How to use Flarex
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Flarex, 1 mg/ml, Eye Drops, Suspension
Fluorometholone Acetate
Read the Package Leaflet Carefully Before Using the Medication, as it Contains Important Information for the Patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medication has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medication may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet
- 1. What is Flarex and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Flarex
- 3. How to use Flarex
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Flarex
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Flarex and what is it used for
Flarex is intended for the treatment of symptomsof non-infectious inflammatory eye diseases that respond to corticosteroids, such as inflammation of the conjunctiva and cornea, as well as the anterior segment of the eye.
2. Important information before using Flarex
When not to use Flarex eye drops
- if the patient is allergic to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of this medication (listed in section 6),
- if the patient has:
- untreated acute bacterial eye infection,
- herpetic keratitis, chickenpox, shingles, or any other viral eye infection,
- fungal eye infection,
- tuberculous eye infection,
- untreated purulent eye infection.
Corticosteroids should not be used in the presence of infections or injuries limited to the superficial corneal epithelium.
Warnings and precautions
- Flarex should be used exclusively for eye drops (eyes).
- If the patient uses Flarex eye drops for a long period:
- The patient may experience increased eye pressure. The risk of corticosteroid-induced increased eye pressure is higher in children and may occur faster than in adults. Especially when using the medication in children, consult a doctor for advice. The risk of corticosteroid-induced glaucoma and cataract formation is also
higher in patients suffering from other diseases (e.g., patients with diabetes).
- The patient may develop glaucoma with optic nerve damage, decreased visual acuity, and visual field disturbances, as well as posterior subcapsular cataract formation.
- If symptoms worsen or an acute relapse occurs, consult a doctor. The patient may be more susceptible to eye infections.
- If an infection occurs, the doctor will prescribe another medication to treat the infection.
- Topical steroid medications for the eyes may delay the healing of eye injuries. Concurrent topical use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications may cause a risk of eye healing problems.
- If the patient suffers from diseases leading to thinning of the eye tissues, they should consult a doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
- If the patient is using other medications, they should carefully read the section "Flarex and other medications".
- Topical corticosteroid administration may be accompanied by a decrease in cortisol secretion in the urine as well as a decrease in cortisol concentration in the blood. An association between corticosteroids and a decrease in growth rate has been observed in children, especially at high doses and with long-term treatment.
- In patients who have been treated with systemic or topical corticosteroids for other diseases, ocular herpes has occurred. The use of corticosteroid therapy in the treatment of herpes, other than herpetic keratitis, in which it is contraindicated, requires great caution. Periodic microscopic examination with a slit lamp is necessary.
If the patient experiences blurred vision or other visual disturbances, they should consult a doctor.
Before starting to use Flarex, discuss it with a doctor or pharmacist.
Children
It is not recommended to use Flarex eye drops in children.
Flarex and other medications
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medications you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as medications you plan to take, including those available without a prescription.
If you are using other eye drops or ointments, wait at least 5 minutes between administrations of the next medications. Apply eye ointments last.
Concurrent topical use of a steroid medication and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication may cause a risk of eye healing problems.
When using eye drops intended to dilate the pupil (e.g., atropine), which can increase intraocular pressure, this effect may be enhanced when Flarex is used concurrently.
Ocular corticosteroids may increase intraocular pressure, reducing the effectiveness of anti-glaucoma medications.
Some medications may enhance the effect of Flarex, and therefore, the attending doctor may decide to monitor the patient's condition carefully when taking these medications (including some medications used to treat HIV: ritonavir, cobicistat).
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult a doctor or pharmacist before using this medication.
It is not known whether Flarex can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman, or whether it can affect reproductive capacity. Flarex should be administered to a pregnant woman only when the doctor considers it necessary.
It is not known whether the medication is excreted into human milk. Since many medications are excreted into human milk, caution should be exercised when administering Flarex to a breastfeeding woman.
Driving and using machines
Flarex has no or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
For some time after administering Flarex, vision may be blurred. Do not drive or operate machines until this symptom subsides .
Flarex contains benzalkonium chloride
The medication contains 0.5 mg of benzalkonium chloride in every 5 milliliters of suspension, which corresponds to 0.1 mg/ml.
Benzalkonium chloride may be absorbed by soft contact lenses and change their color. Remove contact lenses before administering the drops and wait at least 15 minutes before reinserting them.
Benzalkonium chloride may also cause eye irritation, especially in people with dry eye syndrome or corneal disorders (the transparent layer at the front of the eye). If you experience any abnormal sensations in the eye, stinging, or eye pain after using the medication, consult a doctor.
Flarex contains phosphates
The medication contains 3.5 mg of phosphates in every 5 milliliters of suspension, which corresponds to 0.7 mg of phosphates/ml.
In patients with severe damage to the transparent, anterior part of the eye (cornea), phosphates may, in very rare cases, cause corneal clouding during treatment due to calcium deposition.
3. How to use Flarex
Always use this medication exactly as your doctor has told you.
In case of doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
If the protective cap is loosened after removing the tamper-evident seal, discard it before using the medication.
Adolescents and adults (including elderly patients)
The usual dose of Flarex is one to two drops into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye or eyes, four times a day. During the first 48 hours, the doctor may increase the dose to two drops every 2 hours. If no improvement occurs after two weeks of using the medication, the patient should consult a doctor.
Regular monitoring of intraocular pressure is recommended.
Do not stop treatment prematurely.
The doctor will determine how long to use the medication.
Children
The safety and efficacy of Flarex in children have not been established, and therefore, its use is not recommended in this age group.
If the medication is used in patients with glaucoma, the treatment period should be limited to 2 weeks, unless longer treatment is justified.
Flarex is intended exclusivelyfor administration into the eye.
1
2
3
4
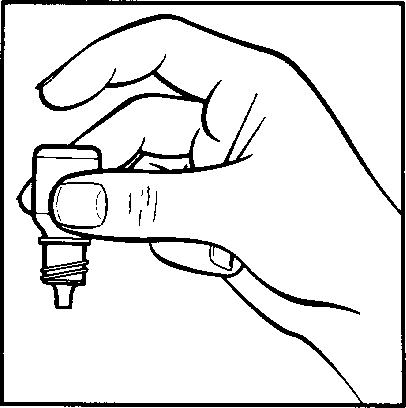
Method of using the eye drops
- 1. Prepare the bottle of eye drops and a mirror.
- 2. Wash your hands thoroughly.
- 3. Shake the bottle well.
- 4. Unscrew the cap.
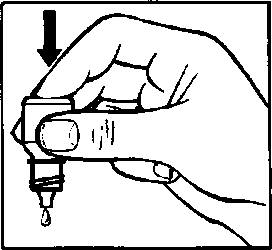
- 5. Hold the bottle in your hand, with the thumb and middle finger, and direct it upwards (drawing 1).
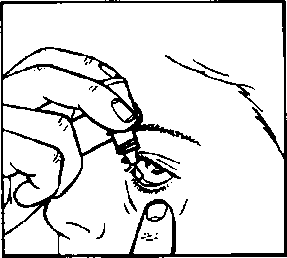
- 6. Tilt your head back. Pull down the lower eyelid with a clean finger to form a "pocket" between the eyelid and the eye; the drop should fall into it (drawing 2).
- 7. Bring the tip of the bottle close to the eye. You can use a mirror to help.
- 8. Do not touch the dropper tip to the eye, eyelid, or surrounding areas.This could cause infection.
- 9. Gently squeeze the bottom of the bottle to release a single drop of Flarex (drawing 3).
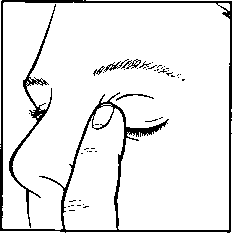
- 10. After administering the eye drops, remove the finger that held the lower eyelid. Close your eye and gently press the inner corner of your eye with your finger for 2 minutes (drawing 4). This will help prevent the medication from entering the entire body.
- 11. If it is necessary to administer drops to both eyes, repeat the above steps for the second eye.
- 12. Immediately after use, screw the bottle cap back on.
- 13. Use one bottle of medication at a time. If a drop misses the eye, repeat the attempt to administer the drop correctly.
Using a higher dose of Flarex than recommended
In case of accidental administration of an excessive amount of drops, rinse your eyes with lukewarm water.
Do not use the medication until the next scheduled dose.
Missing a dose of Flarex
If a dose of Flarex is missed, take the next scheduled dose. However, if there is little time left before the next dose, skip the missed dose and return to the normal administration schedule. Do nottake a double dose to make up for the missed dose.
If you are using other eye drops or ointments, wait at least 5 minutes between administrations of the next medications. Apply eye ointments last.
In case of any doubts about using this medication, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medications, Flarex can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
During the use of Flarex eye drops, the following side effects have been observed:
Uncommon(may affect 1 to 10 in 1000 patients):
eye irritation, eye redness, increased intraocular pressure
Rare(may affect 1 to 10 in 10,000 patients):
eye infection (worsening or secondary infection), eye swelling, eye itching, decreased visual acuity, posterior subcapsular cataract, glaucoma, visual field defect, pupil dilation, eyelid ptosis, hypersensitivity, impaired healing
Very rare(may affect 1 to 10 in 100,000 patients):
corneal perforation
In patients with severe damage to the transparent, anterior part of the eye (cornea), phosphates may, in very rare cases, cause corneal clouding during treatment due to calcium deposition.
Frequency not known(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
increased intraocular pressure, eye pain, eye irritation, discomfort in the eye, foreign body sensation in the eye, blurred vision, eye redness, increased tearing, blurred vision, taste disturbances
Unless the side effects are severe, you can usually continue using the drops.
In case of doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, inform your doctor or pharmacist.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, inform your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Post-Marketing Surveillance of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products,
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medication.
5. How to store Flarex
To prevent infections, the bottle should be discarded 4 weeks after it is first opened. The date of opening the bottle should be written in the space provided below.
Date of first opening: ………..
Medications should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medications that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
Keep the medication out of the sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature below 25°C.
Keep the container tightly closed.
Do not use Flarex after the expiry date stated on the label and carton after: "EXP". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
The batch number on the packaging is marked as "Lot".
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Flarex contains
- The active substance of Flarex is fluorometholone acetate 1 mg/ml.
- The other ingredients are: benzalkonium chloride (solution), disodium edetate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, tyloxapol, sodium chloride, hydroxyethylcellulose, hydrochloric acid, and/or sodium hydroxide (to adjust the pH), purified water.
What Flarex looks like and contents of the pack
Flarex is a liquid (suspension, white to light amber).
The immediate packaging consists of a 5 ml polyethylene bottle with a polyethylene dropper and a polypropylene cap, placed in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder
Immedica Pharma AB
Solnavägen 3H
SE-113 63 Stockholm
Sweden
Manufacturer
Siegfried El Masnou S.A.
Camil Fabra 58
El Masnou
08320 Barcelona
Spain
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterSIEGFRIED El Masnou, S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FlarexDosage form: Drops, 1 mg/mlActive substance: fluorometholonePrescription requiredDosage form: Drops, 1 mg/mlActive substance: fluorometholonePrescription requiredDosage form: Drops, 1 mg/mlActive substance: fluorometholonePrescription required
Alternatives to Flarex in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Flarex in Испания
Online doctors for Flarex
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Flarex – subject to medical assessment and local rules.