

Ovestin

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Ovestin

How to use Ovestin
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Warning! Keep the leaflet! Information on the immediate packaging in a foreign language.
Ovestin
1 mg/g, vaginal cream
Estriol
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Ovestin and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Ovestin
- 3. How to use Ovestin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Ovestin
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Ovestin and what is it used for
Ovestin belongs to a group of medicines known as hormone replacement therapy (HRT) for vaginal use. The medicine contains the female sex hormone estriol (estrogen). Ovestin is used in postmenopausal women, at least 12 months after the cessation of natural menstruation.
Ovestin is used to alleviate menopausal symptoms that occur in the vagina, such as dryness or irritation. In medical terminology, this phenomenon is referred to as "atrophic vaginitis". It is caused by a decrease in estrogen levels in the body and occurs naturally after menopause.
If the ovaries are surgically removed before menopause (a procedure called oophorectomy), estrogen production decreases very quickly.
Estrogen deficiency can cause dryness and increased sensitivity of the vaginal walls, which is the cause of painful intercourse and the occurrence of inflammatory conditions and severe itching of the vagina. Estrogen deficiency can also cause symptoms of urinary incontinence and recurrent urinary tract infections. These symptoms often disappear after the use of estrogen-containing medications. Noticeable improvement usually occurs after a few days or weeks of treatment.
Ovestin works by replacing estrogen, which is normally produced by the woman's ovaries. The medicine is administered vaginally, so the hormone is released where it is needed.
This can alleviate the feeling of discomfort in the vagina.
Improvement may only be noticeable after a few days or even weeks.
In addition to the above indications, Ovestin may also be used for:
- accelerating the healing of postoperative wounds in women who have undergone vaginal surgery
- accurate assessment of cervical smears in postmenopausal women.
2. Important information before using Ovestin
Medical history and regular check-ups
The use of HRT is associated with a risk that should be considered when deciding to start or continue hormone replacement therapy.
Experience with the treatment of women who have premature menopause (due to ovarian failure or after surgery) is limited. In women with premature menopause, the risk associated with HRT may be varied. You should always consult a doctor.
Before starting (or resuming) HRT, the doctor will take a medical history and may decide to perform a physical examination, including a breast examination and/or gynecological examination through the vagina.
After starting Ovestin, you should regularly visit your doctor for check-ups (at least once a year). During the check-up, you should discuss the benefits and risks associated with continuing Ovestin with your doctor.
You should regularly perform breast examinations as recommended by your doctor.
When not to use Ovestin:
Ovestin should not be used if any of the following situations apply to the patient. If in doubt, consult a doctor before using Ovestin.
When not to use Ovestin:
If any of the above conditions occur for the first time while using Ovestin, you should stop using it immediately and contact your doctor.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment, you should inform your doctor if any of the following conditions are currently present or have occurred in the past, as they may return or worsen during Ovestin treatment. If this happens, you should visit your doctor more often:
- uterine fibroids (smooth muscle tumor)
- growth of endometrial cells outside the uterus (endometriosis) or a history of excessive growth of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia)
- increased risk of blood clots [see "Blood clots in veins (venous thrombosis)"]
- increased risk of developing an estrogen-dependent tumor (e.g., breast cancer in the mother, sister, or grandmother)
- high blood pressure
- liver disorders, such as a benign liver tumor
- diabetes with or without vascular complications
- gallstones
- migraine or severe headache
- immune system disease affecting multiple internal organs (systemic lupus erythematosus; chronic connective tissue disease with skin changes throughout the body)
- epilepsy
- asthma
- disease affecting the eardrum and causing hearing impairment (otosclerosis)
- fluid retention in the body due to heart or kidney disease
- hereditary and acquired angioedema.
You should inform your doctor if you have hepatitis C and are being treated with medications such as ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir and dasabuvir with or without ribavirin. Taking these medications with some estrogen-containing medications may cause elevated liver function test results (increased ALT enzyme activity); the risk of this occurring with Ovestin is currently unknown.
You should tell your doctor if you notice any changes in your condition while using Ovestin.
You should stop using Ovestin and contact your doctor immediatelyif any of the following symptoms occur while using HRT:
- any of the conditions listed in "When not to use Ovestin"
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), which may be a sign of liver disease
- swelling of the face, tongue, and/or throat, and/or difficulty swallowing or hives, along with difficulty breathing, suggesting angioedema.
- significant increase in blood pressure (possible symptoms include headache, fatigue, dizziness)
- migraine-like headaches that occur for the first time
- pregnancy
- symptoms indicating the formation of blood clots, such as:
- painful swelling and redness of the legs
- sudden chest pain
- difficulty breathing. More information is provided in "Blood clots in veins (venous thrombosis)".
Note:Ovestin is not a contraceptive. If it has been less than 12 months since your last menstrual period or you are under 50 years old, you may need to use an additional method of birth control. You should consult your doctor.
HRT and tumors
Excessive thickening of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia) and uterine lining cancer (endometrial cancer)
The use of estrogen-only HRT in tablet form for a long time may increase the risk of developing uterine lining cancer (endometrium).
It is not certain whether a similar risk exists with the repeated or long-term (longer than one year) use of Ovestin. However, it has been shown that Ovestin is absorbed into the bloodstream to a very small extent, and therefore, the addition of progestogen is not necessary.
Bleeding or spotting is not usually a cause for concern, but you should consult your doctor. This may be a sign of endometrial thickening.
To prevent endometrial stimulation, you should not exceed the maximum dose or take it for longer than a few weeks (up to 4 weeks).
The risks described below are associated with HRT medications that enter the bloodstream. However, Ovestin is used locally in the vagina and is absorbed into the bloodstream in very small amounts. It is less likely that the conditions listed below will worsen or recur while using Ovestin, but if you have any doubts, you should consult your doctor.
Breast cancer
Data indicate that the use of Ovestin does not increase the risk of breast cancer in women who have never had it before. It is not known whether Ovestin can be safely used in women who have had breast cancer.
You should regularly examine your breasts and consult your doctor if you notice any changes, such as:
- indentation of the skin
- changes in the nipples
- any visible or palpable lumps.
In addition, it is recommended to perform screening mammograms as advised by your doctor.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is rare - much rarer than breast cancer. The use of estrogen-only HRT is associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
The risk of ovarian cancer depends on age. For example, in women between 50 and 54 years old who do not use HRT, ovarian cancer will be diagnosed in about 2 out of 2000 women over a 5-year period.
In women who use HRT for 5 years, ovarian cancer will be diagnosed in about 3 out of 2000 women (i.e., about 1 additional case).
Effect of HRT on the heart or circulatory system
Blood clots in veins (venous thrombosis)
The risk of forming blood clots in the veins is about 1.3 to 3 times higher in women using HRT than in those not using HRT, especially in the first year of treatment.
The formation of blood clots can have serious consequences, and if a clot reaches the lungs, it can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting, or even death.
The likelihood of forming blood clots in the veins increases with age and in the following situations. If any of these situations apply to you, you should inform your doctor:
- prolonged immobilization due to major surgery, injury, or illness (see also section 3 "Need for surgery")
- significant obesity (body mass index over 30 kg/m)
- blood clotting disorders requiring long-term use of anticoagulant medications
- venous thrombosis in the legs or lungs, or other organs in a close relative
- systemic lupus erythematosus (chronic connective tissue disease with skin changes throughout the body)
- cancer.
Symptoms of venous thrombosis are listed in "When to stop using Ovestin and contact your doctor immediately".
Comparison
In women over 50 years old who do not use HRT, venous thrombosis can be expected to occur in about 4 to 7 out of 1000 women over a 5-year period.
In women over 50 years old who have used estrogen-only HRT for more than 5 years, the number of cases will be 5 to 8 out of 1000 women (i.e., 1 additional case).
Heart disease (heart attack)
In women using estrogen-only HRT, the risk of developing heart disease is not increased.
Stroke
The risk of stroke is about 1.5 times higher in women using HRT than in those not using HRT. The number of additional stroke cases associated with HRT increases with age.
Comparison
In women over 50 years old who do not use HRT, stroke can be expected to occur in about 8 out of 1000 women over a 5-year period.
In women of the same age using HRT, the rate is 11 cases per 1000 women over a 5-year period (i.e., 3 additional cases).
Other conditions
HRT will not prevent memory loss. Some evidence suggests a higher risk of memory loss in women who start HRT after the age of 65. You should consult your doctor about this.
Ovestin and other medicines
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take, including those available without a prescription, herbal medicines, or other natural products.
Some medicines may affect the action of Ovestin, which can lead to irregular bleeding. These include:
- antiepileptic drugs(such as phenobarbital, phenytoin, and carbamazepine)
- medicines used to treat tuberculosis(such as rifampicin, rifabutin)
- medicines used to treat HIV infection(such as nevirapine, efavirenz, ritonavir, and nelfinavir)
- herbal products containing St. John's Wort(Hypericum perforatum)
Laboratory tests
If laboratory blood tests are necessary, you should inform your doctor or laboratory staff that you are using Ovestin, as it may affect the results of some tests.
Ovestin with food and drink
Food and drink do not affect the action of Ovestin.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Ovestin is intended for use only in postmenopausal women.
If you become pregnant, you should stop using Ovestin and consult your doctor.
Women who are breastfeeding should consult their doctor before using Ovestin.
Driving and using machines
Using Ovestin should not affect your ability to drive or operate machines. However, individual reactions to the medicine may vary.
Ovestin contains cetyl alcohol and stearyl alcohol.
The medicine may cause local skin reactions (e.g., contact dermatitis).
3. How to use Ovestin
This medicine should always be used as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. If you are unsure, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
In the case of atrophic changes in the lower genital tract, the recommended dose is 1 application per day for the first weeks (up to 4 weeks), then the dose is gradually reduced to 1 application twice a week.
To improve wound healing in postmenopausal women who have undergone vaginal surgery, the recommended dose is 1 application per day for 2 weeks before surgery and 1 application twice a week for 2 weeks after surgery.
To facilitate the interpretation of cervical smear results in postmenopausal women, the recommended dose is 1 application every other day in the week preceding the smear.
Ovestin cream should be used vaginally with an applicator, preferably before going to bed at night.
1 application (applicator filled to the circular mark) contains 0.5 g of cream, which corresponds to 0.5 mg of estriol.
- 1. Remove the cap from the tube, turn it upside down, and open the tube with the sharp end.
- 2. Screw the applicator onto the tube. Make sure the plunger is fully inserted into the applicator.
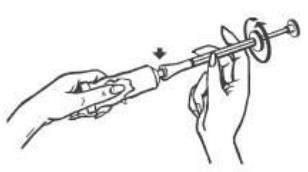
- 3. Slowly squeeze the cream into the applicator until you feel resistance from the plunger (the plunger will stop at the red mark indicated by the arrows in the diagram below).
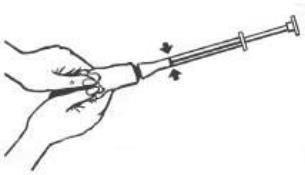
- 4. Unscrew the applicator from the tube and put the cap back on the tube.
- 5. In a lying position, insert the applicator tip with cream deeply into the vagina.
- 6. Slowly push the entire contents of the cream into the vagina using the plunger.
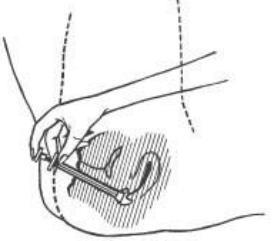
- 7. After use, remove the plunger from the applicator by overcoming the resistance point and wash both parts thoroughly with warm water and soap. Do not use detergents. After washing, rinse both parts well.
- 8. DO NOT PUT THE APPLICATOR IN HOT OR BOILING WATER.
- 9. The device can be reassembled by inserting the plunger into the applicator, overcoming the resistance point.
After the tube is empty, the applicator should be discarded.
Your doctor will try to prescribe the lowest possible dose that should be taken for the shortest time necessary to alleviate the symptoms.
If you feel that the effect of Ovestin is too strong or too weak, you should consult your doctor.
Using a higher dose of Ovestin than recommended
If you use a higher dose of Ovestin than recommended, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist immediately.
If you swallow the cream, it does not pose a risk to your health and life. However, you should inform your doctor. Symptoms of overdose are usually nausea and vomiting. In women, bleeding from the genital tract may also occur after a few days.
Missing a dose of Ovestin
You should not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
If you miss a dose, you should take it as soon as possible, unless you notice the miss on the day of the next application. If you notice the miss on the day of the next application, you should skip the missed dose and continue with the previously established schedule.
Need for surgery
People who are to undergo surgery should tell their surgeon that they are using Ovestin. It may be necessary to stop using Ovestin about 4 to 6 weeks before surgery to reduce the risk of blood clots (see section 2 "Blood clots in veins"). You should ask your doctor when you can start using Ovestin again.
If you have any further doubts about using this medicine, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Ovestin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following diseases are more frequently reported in women using HRT in the form of medications that enter the bloodstream than in women not using HRT. These risks apply to a lesser extent to vaginally administered medications like Ovestin:
- ovarian cancer
- blood clots in the veins of the legs or lungs (venous thromboembolism)
- stroke
- possible memory loss if HRT is started after the age of 65. More information about these side effects can be found in section 2.
Depending on the doses used and the patient's sensitivity, the following side effects may occur:
- swelling and increased tenderness of the breasts
- mild vaginal bleeding
- increased vaginal discharge
- nausea
- fluid retention in the body, usually manifesting as swelling of the ankles or feet
- local irritation or itching
- flu-like symptoms.
In most patients, these symptoms will disappear after a few weeks of treatment.
The following side effects have been reported during the use of other HRT medications:
- inflammation of the gallbladder
- various skin disorders
- skin discoloration, especially on the face or neck, known as "pregnancy spots" (chloasma)
- painful red lumps on the skin (erythema nodosum)
- rash with round redness or ulcers (erythema multiforme).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Medicinal Product Monitoring, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181 C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
By reporting side effects, you can help gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Ovestin
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Do not store above 25°C. Do not freeze.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Ovestin contains
- The active substance of Ovestin is estriol. One gram of cream contains 1 mg of estriol.
- The other ingredients are: octyldodecanol, cetyl palmitate, glycerol (E 422), cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, polysorbate 60, sorbitan stearate, lactic acid, chlorhexidine dihydrochloride, sodium hydroxide, purified water.
What Ovestin looks like and what the package contains
Ovestin is a white to almost white, homogeneous, smooth cream with a characteristic, mild odor.
It is supplied in an aluminum tube with a polyethylene cap and an applicator with a styrene-acrylonitrile cylinder and a polyethylene plunger, in a cardboard box.
Package size: 15 g of cream in a tube.
For more detailed information, you should contact the marketing authorization holder or parallel importer.
Marketing authorization holder in Austria, the country of export:
Aspen Pharma Trading Limited
3016 Lake Drive
Citywest Business Campus
Dublin 24, Ireland
Manufacturer:
Aspen Bad Oldesloe GmbH
Industriestrasse 32-36
D-23843 Bad Oldesloe
Germany
Parallel importer:
InPharm Sp. z o.o.
ul. Strumykowa 28/11
03-138 Warsaw
Repackaged by:
InPharm Sp. z o.o. Services sp. k.
ul. Chełmżyńska 249
04-458 Warsaw
Austrian marketing authorization number:17453
Parallel import authorization number:128/24
Date of leaflet approval: 20.03.2024
[Information about the trademark]
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Marketing authorisation holder (MAH)Aspen Pharma Trading Limited
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to OvestinDosage form: Gel, 50 mcg/gActive substance: estriolManufacturer: Italfarmaco S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Suppositories, 0.5 mgActive substance: estriolManufacturer: Dr. Kade Pharmazeutische Fabrik GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Suppositories, 0.5 mgActive substance: estriolPrescription required
Alternatives to Ovestin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Ovestin in Ukraine
Alternative to Ovestin in Spain
Online doctors for Ovestin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Ovestin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










