
Letrox 150

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Letrox 150

How to use Letrox 150
Package Leaflet: Information for the User
Letrox 50,50 micrograms, tablets
Letrox 75 micrograms,75 micrograms, tablets
Letrox 100,100 micrograms, tablets
Letrox 125 micrograms,125 micrograms, tablets
Letrox 150,150 micrograms, tablets
Levothyroxine sodium
Read the package leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Package Leaflet
- 1. What is Letrox and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking Letrox
- 3. How to take Letrox
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Letrox
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Letrox and what is it used for
Letrox is a medicine that contains the thyroid hormone levothyroxine as the active substance. It has the same effect as the hormone produced naturally.
The purpose of treatment with Letrox is to supplement thyroid hormone deficiencies and/or alleviate thyroid dysfunction.
Letrox is used:
- To supplement thyroid hormone deficiency in hypothyroidism.
- To prevent the recurrence of thyroid goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland) after surgical treatment in patients with normal thyroid function.
- To treat benign goiter in patients with normal thyroid function.
- As an adjunct in the treatment of hyperthyroidism in combination with thyroid inhibitors (drugs that inhibit thyroid function) after achieving normal thyroid function.
- To treat malignant thyroid tumors, especially after thyroid removal surgery, to inhibit tumor growth and supplement thyroid hormone deficiency.
- In tests that evaluate thyroid function (thyroid suppression test).
Letrox is indicated for use in all age groups.
2. Important information before taking Letrox
When not to take Letrox
- If you are allergic to levothyroxine sodium or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have any of the following diseases or conditions:
- untreated hyperthyroidism
- untreated adrenal insufficiency and you are not receiving appropriate replacement therapy
- untreated hypopituitarism, if it leads to adrenal insufficiency requiring treatment
- acute myocardial infarction
- acute myocarditis
- acute pericarditis (inflammation of the heart).
In case of pregnancy, do not take Letrox at the same time as drugs that inhibit thyroid function (so-called antithyroid drugs) (see also section "Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility").
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Letrox, discuss it with your doctor if you have adrenal insufficiency.
Investigations for other conditions
Before starting treatment with Letrox, your doctor should rule out or treat the following diseases or conditions:
- coronary heart disease
- chest pain with pressure (angina pectoris)
- high blood pressure (hypertension)
- hypopituitarism and/or adrenal insufficiency
- areas in the thyroid gland that produce hormones uncontrollably (autonomous thyroid nodule).
Before performing the so-called thyroid suppression test to evaluate thyroid function, your doctor should rule out or treat the above diseases. The exception is autonomous thyroid function, as the test is also used to identify it.
Particular caution should be exercised when taking Letrox:
- in patients with a history of myocardial infarction, coronary heart disease, heart failure, or arrhythmias (tachycardia), myocarditis without acute course, or in case of long-term hypothyroidism. In such cases, it is necessary to avoid too high a concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood. It is necessary to more frequently determine the concentration of thyroid hormones. If mild symptoms of hyperthyroidism associated with taking Letrox occur, you should discuss it with your doctor (see section 4 "Possible side effects").
- in patients with hypothyroidism caused by hypopituitarism. If there is concomitant adrenal insufficiency, the doctor should first start treating it, as acute adrenal insufficiency (Addison's crisis) may occur.
- if there is a suspicion of the presence of areas in the thyroid gland that produce hormones uncontrollably. Before starting treatment, the doctor will prescribe additional tests to evaluate thyroid function.
- in postmenopausal women with an increased risk of bone loss (osteoporosis). The attending physician should more frequently control thyroid function to avoid too high concentrations of thyroid hormone in the blood serum and ensure the use of the smallest effective dose of the medicine.
- in patients with diabetes. For further information, see section "Letrox and other medicines".
- in patients treated with anticoagulant medicines (e.g., dicumarol) and medicines that affect the thyroid gland (e.g., amiodarone, tyrosine kinase inhibitors [cancer medicines], salicylates, and high doses of furosemide). For further information, see section "Letrox and other medicines".
- in case of patients taking sevelamer. The attending physician will monitor the TSH concentration in the blood to assess the effectiveness of levothyroxine treatment (see also "Letrox and other medicines").
- if the patient has ever had epilepsy, due to the increased risk of seizures.
- if the patient has had an allergic reaction (see section 4 "Possible side effects"). You should immediately contact your doctor or healthcare provider or go to the emergency department of the nearest hospital.
- if the patient is to undergo laboratory tests to check thyroid hormone levels, the patient should inform the doctor or laboratory staff about current or recent biotin use (also known as vitamin H, vitamin B7, or vitamin B8). Biotin may affect laboratory test results. Depending on the type of test, the results may be falsely elevated or falsely decreased due to biotin use. The doctor may advise the patient to stop taking biotin before undergoing laboratory tests. It should also be remembered that other products taken by the patient, such as multivitamins or supplements for hair, skin, and nails, may also contain biotin. This may affect laboratory test results. If the patient is taking such products, they should inform the doctor or laboratory staff (see information in section "Letrox and other medicines").
Misuse
Letrox should not be used to reduce body weight. In patients with normal thyroid hormone levels in the blood serum, taking additional thyroid hormones will not lead to weight loss. Taking excessive amounts of thyroid hormones or increasing the dose without special doctor's recommendations may cause serious, even life-threatening side effects, especially in combination with other weight-reducing medicines.
Change of treatment
In case of a need to switch to another levothyroxine-containing medicine, thyroid function imbalance may occur. In case of any questions about switching medicines, discuss it with your doctor. Patients should be closely monitored (clinically and biologically) during the transition period. If any side effects occur, inform your doctor, as this may indicate the need to adjust the dose (increase or decrease the dose).
Elderly patients
In elderly patients (especially those with heart problems), the dose should be increased with caution, and patients should undergo medical check-ups more frequently.
Children and adolescents
When starting levothyroxine treatment in premature infants with very low birth weight, blood pressure should be regularly monitored, as a sudden drop in blood pressure (so-called circulatory collapse) may occur (see section 4 "Possible side effects").
Letrox and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines you plan to take.
Letrox affects the action of the following medicinal substances and groups of medicines:
- Antidiabetic medicines (medicines that lower blood sugar levels, such as metformin, glimepiride, glibenclamide, and insulin): In diabetic patients, blood sugar levels should be regularly monitored, especially at the beginning and after the end of thyroid hormone treatment. If necessary, the doctor may adjust the dose of the medicine that lowers blood sugar levels, as levothyroxine may weaken its effect.
- Coumarin derivatives (anticoagulant medicines): When taking Letrox at the same time as coumarin derivatives (e.g., dicumarol), blood coagulation parameters should be regularly monitored. If necessary, the doctor may adjust the dose of the anticoagulant medicine, as levothyroxine may enhance its effect.
The doctor may adjust the dose of the anticoagulant medicine, as levothyroxine may enhance its effect.
The action of Letrox may be affected by the following medicines:
- Ion exchange resins: Medicines used to reduce blood fat levels (e.g., cholestyramine, colestyramine) or reduce high potassium levels in the blood (calcium or sodium polystyrene sulfonate) should be taken 4 to 5 hours after taking Letrox. Otherwise, these medicines may inhibit the absorption of levothyroxine from the intestines and thus weaken its effectiveness.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): Proton pump inhibitors (such as omeprazole, esomeprazole, pantoprazole, rabeprazole, and lansoprazole) used to reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach may inhibit the absorption of levothyroxine from the intestines and thus weaken its effectiveness. If a patient takes levothyroxine while being treated with proton pump inhibitors, the doctor should monitor thyroid function and adjust the dose of Letrox if necessary.
- Sevelamer and lanthanum carbonate: Sevelamer and lanthanum carbonate (medicines used to lower elevated phosphate levels in the blood serum of dialyzed patients) may reduce the absorption and effectiveness of levothyroxine. The attending physician will perform more frequent checks of thyroid function (see also section "Warnings and precautions").
- Bile acid sequestrants: Colesevelam (a medicine that lowers high cholesterol levels in the blood) binds to levothyroxine, thereby reducing its absorption from the intestine. Therefore, Letrox should be taken 4 hours before taking colesevelam.
- Antacids and medicines containing aluminum, iron, or calcium: Letrox should be taken at least 2 hours before taking antacids containing aluminum (antacids, sucralfate), iron-containing medicines, or calcium-containing medicines, as these medicines may weaken the absorption of levothyroxine from the intestines.
- Propylthiouracil, glucocorticoids, beta-adrenolytics (especially propranolol): Propylthiouracil (a medicine used in hyperthyroidism), glucocorticoids (adrenal cortex hormones, "cortisone"), and beta-adrenolytics (medicines that slow down heart activity and lower blood pressure) may reduce the effectiveness of Letrox.
- Amiodarone and iodine-containing contrast agents: Amiodarone (a medicine used to treat arrhythmias) and iodine-containing contrast agents (mainly medicines used in X-ray diagnostics) may, due to their high iodine content, cause both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism. Particular attention should be paid to patients with nodular goiter, who may have unrecognized autonomous thyroid nodules that release hormones uncontrollably. If necessary, the attending physician will adjust the dose of Letrox.
- Salicylates, especially doses above 2 g per day (pain-relieving and antipyretic medicines).
- Dicumarol (an anticoagulant medicine).
- Furosemide (a diuretic) in high doses (250 mg).
- Clofibrate (a medicine that lowers high blood fat levels).
- Contraceptives and hormone replacement therapy:
Contraceptives containing estrogens ("birth control pills") and postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy may increase the need for levothyroxine.
- Sertraline, chloroquine/proguanil: Sertraline (a medicine used to treat depression) and chloroquine and proguanil (medicines used to treat malaria and rheumatoid arthritis) reduce the effectiveness of levothyroxine.
- Rifampicin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, barbiturates, and medicines containing St. John's Wort: Rifampicin (an antibiotic), carbamazepine (used to treat epilepsy), phenytoin (used to treat epilepsy and arrhythmias), barbiturates (used to treat seizures; some sleeping medicines), and medicines containing St. John's Wort (a herbal medicinal product) may weaken the effect of levothyroxine.
- Protease inhibitors (medicines used to treat HIV and hepatitis C virus infections): The doctor should closely monitor the symptoms of the disease and control thyroid function in patients taking levothyroxine and protease inhibitors (lopinavir, ritonavir) at the same time. During the simultaneous use of levothyroxine with lopinavir and/or ritonavir, its effectiveness may be reduced.
- Tyrosine kinase inhibitors (medicines used to treat cancer): The doctor should closely monitor clinical symptoms and control thyroid function in patients taking levothyroxine and tyrosine kinase inhibitors (e.g., imatinib, sunitinib, sorafenib, motesanib) at the same time. The effectiveness of levothyroxine may be reduced; if necessary, the doctor will adjust the dose of levothyroxine.
- Semaglutide: If a patient takes levothyroxine at the same time as semaglutide (an antidiabetic medicine), it may affect the level of levothyroxine, and the doctor may recommend monitoring thyroid hormone levels and adjusting the dose of Letrox.
- Orlistat: Orlistat (used to treat obesity) may reduce the absorption of levothyroxine.
- Biotin (also known as vitamin H, vitamin B7, or vitamin B8): If a patient is currently taking or has recently taken biotin, they must inform their doctor or laboratory staff if they are to undergo laboratory tests for thyroid hormone levels. Biotin may affect laboratory test results (see "Warnings and precautions").
Letrox with food and drink
Letrox should not be taken with food, especially a diet rich in calcium (e.g., milk and dairy products), as this may significantly weaken the absorption of levothyroxine.
In the case of a soy-based diet, the doctor will more frequently monitor thyroid hormone levels in the blood. During such a diet and after its completion, it may be necessary to adjust the dose of Letrox by the doctor, as soy products disrupt the absorption of levothyroxine in the intestines, thereby weakening its effectiveness.
Letrox should not be taken with coffee, as this may reduce the absorption of levothyroxine in the intestines and thus weaken its effectiveness. After taking Letrox, you should wait at least half an hour to an hour before drinking coffee. It is recommended that patients taking levothyroxine do not change their coffee drinking habits without checking and controlling their levothyroxine levels by their doctor.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine.
Proper treatment with thyroid hormones is particularly important for the health of the mother and fetus during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Therefore, treatment should be continued under the control of the attending physician.
Despite the widespread use of levothyroxine during pregnancy, its negative effect on the course of pregnancy or on the health of the fetus or newborn remains unknown to date.
If you are breastfeeding, you should continue taking levothyroxine as recommended by your doctor.
Even during treatment with high doses of levothyroxine during breastfeeding, the amount of levothyroxine that passes into breast milk is very small.
Thyroid function should be monitored both during and after pregnancy, as it may be necessary to adjust the dose by the doctor during pregnancy.
Letrox should not be taken at the same time as antithyroid medicines during pregnancy.
The thyroid suppression test should not be performed in pregnant and breastfeeding women.
Hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism may affect fertility.
During the treatment of patients with hypothyroidism, the dose of Letrox should be adjusted based on laboratory test results, as an insufficient dose may not improve hypothyroidism, and an overdose may lead to hyperthyroidism.
Driving and using machines
No studies have been conducted on the effect of Letrox on the ability to drive and use machines.
Letrox contains sodium
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per tablet, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to take Letrox
This medicine should always be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
The doctor will determine the daily dose for each patient based on clinical evaluation and laboratory tests.
Dosage
Letrox is available in tablets with different active substance content (25-150 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium), which means that most patients will take one tablet per day.
The doctor will prescribe tablets with the appropriate active substance content when starting treatment and when increasing the dose.
Depending on the symptoms, the doctor will adjust the dose according to the following recommendations:
- In the treatment of hypothyroidism, the initial dose for adults is 25-50 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium per day. The doctor may recommend increasing the dose by 25-50 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium at 2-4 week intervals until a daily dose of 100-200 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium is reached.
- To prevent the recurrence of goiter after its removal and in the treatment of benign goiter, the daily dose is 75-200 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium.
- As an adjunct in the treatment of hyperthyroidism in combination with thyroid inhibitors, the daily dose is 50-100 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium.
- After thyroid removal surgery due to malignant thyroid tumors, the daily dose is 150-300 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium.
- In tests that evaluate thyroid function during the thyroid suppression test, the daily dose is 200 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium taken for 14 days until the radiological examination (scintigraphy) is performed.
A smaller dose of thyroid hormone may also be sufficient.
Use in children and adolescents
The maintenance dose during long-term treatment of hypothyroidism (congenital or acquired) is usually 100-150 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium per m² of body surface area per day.
In the case of newborns and infants with congenital hypothyroidism, it is particularly important to start treatment as soon as possible to achieve normal development. The recommended initial dose is 10-15 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium per kg of body weight per day for the first 3 months. Then, the doctor will adjust the daily dose individually based on the results of the clinical examination (in particular, based on the levels of thyroid hormones and TSH in the blood).
In children with acquired hypothyroidism, the recommended initial dose is 12.5-50 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium per day. The doctor will gradually increase the daily dose at 2-4 week intervals until the appropriate replacement dose is achieved. To this end, the doctor will particularly monitor the levels of thyroid hormones and TSH in the blood.
Elderly patients, patients with coronary heart disease, patients with hypothyroidism
In elderly patients, patients with coronary heart disease, and patients with severe or long-term hypothyroidism, treatment with thyroid hormones should be started with caution (small initial dose, which should then be slowly increased over a long period, with frequent monitoring of thyroid hormone levels and TSH values).
Patients with low body weight and patients with large goiter
Experience indicates that smaller doses are also sufficient in patients with low body weight and in patients with large goiter.
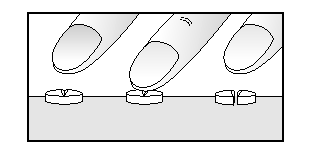
Dividing tablets
The tablet can be divided into equal doses.
Place the tablet on a flat, hard surface, with the scored side facing up. Press the tablet with your finger, and you will get two equal halves of the tablet.
Method of administration
Take the entire daily dose in the morning, washed down with a large amount of liquid, preferably a glass of water, on an empty stomach, at least half an hour before breakfast. The active substance is better absorbed on an empty stomach than before or after a meal.
Children should take the entire daily dose at least half an hour before the first meal. The tablets can also be dissolved in an appropriate amount of water (10-15 ml), and the resulting suspension (the tablets must be dissolved just before administration!) should be given with a small additional amount of liquid (5-10 ml).
Duration of treatment
Letrox is usually taken for life in hypothyroidism and after thyroid removal surgery due to malignant thyroid tumors, and in the case of benign goiter and prevention of goiter recurrence, treatment lasts for several months or years, or even for life.
In supportive therapy for hyperthyroidism, Letrox should be taken for as long as thyroid inhibitors are taken. Treatment of benign goiter with normal thyroid function should last from 6 months to 2 years. If treatment with Letrox does not produce the expected effect during this time, the doctor will consider other treatment options.
The doctor decides on the duration of treatment.
Overdose of Letrox
In case of taking a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, you should immediately consult a doctor.
After an overdose, symptoms of hyperthyroidism may occur.
The symptoms of overdose are described in section 4 "Possible side effects".
Missing a dose of Letrox
If you ever take too little of the medicine or miss a dose, do not take a double dose to make up for the missed dose. Continue taking the medicine as recommended by your doctor.
Stopping treatment with Letrox
To achieve the desired therapeutic effect, Letrox should be taken regularly in the dose recommended by the doctor.
Under no circumstances should the treatment be changed, interrupted, or terminated prematurely without consulting a doctor, as the symptoms may recur.
If you have any further questions about the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Letrox can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Hypersensitivity to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of Letrox
In case of hypersensitivity to levothyroxine or any of the other ingredients of Letrox, allergic reactions may occur on the skin and allergic reactions related to the respiratory system (either immediately or within a few days of administration), which can be life-threatening. These symptoms may include rash, itching, difficulty breathing, shortness of breath, swelling of the face, lips, throat, or tongue. You should immediately contact your doctor or healthcare provider or go to the emergency department of the nearest hospital.
Intolerance to the prescribed dose, overdose
In individual cases, when the prescribed dose is not tolerated or the medicine is overdosed, especially when the dose is increased too quickly at the beginning of treatment, typical symptoms of hyperthyroidism may occur.
Very common: may affect more than 1 in 10 patients
- Palpitations
- Insomnia
- Headache
Common: may affect up to 1 in 10 patients
- Fast heart rate (tachycardia)
- Nervousness
Rare: may affect up to 1 in 1000 patients
- Increased intracranial pressure (especially in children)
Frequency not known: cannot be estimated from the available data
- Hypersensitivity
- Arrhythmias
- Chest pain with a feeling of pressure (angina pectoris)
- Skin allergic reactions (e.g., angioedema [difficulty breathing or swelling of the face, lips, throat, or tongue], rash, urticaria)
- Restlessness
- Muscle weakness, muscle cramps
- Osteoporosis during long-term treatment with high doses of levothyroxine, especially in postmenopausal women, mainly those taking the medicine for a long time
- Feeling of heat, intolerance to high temperatures, circulatory collapse in premature infants with low birth weight (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions")
- Menstrual disorders
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Weight loss
- Tremors
- Excessive sweating
- Fever
Tell your doctor about any side effects. They will decide whether to reduce the daily dose or stop taking the medicine for a few days. Once the side effects have disappeared, the doctor may cautiously restart treatment, adjusting the dose.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Letrox
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the blister pack and outer packaging after the abbreviation "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
Do not store above 30°C. Store in the original blister pack to protect from light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Letrox contains
The active substance of Letrox is levothyroxine sodium.
Letrox 50: Each tablet contains 53.2-56.8 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium x H2O (which corresponds to 50 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium).
Letrox 75 micrograms: Each tablet contains 79.8-85.2 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium x H2O (which corresponds to 75 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium).
Letrox 100: Each tablet contains 106.4-113.6 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium x H2O (which corresponds to 100 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium).
Letrox 125 micrograms: Each tablet contains 133.0-142.0 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium x H2O (which corresponds to 125 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium).
Letrox 150: Each tablet contains 159.6-170.4 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium x H2O (which corresponds to 150 micrograms of levothyroxine sodium).
Other ingredients are:
Cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate (partially present in the tablet as cystine), microcrystalline cellulose, cornstarch, pregelatinized starch, magnesium oxide, light, talc.
What Letrox looks like and contents of the pack
Letrox is a white to beige, round, slightly convex tablet with a dividing line on one side.
The tablet can be divided into equal doses.
The pack contains 25, 50, 84, or 100 tablets.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
BERLIN-CHEMIE AG
Glienicker Weg 125
12489 Berlin, Germany
For more information about this medicine, contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Berlin-Chemie/Menarini Polska Sp. z o.o.
Phone: +48 22 566 21 00
Fax: +48 22 566 21 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:02/2024
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterBerlin-Chemie AG
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Letrox 150Dosage form: Tablets, 25 mcgActive substance: levothyroxine sodiumPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 50 mcgActive substance: levothyroxine sodiumPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 75 mcgActive substance: levothyroxine sodiumPrescription required
Alternatives to Letrox 150 in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Letrox 150 in Spain
Alternative to Letrox 150 in Ukraine
Online doctors for Letrox 150
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Letrox 150 – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










