

Oestrogel

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Oestrogel

How to use Oestrogel
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Oestrogel, 0.75 mg/dose, transdermal gel
Estradiol
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Oestrogel and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Oestrogel
- 3. How to use Oestrogel
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Oestrogel
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Oestrogel and what is it used for
Oestrogel is a medicine used for hormone replacement therapy (HRT). The medicine contains the female hormone estradiol. After applying the gel to the skin, the hormone is absorbed and enters the bloodstream.
Oestrogel is used in postmenopausal women, at least 6 months after their last natural menstrual period.
Oestrogel is used in the following situations:
Relieving symptoms that occur after menopause
During menopause, the amount of estrogen produced by the woman's body decreases. This can lead to symptoms such as a feeling of heat on the face, neck, and chest ("hot flashes"). Oestrogel relieves these symptoms that occur after menopause. Oestrogel is prescribed only when the symptoms significantly affect the patient's daily life.
Preventing osteoporosis
After menopause, some women may develop brittle bones (osteoporosis). All possible treatment options should be discussed with a doctor.
If the patient is at increased risk of fractures due to osteoporosis and other medicines are not suitable, Oestrogel can be used to prevent osteoporosis after menopause.
2. Important information before using Oestrogel
Medical history and regular check-ups
Using HRT involves risks that should be considered when deciding to start or continue therapy.
Experience with the use of therapy in women with premature menopause (caused by ovarian failure or surgical procedures) is limited. In the case of women with premature menopause, the risk of using HRT may be different. Consult a doctor.
Before starting (or reusing) HRT, the doctor will conduct a medical interview with the patient and their family. The doctor may perform a physical examination, including a breast examination and (or) internal organs, if necessary.
After starting Oestrogel, regular check-ups (at least once a year) should be attended. During these visits, the benefits and risks of continuing to use Oestrogel should be discussed with the doctor.
According to the doctor's or nurse's recommendations, regular breast exams should be performed.
When not to use Oestrogel:
If any of the following points apply to the patient. In case of doubts regarding any of the following points, consult a doctor before using Oestrogel.
- if the patient currently has or has had breast cancer or if there is a suspicion of it;
- if the patient has a malignant tumor sensitive to estrogen, such as endometrial cancer (endometrium) or if there is a suspicion of it;
- if there is vaginal bleeding of unknown cause;
- if the patient has untreated, excessive thickening of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia);
- if the patient has had or currently has blood clots in the veins (thrombosis), such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism;
- if the patient has a blood clotting disorder (such as protein C, protein S, or antithrombin deficiency);
- if the patient has had or currently has a disease caused by blood clots in the arteries, such as a heart attack, stroke, or angina;
- if the patient has had or currently has liver disease, and liver function tests have not returned to normal;
- if the patient has a rare blood disease called porphyria, which is inherited;
- if the patient is allergic (hypersensitive) to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6). If any of the above symptoms occur for the first time while using Oestrogel, the patient should stop using it and consult a doctor immediately.
When to exercise special caution when using Oestrogel
The doctor should be informed if the patient currently has or has had any of the following conditions, as they may recur or worsen during treatment with Oestrogel.
More frequent check-ups may be necessary if any of the following situations apply to the patient:
• uterine fibroids;
• endometriosis or previous cases of excessive thickening of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia);
• increased risk of blood clotting disorders [see "Blood clots in the veins (thrombosis)"];
• increased risk of estrogen-sensitive tumors (e.g., if the patient's mother, sister, or grandmother had breast cancer);
• high blood pressure;
• liver disease, such as a benign liver tumor;
• diabetes;
• gallstones;
• migraine or severe headaches;
• a disease of the immune system that affects many organs in the body (systemic lupus erythematosus, SLE);
• epilepsy;
• asthma;
• a disease that affects the eardrum and hearing (otosclerosis);
• very high levels of fats in the blood (triglycerides);
• fluid retention in the body due to heart or kidney disease;
• inherited or acquired angioedema.
Stop using Oestrogel and consult a doctor immediately if any of the following conditions occur during HRT:
- any of the diseases listed in the "When not to use Oestrogel" section,
- yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice), which may be symptoms of liver disease;
- swelling of the face, tongue, and (or) throat, and (or) difficulty swallowing or hives with breathing difficulties, which suggest angioedema;
- significant increase in blood pressure (symptoms may include headache, fatigue, dizziness);
- migraine-like headaches that occur for the first time;
- pregnancy;
- signs of a blood clot, such as:
- painful swelling and redness of the legs;
- sudden chest pain;
- difficulty breathing;
More information is provided in the "Blood clots in the veins (thrombosis)" section.
Note: Oestrogel is not a contraceptive. If it has been less than 12 months since the last menstrual period or if the patient is under 50 years old, additional contraceptive measures may be necessary to prevent pregnancy. Consult a doctor.
HRT and malignant tumors
Excessive thickening of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia) and uterine lining cancer (endometrial cancer)
Using only estrogen HRT increases the risk of excessive thickening of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia) and uterine lining cancer (endometrial cancer).
Additional use of progestogen for at least 12 days in each 28-day cycle protects the patient from this increased risk. The doctor will prescribe progestogen separately if the patient has a preserved uterus. If the uterus has been removed (hysterectomy), the doctor should be consulted to determine if using this medicine without progestogen is safe.
In the case of women with a preserved uterus who do not use HRT, endometrial cancer is diagnosed in approximately 5 out of 1,000 women between the ages of 50 and 65.
In women between the ages of 50 and 65 with a preserved uterus who use only estrogen HRT, endometrial cancer is diagnosed in 10-60 out of 1,000 women (i.e., 5-55 additional cases), depending on the dose and duration of treatment.
Oestrogel contains a higher dose of estrogen than other HRT products containing only estrogen. The risk of endometrial cancer during treatment with Oestrogel in combination with progestogen is not known.
Irregular bleeding
During the first 3 to 6 months of treatment with Oestrogel, irregular or light bleeding (spotting) may occur. However, if irregular bleeding:
- lasts longer than 6 months,
- starts after using Oestrogel for more than 6 months,
- persists after stopping Oestrogel, consult a doctor immediately.
Bleeding of unknown cause
During treatment with Oestrogel and progestogen (i.e., progesterone) once a month, bleeding (so-called withdrawal bleeding) will occur. However, if bleeding of unknown cause or spotting outside of withdrawal bleeding occurs, which:
- lasts longer than the first 6 months,
- occurs when the patient has been using Oestrogel for more than 6 months,
- persists after stopping Oestrogel, consult a doctor immediately.
HRT and breast cancer
Data confirm that taking hormonal replacement therapy (HRT), in the form of a combination of estrogen and progestogen or only estrogen, increases the risk of breast cancer. The additional risk depends on how long the patient uses HRT. This additional risk becomes apparent after 3 years of HRT. After stopping HRT, the additional risk will decrease over time, but the risk may persist for 10 years or longer if HRT lasted more than 5 years.
Comparison
In the case of women between the ages of 50 and 54 who do not use HRT, breast cancer will be diagnosed in approximately 13 to 17 out of 1,000 women over a 5-year period.
In the case of 50-year-old women who start 5-year estrogen-only HRT, the number of cases will be 16-17 out of 1,000 patients (i.e., 0 to 3 additional cases).
In the case of 50-year-old women who start 5-year estrogen-progestogen HRT, the number of cases will be 21 out of 1,000 patients (i.e., 4 to 8 additional cases).
In the case of women between the ages of 50 and 59 who do not use HRT, breast cancer will be diagnosed in approximately 27 out of 1,000 women over a 10-year period.
In the case of 50-year-old women who start 10-year estrogen-only HRT, the number of cases will be 34 out of 1,000 patients (i.e., 7 additional cases).
In the case of 50-year-old women who start 10-year estrogen-progestogen HRT, the number of cases will be 48 out of 1,000 patients (i.e., 21 additional cases).
- Regular breast exams should be performed. Consult a doctor if any changes occur, such as:
- indentations on the skin,
- changes in the nipple area,
- any visible or palpable lumps. Additionally, participation in offered breast cancer screening programs is recommended. It is essential to inform the screening personnel about HRT use, as the medicine may cause an increase in breast density, which can affect the mammography result. In areas with increased density, mammography may not detect all lumps.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is rare - much rarer than breast cancer. Using HRT that contains only estrogen or a combination of estrogen and progestogen is associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
The risk of ovarian cancer depends on age. For example, in women between the ages of 50 and 54 who do not use HRT, ovarian cancer will be diagnosed in 2 out of 2,000 women over a 5-year period. In women who have used HRT for 5 years, ovarian cancer will occur in approximately 3 out of 2,000 users (i.e., about 1 additional case).
Effect of HRT on the heart and circulation
Blood clots in the veins (thrombosis)
The risk of venous thrombosisis about 1.3 to 3 times higher in women using HRT, especially in the first year of treatment, than in women not using HRT.
Blood clots can be serious and, if they reach the lungs, can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, fainting, or even death.
The likelihood of blood clots in the veins increases with age and depends on the presence of the following factors. The doctor should be informed if any of the following situations apply to the patient:
- the patient is unable to walk for an extended period due to a prolonged surgical procedure, injury, or illness (see also section 3 "If surgery is necessary"),
- the patient is obese (BMI >30 kg/m),
- the patient has blood clotting disorders that require long-term treatment with anticoagulant medication,
- any close relatives have had a blood clot in the leg, lung, or other organ,
- the patient has systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE),
- the patient has cancer. Symptoms indicating the presence of blood clots, see the "Stop using Oestrogel and consult a doctor immediately" section.
Oestrogel and consult a doctor immediately
In women between the ages of 50 and 59 who do not use HRT, venous thrombosis will occur in approximately 4-7 out of 1,000 women over a 5-year period.
In women between the ages of 50 and 59 who have used combined estrogen-progestogen HRT for more than 5 years, venous thrombosis will occur in 9-12 out of 1,000 women (i.e., 5 additional cases).
In women between the ages of 50 and 59 who have had their uterus removed and have used only estrogen HRT for 5 years, venous thrombosis will occur in 5-8 out of 1,000 women (i.e., 1 additional case).
Heart disease (heart attack/heart failure)
There is no scientific evidence that HRT can prevent heart attacks.
Women over 60 years old who use combined estrogen-progestogen HRT are slightly more likely to develop heart disease than women who do not use HRT.
In the case of women who have had their uterus removed and use only estrogen therapy, there is no increased risk of heart disease.
Stroke
The risk of stroke is about 1.5 times higher in people using HRT than in those not using it. The number of additional stroke cases due to HRT increases with age.
In women between the ages of 50 and 59 who do not use HRT, a stroke will occur in approximately 8 out of 1,000 women over a 5-year period.
In women between the ages of 50 and 59 who use HRT, a stroke will occur in 11 out of 1,000 women over a 5-year period (i.e., 3 additional cases).
Children
Estradiol in the form of a gel can be accidentally transferred from the patient's skin to other people.
Others, especially children, should not come into contact with the exposed area of the patient's skin, and the area should be covered after the gel has dried.
If a child comes into contact with the area of skin where estradiol has been applied, the child's skin should be washed with soap and water as soon as possible. Due to the transfer of estradiol, small children may exhibit unexpected symptoms of sexual maturation (e.g., breast budding). In most cases, these symptoms will resolve when the child is no longer exposed to estradiol in the form of a gel.
If a child who may have been accidentally exposed to estradiol in the form of a gel exhibits any signs or symptoms of sexual maturation (breast development or other sexual changes), a doctor should be consulted.
Other conditions
- Using Oestrogel may lead to fluid retention in the body. Therefore, in the case of heart or kidney disease, the patient should be closely monitored while using Oestrogel.
- HRT does not prevent memory loss. There is some evidence that the risk of memory loss may be higher in women who start HRT after the age of 65. Consult a doctor.
Using Oestrogel with other medicines
Certain medicines may affect the action of Oestrogel. This may lead to irregular bleeding. This applies to the following medicines:
- other medicines used on the skin (e.g., anticancer medicines);
- medicines used to treat epilepsy(such as phenobarbital, phenytoin, and carbamazepine);
- medicines used to treat tuberculosis(such as rifampicin, rifabutin);
- medicines used to treat HIV infection(such as nevirapine, efavirenz, ritonavir, and nelfinavir);
- herbal products containing St. John's Wort(Hypericum perforatum). HRT may affect the action of other medicines:
- the epilepsy medicine lamotrigine, as the frequency of seizures may increase.
- medicines used to treat viral hepatitis C (HCV) (such as the combination therapy of ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir with dasabuvir or without dasabuvir, and the combination therapy of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir), as they may cause an increase in liver function test results [increase in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) enzyme activity] in women using combined hormonal contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol. Oestrogel contains estradiol instead of ethinyl estradiol. It is not known whether the use of Oestrogel with these HCV treatment regimens may cause an increase in ALT enzyme activity.
Tell the doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the patient is currently taking or has recently taken, including those obtained without a prescription, herbal medicines, other natural products, or skin care cosmetics containing alcohol, cleansers, or detergents. The doctor will provide advice.
Laboratory tests
If a blood test is necessary, the laboratory staff should be informed about the use of Oestrogel, as it may affect the results of some tests.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Oestrogel is recommended for use only in postmenopausal women.
If the patient becomes pregnant, she should stop using Oestrogel and consult a doctor.
Oestrogel contains ethanol
This medicine contains 500 mg of alcohol (ethanol) per 1.25 g dose, which is equivalent to 400 mg/g (40% w/w). It may cause a burning sensation on damaged skin. The medicine is flammable until it dries.
3. How to use Oestrogel
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
The doctor will prescribe the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible duration. If the patient feels that the action of the medicine is too strong or too weak, they should tell their doctor.
Oestrogel is a gel containing the female hormone estradiol. After applying the gel to the skin, it dries within 5 minutes, and the hormone is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream.
Apply a thin layer of gel to the entire arm, on the inner and outer side from the wrist to the shoulder and (or) on the inner surface of the thighs. Spread the gel over as large a skin surface as possible.
DO NOT apply the gel to the breasts or mucous membranes, especially not to the vaginal mucosa.
Before using a new bottle of gel, first fill the pump by pressing it and discard the first dose.
One press of the pump delivers 1.25 g of gel (1 dose), which corresponds to 0.75 mg of estradiol.
Where to apply Oestrogel
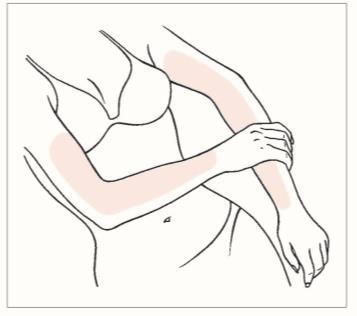

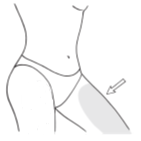
- The usual minimum dose is ONE dose (1.25 g of gel); it should be applied to one arm, from the wrist to the shoulder, and (or) to the inner surface of the thigh. The container holds at least 60 doses (1.25 g each) of gel. Apply one dose of Oestrogel gel daily for 21 days (3 weeks) and then take a 7-day break (1 week) (see "Applying Oestrogel gel" below).
Applying Oestrogel gel:
- the patient must apply the gel themselves,
- apply the gel in the evening or morning, preferably after washing, at the same time every day.
- for one hour after applying the gel, avoid contact between the skin and other adults and children. Spread the gel over as large a skin surface as possible on the arm from the wrist to the shoulder and (or) on the inner surface of the thighs, on undamaged healthy skin. If the skin remains sticky after 5 minutes of applying the gel, it means that the gel has not been spread thinly enough. Next time, spread the gel over a larger area of the arms and shoulders and/or the inner surface of the thighs. After applying the gel to the skin, always wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Do not allow others to touch the area of skin where the gel has been applied until it has dried, and cover it with clothing if necessary.
- Patients with a preserved uterus:The doctor will prescribe the lowest effective dose necessary. Apply one dose of Oestrogel gel daily for 21 days (3 weeks) and then take a 7-day break (1 week). Long-term use of estrogens without the addition of progestogen (e.g., progesterone) increases the risk of endometrial cancer in women with a preserved uterus. To this end, estrogens should be used in combination with progesterone for at least 12 to 14 days per month. The doctor will likely prescribe progesterone. Progesterone should be taken for at least 12 to 14 days in the monthly cycle. In the 4th week, when estrogen is not used, progestogen is also not used. Withdrawal bleeding ("menstruation") may occur then.
- Patients after uterus removal:In the case of a disease where uterine lining cells are also found in other locations outside the uterus (endometriosis), estrogen therapy should not be combined with progestogen if the patient has had their uterus removed. If the patient is using Oestrogel to treat postmenopausal symptoms and feels that the action of Oestrogel is too strong or too weak, they should consult a doctor.
Duration of treatment
The doctor will inform the patient how long to use Oestrogel. It is essential to follow this recommendation. Do not stop treatment prematurely; consult a doctor first.
Using a higher dose of Oestrogel than recommended
Unpleasant breast sensation (breast tension), bleeding, or nervousness may be symptoms of overdose, which usually resolve after reducing the amount of gel used.
In such cases, the dose of Oestrogel should be reduced with the doctor's consent.
In case of using a higher dose of Oestrogel than recommended, consult a doctor or pharmacist immediately.
Missing a dose of Oestrogel
Do not use a double dose the next day to make up for a missed dose. If there are less than 12 hours left until the next dose, take the dose at the usual time. If there are more than 12 hours left until the next dose, take the missed dose immediately and take the next dose at the usual time.
If surgery is necessary
Before surgery, inform the surgeon about the use of Oestrogel. It may be necessary to stop using Oestrogel 4 to 6 weeks before surgery to reduce the risk of blood clots [see section 2 "Blood clots in the veins (thrombosis)"]. Consult a doctor about when to resume using Oestrogel.
In case of any further doubts about using this medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following diseases are reported more frequently in women using HRT than in women not using HRT:
• breast cancer,
• abnormal growth or tumors of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia or cancer),
• ovarian cancer,
• blood clots in the legs or lungs (venous thromboembolism),
• heart disease,
• stroke,
• risk of dementia, if HRT is started after the age of 65.
More information about these side effects can be found in section 2.
Frequent: may occur in up to 1 in 10 people:painful menstruation, heavy menstrual bleeding, light bleeding (spotting), menstrual problems, vaginal discharge, unexpected vaginal bleeding, abnormal thickening of the uterine lining (endometrial hyperplasia), abdominal pain and cramps, abdominal swelling, nausea or vomiting, headache, muscle spasms, limb pain, nervousness and depression.
Uncommon: may occur in up to 1 in 100 people:benign breast tumor, uterine polyps, uterine fibroid growth, abnormal growth of uterine lining cells in inappropriate locations, causing pain (endometriosis), breast pain (mastodynia), worsening of estrogen-dependent tumors, migraine, dizziness, drowsiness, joint pain (arthralgia), superficial or deep vein thrombosis, vein pain and swelling (thrombophlebitis), peripheral edema, itching, sodium retention, feeling of swelling, weight change, rash, itching, brown spots on the skin (chloasma), abnormal liver function test results, liver tumors, gallstones.
Rare: may occur in up to 1 in 1,000 people:intolerance to contact lenses, severe allergic reactions (life-threatening), abnormal liver function test results, yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes indicating liver function disorders, glucose intolerance (especially in diabetic patients), bone pain, worsening of epilepsy (seizures), changes in sex drive, skin discoloration, acne, high blood pressure.
During HRT, the following side effects may occur:
- benign and malignant tumors that are affected by estrogen hormones, e.g., uterine lining cancer (endometrial cancer);
- heart attack and stroke;
- gallbladder disease;
- various skin disorders:
- skin discoloration, especially on the face or neck, known as "pregnancy spots" (chloasma);
- painful red skin nodules (erythema nodosum);
- rash with red, patchy, or ring-shaped lesions (erythema multiforme).
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any not listed in this leaflet, tell the doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel. +48 22 49 21 301, fax +48 22 49 21 309, website https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Oestrogel
Keep the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
This medicine does not require special storage precautions.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date, which is stated on the carton after the words "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month shown. The "Lot" abbreviation means batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask a pharmacist how to dispose of unused medicines. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Oestrogel contains
- The active substance of the medicine is estradiol (Estradiolum).
- The other ingredients are: ethanol 96% (see section 2 Oestrogel contains ethanol), carbomer, tromethamine, and purified water.
What Oestrogel looks like and contents of the pack
Oestrogel is available in packs containing 1, 2, or 3 multidose containers. Each 80 g pack consists of a container with a metering valve. One press of the pump delivers 1.25 g of gel containing 0.75 mg of estradiol. Each container holds 80 g of gel and provides at least 60 doses of 1.25 g each.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
Besins Healthcare SA
Rue Washington 80
1050 Ixelles – Belgium
Manufacturer
Besins Manufacturing Belgium
Groot-Bijgaardenstraat, 128 – B-1620 Drogenbos – Belgium
or
Laboratoires Besins International
13 rue Périer
Montrouge 92120
France
This medicine is authorized in the European Economic Area member states under the following names:
Belgium – Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg/dose gel transdermique
Bulgaria - Естрогел 0.75 mg/доза трансдермален гел
Czech Republic - Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg/dávka transdermální gel
Croatia - Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg po potisku transdermalni gel
Estonia - Estradiol Besins 0.75mg/annus transdermaalne geel
Lithuania – Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg / dozėje transderminis gelis
Luxembourg – Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg/ dose transdermal gel
Latvia - Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg/devā transdermālais gels
Netherlands - Oestrogel 0.75 mg/dosis transdermale gel
Norway - Estrogel 0.75 mg/dose transdermalgel
Poland – Oestrogel, 0.75 mg/dose, transdermal gel
Romania - Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg/doză gel transdermic
Slovakia - Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg/dávka transdermálny gél
Slovenia - Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg/potisk transdermalni gel
Sweden - Estrogel 0.75 mg/dos transdermal gel
Hungary - Estradiol Besins 0.75 mg/adag transzdermális gél
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 12/2023
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterBesins Manufacturing Belgium Laboratoires Besins International
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to OestrogelDosage form: Gel, 0.5 mgActive substance: estradiolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription requiredDosage form: Gel, 1 mgActive substance: estradiolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription requiredDosage form: Gel, 1 mg/gActive substance: estradiolPrescription required
Alternatives to Oestrogel in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Oestrogel in Spain
Alternative to Oestrogel in Ukraine
Online doctors for Oestrogel
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Oestrogel – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










