
Microlax

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Microlax

How to use Microlax
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Microlax, 4.465 g/5 ml + 0.45 g/5 ml + 0.0645 g/5 ml, rectal solution
liquid sorbitol (crystallizing) sodium citrate + sodium lauryl sulfoacetate 70%
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
This medicine should always be used exactly as described in the patient leaflet or according to the doctor's or pharmacist's instructions.
- This leaflet should be kept in case it needs to be read again.
- If advice or additional information is needed, the pharmacist should be consulted.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any possible side effects not listed in the leaflet, the doctor or pharmacist should be informed. See section 4.
- If there is no improvement after a few days or the patient feels worse, the doctor should be contacted.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Microlax and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Microlax
- 3. How to use Microlax
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Microlax
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Microlax and what is it used for
Pharmacotherapeutic group: rectal solution, ATC code: A06AG11
Microlax belongs to a group of medicines called laxatives. It works by softening the stool and causing bowel emptying (defecation).
Microlax is used to treat occasional constipation.
The medicine can only be used in adults.
2. Important information before using Microlax
When not to use Microlax:
- if the patient is allergic to the active substances (sorbitol, sodium citrate, sodium lauryl sulfoacetate) or any of the other ingredients of this medicine listed in section 6;
- if the patient has abdominal pain of unknown cause;
- if the patient is taking a cation exchange resin based on calcium or sodium sulfonate polystyrene (orally or rectally) - a medicine used to treat hyperkalemia.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Microlax, the doctor or pharmacist should be consulted.
The doctor should be informed if the patient has:
- hemorrhoids;
- anal fissure (a change in the anal canal that causes pain during bowel movements, which can last for several hours);
- Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis (diseases associated with inflammation of the rectum and colon, characterized by symptoms such as abdominal pain,
diarrhea with mucus or blood, and frequent fatigue).
Microlax and other medicines
The doctor or pharmacist should be told about all medicines the patient is taking, has recently taken, or plans to take.
Microlax should not be used with calcium or sodium sulfonate polystyrene (taken orally/rectally).
No other rectal medicines should be taken at the same time as Microlax, as they may be removed from the gut and not absorbed.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a baby, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Driving and using machines
This medicine has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
Microlax contains sorbic acid, which may cause local skin reactions (e.g., contact dermatitis).
3. How to use Microlax
This medicine should always be used exactly as described in the patient leaflet or according to the doctor's or pharmacist's instructions. If in doubt, the doctor or pharmacist should be consulted.
Dosage
The recommended dose is one tube per day.
Method of administration
The medicine is used rectally. It is not necessary to lie down to use the medicine or while waiting for it to work.
- 1. Break the tip, then gently press the tube until a drop appears
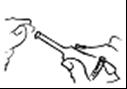
a drop.
- 5. Withdraw the applicator while continuing to press the tube.
The medicine usually works within 5 to 20 minutes.
If the patient remains in a lying position for a long time, the effects may be observed after a longer period (more than 1 hour).

- 2. Spread this drop on the tip of the applicator.

- 3. Insert the entire tip of the applicator into the rectum.

- 4. Squeeze the entire contents of the tube.

Duration of treatment
Without consulting a doctor, the medicine should not be used for more than a few days.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been reported with an unknown frequency:
- Abdominal pain
- Perianal discomfort
- Loose stools
- Hypersensitivity reactions (e.g., hives)
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, the doctor or pharmacist should be informed. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products
of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, phone: 22 49-21-301, fax: 22 49-21-309,
e-mail: [email protected]
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Microlax
No special precautions are required for storage.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The medicine should not be used after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The pharmacist should be asked how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Microlax contains
- The active substances of the medicine are: Sorbitol, liquid (crystallizing) ……………4.4650 g Sodium citrate …………………………….. 0.4500 g Sodium lauryl sulfoacetate 70% ………..... 0.0645 g in 5 ml of rectal solution.
- The other ingredients are sorbic acid (see section 2), glycerol, and purified water.
What Microlax looks like and what the packaging contains
The medicine is a rectal solution.
It is a colorless, viscous solution containing small air bubbles, placed in single-dose containers.
The packaging contains 4, 6, 12, or 50 single-dose containers.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
McNeil AB
Box 941
251 09 Helsingborg
Sweden
Manufacturer
Delpharm Orléans
5 Avenue de Concyr
45071 Orléans Cedex 2
France
Janssen Cilag – Val de Reuil
Domaine de Maigremont
27100 Val de Reuil
France
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
France:
Sorbitol / Citrate de sodium / Laurilsulfoacétate de sodium Johnson & Johnson
Bulgaria:
Microlax
Croatia:
Microlax
Cyprus:
Microlax
Greece:
Microlax
Poland:
Microlax
Romania:
Microlax
Slovakia:
Microlax
Slovenia:
Microlax
Hungary:
Microlax végbéloldat
Italy:
Stitilax
Date of last revision of the leaflet: January 2024
<----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------->
INFORMATION ABOUT CONSTIPATION
What to know
Constipation is defined as a limitation of the number of bowel movements to less than 3 per week.
This definition is not absolute. The standard duration of intestinal transit, and thus the frequency of bowel movements, can vary greatly from person to person. It is therefore important to consider the discomfort or problems associated with slowed transit.
In the case of constipation, there may be a feeling of discomfort in the abdominal cavity. Defecation is difficult, and even painful. It is often accompanied by a feeling of incomplete emptying. The stools are hard and small. Cramps or bloating may occur.
Occasional constipation usually results from changes in daily habits (traveling abroad, changes in diet, stress, etc.) or from withholding stool.
Dietary habits and lifestyle (lack of physical activity) can also disrupt bowel function, leading to longer periods of constipation (chronic constipation).
Other factors that may lead to constipation: certain medications (certain painkillers, antidepressants, antitussives, antacids containing aluminum compounds, etc.); in women: certain periods of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, or menopause.
What actions can be taken
Isolated cases of constipation, although unpleasant, are not serious.
Simple recommendations for a healthy lifestyle usually facilitate intestinal transit and bowel movements:
- Green vegetables rich in fiber and fresh fruits that facilitate intestinal transit should be eaten.
Whole grain bread or biscuits with bran can also be gradually introduced into the diet in moderate amounts.
- Fatty and sweet foods should be avoided.
- A sufficient amount of fluids should be taken regularly throughout the day (at least 1.5 liters per day): water, fruit juices, or soups should not be limited.
- The toilet should be visited at a set time (usually 30 to 60 minutes after meals) without making excessive attempts to defecate. The body will get used to a regular schedule. Time should be allowed.
- Exercise and physical activity, such as walking, which are an excellent way to combat constipation, should not be forgotten.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterDelpharm Orlenas JNTL Consumer Health (France) SAS
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to MicrolaxDosage form: Solution, (32.2 mg + 139 mg)/mlActive substance: sodium phosphateManufacturer: Laboratorium Galenowe Olsztyn Sp. z o.o.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Powder, 13.7 gActive substance: macrogol, combinationsPrescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 5 mgActive substance: bisacodylPrescription not required
Alternatives to Microlax in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Microlax in Ukraine
Alternative to Microlax in Spain
Online doctors for Microlax
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Microlax – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














