

Intralipid 10%

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Intralipid 10%

How to use Intralipid 10%
Leaflet attached to the packaging: information for the user
Intralipid 10%
100 mg/ml, infusion emulsion
Raffinated soybean oil
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Intralipid 10% and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Intralipid 10%
- 3. How to use Intralipid 10%
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Intralipid 10%
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Intralipid 10% and what is it used for
Intralipid 10% is a fat emulsion for parenteral nutrition. The medicine contains refined soybean oil, which provides the body with fatty acids necessary for energy production. The medicine should be used as a component of parenteral nutrition in combination with appropriate amounts of carbohydrate solutions, proteins, electrolytes, vitamins and trace elements. The medicine is administered by intravenous infusion. Indications for use: Intralipid 10% is indicated for use as a source of energy and fatty acids in parenteral nutrition. It is also intended for use in patients with fatty acid deficiency, in whom it is not possible to maintain or restore a normal level of these acids after oral administration.
2. Important information before using Intralipid 10%
When not to use Intralipid 10%
Do not use the medicine:
- if the patient is allergic to egg protein, soy or peanuts, to the active substance or to any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient is in acute shock (a set of disease symptoms caused by hypoxia of vital organs);
- if the patient has severe hyperlipemia (significant increase in cholesterol levels in the blood);
- if the patient has severe liver failure;
- if the patient has been diagnosed with hemophagocytic syndrome (a rare, life-threatening hereditary disease characterized by high fever, liver and/or spleen enlargement, and a significant decrease in the number of all blood cells in the blood).
Warnings and precautions
Intralipid 10% should be used with caution if the patient has:
- disturbed fat metabolism;
- kidney failure;
- uncontrolled diabetes;
- pancreatitis;
- liver function disorders;
- hyperthyroidism (if hypertriglyceridemia occurs - significantly elevated triglyceride levels in the blood);
- sepsis (a systemic inflammatory response syndrome due to infection). During the use of Intralipid 10% in these patients, the doctor will order blood tests (triglyceride level measurement).
Intralipid 10% should be used with caution in newborns and premature infants with hyperbilirubinemia (significantly elevated levels of the pigment causing jaundice in the blood) and in cases of suspected pulmonary hypertension (a condition in which blood pressure in the pulmonary arteries increases). During prolonged administration of Intralipid 10% to newborns, especially premature infants, the doctor will order blood tests (platelet count, liver enzyme activity, and triglyceride level measurement). This medicine affects the results of some tests. You should inform your doctor about the use of this medicine before performing the test. Intralipid 10% may rarely cause allergic reactions. Allergic reactions have also been observed after administration of this medicine and consumption of peanuts. When used in newborns and children under 2 years of age, the solution (in the bag and administration set) should be protected from light until the end of administration (see section 2).
Intralipid 10% and other medicines
Tell your doctor about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take. Inform your doctor if you are taking:
- insulin (a medicine used to treat diabetes);
- heparin or coumarin derivatives (medicines used to reduce blood clotting).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before taking this medicine. The doctor will decide whether to use this medicine in pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Driving and using machines
Not applicable.
3. How to use Intralipid 10%
This medicine is administered only by medical personnel. The medicine must not be used by itself. In case of doubts, consult a doctor. The dose is determined by the doctor individually for each patient, depending on age, body weight, and health status. Medical personnel may monitor the patient's health status during treatment. When used in newborns and children under 2 years of age, the solution (in the bag and administration set) should be protected from light until the end of administration (see section 2).
Using a higher dose of Intralipid 10% than recommended
It is unlikely that the patient will receive too much of this medicine, as it is administered by medical personnel. In case of overdose, there is a risk of taking too much fat. This symptom is called "fat overload syndrome". For more information, see section 4: Possible side effects. If the patient notices the above symptoms or thinks they have received a higher dose of Intralipid 10% than recommended, they should immediately inform their doctor or nurse. Acute overdose can lead to acidosis (accumulation of excessive amounts of acidic substances or a decrease in the concentration of alkaline substances in the blood), especially when carbohydrates are not administered. In case of any further doubts about the use of this medicine, consult a doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Uncommon side effects(more than 1 in 100 patients and less than 1 in 1,000 patients):
- headache;
- increased body temperature;
- tremors;
- chills;
- feeling of fatigue;
- abdominal pain;
- nausea;
- vomiting.
Rare side effects(less than 1 in 10,000 patients):
- allergic reaction (hypersensitivity), which manifests as skin rash, swelling (especially of the lips, face, eyelids, tongue, and throat), shortness of breath, or fainting. You should immediately contact your doctor.
- increased or decreased blood pressure;
- transiently elevated liver enzyme activity. Your doctor will inform you about the occurrence of this side effect.
- abdominal pain;
- thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count, manifested by bruising, easy bruising, and bleeding);
- hemolysis (red blood cell breakdown);
- reticulocytosis (increased number of immature red blood cells);
- priapism (prolonged, painful erection);
- urticaria (light red, itchy blisters on the skin);
- skin rash.
Intralipid 10% may cause increased body temperature and, less often, tremors, chills, and nausea or vomiting (occurring less frequently than in 1 in 100 patients). After prolonged treatment:
- in infants, thrombocytopenia and increased cholesterol levels have been observed;
- with or without the use of Intralipid 10%, transiently elevated liver enzyme activity has been observed.
Fat overload syndrome
Fat overload syndrome occurs when the body has problems with fat metabolism due to the administration of an excessive amount of Intralipid 10%. It can also occur due to a sudden change in the patient's health status (e.g., kidney problems or infection). Possible symptoms include fever, increased fat levels in the blood, cells, and tissues, disorders of many organs, and coma. All these symptoms usually disappear after the infusion is discontinued.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Intralipid 10%
Store the medicine out of the sight and reach of children. The doctor or pharmacist is responsible for ensuring proper storage, use, and disposal of Intralipid 10%. Store in a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month. When used in newborns and children under 2 years of age, the solution (in the bag and administration set) should be protected from light until the end of administration (see section 2).
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Intralipid 10% contains
- The active substance of the medicine is soybean oil. 1000 ml of the emulsion contains 100 g of refined soybean oil (Soiae oleum raffinatum).
- The other ingredients (excipients) are: purified egg phospholipids, anhydrous glycerol, sodium hydroxide, water for injections.
Osmolality: 300 mOsm/kg water, pH: approximately 8, Energy value: 4.6 MJ (1100 kcal)/1000 ml, Organic phosphate content: 15 mmol/1000 ml
What Intralipid 10% looks like and what the packaging contains
The medicine is a white, homogeneous emulsion. Packaging of the medicine: Bottle, Glass type II bottles with a butyl rubber stopper and an aluminum-plastic cap. Packaging sizes: 100 ml in 1 bottle, 500 ml in 1 bottle, Bag, The packaging consists of an inner Biofine bag and an outer bag. The inner Biofine bag is made of plastic. Between the inner and outer bags, there is an oxygen absorber and a bag wall damage indicator. Packaging sizes: 100 ml in 1 bag, 500 ml in 1 bag. Not all packaging sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Fresenius Kabi AB, S-751 74 Uppsala, Sweden
Manufacturer
Bottles, Fresenius Kabi Austria GmbH, Hafnerstrasse 36, A-8055 Graz, Austria, Fresenius Kabi AB, S-751 74 Uppsala, Sweden, Bags, Fresenius Kabi AB, S-751 74 Uppsala, Sweden. For more detailed information, please contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder: Fresenius Kabi Polska Sp. z o.o., Al. Jerozolimskie 134, 02-305 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 345 67 89, Date of last update of the leaflet:16.07.2021
Information intended only for healthcare professionals:
Dosage and administration
The dose and rate of administration of Intralipid 10% should be dependent on the patient's ability to eliminate fat. See "Fat elimination". Dosage: 1 g of triglycerides corresponds to 10 ml of Intralipid 10%. Adult patients: The recommended maximum dose is 3 g of triglycerides/kg body weight/day. With this upper limit in mind, Intralipid 10% can be used to cover up to 70% of the energy requirement, also in patients with significantly increased energy requirements. The rate of infusion of Intralipid 10% should not exceed 500 ml in 5 hours. Newborns and infants: The recommended dose for newborns and infants is 0.5 to 4.0 g of triglycerides/kg body weight/day. The infusion rate should not exceed 0.17 g of triglycerides/kg body weight/hour (4 g/day). Premature infants and newborns with low birth weight should be given Intralipid 10% at an initial dose of 0.5 to 1.0 g/kg body weight/day, gradually increased by 0.5 to 1.0 g/kg body weight/day to a dose of 2 g/kg body weight/day in continuous infusion over 24 hours. Further increase in the dose to 4 g/kg body weight/day is possible only under strict control of triglyceride levels in the blood serum, liver enzyme activity, and oxygen saturation. The above infusion rates are maximum and should not be exceeded in order to quickly replenish missed doses. Administration method: When used in newborns and children under 2 years of age, the solution (in the bag and administration set) should be protected from light until the end of administration. Essential fatty acid deficiency (EFAD): To prevent or treat essential fatty acid deficiency, 4-8% of non-protein energy should be provided in the form of Intralipid 10%, which ensures an adequate amount of linoleic and linolenic acid. When essential fatty acid deficiency is associated with stress, the amount of medicine needed to correct the deficiency may be significantly increased.
Fat elimination
Adult patients: It is necessary to closely monitor the patient's ability to eliminate fat in the conditions listed in section 4.4 "Special warnings and precautions for use" in the Summary of Product Characteristics and in patients who have been administered Intralipid 10% for more than one week. To do this, blood samples should be taken for tests 5-6 hours after the end of the fat emulsion infusion. Blood cells should be separated from serum by centrifuging the blood sample. The infusion must not be continued if the serum is opalescent. The sensitivity of this method is not sufficient to detect hypertriglyceridemia. Therefore, it is recommended to measure the triglyceride level in the blood serum in patients suspected of having impaired fat tolerance. Newborns and infants: In newborns and infants, it is necessary to regularly monitor the ability to eliminate fat. The only reliable method is to measure the triglyceride level in the blood serum.
Overdose
Fat overload syndrome: Disorders of Intralipid 10% elimination can lead to fat overload syndrome due to the administration of a higher dose of the medicine than recommended. This syndrome can also occur during the use of recommended infusion rates due to a sudden change in the patient's clinical condition, e.g., kidney disorders or infection. The syndrome is characterized by hyperlipemia, fever, fat infiltration, and disorders of many organs, as well as coma. All symptoms of fat overload usually disappear after the infusion of Intralipid 10% is discontinued. Acute overdose caused by the administration of a fat emulsion containing triglycerides can lead to acidosis, especially when carbohydrates are not administered.
Preparation of the medicine for use
Do not use if the packaging is damaged. Check the bag wall damage indicator (Oxalert) before removing the outer bag. If the indicator is black, the outer bag is damaged and the medicine should be destroyed. The outer bag, oxygen absorber, and bag wall damage indicator should be removed after opening the outer bag. In case of adding other nutrients, tear off the labeled tab of the one-time use plug protecting the white administration port for adding these substances. If no additional substances are added, proceed to point 5.
Special warnings and precautions for use
Exposure of parenteral nutrition solutions to light, especially after the addition of trace elements and/or vitamins, may have undesirable effects on the clinical response in newborns due to the formation of hydroperoxides and other degradation products. When used in newborns and children under 2 years of age, Intralipid 10% should be protected from light until the end of administration.
Incompatibilities
Additional substances should be combined with the medicine under aseptic conditions. Do not add electrolyte solutions alone to Intralipid 10%. Only medicines, nutrient solutions, or electrolyte solutions with documented compatibility should be added. On request, information can be obtained about the compatibility of the medicine with other solutions and additives, as well as the storage periods of prepared mixtures.
Storage conditions
Store in a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze. Storage after addition of other nutrients: Mixing in a plastic bag (not containing phthalates): the components of the mixture prepared under aseptic and validated conditions should be used within 7 days of preparation. The bag with the nutrient mixture can be stored for no more than 6 days in the refrigerator, at a temperature of 2 to 8°C, and then infused within 24 hours.
Disposal of leftovers
Any unused medicine or waste material should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Special precautions for disposal and preparation of the medicinal product for use
When used in newborns and children under 2 years of age, protect from light until the end of administration. Exposure of Intralipid 10% to light, especially after the addition of trace elements and/or vitamins, leads to the formation of hydroperoxides and other degradation products, which can be limited by protecting from light.
Instructions for preparing the Biofine bag for use (attached only to the Biofine bag)
- 1.
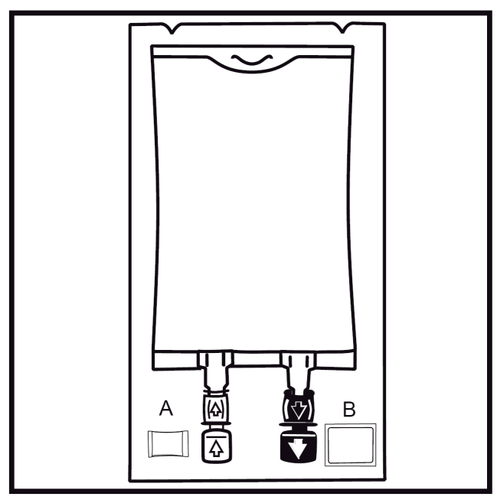
Check the bag wall damage indicator (Oxalert) Abefore removing the outer bag. If the indicator is black, it means that the outer bag is damaged and the medicine should be destroyed.
- 2.
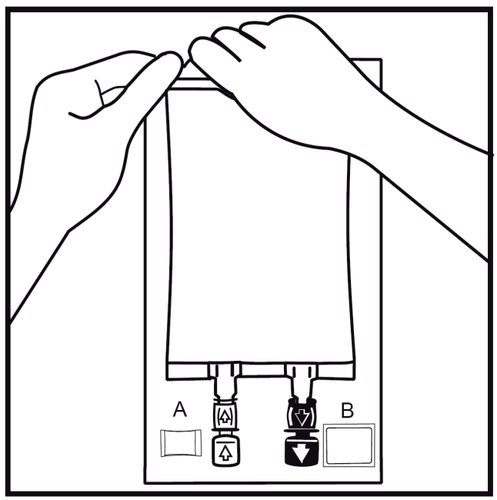
Remove the outer bag by tearing the weld at the top and pulling along the packaging. The bag wall damage indicator Aand oxygen absorber Bshould be removed.
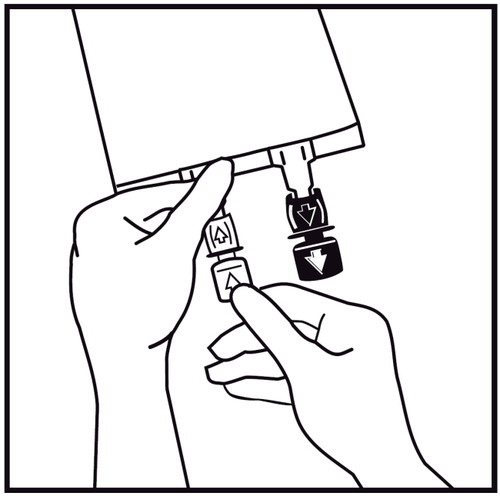
- 3.
In case of adding other substances, tear off the labeled tab of the one-time use plug protecting the white administration port for adding these substances. If no additional substances are added, proceed to point 5.
- 4.
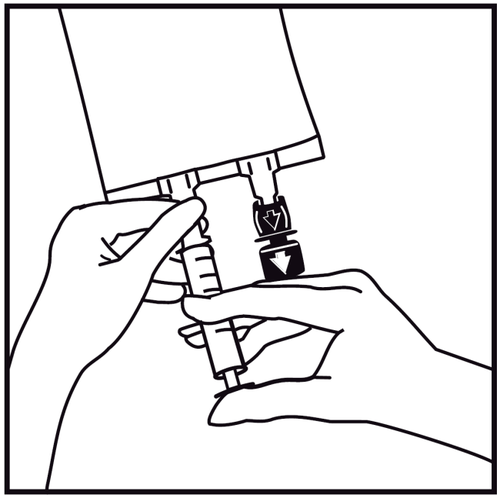
Insert the needle and administer additional substances (with established compatibility) through the center of the injection site. Use syringes with needles with a diameter of 18 to 23 G and a maximum length of 40 mm.
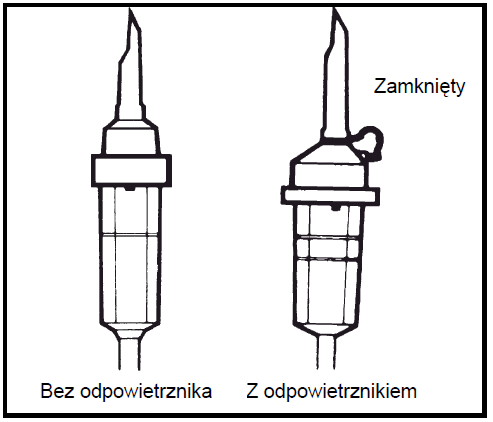
- 5.
Use an infusion device without an air vent or close the air inlet in case of a device with an air vent. Follow the instructions for the infusion device. Use an infusion device with a diameter specified in ISO standard 8536-4, 5.6 ± 0.1 mm.
- 6.
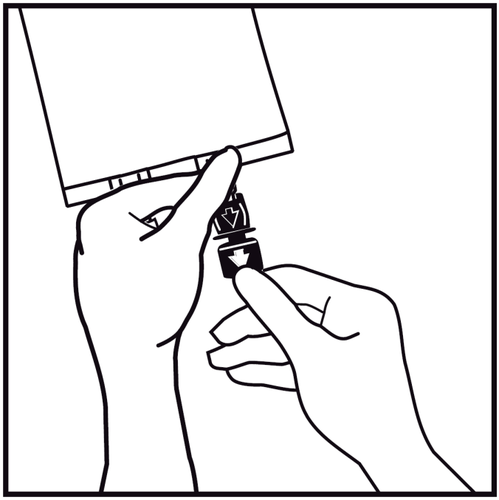
Remove the one-time use plug protecting the blue infusion port.
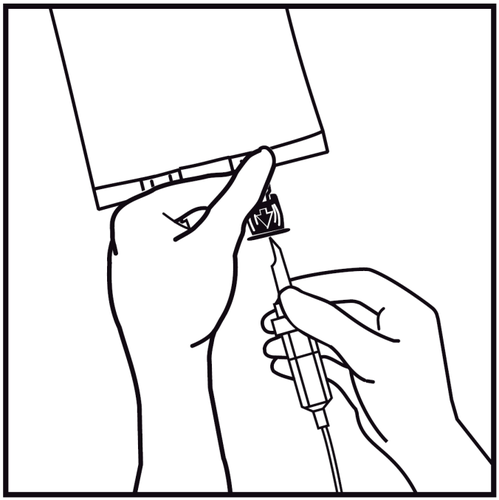
- 7.
Hold the base of the infusion port. Insert the spike of the infusion device into the infusion port and gently screw it in until it is fully inserted.
- 8.
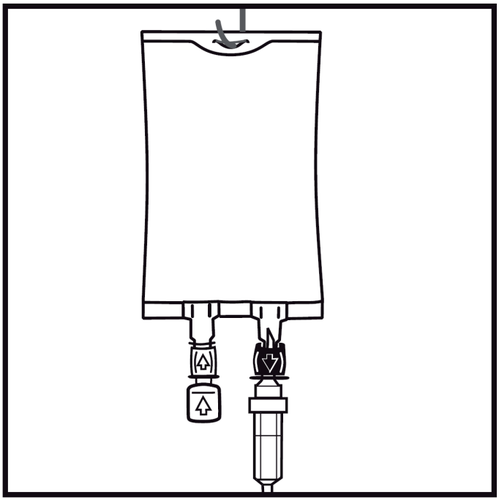
Suspend the bag using the prepared hanger and start the infusion.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterFresenius Kabi AB Fresenius Kabi AB Fresenius Kabi Austria GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Intralipid 10%Dosage form: Emulsion, -Active substance: fat emulsionsManufacturer: Baxter S.A.Prescription not requiredDosage form: Emulsion, 200 mg/mlActive substance: fat emulsionsManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi AB Fresenius Kabi ABPrescription not requiredDosage form: Emulsion, 200 mg/mlActive substance: fat emulsionsManufacturer: B. Braun Melsungen AGPrescription not required
Alternatives to Intralipid 10% in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Intralipid 10% in Ukraine
Alternative to Intralipid 10% in Spain
Online doctors for Intralipid 10%
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Intralipid 10% – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














