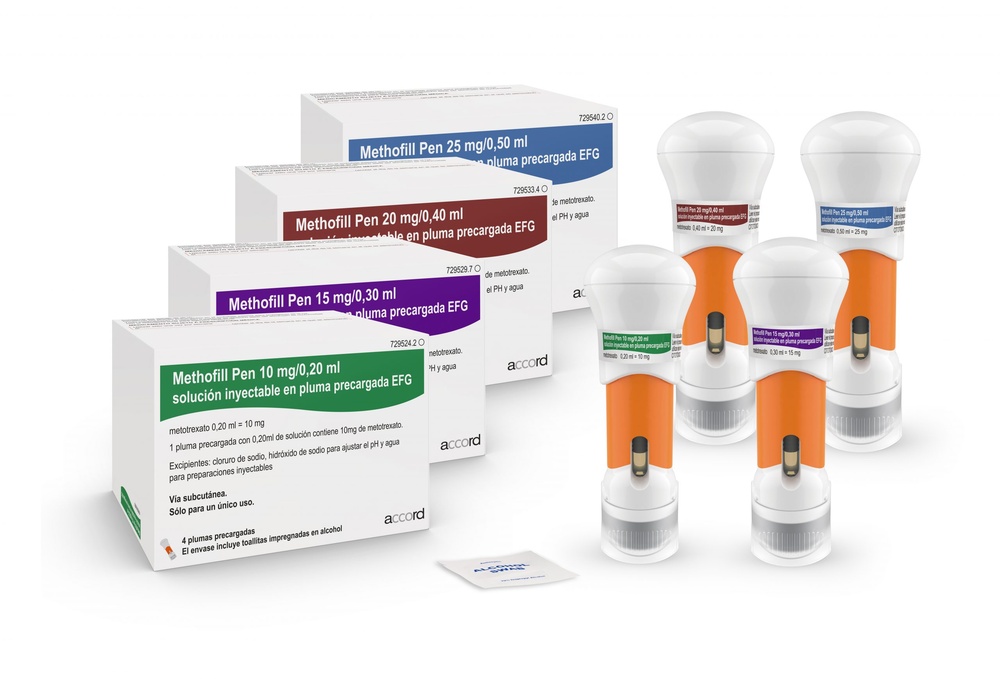
How to use Methofill Sd
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Methofill SD, 7.5 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 10 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 12.5 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 15 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 17.5 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 20 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 22.5 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 25 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 27.5 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methofill SD, 30 mg, solution for injection in a pre-filled injector
Methotrexate
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if you have any doubts.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse (see section 4).
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Methofill SD and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Methofill SD
- 3. How to use Methofill SD
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Methofill SD
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Methofill SD and what is it used for
The active substance of Methofill SD is methotrexate.
Methotrexate has the following properties:
- It inhibits the growth of certain rapidly dividing cells
- It reduces the activity of the immune system (the body's defense mechanisms)
- It has anti-inflammatory effects
Indications for the use of Methofill SD:
- Rheumatoid arthritis in adults (RA) is a chronic disease characterized by inflammation of the joint lining. The synovial membranes produce fluid that acts as a lubricant for many joints. Inflammation causes thickening of the membranes and swelling of the joints.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis, if treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) has been ineffective. (Juvenile arthritis occurs in children and adolescents under the age of 16.)
- Severe psoriatic arthritis in adults (psoriatic arthritis particularly affects the fingers and toes, with psoriatic lesions on the skin and nails).
- Severe psoriasis resistant to other treatments (psoriasis is a common chronic skin disease characterized by red patches covered with thick, dry, silvery, tightly adhering scales).
- Crohn's disease in adults (it is an inflammatory bowel disease that causes symptoms such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, or weight loss).
Methofill SD modifies and slows down the progression of the disease.
2. Important information before using Methofill SD
When not to use Methofill SD
- if the patient is allergic to methotrexate or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has severe liver or kidney disease or blood disorders;
- if the patient regularly consumes large amounts of alcohol;
- if the patient has a severe infection, such as tuberculosis, HIV infection, or other immune deficiency syndromes;
- if the patient has ulcers in the mouth, stomach, or intestines;
- if the patient is receiving a vaccine containing live microorganisms;
- if the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding (see "Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility").
Warnings and precautions
Before starting Methofill SD, discuss with your doctor or pharmacist:
- if the patient is elderly, frail, or in poor general condition;
- if the patient has liver function disorders;
- if the patient has dehydration (lack of water in the body);
- if the patient has diabetes and is being treated with insulin.
During methotrexate treatment, cases of acute bleeding from the lungs have been reported in patients with underlying rheumatologic disease. If the patient experiences hemoptysis, i.e., coughing up sputum with blood, they should immediately consult a doctor.
Special precautions for use of Methofill SD
Methotrexate temporarily disrupts the production of sperm and egg cells; in most cases, this effect disappears. Methotrexate can cause miscarriage and severe birth defects. Female patients should avoid becoming pregnant while taking methotrexate and for at least 6 months after stopping treatment. Male patients should avoid impregnating their partner while taking methotrexate and for at least 3 months after stopping treatment. See also "Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility".
Recommended tests and precautions:
Even if methotrexate is used in low doses, severe side effects may occur. To detect them early, the doctor must perform tests and laboratory tests.
Before starting treatment
Before starting treatment, blood tests will be performed to check if the patient has a sufficient number of blood cells. Blood will also be tested for liver function to determine if the patient has hepatitis. Additionally, serum albumin (protein in the blood), hepatitis infection, and kidney function will be checked. The doctor may also decide to perform other liver tests, including imaging tests or a liver biopsy.
During treatment
The doctor may perform the following tests:
- examination of the mouth and throat for mucosal changes, such as inflammation or ulcers;
- blood tests/morphology with assessment of blood cell count and measurement of methotrexate concentration in serum;
- blood tests to monitor liver function;
- imaging tests to monitor liver condition;
- liver biopsy for further examination;
- blood tests to monitor kidney function;
- monitoring of respiratory function and, if necessary, lung function tests.
It is very important for the patient to attend scheduled tests.
If the results of any of these tests are abnormal, the doctor will adjust the treatment accordingly.
Elderly patients
Elderly patients treated with methotrexate should be closely monitored by the doctor to detect any potential side effects as early as possible. Age-related liver and kidney function disorders, as well as low folate reserves in the elderly, require relatively low doses of methotrexate.
Methotrexate may affect the immune system and vaccination results. It may also affect the results of immunological tests. During methotrexate treatment, latent chronic diseases (e.g., shingles, tuberculosis, hepatitis B or C) may reactivate.
During Methofill SD treatment, live vaccines should not be administered.
Methotrexate may increase skin sensitivity to sunlight. Intensive sun exposure should be avoided, and sunbeds or tanning lamps should not be used without consulting a doctor.
To protect the skin from intense sunlight, appropriate clothing or a high-protection sunscreen should be used.
A recurrence of radiation-induced skin reactions and sunburn (so-called "recall reaction") may occur during methotrexate treatment. Psoriatic skin lesions may worsen during UV light exposure and concurrent methotrexate administration.
Lymphoma (lymph node enlargement) may occur. In such cases, treatment should be discontinued.
Diarrhea may be a sign of toxic effects of Methofill SD and requires treatment discontinuation.
If the patient experiences diarrhea, they should inform their doctor.
There have been reports of certain brain disorders (encephalopathy/leukoencephalopathy) in oncology patients receiving methotrexate. It cannot be excluded that these side effects may occur in patients taking methotrexate for other indications.
If the patient, their partner, or caregiver notices new or worsening neurological symptoms, including general muscle weakness, vision disturbances, changes in thinking, memory, and orientation leading to disorientation and personality changes, they should immediately consult a doctor, as these may be symptoms of a very rare, severe brain infection called progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML).
Methofill SD and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take. This includes medicines that you will take in the future.
Concomitant use of certain medicines may affect the action of Methofill SD:
- antibiotics such as tetracyclines, chloramphenicol, non-absorbable broad-spectrum antibiotics, penicillins, glycopeptides, sulfonamides, ciprofloxacin, and cephalothin (medicines used to prevent and treat certain infections);
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or salicylates [pain-relieving and/or anti-inflammatory medicines such as acetylsalicylic acid, diclofenac, and ibuprofen or pyrazoles];
- probenecid (used to treat gout);
- weak organic acids such as loop diuretics (diuretics);
- medicines that may harm bone marrow function, such as trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (a bactericidal agent) or pyrimethamine;
- other medicines used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, such as leflunomide, sulfasalazine, and azathioprine);
- cyclosporine (an immunosuppressive agent);
- mercaptopurine (a cytostatic agent);
- retinoids (medicines used to treat psoriasis and other skin diseases);
- theophylline (a medicine used to treat asthma and other lung diseases);
- certain medicines used to treat stomach diseases, such as omeprazole and pantoprazole;
- blood glucose-lowering medicines (medicines that reduce blood sugar levels).
It is especially important to inform your doctor about the use of:
- metamizole (synonyms: novaminsulfone and dipyrone) (a strong pain-relieving and/or antipyretic medicine).
Vitamin products containing folic acid should only be used if prescribed by a doctor, as they may reduce the effect of methotrexate.
Methofill SD with food, drink, and alcohol
During Methofill SD treatment, avoid consuming alcohol and large amounts of coffee, caffeinated beverages, and black tea.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Pregnancy
Do not use Methofill SD if you are pregnant or trying to become pregnant. Methotrexate may cause birth defects, harm the unborn child, or cause miscarriage. This is related to developmental abnormalities of the skull, face, heart, blood vessels, brain, and limbs. Therefore, it is very important that female patients do not take methotrexate if they are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. If the patient is of childbearing age, it must be definitively confirmed that she is not pregnant before starting treatment, by taking appropriate measures, such as a pregnancy test. The patient should avoid becoming pregnant while taking methotrexate and for at least 6 months after stopping treatment, using reliable contraception methods throughout this period (see also "Warnings and precautions").
If the patient becomes pregnant during treatment or suspects that she may be pregnant, she should consult a doctor as soon as possible. The patient should receive advice on the potential harmful effects of treatment on the child.
If the patient plans to become pregnant, she should consult her doctor, who may refer her to a specialist for advice before planned treatment begins.
Male fertility
Available evidence does not indicate an increased risk of birth defects or miscarriages after the father has taken methotrexate at a dose below 30 mg/week. However, this risk cannot be entirely excluded. Methotrexate may be genotoxic, meaning it can cause genetic mutations. Methotrexate may affect sperm and cause birth defects. Therefore, male patients should avoid impregnating their partner and should not donate sperm while taking methotrexate and for at least 3 months after stopping treatment.
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding should be discontinued before starting and during Methofill SD treatment.
Driving and using machines
During Methofill SD treatment, side effects such as fatigue and dizziness may occur. Therefore, the ability to drive vehicles or operate machinery may be impaired in some cases.
In case of drowsiness or fatigue, do not drive or operate machinery.
Methofill SD contains sodium
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per dose, which means it is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to use Methofill SD
This medicine should always be used as directed by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
The doctor will decide on the dosage, which will be individualized for the patient.
The effects of treatment are usually visible only after 4-8 weeks.
Methofill SD is administered subcutaneously (under the skin) by a doctor or medical staff, or under their supervision, only once a week. The day of injection should be determined by the patient in consultation with their doctor.
Important warning regarding Methofill SD dosing (methotrexate):
In the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis, and Crohn's disease, Methofill SD should be used only once a week. Using too high a dose of Methofill SD (methotrexate) can be fatal. Read section 3 of this leaflet carefully. If you have any questions before using this medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Use in children and adolescents
The doctor will decide on the appropriate dose for children and adolescents with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Methofill SD is not recommended for use in children under 3 years of age due to insufficient experience in this age group.
Method and duration of administration
Methofill SD is injected once a week!
The treatment duration is determined by the doctor.
Instructions for administration:
Read the entire instruction manual for Methofill SD in the pre-filled injector.
Self-administration of the injector requires proper training by a doctor.
In case of any doubts, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Before administration:
- choose a clean and well-lit place,
- check the expiration date of the medicine; do not use it if the date has expired,
- prepare an alcohol swab and a sharps container.
Preparation for administration:

- Wash your hands with soap and warm water
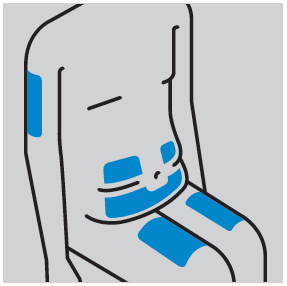
- Choose the injection site (abdomen or thigh if the patient is self-administering, or optionally the back of the arm if the injection is administered by a doctor or caregiver)
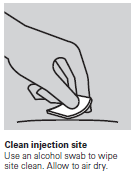
- Clean the area around the chosen injection site with an alcohol swab. Let it dry.
Before injection:

- Visually inspect the solution for color, turbidity, or presence of particles before administration.
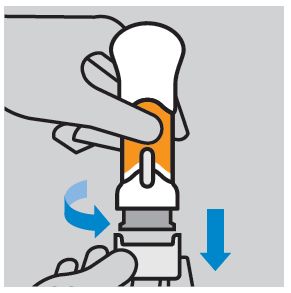
- Remove the protective plastic cap: twist and pull it down. After removing the cap, do not touch the needle shield. Discard the cap and do not replace it. Do not administer the injection if the injector is pressed after removing the cap.
- Administer the injection within 5 minutes of removing the cap.
Injection:
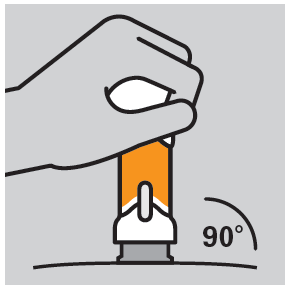
- Apply the injector to the chosen injection site at a right angle (90°).
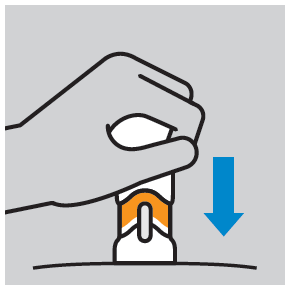
- Press the injector plunger until the entire dose is administered. Administer the injection at a comfortable speed for the patient. Do not change the position of the injector during administration.
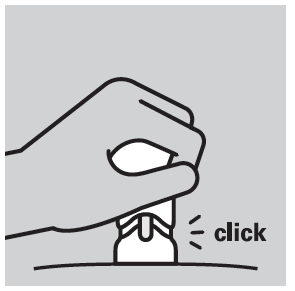
- Maximum plunger depression is indicated by a characteristic click; the orange dose indicator becomes invisible.
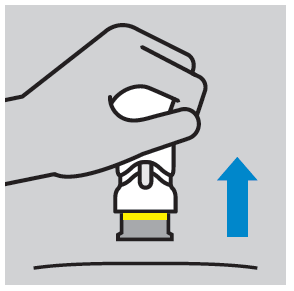
- After the injection, a yellow ring is visible, indicating the needle shield lock.
Disposal:

- Dispose of the used Methofill SD injector by throwing it into a sharps container. Guidelines for handling such waste may vary depending on the country/region. For current guidelines, consult your doctor or pharmacist. Do not throw the used injector into a regular trash can.
Avoid contact between methotrexate and skin or mucous membranes. In case of contamination, rinse the contaminated area with plenty of water immediately.
If the patient or someone in their environment is injured by the injector needle, they should immediately inform their doctor and not use that injector.
Taking a higher dose of Methofill SD than recommended
In case of taking a higher dose than recommended, inform your doctor immediately.
Missing a dose of Methofill SD
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping Methofill SD treatment
In case of stopping Methofill SD treatment, inform your doctor immediately.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Methofill SD can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The frequency and severity of side effects depend on the dose and frequency of administration. Since severe side effects may occur even at low doses, regular medical tests are necessary. The treating doctor should order tests to rule out abnormalities in blood parameters (e.g., low white blood cell count, platelet count, or lymphoma) and changes in liver and kidney function.
Tell your doctor immediatelyif you experience any of the following symptoms, as they may indicate severe, potentially life-threatening side effects that require urgent treatment:
- persistent, non-productive dry cough, shortness of breath, and fever; these may be symptoms of pneumonia [common]
- hemoptysis, i.e., coughing up sputum with blood;these may be symptoms of pulmonary bleeding [frequency not known]
- symptoms of liver damage, such as yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes; methotrexate may cause chronic liver damage (liver cirrhosis), scarring (liver fibrosis), fatty liver degeneration [all uncommon], acute liver inflammation (acute hepatitis) [rare], and liver failure [very rare]
- allergy symptoms, such as skin rash, including red, itchy skin, swelling of hands, feet, ankles, face, lips, mouth, or throat (which may cause difficulty swallowing or breathing and a feeling of impending fainting; these may be symptoms of severe allergic reactions or anaphylactic shock [rare]
- symptoms of kidney damage, such as swelling of hands, feet, or ankles, or changes in urine frequency (oliguria) or decreased urine volume (anuria); these may be symptoms of kidney failure [rare]
- infection symptoms, such as fever, chills, pain, or sore throat; methotrexate may increase the risk of infections. Severe infections, such as a specific type of pneumonia (Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia) or sepsis [rare]
- symptoms such as weakness on one side of the body (stroke) or pain, swelling, redness, and warmth in one leg (deep vein thrombosis). This can happen when a blood clot blocks the blood vessel. (thromboembolic event) [rare]
- fever and severe deterioration of general health or sudden fever, accompanied by sore throat or mouth ulcers;methotrexate may cause severe reduction of white blood cell count (agranulocytosis) and severe bone marrow suppression [very rare]
- unexpected bleeding, such as bleeding from the gums, blood in the urine, or appearance of blood blisters;these may be symptoms of significant reduction of platelet count due to severe bone marrow suppression [very rare]
- symptoms such as severe headache, often accompanied by fever, stiff neck, nausea, vomiting, disorientation, and sensitivity to lightmay indicate meningitis (acute aseptic meningitis) [very rare]
- in patients with cancer receiving methotrexate, certain brain disorders (encephalopathy/leukoencephalopathy) have been reported. It cannot be excluded that these side effects may occur in patients taking methotrexate for other indications. Symptoms of these brain disorders may include: altered mental state, movement disorders (ataxia), vision disturbances, or memory disturbances [frequency not known]
- severe skin rash or blisters on the skin (which may also occur in the mouth, eyes, and genital area);these may be symptoms of very rare conditions called Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome) [very rare]
Other side effects that may occur:
Very common:may occur in more than 1 in 10 people
- mouth ulcers, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, abdominal pain
- abnormal liver function test results (ASAT, ALAT, bilirubin, alkaline phosphatase)
Common:may occur in up to 1 in 10 people
- mouth ulcers, diarrhea
- skin rash, redness, itching
- headache, fatigue, drowsiness
- reduced blood cell production leading to reduced white blood cell, red blood cell, and/or platelet count
Uncommon:may occur in up to 1 in 100 people
- throat inflammation
- inflammation of the intestines, vomiting, pancreatitis, black or tarry stools, ulcers, and bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract
- reactions similar to sunburn due to increased skin sensitivity to sunlight, hair loss, increased number of rheumatoid nodules, shingles, blood vessel inflammation, rash similar to herpes, hives
- diabetes onset
- dizziness, confusion, depression
- reduced serum albumin levels
- reduced blood cell count, including platelets
- inflammation and ulcers of the bladder or vagina, kidney function disorders, urination disorders
- joint pain, muscle pain, reduced bone density
Rare:may occur in up to 1 in 1000 people
- gum inflammation
- increased skin pigmentation, acne, blue spots on the skin due to bleeding from blood vessels (bruises, petechiae)
- allergic blood vessel inflammation
- reduced antibody levels in the blood
- infections (including reactivation of latent, chronic infections), eye redness (conjunctivitis)
- mood changes
- vision disturbances
- inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart, fluid accumulation in the sac, heart function disorders due to fluid accumulation in the sac
- low blood pressure
- scarring of lung tissue (pulmonary fibrosis), shortness of breath, and asthma; fluid accumulation in the lung lining
- stress fractures of bones
- electrolyte disturbances
- fever, impaired wound healing
Very rare:may occur in up to 1 in 10,000 people
- acute toxic dilation of the intestine (toxic megacolon)
- increased nail pigmentation, acute paronychia (infection of the nail bed), furunculosis (boils), visible enlargement of small blood vessels
- local damage (sterile abscess formation, changes in fatty tissue) at the injection site
- pain, muscle weakness, or numbness, tingling, or reduced reaction to stimuli, changes in taste (metallic taste), seizures, paralysis, acute aseptic meningitis
- non-inflammatory eye disease (retinopathy), vision impairment
- reduced libido, impotence, breast enlargement in men
- sperm production disorders (oligospermia), menstrual disorders, vaginal discharge
- lymph node enlargement (lymphoma)
- lymphoproliferative disorders (overproduction of white blood cells)
Frequency not known:cannot be estimated from available data
- increased white blood cell count
- nosebleeds
- proteinuria
- weakness (asthenia)
- pulmonary bleeding
- jawbone damage (due to overproduction of white blood cells)
- tissue damage at the injection site
- skin redness and peeling
- swelling
Subcutaneously administered methotrexate doses are locally well-tolerated. Only mild, local skin reactions (such as burning sensation, redness, swelling, discoloration, itching, severe itching) have been observed, which decrease during treatment.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C
02-222 Warsaw
phone: +48 22 49 21 301
fax: +48 22 49 21 309
website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Methofill SD
Keep the medicine out of sight and reach of children.
Store at a temperature below 30°C.
Keep in the original packaging to protect from light.
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the label or carton after EXP. The expiration date refers to the last day of the month.
Do not use Methofill SD if you notice any changes in the solution color or the presence of particles.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Methofill SD contains
The active substance is methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.15 ml solution contains 7.5 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.20 ml solution contains 10 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.25 ml solution contains 12.5 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.30 ml solution contains 15 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.35 ml solution contains 17.5 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.40 ml solution contains 20 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.45 ml solution contains 22.5 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.50 ml solution contains 25 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.55 ml solution contains 27.5 mg methotrexate.
1 injector with 0.60 ml solution contains 30 mg methotrexate.
Other ingredients are sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), and water for injections.
What Methofill SD looks like and contents of the packaging
The solution for injection in a pre-filled injector is a clear, yellow to brown solution.
The following pack sizes are available:
Injectors with 0.15 ml, 0.20 ml, 0.25 ml, 0.30 ml, 0.35 ml, 0.40 ml, 0.45 ml, 0.50 ml, 0.55 ml, and 0.60 ml solution are available in packs containing 1, 4, or 8 injectors, each in a cardboard box.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o.
Taśmowa Street 7
02-677 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 577 28 00
Manufacturer/Importer
Accord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o.
Lutomierska Street 50
95-200 Pabianice
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
| Member State | Medicine name |
| Ireland | Methofill 7.5 mg/10 mg/12.5 mg/15 mg/17.5 mg/20 mg/22.5 mg/25 mg/27.5 mg/30 mg solution for injection in pre-filled injector |
| Poland | Methofill SD |
| Sweden | Injexate |
| United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) | Methofill 7.5 mg/10 mg/12.5 mg/15 mg/17.5 mg/20 mg/22.5 mg/25 mg/27.5 mg/30 mg solution for injection in pre-filled injector |
Date of last revision of the leaflet: December 2024
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterAccord Healthcare Polska Sp. z o.o.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Methofill SdDosage form: Solution, 20 mg/mlActive substance: methotrexatePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 7.5 mgActive substance: methotrexatePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 12.5 mgActive substance: methotrexatePrescription required
Alternatives to Methofill Sd in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Methofill Sd in Spain
Alternative to Methofill Sd in Ukraine
Online doctors for Methofill Sd
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Methofill Sd – subject to medical assessment and local rules.