

Magnesium sulfate Kalceks

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Magnesium sulfate Kalceks

How to use Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Magnesium sulfate Kalceks, 200 mg/ml, Solution for Injection/Infusion
Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
- You should keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their signs of illness are the same as yours.
- If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. See section 4.
Contents of the pack and other information
- 1. What is Magnesium sulfate Kalceks and what is it used for
- 2. Before you are given Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
- 3. How to use Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Magnesium sulfate Kalceks and what is it used for
Magnesium sulfate Kalceks contains magnesium (as magnesium sulfate heptahydrate).
Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (hereinafter referred to as magnesium sulfate) is a magnesium salt. It is
used:
- to treat deficiency (lack) of magnesium;
- to prevent and treat low magnesium levels in the blood in patients who are fed entirely by intravenous nutrition (nutrients are given directly into the bloodstream);
- to treat a heart rhythm disorder called torsade de pointes;
- to treat and prevent seizures in severe pre-eclampsia (a severe complication of pregnancy characterized by high blood pressure and the presence of protein in the urine);
- to treat and prevent recurrence of seizures in eclampsia (seizures due to pre-eclampsia).
The medicine is indicated for use in adults, adolescents, and children.
2. Before you are given Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
When not to use Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
- if you are allergic to magnesium, its salts, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if you have high magnesium levels in the blood;
- if you have severe kidney impairment or kidney failure (when dialysis or other methods of blood purification are not available).
If you are unsure whether any of the above applies to you, consult your doctor or nurse before using Magnesium sulfate Kalceks.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Magnesium sulfate Kalceks, discuss with your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse:
- if you have a disease that causes muscle weakness and fatigue, called myasthenia gravis;
- if you have kidney problems (you may need a lower dose);
- if you have a tendency to form kidney stones (a tendency to form calcium-magnesium-ammonium-phosphate stones);
- if you have liver problems;
- if you have heart problems.
Too rapid administration can lead to rapidly progressing vasodilation and hypotension.
Tell your doctor or nurse if you experience flushing of the skin and sweating.
With the administration of magnesium sulfate in the form of injections, pain, redness, swelling, or warmth at the injection site, leakage at the injection site, prolonged bleeding, inflammation of the connective tissue, aseptic abscess, signs of an allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing or facial swelling, damage to surrounding structures (blood vessels, bones, or nerves), accidental intravascular or intramuscular injection can cause tissue necrosis; poor absorption may occur due to the large volume of the injection.
As with all parenteral medicines, this medicine may irritate the veins; leakage of the medicine from the blood vessel into the surrounding tissue can cause tissue damage.
During treatment, magnesium and calcium levels in the blood will be monitored.
Reflexes, breathing, and urine output will also be monitored during magnesium sulfate administration.
Magnesium sulfate Kalceks with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking now or recently, and about any medicines you plan to take.
Medicines that may interact with magnesium sulfate include:
- muscle relaxants, such as vecuronium;
- nifedipine (used to treat high blood pressure or chest pain);
- calcium antagonists (medicines used to treat high blood pressure and chest pain);
- diuretics (medicines that increase urine production), such as thiazides and furosemide;
- calcium salts;
- digitalis glycosides, such as digoxin (a medicine used to treat heart conditions);
- aminoglycoside antibiotics (medicines used to treat bacterial infections);
- barbiturates (medicines used to treat anxiety disorders, insomnia);
- opioids (medicines used to treat chronic pain), such as morphine;
- sleeping pills (medicines used to treat sleep disorders).
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor for advice before taking this medicine.
Magnesium sulfate may be used to treat seizures associated with pre-eclampsia and eclampsia, a serious complication of pregnancy. If you are pregnant and receiving magnesium sulfate, your baby's heart rate will be closely monitored; magnesium sulfate should be avoided for 2 hours before delivery. Magnesium sulfate has no effect on fertility.
Driving and using machines
It is unlikely that magnesium sulfate will affect your ability to drive or use machines. However, some people may experience dizziness or drowsiness after receiving a dose of magnesium sulfate. If you experience these side effects, do not drive or use machines.
Magnesium sulfate Kalceks contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per 1 ml, which means it is essentially 'sodium-free'.
3. How to use Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
Magnesium sulfate Kalceks will be given to you by a doctor or nurse by slow intravenous injection or infusion, into a muscle or under the skin.
Your doctor will decide how much magnesium sulfate to give you. The dose depends on your individual needs and response to treatment.
Adults
Treatment of magnesium deficiency
The recommended dose is usually 8 to 12 g of magnesium sulfate over the first 24 hours, and then 4 to 6 g per day for 3 or 4 days to replenish the deficiency in the body. Typically, 10 to 20 ml of Magnesium sulfate Kalceks, 200 mg/ml, solution for injection/infusion, is administered slowly intravenously, as needed.
In patients receiving total parenteral nutrition, the dose is strictly individual. As a general guideline, 1 to 3 g per day is administered intravenously.
Prevention and treatment of seizures in severe pre-eclampsia and eclampsia
After an initial loading dose of 4 g of magnesium sulfate, diluted to an appropriate volume, administered intravenously, either intravenous infusion of 1 to 2 g per hour or regular intramuscular injections are given until the seizures stop.
Torsade de pointes
A single dose of 2 g is administered over 2-3 minutes. The intravenous infusion is started at a rate of 2 to 4 mg per minute. In case of recurrence of torsade de pointes, a further 2 g dose is administered, and the infusion rate is increased to 6 to 8 mg per minute.
Patients with renal impairment
Patients with renal impairment usually require a reduced dose.
Patients with hepatic impairment
There are no specific dosage recommendations.Patients over 65 years
There are no specific dosage recommendations. However, caution should be exercised in this age group, as kidney and/or liver disease is more common, and the risk of side effects is higher.
Use in children and adolescentsIn children, magnesium sulfate at a concentration of 100 mg/ml can be administered intravenously to replenish the deficiency in the body. In children receiving total parenteral nutrition, the dose is strictly individual.
Overdose of Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
Since this medicine will be given to you by a doctor or nurse, it is unlikely that you will be given too much. If you have any concerns, tell your doctor or nurse.
Missed dose of Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
Missing a dose is unlikely, as it will be given to you by a doctor or nurse. Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose. Ask your doctor or nurse when the next dose will be given.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Allergic reactions
- High magnesium levels in the blood
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Breathing difficulties
- Nausea or vomiting
- Drowsiness
- Confusion
- Slurred speech
- Double vision
- Loss of tendon reflexes
- Irregular heartbeat
- Cardiac arrest
- Abnormal electrocardiogram
- Slow heart rate
- Flushing of the skin and low blood pressure due to vasodilation
- Muscle weakness
- Thirst
- Coma
Very rarely, with the use of high doses of magnesium sulfate, low calcium levels in the blood have been reported in pregnant women and their unborn babies.
Reporting of side effects
If you get any side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. Side effects can be reported to the national reporting system via:
Department of Medicinal Product Monitoring,
Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych, Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych,
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C,
PL-02 222 Warszawa,
Tel.: + 48 22 49 21 301,
Fax: + 48 22 49 21 309,
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
Keep this medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not freeze.
Shelf life after first opening
The medicinal product should be used immediately after opening the ampoule.
Shelf life after dilution
Chemical and physical stability has been demonstrated for 72 hours at 30°C and between 2°C and 8°C after dilution with sodium chloride 0.9% or glucose 5% solution.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately. If not used immediately, in-use storage times and conditions are the responsibility of the user and normally should not be longer than 24 hours at 2°C to 8°C, unless dilution has taken place in controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date which is stated on the label after “EXP” and on the carton after “Expiry Date (EXP)”. The expiry date refers to the last day of that month.
Do not use this medicine if you notice any visible signs of deterioration (e.g. visible particles).
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Magnesium sulfate Kalceks contains
The active substance is magnesium sulfate heptahydrate.
Magnesium sulfate Kalceks 200 mg/ml
Each 1 ml of solution contains 200 mg of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate.
Each 10 ml ampoule contains 2000 mg of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate.
The other ingredients are: sulfuric acid (for pH adjustment), sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), water for injections.
What Magnesium sulfate Kalceks looks like and contents of the pack
Clear, colorless solution, free from visible particles.
10 ml solution in colorless glass ampoules with one break point.
Ampoules are packed in PVC foil blisters. The blisters are placed in a cardboard box.
Pack sizes:
5, 10, or 100 ampoules.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
AS KALCEKS
Krustpils iela 71E
LV-1057 Rīga
Latvia
Tel.: +371 67083320
Email: [email protected]
Manufacturer
Akciju sabiedrība “Kalceks”
Krustpils iela 71E
LV-1057 Rīga
Latvia
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 01/2022
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Dosage
1 g of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate = 98.6 mg or 8.1 mEq or 4.1 mmol of magnesium.
Therapeutic levels are achieved almost immediately after intravenous administration and within 60 minutes after intramuscular injection.
Adults
Hypomagnesemia
The dose is strictly individual. As a general guideline, 8 to 12 g of magnesium sulfate can be administered over the first 24 hours, and then 4 to 6 g per day for 3 or 4 days to replenish the deficiency in the body. The maximum infusion rate should not exceed 2 g per hour. The goal should be to maintain a serum magnesium level above 0.4 mmol per liter.
Typically, 10 to 20 ml of Magnesium sulfate Kalceks, 200 mg per ml, solution for injection/infusion, is administered slowly intravenously (at a rate of 300 mg per minute, i.e., 1.5 ml per minute), intramuscularly, or, in exceptional cases, subcutaneously (painful), as needed.
Prevention and treatment of hypomagnesemia in total parenteral nutrition
The dose is strictly individual. As a general guideline, 1 to 3 g per day of magnesium sulfate can be administered intravenously.
Severe pre-eclampsia or eclampsia
An initial loading dose of 4 g can be administered intravenously, diluted to an appropriate volume, e.g., 4 g of magnesium sulfate in 250 ml of glucose 5% or sodium chloride 0.9% solution, at a maximum rate of 4 ml per minute (= 64 mg per minute). Then, a maintenance scheme is used, either intravenous infusion at a rate of 1 to 2 g per hour, e.g., 5 g of magnesium sulfate dissolved in 1 liter of glucose 5% or sodium chloride 0.9% solution at a rate of 200 ml per hour (= 1 g per hour), or regular intramuscular injections, depending on the continued presence of a patellar reflex and adequate respiratory and urinary function. Therapy should be continued until the seizures stop.
It is essential to perform the following clinical observations before each injection when administering magnesium sulfate according to any of these schemes:
- deep tendon reflexes must be present;
- the respiratory rate must be at least 16 per minute; and
- at least 100 ml of urine must have been excreted since the last injection.
In addition, 1 g of calcium gluconate should be available as an antidote for hypermagnesemia.
Intramuscular injections are painful and may cause local complications, such as abscess formation, in 0.5% of cases. The intravenous route is therefore preferred. However, the intramuscular scheme becomes a better option when intravenous infusion pumps are not available, continuous monitoring is not feasible, or the patient needs to be transferred to another facility.
Torsade de pointes
As a general guideline, a single intravenous bolus of 2 g should be administered over 2 to 3 minutes. The intravenous infusion of magnesium should be started at a rate of 2 to 4 mg per minute. In case of recurrence of torsade de pointes, a further 2 g dose should be administered, and the infusion rate should be increased to 6 to 8 mg per minute. A third bolus of 2 g is rarely required.
Use in children and adolescents
Hypomagnesemia
Magnesium sulfate at a concentration of 100 mg per ml can be administered intravenously to children. When administered intravenously to children, the rate of administration should not exceed 0.1 ml per kg per minute (10 mg per kg body weight per minute) of magnesium sulfate 100 mg per ml solution (which corresponds to 0.04 mmol per kg body weight per minute of magnesium = 0.001 g per kg body weight per minute of magnesium).
Prevention and treatment of hypomagnesemia in total parenteral nutrition
The dose is strictly individual. As a general guideline, the following intravenous doses of magnesium sulfate can be administered:
Patients with renal impairment
Patients with renal failure should receive 25 to 50% of the initial dose recommended for patients with normal renal function. It is recommended to monitor the ECG with high doses and in elderly patients.
Patients with hepatic impairment
Due to insufficient data, there are no specific dosage recommendations for patients with hepatic impairment.
Patients over 65 years
There are no specific dosage recommendations for patients over 65 years. However, magnesium sulfate for parenteral administration should be used with caution in elderly patients, as kidney and/or liver disease is more common in this age group, and the tolerance to side effects may be lower.
Method of administration
Intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous administration, as indicated for each indication.
The medicine should not be administered into muscles that are wasted or atrophic. When administering intramuscularly, the gluteal or femoral nerve should be avoided.
If the total dose to be administered exceeds 5 ml, the injection volume should be divided into more than one deep intramuscular injection site.
Pain, redness, swelling, or warmth at the injection site, leakage at the injection site, prolonged bleeding, inflammation of the connective tissue, aseptic abscess, signs of an allergic reaction, such as difficulty breathing or facial swelling, damage to surrounding structures (blood vessels, bones, or nerves), accidental intravascular or intramuscular injection can cause tissue necrosis; poor absorption may occur due to the large volume of the injection.
Incompatibilities
Magnesium sulfate is incompatible with calcium salts (gluconate, gluceptate), alkaline carbonates (forming insoluble magnesium carbonate), hydroxides, phosphates, salicylates, polymyxin B sulfate, tobramycin sulfate, streptomycin sulfate, amphotericin B, tetracycline, aminoglycosides, clindamycin, benzylpenicillin, nafcillin, dobutamine, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, procaine, emulsions.
Instructions for use, disposal, and other handling
For single use only.
It can be diluted with sodium chloride 0.9% or glucose 5% solution.
The medicine should be used immediately after opening the ampoule. Any unused remainder should be discarded.
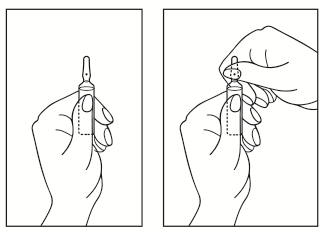
Instructions for opening the ampoule:
- 1) Turn the ampoule with the colored break point upwards. If there is any solution in the upper part of the ampoule, gently tap with your finger to get all the solution into the lower part of the ampoule.
- 2) Use both hands to open; holding the lower part of the ampoule in one hand, use the other hand to break off the upper part of the ampoule, in the direction away from the colored break point (see pictures below).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterAS Kalceks
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Magnesium sulfate KalceksDosage form: Tablets, 34 mgActive substance: magnesium aspartatePrescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 20 mgActive substance: magnesium aspartatePrescription not requiredDosage form: Tablets, 32 mg Mg 2+ + 54 mg Ca 2+Active substance: magnesium chlorideManufacturer: Zakłady Chemiczno-Farmaceutyczne "VIS" Sp. z o.o.Prescription not required
Alternatives to Magnesium sulfate Kalceks in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Magnesium sulfate Kalceks in Ukraine
Alternative to Magnesium sulfate Kalceks in Spain
Online doctors for Magnesium sulfate Kalceks
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Magnesium sulfate Kalceks – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














