Moxifloxacin Kabi

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Moxifloxacin Kabi

How to use Moxifloxacin Kabi
Leaflet attached to the packaging: information for the user
Moxifloxacin Kabi, 400 mg/250 ml, solution for infusion
Moxifloxacin
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if you need to.
If you have any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
If the patient experiences any adverse reactions, including any adverse reactions not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist.
See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Moxifloxacin Kabi and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Moxifloxacin Kabi
- 3. How to use Moxifloxacin Kabi
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Moxifloxacin Kabi
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Moxifloxacin Kabi and what is it used for
Moxifloxacin Kabi contains the active substance - moxifloxacin, which belongs to a group of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones. Moxifloxacin Kabi has a bactericidal effect on bacteria that cause infections, if these bacteria are sensitive to moxifloxacin.
Moxifloxacin Kabi is used in adult patients to treat the following bacterial infections:
community-acquired pneumonia (pneumonia acquired outside the hospital);
skin and soft tissue infections.
Moxifloxacin Kabi is used to treat the above infections only when commonly used antibiotics cannot be used or are ineffective.
2. Important information before using Moxifloxacin Kabi
If the patient has any doubts about whether they belong to any of the groups described below, they should consult a doctor.
When not to use Moxifloxacin Kabi
If the patient is allergic to moxifloxacin, other antibiotics from the quinolone group, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
During pregnancy or breastfeeding.
In patients under 18 years of age.
If the patient has a history of disease or disorders of tendon function related to treatment with antibiotics from the quinolone group (see sections Warnings and precautionsand 4. Possible side effects).
If the patient has a congenital or acquired irregular heart rhythm (visible on an ECG - a test of the electrical activity of the heart).
If the patient has electrolyte imbalance disorders (especially low potassium or magnesium levels in the blood).
If the patient has: a very slow heart rate (called "bradycardia"), a weak heart (heart failure), a history of heart rhythm disorders, or if the patient is taking medications that cause abnormal changes in the ECG (see section Moxifloxacin Kabi and other medicines). Moxifloxacin Kabi may cause changes in the ECG, called QT interval prolongation, which means a delay in the conduction of electrical signals in the heart.
If the patient has severe liver disease or liver enzyme activity (aminotransferases) exceeding 5 times the upper limit of normal.
Warnings and precautions
Before taking this medicine
You should not take antibacterial medicines containing fluoroquinolones or quinolones, including Moxifloxacin Kabi, if you have experienced any severe adverse reaction while taking a quinolone or fluoroquinolone in the past. In such a situation, you should inform your doctor as soon as possible.
Before starting treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi, you should discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist.
It is essential to know the following before starting treatment:
Moxifloxacin Kabi may change the ECG recording of the heart, especially in women and elderly patients;
if you are taking medicines that lower potassium levels in the blood, you should consult your doctor before starting treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi (see also sections When not to use Moxifloxacin Kabiand Moxifloxacin Kabi and other medicines);
if you have diabetes, you should consult your doctor before starting treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi, as moxifloxacin may cause a risk of changing blood sugar levels;
if you have ever experienced a severe skin rash or peeling of the skin after taking moxifloxacin, you should consult your doctor before starting treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi;
if you have epilepsyor conditions that may cause seizures, you should inform your doctor before starting treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi;
if you have or have had mental health problems, you should consult your doctor before starting treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi;
if you have myasthenia(a rare disease that leads to muscle weakness), taking Moxifloxacin Kabi may worsen the symptoms of the disease; if this happens, you should consult your doctor immediately;
if you have been diagnosed with enlargement of a large blood vessel(aortic or large peripheral artery aneurysm), you should consult your doctor;
if you have had aortic dissection(tear of the aortic wall), you should consult your doctor;
if you have been diagnosed with mitral valve regurgitation, you should consult your doctor;
if there have been cases of aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection in your family, or congenital heart valve disease, or other risk factors or conditions (e.g., connective tissue diseases such as Marfan syndrome or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, Turner syndrome, Sjögren's syndrome [an autoimmune inflammatory disease] or vascular diseases such as Takayasu arteritis, giant cell arteritis, Behcet's disease, hypertension, or confirmed atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis [joint disease] or endocarditis [heart infection]), you should consult your doctor;
if you or anyone in your family has glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency(a rare inherited disease), you should inform your doctor, who will assess whether Moxifloxacin Kabi is a suitable medicine;
Moxifloxacin Kabi can only be administered intravenously (into a vein), and not intra-arterially.
Circumstances in which Moxifloxacin Kabi should be discontinued immediately
There is a small risk of severe, sudden allergic reaction(anaphylactic reaction or anaphylactic shock) even after the first dose. You should inform your doctor if you experience symptoms that may include: chest tightness, dizziness, nausea, or fainting, and a feeling of spinning when standing up.
Moxifloxacin Kabi may cause liver inflammation with a rapid and severe course, which can lead to life-threatening liver failure (including fatal outcomes, see section 4. Possible side effects). If you experience symptoms such as sudden deterioration of well-being, yellowing of the whites of the eyes, dark urine, itching of the skin, tendency to bleed, and disorders of thinking or insomnia, you should contact your doctor before taking the next dose.
Antibiotics from the quinolone group, including Moxifloxacin Kabi, may cause seizures. If seizures occur, you should discontinue Moxifloxacin Kabi immediately.
Mental health problemsmay occur, even after the first administration of a quinolone antibiotic, including Moxifloxacin Kabi. Very rarely, depression or mental health problems may lead to suicidal thoughts and self-aggressive behaviors, such as suicide attempts (see section 4. Possible side effects). If you experience such reactions, you should discontinue Moxifloxacin Kabi immediately.
Rarely, joint and tendon pain, as well as tendon inflammation or rupturemay occur. The risk is increased in elderly people (over 60 years old), after organ transplantation, in cases of kidney problems, or during corticosteroid treatment. Tendon inflammation and rupture may occur within the first 48 hours of treatment and even several months after discontinuation of Moxifloxacin Kabi. After the first symptoms of pain or tendon inflammation (e.g., in the ankle, wrist, elbow, shoulder, or knee), you should discontinue Moxifloxacin Kabi, consult your doctor, and rest the affected area. You should avoid excessive exertion, as it may increase the risk of tendon rupture (see sections When not to use Moxifloxacin Kabiand 4. Possible side effects).
Symptoms that should be reported to the doctor immediately if they occur during treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi
Heart palpitations or irregular heartbeatoccurring during treatment. Your doctor may order an ECG to check your heart rhythm.
Severe skin reactions
During treatment with moxifloxacin, severe skin reactions have been reported, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS).
Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN may initially appear as red spots with a target-like appearance or round spots, often with blisters on the torso. There may also be ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes (red and swollen eyes). The onset of these severe skin rashes is often preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms. The rash may progress to widespread skin peeling and life-threatening complications or lead to death.
AGEP appears at the beginning of treatment as a red, scaly, generalized rash with papules and blisters, accompanied by fever. The most common location is localized mainly on skin folds, torso, and upper limbs.
In DRESS syndrome, flu-like symptoms and a rash on the face appear initially, followed by a widespread rash with high body temperature, abnormal liver function tests, and an increased number of white blood cells (eosinophilia), as well as swollen lymph nodes.
If you experience a severe rash or any of these skin symptoms, you should discontinue moxifloxacin and consult your doctor or seek immediate medical attention.
The patient may rarely experience nerve damage symptomssuch as pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and weakness, especially in the feet and legs, as well as hands and arms. In such a case, you should discontinue Moxifloxacin Kabi and immediately inform your doctor to prevent the development of potentially irreversible disease.
Diarrheaoccurring during or after the use of antibiotics, including Moxifloxacin Kabi. If it worsens or persists, or if blood or mucus appears in the stool, you should discontinue Moxifloxacin Kabi and consult your doctor. In such a situation, you should not use medications that slow down or stop bowel movements (peristalsis).
In case of sudden severe abdominal, back, or chest pain, which may be a sign of an aortic aneurysm or aortic dissection, you should immediately go to the emergency department. The risk of these changes may be higher in patients treated with systemic corticosteroids.
In case of sudden shortness of breath, especially when lying down, or swelling of the ankles, feet, or abdomen, or palpitations (feeling of rapid or irregular heartbeat), you should immediately consult your doctor.
Visual disturbances or any vision problems.If these symptoms occur during treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist (see sections Driving and using machinesand 4. Possible side effects).
Fluoroquinolone antibiotics may cause an increase in blood sugar levelsto above normal levels (hyperglycemia) or a decrease in blood sugar levels to below normal levels (hypoglycemia), which may potentially lead to loss of consciousness (hypoglycemic coma) in severe cases (see section 4. Possible side effects). In patients with diabetes, blood sugar levels should be closely monitored.
During treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi, the patient should be aware that:
The risk of heart problemsmay increase with increasing dose and infusion rate into a vein;
elderly patients with kidney problemsshould drink an adequate amount of fluids, as dehydration may increase the risk of kidney failure;
quinolone antibiotics may increase sensitivity of the skin to sunlight and UV radiation; during treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi, you should avoid prolonged exposure to sunlight, strong sunlight, and use of sunbeds or other sources of UV radiation (see section 4. Possible side effects);
there is limited experience with sequential therapy (initial intravenous administration, followed by oral administration) with Moxifloxacin Kabi in the treatment of community-acquired pneumonia;
the efficacy of Moxifloxacin Kabi has not been established in the treatment of severe burns, deep tissue infections, and diabetic foot infections with osteomyelitis (bone infection).
Long-term, disabling, and potentially irreversible severe side effects
Fluoroquinolone/quinolone antibacterial medicines, including Moxifloxacin Kabi, have been associated with very rare but severe side effects. Some of these have been long-lasting (lasting for months or years), disabling, or potentially irreversible. These include: tendon pain, muscle pain, and joint pain in the upper and lower limbs, walking difficulties, abnormal sensations such as tingling, burning, itching, numbness, or pain (paresthesia), sensory disturbances, including vision, taste, and smell disorders, depression, memory impairment, severe fatigue, and severe sleep disturbances.
If any of these side effects occur after taking Moxifloxacin Kabi, you should immediately consult your doctor before continuing treatment. The patient and doctor will decide whether to continue treatment, also considering antibiotics from another group.
Children and adolescents
This medicine should not be used in children and adolescents under 18 years of age, as its efficacy and safety have not been established for this age group (see section When not to use Moxifloxacin Kabi).
Moxifloxacin Kabi and other medicines
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking, or have recently taken, and about any medicines you plan to take.
What to know when taking Moxifloxacin Kabi with other medicines
When taking Moxifloxacin Kabi with other medicines that affect heart function, the risk of heart rhythm disorders increases. Therefore, you should not take Moxifloxacin Kabi at the same time as the following medicines:
medicines belonging to the group of antiarrhythmic medicines (e.g., quinidine, hydroquinidine, disopyramide, amiodarone, sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide);
antipsychotic medicines (e.g., phenothiazines, pimozide, sertindole, haloperidol, sultopride);
tricyclic antidepressant medicines;
certain antibacterial medicines (e.g., saquinavir, sparfloxacin, intravenous erythromycin, pentamidine, antimalarial medicines, especially halofantrine);
certain antihistamine medicines (e.g., terfenadine, astemizole, mizolastine);
other medicines, such as cisapride, intravenous vincamine, bepridil, and difemanil.
You should tell your doctor:
if you are taking other medicines that may lower potassium levels in the blood [e.g., certain diuretics, certain laxatives, and enemas (large doses) or corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory medicines), amphotericin B];
if you are taking other medicines that may slow down your heart rate, as they may also increase the risk of serious heart rhythm disorders during treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi;
if you are taking oral anticoagulant medicines (e.g., warfarin), your doctor may order blood clotting tests.
Moxifloxacin Kabi with food, drink, and alcohol
Food, including dairy products, does not affect the action of Moxifloxacin Kabi.
You should not drink alcohol during treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a baby, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Do not useMoxifloxacin Kabi during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Animal studies do not show any fertility problems related to the use of this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Moxifloxacin Kabi may cause dizziness and a feeling of fainting, sudden, short-term (transient) loss of vision, or may cause short-term fainting. If you experience such symptoms, you should not drive vehicles or operate machines.
Moxifloxacin Kabi contains sodium
The maximum recommended daily dose of this medicine contains 1206 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt). This corresponds to 60% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
3. How to use Moxifloxacin Kabi
Moxifloxacin Kabi is always administered by a doctor or qualified medical staff.
The recommended dose for adult patients is one bottle or bag, once a day.
Moxifloxacin Kabi is intended for intravenous administration (into a vein). Your doctor should ensure that the medicine is administered in a continuous infusion lasting at least 60 minutes.
There is no need to modify the dose in elderly patients, patients with low body mass, or patients with impaired kidney function.
Duration of treatment
Your doctor will decide how long the treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi should last. In some cases, your doctor may start treatment with Moxifloxacin Kabi in the form of an infusion solution, and then continue treatment with an appropriate oral medicine.
The duration of treatment depends on the type of infection and the patient's response to treatment. The recommended duration of treatment is given below.
| Indication | Duration of treatment |
| Community-acquired pneumonia (pneumonia acquired outside the hospital) In most patients with pneumonia, treatment was switched to an oral medicine within 4 days. | 7-14 days |
| Skin and soft tissue infections In patients with complicated skin and soft tissue infections, the average duration of intravenous treatment was approximately 6 days, and the average total duration of treatment (infusion and then tablets) was 13 days. | 7-21 days |
It is essential to complete the full treatment cycle, even if you feel better after a few days. If the administration of the medicine is stopped too early, the infection may not be completely cured, and the disease may recur or worsen.
Do not exceed the recommended dose and duration of treatment.
Use of a higher than recommended dose of Moxifloxacin Kabi
If you suspect that you have received too high a dose of Moxifloxacin Kabi, you should immediately inform your doctor.
Missing a dose of Moxifloxacin Kabi
If you suspect that a dose of Moxifloxacin Kabi has been missed, you should immediately inform your doctor.
Discontinuation of Moxifloxacin Kabi
If the administration of the medicine is stopped too early, the infection may not be completely cured. If you want to stop taking Moxifloxacin Kabi earlier, you should consult your doctor.
In case of any further doubts about the use of this medicine, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
You should immediately consult your doctor and discontinue treatmentif you experience the following side effects, which may be life-threatening.
Rare side effects(may occur in less than 1 in 1,000 patients):
severe, rapidly spreading allergic reaction, including very rare life-threatening anaphylactic shock (e.g., difficulty breathing, low blood pressure, rapid heartbeat), angioedema (which may be life-threatening);
depression (very rarely leading to self-harm, e.g., suicidal thoughts or attempts);
severe diarrhea with blood and/or mucus in the stool (antibiotic-associated colitis, including very rare life-threatening pseudomembranous colitis);
increased blood sugar levels;
decreased urine output, swelling of the feet, ankles, or hands, fatigue, nausea, drowsiness, shortness of breath, or confusion in elderly patients with kidney disease (these may be signs of kidney failure).
Very rare side effects(may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
depersonalization (feeling of changed identity), psychosis (which may lead to self-harm, e.g., suicidal thoughts or attempts);
life-threatening irregular heartbeat (torsades de pointes) or cardiac arrest;
fulminant hepatitis, which may lead to life-threatening liver failure (including fatal outcomes, see section 4. Possible side effects);
severe skin rash, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. It may appear as red spots with a target-like appearance or round spots, often with blisters on the torso, peeling skin, ulcers in the mouth, throat, nose, genitals, and eyes, and may be preceded by fever and flu-like symptoms (these side effects may be life-threatening);
syndrome associated with impaired water excretion and low sodium levels (SIADH);
vasculitis (which may manifest as red spots on the skin, usually on the lower legs, and joint pain);
tendon rupture, joint inflammation, muscle cramps, muscle weakness;
worsening of myasthenia symptoms;
decreased blood sugar levels;
loss of consciousness due to significantly decreased blood sugar levels (hypoglycemic coma).
Frequency not known(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight or UV radiation (see also section 2. Warnings and precautions);
acutely limited, red, scaly patches with blisters or without blisters, which appear within a few hours of moxifloxacin administration and heal with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation; they usually recur in the same area of skin or mucous membrane after re-exposure to moxifloxacin.
- increased sensitivity of the skin to sunlight or UV radiation (see also section 2. Warnings and precautions);
- acutely limited, red, scaly patches with blisters or without blisters, which appear within a few hours of moxifloxacin administration and heal with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation; they usually recur in the same area of skin or mucous membrane after re-exposure to moxifloxacin.
The following side effects have been observed more frequently in patients receiving moxifloxacin intravenously.
Common side effects(may occur in less than 1 in 10 patients):
increased activity of the liver enzyme gamma-glutamyltransferase in the blood.
Uncommon side effects(may occur in less than 1 in 100 patients):
abnormally fast heart rate;
low blood pressure;
swelling (of hands, feet, ankles, lips, mouth, throat);
severe diarrhea with blood and/or mucus (antibiotic-associated colitis), very rarely leading to life-threatening complications;
seizures;
hallucinations;
kidney problems (including increased values of kidney function tests, such as urea and creatinine), kidney failure.
The following side effects have been reported with other quinolone antibiotics and may also occur with Moxifloxacin Kabi.
Very rare side effects(may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
increased sodium levels in the blood, increased calcium levels in the blood;
increased breakdown of red blood cells (hemolytic anemia).
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, you should inform your doctor or pharmacist before taking the next dose.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
tel.: +48 22 49 21 301
fax: +48 22 49 21 309
website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Moxifloxacin Kabi
The medicine is administered by qualified medical staff, who are responsible for the proper storage of the medicine both before and during administration to the patient, as well as for its proper disposal.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the bottle or bag after "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Do not store in a refrigerator or freeze.
Store the bottle in the outer packaging to protect it from light.
For single use only. Unused solution should be discarded.
Storage at low temperatures may cause the formation of a precipitate, which will redissolve at room temperature.
Do not use this medicine if you can see any particles or if the solution is cloudy.
Your doctor or medical staff are responsible for the storage of Moxifloxacin Kabi, the quality of the medicine after opening the packaging, and if it is not used immediately. They are also responsible for the proper disposal of unused medicine.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Moxifloxacin Kabi contains
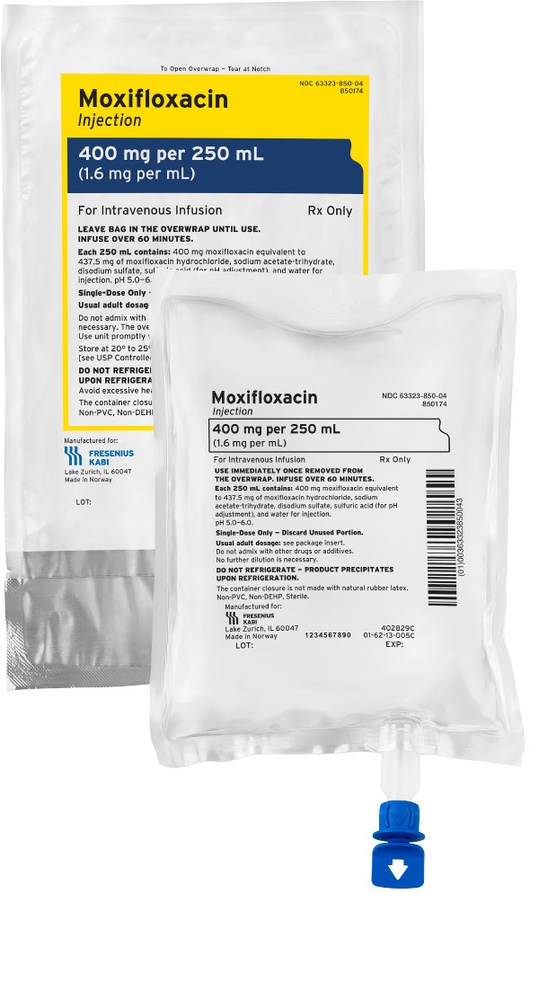
The active substance of the medicine is moxifloxacin. Each bottle or bag with a capacity of 250 ml contains 400 mg of moxifloxacin (in the form of moxifloxacin hydrochloride). 1 ml contains 1.6 mg of moxifloxacin (in the form of moxifloxacin hydrochloride).
The other ingredients are: sodium acetate trihydrate, sodium sulfate anhydrous, sulfuric acid (to adjust pH), and water for injections (see section Moxifloxacin Kabi contains sodium).
What Moxifloxacin Kabi looks like and what the packaging contains
Moxifloxacin Kabi is a clear, yellow solution for infusion.
1, 10, 20, 25, or 40 bags in a cardboard box.
A polyolefin bag (freeflex) with two ports (injection port and infusion port), placed in an outer aluminum bag, containing 250 ml of solution.
1, 10, 20, 25, or 40 bottles in a cardboard box.
LDPE (KabiPac) bottles containing 250 ml of solution.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Fresenius Kabi Polska Sp. z o.o.
Al. Jerozolimskie 134
02-305 Warsaw
Manufacturer
KabiPac bottles
Fresenius Kabi Polska Sp. z o.o.
ul. Sienkiewicza 25
99-300 Kutno
Freeflexbags
HP Halden Pharma AS
Svinesundsveien 80
1788 Halden
Norway
To obtain more detailed information, you should contact the marketing authorization holder:
Fresenius Kabi Polska Sp. z o.o.
Al. Jerozolimskie 134
02-305 Warsaw
tel.: +48 22 345 67 89
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Austria
Moxifloxacin Kabi 400 mg Infusionslösung
Belgium
Moxifloxacine Fresenius Kabi 400 mg/250 ml oplossing voor infusie
Bulgaria
Моксифлоксацин Каби 400 mg/250 ml инфузионен разтвор
Croatia
Moxifloxacin Kabi 400 mg/250 ml otopina za infuziju
Czech Republic
Moxifloxacin Kabi 400 mg/250 ml infuzní roztok
Denmark
Moxifloxacin Fresenius Kabi
Finland
Moxifloxacin Fresenius Kabi 400 mg/250 ml infuusioneste, liuos
Spain
Moxifloxacino Kabi 400 mg/250 ml solución para perfusión
Netherlands
Moxifloxacine Fresenius Kabi 400 mg/250 ml oplossing voor infusie
Ireland
Moxifloxacin 400 mg/250 ml solution for infusion
Luxembourg
Moxifloxacin Kabi 400 mg/250 ml solution pour perfusion
Germany
Moxifloxacin Kabi 400 mg Infusionslösung
Poland
Moxifloxacin Kabi
Romania
Moxifloxacina Kabi 400 mg/250 ml soluţie perfuzabilă
Slovakia
Moxifloxacin Kabi 400 mg/250 ml infúzny roztok
Slovenia
Moksifloksacin Kabi 400 mg/250 ml raztopina za infundiranje
Sweden
Moxifloxacin Fresenius Kabi 400 mg/250 ml, infusionsvätska, lösning
Hungary
Moxifloxacin Kabi 400 mg/250 ml oldatos infúzió
Date of last revision of the leaflet:01.05.2024
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Moxifloxacin Kabi can be administered through a three-way tap together with the following solutions:
water for injections, 0.9% sodium chloride solution, 5% and 10% glucose solution, Ringer's solution, and complex sodium lactate solution (Hartmann's solution, Ringer's solution with lactate).
Moxifloxacin Kabi should not be administered with other medicines.
The following solutions have been found to be incompatible with moxifloxacin in solution for infusion:
10% and 20% sodium chloride solutions;
4.2% and 8.4% sodium bicarbonate solutions.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterFresenius Kabi Polska Sp. z o.o. HP Halden Pharma AS
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Moxifloxacin KabiDosage form: Tablets, 400 mgActive substance: moxifloxacinManufacturer: Lek Pharmaceuticals d.d. Lek Pharmaceuticals d.d. LEK S.A. Salutas Pharma GmbH S.C. Sandoz S.R.L.Prescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 400 mgActive substance: moxifloxacinPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 400 mgActive substance: moxifloxacinManufacturer: Krka, d.d., Novo mesto Krka-Farma d.o.o. TAD Pharma GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Moxifloxacin Kabi in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Moxifloxacin Kabi in Spain
Alternative to Moxifloxacin Kabi in Ukraine
Online doctors for Moxifloxacin Kabi
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Moxifloxacin Kabi – subject to medical assessment and local rules.