
Furosemide Kalceks
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Furosemide Kalceks

How to use Furosemide Kalceks
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Furosemide Kalceks, 10 mg/ml, solution for injection/infusion
Furosemide
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed for a specific person. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Furosemide Kalceks and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Furosemide Kalceks
- 3. How to use Furosemide Kalceks
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Furosemide Kalceks
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Furosemide Kalceks and what is it used for
The active substance of Furosemide Kalceks, 10 mg/ml, solution for injection/infusion is furosemide. Furosemide belongs to a group of diuretic medicines. This medicine works by increasing the amount of urine produced. This helps to relieve symptoms caused by having too much fluid in the body.
It is used when oral furosemide administration does not produce a sufficient urine output or when oral administration is not possible.
Furosemide Kalceks is indicated:
- for the treatment of fluid retention (edema) and/or fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity (ascites) caused by heart or liver disease;
- for the treatment of fluid accumulation in tissues (edema) caused by kidney disease;
- for the treatment of fluid accumulation in lung tissue (pulmonary edema) (e.g., in acute heart failure);
- for the treatment of very high blood pressure (hypertensive crisis), in combination with other therapeutic agents.
2. Important information before using Furosemide Kalceks
When not to use Furosemide Kalceks:
- if the patient is allergic to furosemide or any of the other ingredients of the medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient is allergic to sulfonamide antibiotics;
- in case of kidney failure and lack of urine production, despite furosemide administration;
- in case of kidney failure caused by toxic substances to the kidneys or liver;
- in case of kidney failure associated with hepatic coma;
- if the patient is in a coma caused by liver failure;
- if the patient has significantly low levels of potassium or sodium in the blood;
- if the patient has low blood volume or is severely dehydrated (has lost significant amounts of fluid, e.g., due to severe diarrhea or vomiting);
- if the patient is breastfeeding. If the patient is unsure whether any of the above applies to them, they should talk to their doctor or nurse before using this medicine.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use this medicine, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or nurse:
- if the patient has low blood pressure;
- if the patient has diabetes (regular blood sugar monitoring is necessary);
- if the patient has gout (high levels of uric acid in the blood, which can cause joint pain or inflammation), caused by high uric acid levels in the blood (regular monitoring of uric acid levels in the blood is necessary);
- if the patient has difficulty urinating (e.g., due to prostate enlargement, hydronephrosis, urethral stricture);
- in case of decreased protein levels in the blood;
- if the patient has liver disease;
- if the patient has rapidly worsening kidney function associated with severe liver disease (e.g., liver cirrhosis);
- if the patient is at risk of significant blood pressure drop (e.g., has cerebral or coronary circulation disorders);
- if the patient is dehydrated (has lost fluid due to severe diarrhea, vomiting, or excessive sweating);
- if the patient has systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), an inflammatory disease;
- if the patient has hearing disorders;
- if the patient is elderly, especially if they have dementia (causes memory, speech, and understanding problems, recognition of people, things, and places, and orientation difficulties) and if the patient is taking risperidone (for psychiatric disorders);
- if the patient is taking other medicines that may cause low blood pressure, or if they have other conditions that increase the risk of low blood pressure. If the patient is unsure whether any of the above applies to them, they should talk to their doctor or nurse before using this medicine.
Especially during long-term use of the medicine, the doctor should regularly monitor the levels of potassium, sodium, calcium, magnesium, bicarbonate, chloride, creatinine, urea, and uric acid in the blood, as well as blood sugar levels.
The reduction in body weight due to increased urine production should not exceed 1 kg per day.
Children
Administration of furosemide to premature infants may cause kidney stones or kidney calcification. In premature infants, the duct between the pulmonary artery and the aorta, which is open in the unborn child, may remain open after birth.
Furosemide Kalceks and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take. This is important because some medicines should not be used at the same time as Furosemide Kalceks, or the dose of furosemide or the other medicine may need to be adjusted.
The following medicines may affect the action of Furosemide Kalceks:
- anti-inflammatory medicines, including NSAIDs (e.g., diclofenac, ibuprofen, indomethacin, celecoxib) and high doses of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin);
- probenecid (used to treat gout);
- methotrexate (used to treat certain cancers or severe arthritis);
- phenytoin (used to treat epilepsy);
- sucralfate (used to treat stomach ulcers). Furosemide should not be taken within 2 hours of taking sucralfate, as the action of furosemide may be weakened.
Furosemide Kalceks may affect the action of the following medicines:
- medicines used to treat heart conditions (e.g., digoxin);
- medicines used to treat heart rhythm disorders (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol, dofetilide, ibutilide);
- terfenadine (used to treat allergies);
- lithium (used to treat mood disorders);
- medicines used to treat high blood pressure, so-called "ACE inhibitors" (e.g., lisinopril) or "angiotensin II receptor antagonists" (e.g., losartan);
- other diuretic medicines (e.g., bendroflumethiazide or hydrochlorothiazide);
- theophylline (used to treat asthma);
- medicines given by injection during surgical procedures (e.g., tubocurarine, succinylcholine);
- medicines used to treat diabetes (e.g., metformin and insulin);
- medicines that increase blood pressure (e.g., adrenaline, noradrenaline);
- risperidone (used to treat psychiatric disorders);
- levothyroxine (used to treat hypothyroidism).
The following medicines increase the risk of side effects when used with Furosemide Kalceks:
- corticosteroids (used to treat inflammation or allergies, e.g., prednisolone, dexamethasone);
- carbenoxolone (used to treat stomach ulcers);
- antibiotics used to treat infections (aminoglycosides, cephalosporins, polymyxins), as concurrent use with furosemide may increase the risk of kidney damage or hearing disorders (sometimes irreversible);
- cisplatin (used to treat cancer);
- medicines that suppress the immune system (e.g., cyclosporine used to prevent transplant rejection);
- medicines used as injections before X-ray examinations (contrast agent);
- chloral hydrate (used to treat sleep disorders). It is not recommended to administer furosemide at the same time as chloral hydrate, as side effects such as feeling hot, sweating, restlessness, nausea, increased blood pressure, and rapid heartbeat may occur within 24 hours of taking chloral hydrate;
- phenobarbital, carbamazepine (used to treat epilepsy);
- aminoglutethimide (used to treat Cushing's syndrome);
- laxatives.
Furosemide Kalceks with food and drink
High doses of licorice in combination with furosemide may lead to increased potassium loss.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a baby, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine. Furosemide may be used during pregnancy only if the doctor considers it necessary. This medicine may stimulate urine production in the fetus. Furosemide passes into breast milk. It inhibits the production and secretion of breast milk. Therefore, breastfeeding women should not use furosemide.
Driving and using machines
This medicine may affect the patient's ability to react, impairing their ability to drive vehicles, operate machinery, or perform hazardous activities. The risk is greater at the beginning of treatment, when increasing the dose, when switching medicines, and in combination with alcohol.
Furosemide Kalceks contains sodium
The medicine contains 3.686 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per ml of solution. This corresponds to 0.18% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium in the diet for adults.
3. How to use Furosemide Kalceks
The doctor will determine the required dose, administration time, and duration of treatment.
Furosemide Kalceks is administered by a doctor or nurse via slow intravenous injection or infusion, or intramuscularly.
Therapy will be switched to oral as soon as possible.
Using a higher dose of Furosemide Kalceks than recommended
If the patient is concerned that they have received too high a dose of furosemide, they should immediately consult their doctor. The symptoms that may occur after administration of too high a dose depend on the degree of loss of salts and fluids. Symptoms of overdose include dryness of the mucous membranes, increased thirst, irregular heartbeat, mood changes, muscle cramps or pain, nausea or vomiting, extreme fatigue or weakness, slow or weak pulse, or loss of appetite.
If the patient has any further questions about using this medicine, they should ask their doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Furosemide Kalceks can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The patient should immediatelyinform their doctor or nurse if they notice any of the following symptoms:
- Severe allergic reactions, which may include rash, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat, difficulty breathing, and loss of consciousness (anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reaction) (may occur in less than 1 in 1,000 people)
- Severe skin reactions (which may also affect mucous membranes) such as blisters or peeling of the skin (Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), drug rash, which appears as small, itchy, reddish-purple spots on the skin, genitals, or mouth) (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Muscle damage called "rhabdomyolysis". Symptoms may include persistent muscle pain, muscle cramps, muscle weakness, tea-colored urine, and (or) nausea (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- A significant decrease in certain types of white blood cells called "agranulocytosis". Symptoms may include fever with chills, changes in the mucous membranes, and throat pain (may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 people)
Other side effects
Very common(may occur in more than 1 in 10 people)
- Loss of body fluids and related disorders due to loss of minerals (sodium, potassium, magnesium, calcium), low blood volume (especially in elderly people)
- Increased levels of certain lipids in the blood (triglycerides)
- Low blood pressure, dizziness, or fainting when standing up from a sitting or lying position (when administered intravenously)
- Increased creatinine levels in the blood (indicating how well the patient's kidneys are working)
Common(may occur in less than 1 in 10 people)
- Concentration of the blood (when the patient urinates more frequently than normal)
- Low levels of sodium and chloride in the blood (especially when sodium chloride intake is restricted). Symptoms of low sodium levels in the blood may include apathy, calf cramps, loss of appetite, weakness, drowsiness, vomiting, and disorientation
- Low levels of potassium in the blood (especially when potassium intake is restricted or when potassium is lost due to vomiting or diarrhea). Symptoms of low potassium levels may include muscle weakness, discomfort in the limbs (e.g., tingling, numbness, or painful burning), inability to move a part of the body (paralysis), vomiting, constipation, excessive gas in the intestines, excessive urine production, pathological thirst, and slow or irregular pulse. Significant potassium loss can lead to intestinal paralysis (paralytic ileus) or changes in consciousness, and even coma
- Increased cholesterol levels in the blood
- Increased uric acid levels in the blood
- Gout attacks
- Brain function disorders due to severe liver disease (hepatic encephalopathy)
- Increased urine production
Uncommon(may occur in less than 1 in 100 people)
- Low platelet count
- Increased blood sugar levels. In patients with known diabetes, this may worsen. In patients with undiagnosed diabetes, it may lead to its discovery
- Hearing disorders, mainly temporary, especially in patients with kidney disorders or when administered intravenously too quickly
- Deafness (sometimes irreversible)
- Nausea
- Itching, hives, rash, skin and mucous membrane reactions with redness, blistering, or peeling (e.g., conditions such as blistering skin disease, erythema multiforme, pemphigus, exfoliative dermatitis, photosensitivity)
Rare(may occur in less than 1 in 1,000 people)
- Increased number of a certain type of white blood cell (eosinophilia)
- Decreased number of white blood cells (leukopenia)
- Tingling, numbness, or painful burning of the limbs
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Vasculitis (inflammation of blood vessels)
- Vomiting, diarrhea
- Kidney damage (interstitial nephritis)
- Fever
Very rare(may occur in less than 1 in 10,000 people)
- Red blood cell deficiency due to their abnormal breakdown (hemolytic anemia)
- A condition in which the bone marrow stops producing enough new blood cells (aplastic anemia)
- Acute pancreatitis
- Liver disorders called "intrahepatic cholestasis" and increased liver enzyme activity in the blood, which can cause jaundice (yellow skin, dark urine, fatigue)
Frequency not known(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Worsening or activation of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Low levels of calcium in the blood (may cause tetany - muscle cramps in hands and feet, muscle twitching, throat spasms with breathing difficulties, nausea, vomiting, seizures, and pain in rare cases)
- Low levels of magnesium in the blood (may cause tetany or heart rhythm disorders in rare cases)
- Dizziness, fainting, and loss of consciousness, headache
- Blockage of a blood vessel due to a blood clot (thrombosis, especially in elderly patients) In case of excessive urine production, especially in elderly patients and children, circulatory problems (leading to circulatory collapse) may occur, mainly manifested as headache, dizziness, blurred vision, dry mouth, and thirst, low blood pressure
- Decreased blood pH (metabolic acidosis)
- Pseudo-Bartter syndrome (kidney function disorders associated with abuse and/or long-term use of furosemide)
- Increased sodium levels in urine, increased chloride levels in urine, increased urea levels in blood, symptoms of urinary tract obstruction (e.g., in patients with prostate enlargement, hydronephrosis, urethral stricture) up to urinary retention; kidney calcification and/or kidney stones in premature infants, kidney failure
- The duct between the pulmonary artery and the aorta, which is open in unborn children, may remain open if premature infants are treated with furosemide in the first weeks of life
- Pain after intramuscular injection
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any not listed in the leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Furosemide Kalceks
Store the ampoules in the outer packaging to protect them from light. Do not store in the refrigerator or freeze.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton after: Expiry Date (EXP) and ampoule after: EXP. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Furosemide Kalceks contains
- The active substance of the medicine is furosemide. Each 1 ml of solution contains 10 mg of furosemide. Each 2 ml ampoule contains 20 mg of furosemide. Each 4 ml ampoule contains 40 mg of furosemide. Each 5 ml ampoule contains 50 mg of furosemide. Each 25 ml ampoule contains 250 mg of furosemide.
- The other ingredients are sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide, sodium hydroxide (for pH adjustment), water for injections.
What Furosemide Kalceks looks like and contents of the pack
Clear, colorless or almost colorless solution, free from visible particles.
Ampoules made of orange type I glass with one break point and a colored ring in a PVC sleeve in a cardboard box containing 2 ml, 4 ml, 5 ml, or 25 ml of solution.
Pack sizes:
5, 10, 25, or 50 ampoules of 2 ml
5, 10, 25, or 50 ampoules of 4 ml
5, 10, 25, or 50 ampoules of 5 ml
1, 5, 10, or 50 ampoules of 25 ml
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
AS KALCEKS
Krustpils iela 71E
LV-1057 Rīga
Latvia
Phone: +371 67083320
Email: [email protected]
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
Finland, Czech Republic, Denmark, Norway, Poland, Sweden
Furosemide Kalceks
Austria
Furosemide Kalceks 10 mg/ml Injektions-/Infusionslösung
France
FUROSEMIDE KALCEKS 10 mg/mL, solution injectable/pour perfusion
Germany
Furosemide Kalceks 10 mg/ml Injektions-/Infusionslösung
Latvia
Furosemide Kalceks 10 mg/ml šķīdums injekcijām/infūzijām
Lithuania
Furosemide Kalceks 10 mg/ml injekcinis ar infuzinis tirpalas
Slovenia
Furosemide Kalceks 10 mg/ml raztopina za injiciranje/infundiranje
Netherlands
Furosemide Kalceks 10 mg/ml oplossing voor injectie/infusie
United Kingdom (Northern Ireland)
Furosemide 10 mg/ml solution for injection/infusion
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 04/2023
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Incompatibilities
Furosemide Kalceks, solution for injection/infusion, should not be mixed with solutions for injection/infusion that have an acidic or slightly acidic pH and significant buffer capacity in the acidic range. In the case of these mixtures, the pH value is shifted to the acidic range, and the poorly soluble furosemide precipitates as a crystalline sediment.
Furosemide Kalceks, 10 mg/ml, solution for injection/infusion, should not be administered together with other medicines in the same syringe (solvents see "Instructions for use" below).
Silicone tubes are not suitable for administering the product.
Instructions for use
For single use only.
Use immediately after opening. Discard any remaining contents.
Before use, the solution should be inspected for the presence of solid particles. It should not be used if signs of deterioration are visible (e.g., solid particles or discoloration).
The product can be diluted with:
- sodium chloride 9 mg/ml (0.9%) solution for injection
- Ringer's solution
- Ringer's solution with lactate
It has been shown that furosemide is compatible with polypropylene (PP) or polycarbonate (PC) syringes, polyethylene (PE) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC) tubes, and PE, PVC, and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) bags after dilution to concentrations from 0.02 to 3 mg/ml with the above-mentioned solutions for injection.
It should be ensured that the pH of the solutions used is slightly alkaline to neutral (pH not less than 7). Acidic solutions should not be used, as the active substance may precipitate (see "Incompatibilities" above).
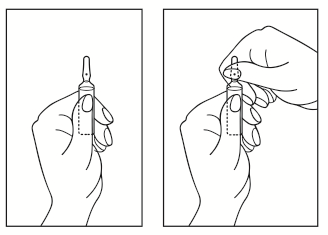
Instructions for opening the ampoule
- 1) Turn the ampoule so that the colored point is at the top. If there is solution in the upper part of the ampoule, gently tap with your finger to make the solution flow to the lower part of the ampoule.
- 2) Use both hands to open the ampoule; holding the lower part of the ampoule in one hand, break the upper part of the ampoule in the direction of the colored point (see pictures below).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterAS Kalceks
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Furosemide KalceksDosage form: Solution, 10 mg/mlActive substance: furosemidePrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 10 mg/mlActive substance: furosemidePrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 10 mg/mlActive substance: furosemideManufacturer: Laboratórios Basi - Indústria Farmacêutica, S.A.Prescription required
Alternatives to Furosemide Kalceks in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Furosemide Kalceks in Spain
Alternative to Furosemide Kalceks in Ukraine
Online doctors for Furosemide Kalceks
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Furosemide Kalceks – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










