

Fragmin

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fragmin

How to use Fragmin
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
FRAGMIN
2,500 anti-Xa IU/0.2 mL, solution for injection
FRAGMIN
5,000 anti-Xa IU/0.2 mL, solution for injection
FRAGMIN
7,500 anti-Xa IU/0.3 mL, solution for injection
FRAGMIN
10,000 anti-Xa IU/0.4 mL, solution for injection
FRAGMIN
12,500 anti-Xa IU/0.5 mL, solution for injection
FRAGMIN
15,000 anti-Xa IU/0.6 mL, solution for injection
FRAGMIN
18,000 anti-Xa IU/0.72 mL, solution for injection
Dalteparinum natricum
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet so that you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Fragmin and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Fragmin
- 3. How to use Fragmin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Fragmin
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Fragmin and what is it used for
Fragmin is an anticoagulant medicine, in the form of dalteparin sodium. Dalteparin sodium is a low molecular weight heparin. The anticoagulant effect of dalteparin is related to its ability to enhance the inhibition of factor Xa and thrombin.
Fragmin is indicated for use in adult patients over 18 years of age in:
- Treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis.
- Unstable angina (e.g., rest angina, myocardial infarction without Q-wave).
- Chronic treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism (proximal deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) to reduce the risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer.
- Prevention of blood clotting in extracorporeal circulation, e.g., during hemodialysis and hemofiltration in acute or chronic renal failure.
- Prophylactic anticoagulation associated with surgical procedures.
- Prophylactic anticoagulation in medically immobilized patients: with congestive heart failure in class III or IV NYHA or acute respiratory failure, with acute infection, with acute rheumatic disease or acute inflammatory bowel disease, and at least one additional risk factor for deep vein thrombosis, e.g., age over 75 years, obesity, cancer, history of deep vein thrombosis.
Fragmin is indicated for use in children in:
- Treatment of blood clots in the veins (venous thromboembolism (VTE)) in children and adolescents from 1 month of age and older.
2. Important information before using Fragmin
When not to use Fragmin
- If the patient is allergic to dalteparin sodium or other low molecular weight heparins, or unfractionated heparin, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- Confirmed or suspected heparin-induced thrombocytopenia of immunological origin;
- Active bleeding, e.g., from the gastrointestinal tract or cerebral vessels;
- Severe coagulation disorders;
- Acute or subacute bacterial endocarditis;
- Recent injuries or surgical procedures in the central nervous system, eyes, and/or ears. Due to the increased risk of bleeding, high doses of dalteparin sodium (e.g., those used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or unstable angina) should not be used in patients who have undergone spinal anesthesia or epidural or spinal puncture.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Fragmin, you should discuss it with your doctor or pharmacist.
- In patients before spinal anesthesia (epidural or spinal) or spinal puncture. Patients receiving such anticoagulant medications as low molecular weight heparins or heparinoids for the prevention of thromboembolic complications are at risk of developing an epidural or spinal hematoma, which can cause long-term or permanent paralysis. The risk of such complications is increased in cases where a permanent catheter is inserted into the epidural space for the administration of anesthetics, and in cases where anticoagulant medications that affect hemostasis, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antiplatelet agents, and other anticoagulant medications, are used concurrently. Traumatic or repeated epidural or spinal puncture also appears to increase this risk. Such patients should be monitored frequently, checking for signs of neurological changes.
- In patients with a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, platelet disorders, severe liver or kidney dysfunction, uncontrolled or untreated hypertension, or hypertensive retinopathy or diabetic retinopathy. High doses of dalteparin sodium, such as those used in the treatment of deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, or unstable angina, should be used with caution in patients who have recently undergone surgical procedures or other conditions that may increase the risk of bleeding.
- In patients with thrombocytopenia, platelet disorders, severe liver or kidney dysfunction, or uncontrolled or untreated hypertension. The doctor should recommend platelet count tests before starting treatment with Fragmin and regular monitoring of this parameter during treatment. In all cases, it is recommended to perform an in vitro test for anti-platelet antibodies in the presence of unfractionated heparin or low molecular weight heparins. If the result of this test is positive or unclear, or if such a test is not performed, the doctor should discontinue treatment with Fragmin.
- In pediatric patients, patients with renal impairment, or patients with significant underweight or obesity, pregnant women, or individuals at increased risk of bleeding or recurrence of thrombosis, in whom the doctor should consider monitoring the anticoagulant effect of dalteparin sodium. The doctor will recommend the necessary tests.
- In patients undergoing long-term dialysis, the doctor will recommend appropriate dose adjustment of Fragmin after performing anti-Xa activity tests. In patients undergoing hemodialysis for acute indications, frequent monitoring of anti-Xa activity is necessary.
- In patients with unstable angina, i.e., unstable angina or myocardial infarction without Q-wave. In these patients, the doctor may recommend thrombolytic treatment (restoring blood flow in a closed or narrowed blood vessel). Concurrent use of Fragmin and thrombolytic medication increases the risk of bleeding, but this does not mean that Fragmin should be discontinued.
- In patients with unstable angina treated with Fragmin for a long time, in cases of impaired renal function (creatinine levels >150 μmol/L). In these patients, the doctor may consider reducing the dose.
- In patients with allergy or suspected allergy to latex (natural rubber) or in individuals with contact with the needle shield of Fragmin in pre-filled syringes with confirmed or suspected latex allergy (natural rubber). The needle shield of Fragmin in pre-filled syringes may contain latex (natural rubber). In individuals with latex hypersensitivity, severe allergic reactions may occur. Due to the risk of hematoma, it is recommended to avoid performing any intramuscular injections in patients treated with Fragmin at a daily dose above 5,000 IU.
Interchangeability with other anticoagulant medications
Dalteparin cannot be used interchangeably (unit for unit) with unfractionated heparin, other low molecular weight heparins, or synthetic polysaccharides. Each of these medications differs in terms of the raw materials used, the manufacturing process, and physical, chemical, biological, and clinical properties, which leads to differences in dosing and possibly clinical efficacy and safety. Each of these medications is unique and requires adherence to individual medical recommendations for use.
Children
Fragmin should not be used in newborns under 1 month of age.
Fragmin and other medications
You should tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medications you plan to take.
Some medications may affect the action of Fragmin, and Fragmin may reduce the effectiveness of other medications taken at the same time.
Thrombolytic treatment (dissolving blood clots) or certain medications that affect blood clotting may increase the risk of bleeding when used concurrently with Fragmin:
- Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid);
- Medications that inhibit platelet aggregation (used to reduce platelet aggregation and reduce the risk of blood clot formation);
- Thrombolytic medications (used to dissolve blood clots);
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) (medications used to treat inflammatory conditions);
- GP IIb/IIIa receptor antagonists (medications that affect platelet aggregation, used to treat heart diseases);
- Vitamin K antagonists and other types of anticoagulant medications;
- Dextrans (used in some artificial tears).
Medications that increase the effect of Fragmin:
- Medications used to thin the blood (dipyridamole);
- Certain medications used to treat gout (e.g., sulfinpyrazone, probenecid);
- Certain diuretics (e.g., ethacrynic acid);
- Infusion solutions used to increase blood volume;
- Cytostatic medications (used to treat cancer).
Medications that may reduce the effect of Fragmin:
- Medications used to treat allergies and hay fever (e.g., antihistamines);
- Medications used to treat heart failure and cardiovascular diseases (e.g., medications containing digitalis, such as digoxin, digitoxin);
- Tetracycline antibiotics, which are used to treat bacterial infections;
- Vitamin C (e.g., contained in vitamin preparations).
Other medications that may affect the action of Fragmin:
- Medications used to treat angina (e.g., intravenously administered nitroglycerin);
- Antibiotics, such as penicillins administered in high doses, which are used to treat bacterial infections;
- Medications used to prevent and treat malaria (e.g., quinine);
- Nicotine taken due to smoking or smoking cessation preparations.
It should be remembered that if a patient is being treated with Fragmin due to unstable angina, the doctor may adjust the dose of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) accordingly.
Recommendations for dosing in children are based on clinical experience; data from clinical trials are too limited for the doctor to adjust the appropriate dose of Fragmin.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
The medicine should be used during pregnancy only if it is absolutely necessary.
Breastfeeding
Small amounts of dalteparin sodium pass into human milk. The risk to the baby cannot be excluded. Fragmin should be used during breastfeeding, taking into account the benefits of breastfeeding for the baby and the benefits of therapy for the mother.
Fertility
There is no data indicating the effect of Fragmin on fertility.
Driving and using machines
Fragmin does not affect the ability to drive or operate machines.
Fragmin contains sodium
Fragmin 2,500 anti-Xa IU/0.2 mL, Fragmin 5,000 anti-Xa IU/0.2 mL, Fragmin 7,500 anti-Xa IU/0.3 mL, Fragmin 10,000 anti-Xa IU/0.4 mL, Fragmin 12,500 anti-Xa IU/0.5 mL, Fragmin 15,000 anti-Xa IU/0.6 mL, and Fragmin 18,000 anti-Xa IU/0.72 mL contain less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per pre-filled syringe, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free". Patients on a low-sodium diet and parents whose children are being treated with Fragmin can be informed that these medicines are essentially "sodium-free".
This medicine may be diluted with solutions containing sodium. You should inform your doctor if you or your child are on a low-sodium diet.
3. How to use Fragmin
This medicine should always be used exactly as prescribed by your doctor or pharmacist. If you are unsure, you should consult your doctor or pharmacist.
Fragmin is administered subcutaneously, intravenously, or extracorporeally (in the dialysis circuit).
Fragmin should not be administered intramuscularly.
In the treatment of blood clots, Fragmin is administered subcutaneously.
If the patient is undergoing hemodialysis or hemofiltration (processes used to purify the blood), Fragmin is administered intravenously or into the dialysis tube.
Dalteparin can be mixed with isotonic sodium chloride infusion solution (9 mg/mL) or glucose (50 mg/mL) in glass bottles and plastic containers.
Dosing and administration Treatment of acute deep vein thrombosis
Fragmin can be administered subcutaneously in one or two doses per day.
During treatment with Fragmin, concurrent administration of vitamin K antagonists can be started.
- The doctor will recommend the dose of Fragmin based on the patient's weight.
Once-daily administration
Dose of 200 anti-Xa IU/kg body weight subcutaneously once daily. Monitoring of anticoagulant activity is not usually necessary. Do not use a single daily dose greater than 18,000 IU.
Dosing from a pre-filled syringe can be determined based on the following table.
| Body weight (kg) | Dose |
| 46-56 | 10,000 IU |
| 57-68 | 12,500 IU |
| 69-82 | 15,000 IU |
| 83 and above | 18,000 IU |
Twice-daily administration
Alternatively, a dose of 100 anti-Xa IU/kg body weight can be administered subcutaneously twice daily. Generally, monitoring of anticoagulant activity is not necessary, but it should be considered in special patients (see section 2: Warnings and precautions). Blood should be drawn when the maximum concentration of the medication is present in the plasma (3-4 hours after subcutaneous injection). Recommended maximum plasma activities are between 0.5 and 1.0 anti-Xa IU/mL.
Prevention of blood clotting in extracorporeal circulation, e.g., during hemodialysis and hemofiltration in acute or chronic renal failure
Fragmin should be administered intravenously or into the arterial line of the extracorporeal circulation system, choosing the most suitable dosing regimen from the following:
- Patients with chronic renal failure and without increased bleeding riskUsually, only minor adjustments to the dose are necessary, so frequent monitoring of anti-Xa activity is not required in most of these patients.
- Hemodialysis and hemofiltration lasting no longer than 4 hoursA single intravenous bolus injection can be administered at the start of the procedure. The recommended initial dose is 5,000 IU; a lower initial dose may be used if clinically indicated. The initial dose of 5,000 IU for the single-bolus dosing regimen can be adjusted from session to session based on the outcome of the previous dialysis; the dose can be increased or decreased gradually by 500 or 1,000 IU until a satisfactory effect is achieved. Alternatively, an intravenous bolus injection of 30-40 IU/kg body weight can be administered, followed by an intravenous infusion of 10-15 IU/kg body weight per hour.
- Hemodialysis and hemofiltration lasting more than 4 hoursA single intravenous bolus injection of 30-40 IU/kg body weight, followed by an intravenous infusion of 10-15 IU/kg body weight per hour.
- Patients with acute renal failure or increased bleeding riskIntravenous bolus injection of 5-10 IU/kg body weight, followed by an intravenous infusion of 4-5 IU/kg body weight per hour. Such patients may be more unstable and may require monitoring of anti-Xa levels. The anti-Xa concentration in plasma should be between 0.2 and 0.4 IU/mL.
Prophylactic anticoagulation associated with surgical procedures
Fragmin should be administered subcutaneously. Monitoring of anticoagulant activity is not usually necessary. If monitoring is performed, blood should be drawn when the maximum concentration of the medication is present in the plasma (3-4 hours after subcutaneous injection). Recommended plasma activities are generally between 0.1 and 0.4 anti-Xa IU/mL.
- Patients at risk of thromboembolic complications2,500 IU subcutaneously 2 hours before surgery and 2,500 IU subcutaneously every morning after surgery until the patient is mobilized (usually for 5 to 7 days or longer).
- Patients with additional risk factors for thromboembolic complications (e.g., cancer)Administer Fragmin until the patient is mobilized (usually for 5 to 7 days or longer).
- 1. Starting administration on the day before surgery: 5,000 IU subcutaneously in the evening before surgery. After surgery, administer 5,000 IU subcutaneously every evening.
- 2. Starting administration on the day of surgery: 2,500 IU subcutaneously within 2 hours before surgery, and 2,500 IU subcutaneously 8-12 hours later, but not earlier than 4 hours after the end of surgery. After surgery, starting from the next day, administer 5,000 IU subcutaneously every morning.
Orthopedic surgery (e.g., hip replacement surgery)
Administer Fragmin for up to 5 weeks after surgery, choosing one of the following treatment regimens.
- 1. Starting administration before surgery – the evening before surgery: 5,000 IU subcutaneously in the evening before surgery. After surgery, administer 5,000 IU subcutaneously every evening.
- 2. Starting administration before surgery – on the day of surgery: 2,500 IU subcutaneously within 2 hours before surgery, and 2,500 IU subcutaneously 8-12 hours later, but not earlier than 4 hours after the end of surgery. Starting from the day after surgery, administer 5,000 IU subcutaneously every morning.
- 3. Starting administration after surgery: 2,500 IU subcutaneously 4-8 hours after surgery, but not earlier than 4 hours after the end of surgery. Starting from the day after surgery, administer 5,000 IU subcutaneously every morning.
Prophylaxis of acute deep vein thrombosis in medically immobilized patients
The recommended dose of Fragmin is 5,000 IU once daily. Treatment with dalteparin sodium is continued until the end of the patient's immobilization period, up to 14 days or longer. Monitoring of anticoagulant activity is not usually necessary.
Duration of administration
Prophylactic anticoagulation in patients with significantly increased risk of thromboembolism, temporarily immobilized due to severe illness, such as heart failure, respiratory failure, or severe infection, should be continued until the patient is fully mobilized. The duration of use is determined based on the patient's condition and usually lasts 14 days.
Method of administration
The drop at the end of the needle should be removed before injection, as the introduction of dalteparin sodium into the injection channel may lead to the formation of a harmless superficial hematoma or, in rare cases, local irritation.
To learn the exact instructions for administration, see the section below How to inject Fragmin
Fragmin. Unstable angina (unstable angina and myocardial infarction without Q-wave)
Generally, monitoring of anticoagulant activity is not necessary, but it should be considered in special patients (see section 2: Warnings and precautions). Blood should be drawn when the maximum concentration of the medication is present in the plasma (3-4 hours after subcutaneous injection). Recommended maximum plasma activities are between 0.5 and 1.0 anti-Xa IU/mL. It is recommended to administer acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin) concurrently (at a dose of 75-325 mg/day). Administer Fragmin at a dose of 120 IU/kg body weight subcutaneously every 12 hours, up to a maximum dose of 10,000 IU/12 hours. Continue treatment until the patient's clinical condition stabilizes (usually for at least 6 days) or longer if the doctor considers it beneficial. Subsequently, it is recommended to extend treatment with a fixed dose of Fragmin until revascularization procedures (such as percutaneous interventions or coronary artery bypass grafting) are performed. The medication should not be used for more than 45 days. The dose of Fragmin is determined based on the patient's weight and gender:
- In the case of women with a body weight below 80 kg and men with a body weight below 70 kg, administer 5,000 IU subcutaneously every 12 hours.
- In the case of women with a body weight of 80 kg or more and men with a body weight of 70 kg or more, administer 7,500 IU subcutaneously every 12 hours.
Chronic treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism (proximal deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism) to reduce the risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer
Month 1
For the first 30 days of treatment, Fragmin should be administered once daily, subcutaneously (sc.), at a dose of 200 IU/kg body weight. The total daily dose should not exceed 18,000 IU.
Months 2-6
Fragmin should be administered once daily, subcutaneously, at a dose of approximately 150 IU/kg body weight. The size of the dose of Fragmin administered from a single-dose pre-filled syringe is determined based on the following table.
Reducing the dose in case of thrombocytopenia during chemotherapy
The following dosing rules were used in clinical trials:
In the case of chemotherapy-induced thrombocytopenia with a platelet count below 50,000/mm^3, Fragmin administration should be discontinued until the platelet count returns to above 50,000/mm^3. If the platelet count is between 50,000 and 100,000/mm^3, the dose of Fragmin should be reduced by 17% to 33% of the initial dose (depending on the patient's body weight). Once the platelet count returns to ≥100,000/mm^3, the full dose of Fragmin should be resumed.
Table 1. Reducing the dose of Fragmin in case of thrombocytopenia in the range of 50,000 – 100,000/mm^3, dosing using single-dose pre-filled syringes
Renal impairment
In the case of significant renal impairment defined as creatinine levels exceeding three times the upper limit of normal, the dose of Fragmin should be adjusted to maintain a therapeutic anti-Xa level of 1 IU/mL (range 0.5-1.5 IU/mL), measured 4-6 hours after injection. If the anti-Xa level is below or above the therapeutic range, the dose of Fragmin should be increased or decreased accordingly. The measurement of anti-Xa levels should be repeated after administering 3-4 injections at the newly adjusted dose. This dose adjustment scheme should be repeated until anti-Xa levels reach the therapeutic range.
| Body weight (kg) | Dose of Fragmin (IU) |
| ≤56 | 7,500 |
| 10,000 |
| 12,500 |
| 15,000 |
| ≥99 | 18,000 |
| Body weight (kg) | Planned dose of Fragmin (IU) | Reduced dose of Fragmin (IU) | Average dose reduction (%) |
| ≤56 | 7,500 | 5,000 | 33 |
| 10,000 | 7,500 | 25 |
| 12,500 | 10,000 | 20 |
| 15,000 | 12,500 | 17 |
| ≥99 | 18,000 | 15,000 | 17 |
Use in children and adolescents
Treatment of blood clots in the veins (venous thromboembolism (VTE))
The recommended doses depend on the child's weight and age group, and will be calculated by the doctor. The doctor will inform you about the individualized dose of Fragmin according to these criteria. The dosing regimen should not be changed without consulting the doctor.
The following are the recommended initial doses for children and adolescents based on their age:
Children from 1 month to less than 2 years of age:150 IU/kg body weight twice daily.
Children from 2 years to less than 8 years of age:125 IU/kg body weight twice daily.
Children from 8 years to less than 18 years of age:100 IU/kg body weight twice daily.
The effect of Fragmin is monitored after administering the initial dose, and then the dose is adjusted based on blood tests.
How to inject Fragmin
Fragmin is administered subcutaneously. This part of the leaflet explains how to administer Fragmin to yourself or your child. You should follow these instructions only after being trained by a doctor. If you are unsure what to do, you should contact your doctor immediately.
You should inject (administer) the dose of Fragmin at the times of the day recommended by your doctor.
If it is necessary to dilute Fragmin before administration to children, this should be done by medical personnel. You should follow the doctor's recommendations regarding the method and time of administering the diluted Fragmin.
You should perform the following steps
Step 1: Preparing the pre-filled syringe for injection of Fragmin.
Remove the cap from the pre-filled syringe. A air bubble will appear in the pre-filled syringe. It should be there and should be ignored. It is important not to press the plunger yet, as some of the medication may be lost. Air bubbles in single-dose pre-filled syringes should not be expelled before injection, as this may lead to loss of medication and thus reduction of the dose.
The pre-filled syringe is ready for injection. Proceed to step 2.
Step 2: Choosing and preparing the injection site
Choose one of the recommended injection sites below (see shaded areas in Figure 3):
The area around the navel in a "U" shape.
The middle of the thigh.
Figure 3
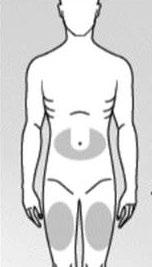
- Each time you administer a dose, inject it into a different site.
- Do not inject into areas where the skin is sensitive, bruised, red, or hard. Avoid areas with scars.
- If the adult or child has psoriasis, do not inject the medication directly into any raised, thick, red, or scaly skin patches ("psoriatic skin lesions").
- Wash and dry your hands.
- Clean the injection site with a new swab dipped in alcohol, making circular motions. The skin should be completely dry. Do not touch the area again before performing the injection.
Step 3: Assuming the correct position
The adult or child should sit or lie down for deep subcutaneous injection. If the patient is administering the injection to themselves, they should sit in a comfortable sitting position so that they can see their stomach (see Figure 4).
Figure 4
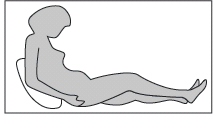
Step 4:
Using your thumb and index finger, grasp a fold of skin with one hand. With the other hand, hold the pre-filled syringe like a pencil. This will be the injection site.
Step 5:
In the case of injecting Fragmin to an adult or to yourself, hold the pre-filled syringe over the skin fold at a right angle (i.e., vertically, as shown, and not at an angle). Insert the needle into the skin until it is fully inserted (see Figure 5).
Figure 5
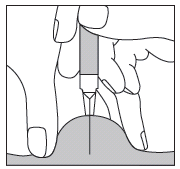
In the case of injecting Fragmin to a child, insert the needle into the skin with a quick, short motion at an angle of 45° to 90° (see Figure 6).
Figure 6
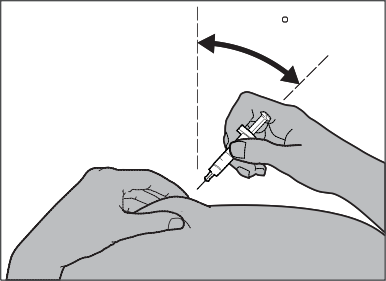
Step 6:
Press the plunger to the end at a slow, steady pace to administer the correct dose.
During injection, continue to hold the skin fold, and then release it and withdraw the needle.
If bleeding occurs at the injection site, apply gentle pressure. Do not rub the injection site, as this may cause bruising.
Apply a swab to the injection site for 10 seconds. Minor bleeding may occur. Do not rub the injection site. The injection site can be covered with a bandage.
| Step 6: If the pre-filled syringe has a Needle-Trap needle guard | |
| needle guard | |
| Place the plastic guard on a hard, stable surface and, with one hand, turn the cylinder of the pre-filled syringe upwards towards the needle, pushing the needle into the sheath, where it will lock into place (see Figure 7 | |
| Continue bending the needle until the pre-filled syringe exceeds an angle of 45 degrees with the flat surface, making it permanently unusable (see Figure 8 | |
Figure 7 Figure 8
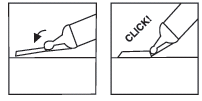
Step 7:
Discard the pre-filled syringe and needle into a sharps container. Keep the sharps container in a location that is inaccessible to others. When the sharps container is almost full, discard it according to the instructions or consult your doctor or nurse.
The dose will be adjusted based on the child's age and body weight. In younger children, a slightly higher dose of Fragmin may be required per kilogram of body weight than in adults. The doctor will adjust the appropriate dose for the patient. To monitor the effect of Fragmin, medical personnel may draw a blood sample during treatment.
Use of Fragmin in patients with renal and hepatic impairment
The medication requires cautious use in patients with renal and hepatic impairment (see section 2: Warnings and precautions).
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. Side effects are listed according to their frequency. Frequent(may occur in no more than 1 in 10 people)
- mild, reversible thrombocytopenia (type I)
- bleeding
- transient increase in liver enzyme activity (aminotransferases, AspAT, AlAT)
- subcutaneous hematoma at the injection site
- pain at the injection site
Infrequent(may occur in no more than 1 in 100 people)
- hypersensitivity
Rare(may occur in no more than 1 in 1,000 people)
- skin necrosis
- transient alopecia
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from the available data)
- heparin-induced immunological thrombocytopenia (type II, with or without thrombotic complications)
- anaphylactic reactions
- intracranial bleeding (some fatal)
- bleeding into the retroperitoneal space (some fatal)
- rash
- subdural or epidural hematoma
Heparin products can cause hypoaldosteronism (decreased aldosterone secretion - a hormone of the adrenal cortex), which can lead to increased potassium levels in the blood (hyperkalemia). Rarely, especially in patients with chronic renal failure and diabetes, clinically significant hyperkalemia may occur. With long-term use of Fragmin, there is a risk of osteoporosis. It is estimated that the side effects in children will be the same as in adults, but there is only limited data on the occurrence of possible side effects during long-term treatment in children.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the representative of the marketing authorization holder or the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Fragmin
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children. Prefilled syringes should be stored at a temperature below 25°C. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated. From a microbiological point of view, the medicine should be used immediately. If it is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the storage time and conditions during use. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. These measures will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Fragmin contains
- The active substance is dalteparin sodium. The potency is expressed in anti-Xa international units (IU) in accordance with the First International Standard for Low Molecular Weight Heparins.
- The other ingredients are:
What Fragmin looks like and contents of the pack
The solution for injection is available in a prefilled syringe with a needle containing a single dose of the medicine (Type I glass) with a needle shield (rubber), plunger stopper (chlorobutyl rubber), and plunger (polypropylene or polystyrene) with or without a Needle-Trap as a safety device. The needle shield may contain latex.
| No. | Volume | Dalteparin sodium (Dalteparinum natricum) |
| 0.2 ml | 2,500 anti-Xa IU |
| 0.2 ml | 5,000 anti-Xa IU |
| 0.3 ml | 7,500 anti-Xa IU |
| 0.4 ml | 10,000 anti-Xa IU |
| 0.5 ml | 12,500 anti-Xa IU |
| 0.6 ml | 15,000 anti-Xa IU |
| 0.72 ml | 18,000 anti-Xa IU |
| No. | Dose/Volume | Excipients |
| 2,500 anti-Xa IU/0.2 ml | sodium chloride, sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (pH 5-7.5 adjustment), water for injections |
| 5,000 anti-Xa IU/0.2 ml | sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (pH 5-7.5 adjustment), water for injections |
| 7,500 anti-Xa IU/0.3 ml | sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (pH 5-7.5 adjustment), water for injections |
| 10,000 anti-Xa IU/0.4 ml | sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (pH 5-7.5 adjustment), water for injections |
| 12,500 anti-Xa IU/0.5 ml | sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (pH 5-7.5 adjustment), water for injections |
| 15,000 anti-Xa IU/0.6 ml | sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (pH 5-7.5 adjustment), water for injections |
| 18,000 anti-Xa IU/0.72 ml | sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid (pH 5-7.5 adjustment), water for injections |
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder
Pfizer Europe MA EEIG, Boulevard de la Plaine 17, 1050 Bruxelles, Belgium
Manufacturer
2,500 anti-Xa IU/0.2 ml; 5,000 anti-Xa IU/0.2 ml; 7,500 anti-Xa IU/0.3 ml: Pfizer Manufacturing Belgium NV, Rijksweg 12, 2870 Puurs-Sint-Amands, Belgium; Catalent France Limoges S.A.S., Z.I. Nord, 53 rue de Dion Bouton, 87280 Limoges, France. 10,000 anti-Xa IU/0.4 ml, 12,500 anti-Xa IU/0.5 ml; 15,000 anti-Xa IU/0.6 ml; 18,000 anti-Xa IU/0.72 ml: Pfizer Manufacturing Belgium NV, Rijksweg 12, 2870 Puurs-Sint-Amands, Belgium. For more detailed information on this medicine, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder: Pfizer Polska Sp. z o.o., tel. 22 335 61 00.
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 06/2025
Detailed and up-to-date information about this product can be obtained by scanning the QR code on the outer packaging using a mobile device. The same information is also available at the URL: https://pfi.sr/ulotka-fragmin and on the website of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: http://www.urpl.gov.pl.
| No. | Dose/Volume | Type and content of packaging |
| 2,500 anti-Xa IU/0.2 ml | 10 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.2 ml each, 20 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.2 ml each |
| 5,000 anti-Xa IU/0.2 ml | 10 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.2 ml each, 20 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.2 ml each |
| 7,500 anti-Xa IU/0.3 ml | 10 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.3 ml each, 20 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.3 ml each |
| 10,000 anti-Xa IU/0.4 ml | 5 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.4 ml each |
| 12,500 anti-Xa IU/0.5 ml | 5 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.5 ml each |
| 15,000 anti-Xa IU/0.6 ml | 5 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.6 ml each |
| 18,000 anti-Xa IU/0.72 ml | 5 prefilled syringes with a needle, 0.72 ml each |
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterCatalent France Limoges S.A.S Z.I. Nord Pfizer Manufacturing Belgium NV
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FragminDosage form: Solution, 5000 IU anti-Xa/0.2 mlActive substance: dalteparinPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 7500 IU anti-Xa/0.3 mlActive substance: dalteparinPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 12,500 IU anti-Xa/0.5 mlActive substance: dalteparinPrescription required
Alternatives to Fragmin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fragmin in Espanha
Online doctors for Fragmin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fragmin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














