
Fentanil Vzf

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fentanil Vzf

How to use Fentanil Vzf
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
FENTANYL WZF, 50 micrograms/ml, solution for injection
Fentanylum
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Fentanyl WZF and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Fentanyl WZF
- 3. How to use Fentanyl WZF
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Fentanyl WZF
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Fentanyl WZF and what is it used for
Fentanyl WZF is a synthetic, opioid, very potent analgesic, which is used:
- in small doses to relieve pain during short surgical procedures,
- in large doses as an analgesic and/or respiratory depressant in patients requiring assisted ventilation,
- to induce surgical analgesia (pain relief) during general anesthesia,
- in combination with neuroleptic agents to perform anesthesia called neuroleptanalgesia,
- as a single agent or in combination with other medications (e.g., benzodiazepines) to perform anesthesia called analgosedation,
- to treat severe pain, such as post-traumatic pain or pain associated with myocardial infarction.
2. Important information before using Fentanyl WZF
When not to use Fentanyl WZF:
- if the patient is allergic to fentanyl or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6), or other opioid analgesics;
- if respiratory depression (respiratory arrest) occurs (except in cases mentioned in section 1.);
- if the patient has obstructive pulmonary disease;
- if there are clinical conditions that may contraindicate the use of epidural or spinal administration.
- Fentanyl WZF should not be used during treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and for 2 weeks after stopping treatment with MAOIs.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Fentanyl WZF, the patient should discuss it with their doctor.
Fentanyl WZF is administered by medical personnel. During treatment with the medicine and after surgery, medical personnel will provide the patient with proper care, and if problems occur, oxygen therapy will be administered and other appropriate actions will be taken to maintain vital functions.
The patient should talk to their doctor before using Fentanyl WZF if:
- the patient or anyone in their family has ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription drugs, or illegal substances ("addiction");
- the patient smokes;
- the patient has ever had mood disorders (depression, anxiety, or personality disorder) or has been treated by a psychiatrist for other mental illnesses;
- the patient has uncontrolled hypothyroidism, lung disease, myasthenia gravis, reduced lung reserve, liver or kidney disease;
- the patient has brain function disorders, as lowering blood pressure may cause transient cerebral hypoperfusion; in such cases, the doctor will adjust the method of fentanyl administration;
- the patient is elderly, weakened - the doctor will reduce the dose of fentanyl; during the administration of the initial dose, the doctor will take into account the patient's reaction to the medicine and, if necessary, administer an additional dose.
As with all potent opioid medications, during the use of fentanyl during surgery, severe respiratory depression (respiratory arrest) may occur, which may persist or recur in the early postoperative period. Medical personnel will exercise caution, especially when administering fentanyl in large doses or by infusion, and will ensure adequate control of spontaneous respiration and its maintenance before transferring the patient to the hospital ward.
Administration of fentanyl during delivery may cause respiratory depression in the newborn.
During the use of fentanyl in patients, seizures may also occur.
Repeated use of opioid analgesics may lead to reduced efficacy of the medicine (the patient becomes accustomed to it). It may also lead to dependence and abuse, which can result in life-threatening overdose. If the patient is concerned that they may become dependent on Fentanyl WZF, they should discuss this with their doctor.
If treatment is discontinued, withdrawal symptoms may occur. If the patient suspects that this is happening, they should inform their doctor or nurse (see also section 4. Possible side effects).
As with other opioid medications, including fentanyl, administration of this medicine may lead to increased pressure in the bile ducts and, in isolated cases, the occurrence of sphincter of Oddi spasm (symptoms: moderate or severe pain, located in the upper abdomen, may be continuous or recurrent).
During the use of fentanyl with serotonergic medications, serotonin syndrome may occur. This syndrome may include changes in mental status (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), disorders of the nervous system (e.g., accelerated heart rate, blood pressure fluctuations, hyperthermia - elevated body temperature), neuromuscular disorders (e.g., increased reflexes, lack of coordination, muscle stiffness), and/or gastrointestinal disorders (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). In case of symptoms or suspected occurrence of serotonin syndrome, the doctor will decide to discontinue fentanyl administration. (See also subsection "Fentanyl WZF and other medications").
Fentanyl WZF and other medications
The patient should inform their doctor about all medications they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as medications they plan to take. In particular, the patient should inform their doctor if they are taking any of the following medications.
- The use of opioid medications in premedication, barbiturates, benzodiazepines, neuroleptic agents, general anesthetics, some medications used to treat neuropathic pain (gabapentin and pregabalin), and other central nervous system depressants (e.g., alcohol) may enhance or prolong respiratory depression caused by fentanyl. If the patient is taking central nervous system depressants, the dose of fentanyl should be lower than usual.
- Concomitant use of Fentanyl WZF and sedative medications, such as benzodiazepines or derivatives, increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), or coma, which can be life-threatening. Therefore, combined treatment should only be considered when other treatment options are not available. If Fentanyl WZF is used with sedative medications, the doctor should limit the dose and duration of concomitant use. The patient should inform their doctor about all sedative medications they are taking and strictly follow the prescribed dose. It may be helpful to inform a family member or close friend of the patient about the possibility of these symptoms. If these symptoms occur, the patient should consult their doctor.
- In case of repeated use of fentanyl and concomitant administration of antiviral medications (e.g., ritonavir), it may be necessary to reduce the dose of fentanyl.
- If the patient is taking antifungal medications, such as fluconazole, voriconazole, they should inform their doctor, as this affects the action of fentanyl.
- Bradycardia (slow heart rate) and cardiac arrest may occur when fentanyl is used with muscle relaxants (which do not have a vagolytic effect).
- During the use of fentanyl with serotonergic medications, serotonin syndrome may occur, which can be potentially life-threatening (see subsection "Warnings and precautions").
- The dose of fentanyl should be reduced if it is used with etomidate and midazolam.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine.
The decision to use the medicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding will be made by the doctor after weighing the risk-benefit ratio of breastfeeding after fentanyl administration.
Fentanyl passes into breast milk. Therefore, breastfeeding or using expressed breast milk is not recommended for 24 hours after administration of the medicine.
Fertility
There are no clinical data on the effects of fentanyl on fertility in men and women.
In animal studies, some tests in rats showed reduced fertility in females after administration of toxic doses to mothers.
Driving and using machines
After administration of fentanyl, the patient should not drive vehicles or operate machines for at least 24 hours, even if they are discharged from the hospital earlier.
Fentanyl WZF contains sodium
The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per 1 ml, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
If the medicine is diluted in a solution that contains sodium before administration, the sodium content of the solution should be taken into account.
3. How to use Fentanyl WZF
Fentanyl WZF is administered by medical personnel. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor.
Fentanyl WZF can be administered intramuscularly, intravenously, subcutaneously, epidurally, or spinally. Fentanyl WZF does not contain preservatives.
The dose of the medicine will be adjusted by the doctor according to the patient's overall condition, age, weight, accompanying diseases, type of surgical procedure, and anesthesia used. The doctor will provide detailed information on the dosing of the medicine.
Use of a higher dose of Fentanyl WZF than recommended
Symptoms of overdose depend on individual patient sensitivity. They include: respiratory disorders, muscle stiffness, bradycardia, significant decrease in blood pressure, brain disorders (called toxic leukoencephalopathy). Appropriate action is taken by medical personnel.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If the patient experiences the first symptoms of hypersensitivity (e.g., facial swelling, lip swelling, tongue swelling, throat swelling, causing difficulty breathing or swallowing), they should immediately inform their doctor.
The frequency of such symptoms has not been determined. The doctor will assess the severity of the symptoms and decide on further action.
Very common (more than 1 in 10 people):
- muscle stiffness (which may also affect the intercostal muscles);
- nausea, vomiting.
Common (less than 1 in 10 people):
- agitation;
- dykinesia (involuntary movements), sedation (excessive calmness), dizziness;
- vision disorders;
- bradycardia, tachycardia, arrhythmia, very low blood pressure, hypertension, vein pain;
- laryngospasm, bronchospasm, apnea;
- allergic skin rash;
- postoperative disorientation.
Uncommon (less than 1 in 100 people):
- euphoric mood;
- headache;
- phlebitis, blood pressure fluctuations;
- respiratory rate increase (hyperventilation), hiccups;
- chills, hypothermia;
- respiratory complications resulting from anesthesia.
Rare (less than 1 in 1,000 people):
- swallowing difficulties.
Unknown (frequency cannot be determined from available data):
- hypersensitivity (such as anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reactions, urticaria) - see information above at the beginning of this section;
- seizures, loss of consciousness, myoclonus (brief, rapid, and strong muscle contractions);
- cardiac arrest;
- respiratory depression; may occur even up to 24 hours after epidural or spinal administration of the medicine.
- itching;
- delirium (symptoms may include agitation, restlessness, disorientation, confusion, anxiety, seeing or hearing things that do not exist, sleep disturbances, nightmares);
- symptoms of withdrawal syndrome (may include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, chills, tremors, and sweating).
During concomitant use of fentanyl with neuroleptic agents, the following have been reported: chills, restlessness, postoperative hallucinations, and extrapyramidal disorders (symptoms, e.g., tremors, stiffness, slow movements, unsteady gait).
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Fentanyl WZF
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Store in a temperature below 25°C.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light. Do not freeze.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the ampoule and carton.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Fentanyl WZF contains
- The active substance of the medicine is fentanyl. Each 1 ml of solution contains 50 micrograms of fentanyl (as fentanyl citrate).
- The other ingredients are: sodium hydroxide 10% (to adjust pH), water for injections.
What Fentanyl WZF looks like and contents of the packaging
Fentanyl WZF is a colorless, clear solution for injection.
The packaging contains: 10 or 50 ampoules of 2 ml or 10 ml, in a cardboard box.
Marketing authorization holder
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Manufacturer
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
Date of last update of the leaflet:December 2024
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals
FENTANYL WZF, 50 micrograms/ml, solution for injection
Fentanyl WZF does not contain preservatives.
Administration method
Fentanyl can only be used in fully equipped departments with equipment that allows monitoring and support of respiratory function and can only be administered by personnel experienced in ensuring and maintaining respiratory function.
To avoid bradycardia, it is recommended to administer a small dose of a cholinolytic agent intravenously before inducing anesthesia.
Fentanyl WZF can be administered:
- intramuscularly,
- intravenously - in a rapid injection (bolus), in a continuous infusion, or by the PCA method (a method in which the patient themselves activates the device that administers the analgesic),
- subcutaneously - in an injection, in a continuous infusion,
- epidurally - in a single dose, in a continuous infusion, or by the PCA method,
- intrathecally - in a single dose or in a continuous infusion.
Note:
Fentanyl WZF solution can be administered with 0.9% NaCl solution or 5% glucose solution.
If necessary, the prepared solution can be stored, at the user's responsibility, for a maximum of 24 hours, provided that the dilution is prepared in controlled and validated aseptic conditions. Unused solution within 24 hours should be discarded.
Fentanyl WZF should not be mixed with thiopental and methohexital, as there is a chemical incompatibility due to the large difference in pH of the solutions.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
When opening the ampoule, it is recommended to wear gloves.
In case of accidental skin exposure, the affected area should be rinsed with water. The use of soap, alcohol, and other cleaning agents that may cause chemical or physical skin irritation should be avoided.
Before opening the ampoule, make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
The ampoule can be gently shaken or tapped with a finger to facilitate the flow of the solution.
A colored dot is placed on each ampoule (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the location of the break point below.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing each other - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
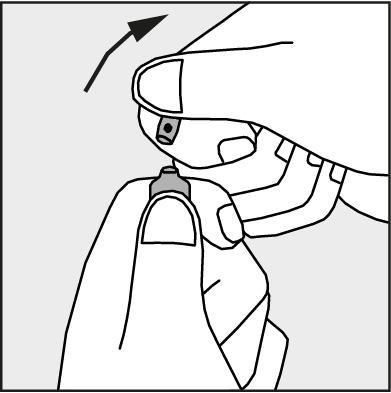
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused product should be disposed of in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1.
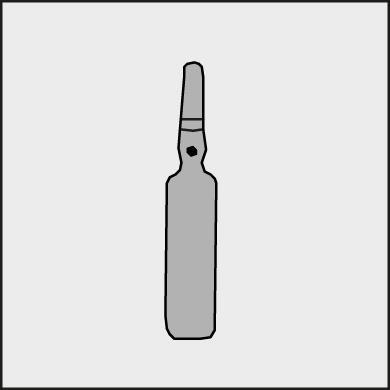
Figure 2.
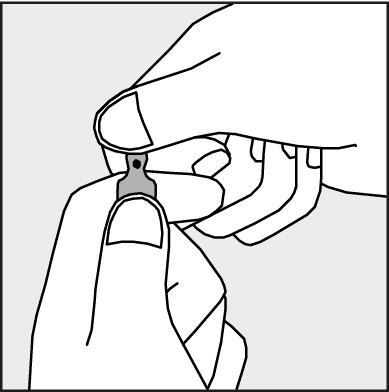
Figure 3.
Dosing
Intravenous administration - in a bolus or infusion
Intramuscular administration
Fentanyl WZF can be administered intravenously to adults and children.
The dose of fentanyl should be adjusted according to the patient's age, weight, overall condition, accompanying diseases, and type of surgical procedure and anesthesia used.
Adults
Usual dosing in adults:
| Initial dose | Additional dose | |
| Spontaneous breathing | 50 to 200 micrograms | 50 micrograms |
| Assisted breathing | 300 to 3500 micrograms | 100 to 200 micrograms |
Doses above 200 micrograms should only be used in anesthesia.
In premedication, 1 to 2 ml (50 to 100 micrograms) of fentanyl can be administered intramuscularly 45 minutes before inducing anesthesia.
Intravenous administration of 2 ml (100 micrograms) of fentanyl to adult patients who have not been premedicated should provide effective pain relief for 10-20 minutes during a procedure that causes minor pain.
Administration of 10 ml (500 micrograms) of fentanyl in a rapid intravenous injection (bolus) provides pain relief for about an hour. The induced analgesia is effective in procedures with moderate pain intensity.
Administration of a dose of 50 micrograms/kg of fentanyl provides pain relief for 4 to 6 hours during a procedure with high pain intensity.
Fentanyl WZF can also be administered in a continuous intravenous infusion.
In patients with controlled breathing, a loading dose of fentanyl can be administered in a rapid infusion of about 1 microgram/kg/min for the first 10 minutes, and then in an infusion of about 0.1 microgram/kg/min.
The loading dose can also be administered in a rapid intravenous injection (bolus).
The rate of infusion should be adjusted according to the patient's reaction to the administered fentanyl; it is recommended to use the lowest possible doses of fentanyl.
If it is not planned to use assisted breathing in the patient in the postoperative period, the infusion should be discontinued 40 minutes before the end of the surgical procedure.
Lower doses of fentanyl, e.g., 0.05 to 0.08 microgram/kg/min, are used in cases where spontaneous breathing is maintained. Higher doses (up to 3 micrograms/kg/min) are used in cardiac surgery.
Due to the large difference in pH, fentanyl shows chemical incompatibility with agents used in the induction of anesthesia, such as thiopental and methohexital.
Children and adolescents
Children aged 12 to 17 years:
Should use adult doses.
Children aged 2 to 11 years:
Usual dosing in children:
| Age | Initial dose | Additional dose | |
| Spontaneous breathing | 2-11 years | 1 to 3 micrograms/kg | 1 to 1.25 micrograms/kg |
| Assisted breathing | 2-11 years | 1 to 3 micrograms/kg | 1 to 1.25 micrograms/kg |
Use in children
Analgesia during surgical procedures, deepening of anesthesia with spontaneous breathing
Techniques that include analgesia in spontaneously breathing children should only be used as part of an anesthesiological technique or as part of a sedation/analgesia technique by qualified medical personnel in conditions that allow for immediate intubation in case of chest stiffness or apnea - administration of oxygen.
Use in elderly and weakened patients
It is recommended to reduce the dose of fentanyl. During the administration of the initial dose, the doctor should take into account the patient's reaction to the medicine and, if necessary, adjust the additional dose.
Obese patients
There is a risk of overdose in obese patients if the dose is calculated based on body weight. Obese patients should have their dose calculated based on their estimated lean body weight.
Renal impairment
In patients with renal failure, the dose of Fentanyl WZF should be reduced and the patient should be closely monitored for signs of fentanyl toxicity.
In addition, for the treatment of severe pain, fentanyl can be administered:
- Subcutaneously: adults - doses are adjusted according to the patient's condition; administered in an injection or continuous infusion. Children with a body weight below 50 kg - initially 0.5 to 2.0 micrograms/kg/h in an injection or continuous infusion. For children under 6 months, the initial dose is ¼ to ⅓ of the dose given above, and subsequent doses are modified according to the effect. Children with a body weight above 50 kg - initially 25 to 75 micrograms every hour.
- Epidurally: single dose - 50 to 100 micrograms (1 to 2 micrograms/kg); continuous infusion - 25 to 100 micrograms/h; PCA method: loading dose - 75 to 100 micrograms; background infusion - 30 to 75 micrograms/h; dose on demand - 10 to 15 micrograms; pump lockout time - 6 minutes.
- Intrathecally: recommended administration in the lumbar segment of the spine. Single dose - 5 to 25 micrograms/dose; continuous infusion - 0.8 microgram/kg/h.
Use in elderly and weakened patients
It is recommended to reduce the dose of fentanyl. During the administration of the initial dose, the doctor should take into account the patient's reaction to the medicine and, if necessary, adjust the additional dose.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Fentanil VzfDosage form: Tablets, 200 mcgActive substance: fentanylPrescription required
Alternatives to Fentanil Vzf in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fentanil Vzf in Spain
Alternative to Fentanil Vzf in Ukraine
Online doctors for Fentanil Vzf
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fentanil Vzf – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














