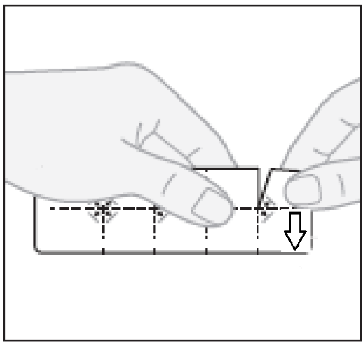
- 1. Separating one tablet:to separate a fragment of the blister with one tablet, tear the blister along the perforated lines.
| These tablets are provided in a special packaging with a child safety lock. | ||
| Each fragment of the blister with one tablet has a number on it. The tablets should be taken in sequence, according to the numbering, starting from number 1. | ||
| Take the tablets one by one, following the numbering on the blister pack. | ||
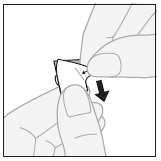
- 2. Tearing off the outer layer:starting from the corner, pry off and tear off the outer layer from the separated fragment of the blister pack.
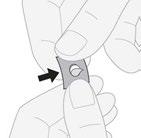
- 3. Removing the tablet:gently push the tablet through the foil.
Marketing authorization holder
GSK PSC Poland sp. z o.o.
ul. Grunwaldzka 189
60-322 Poznań
Manufacturer
Delpharm Poznań Spółka Akcyjna
ul. Grunwaldzka 189
60-322 Poznań
To obtain more detailed information about this medicine, consult a representative of the marketing authorization holder.
GSK Services Sp. z o.o.
tel. (22) 576-90-00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
{marketing authorization holder's logo}
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterDelpharm Poznań S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Oxazepam GskDosage form: Tablets, 10 mgActive substance: oxazepamManufacturer: Tarchomińskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne "Polfa" S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 10 mgActive substance: oxazepamManufacturer: Joint-stock Company "OLAINFARM"Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 0.25 mgActive substance: alprazolamPrescription not required
Alternatives to Oxazepam Gsk in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Oxazepam Gsk in Ukraine
Alternative to Oxazepam Gsk in Spain
Online doctors for Oxazepam Gsk
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Oxazepam Gsk – subject to medical assessment and local rules.









