
Fem 7
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Fem 7

How to use Fem 7
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Warning! The leaflet should be kept. Information on the immediate packaging in a foreign language.
Fem 7 (FemSete 50)
50 μg/24 h (1.5 mg), transdermal system, patch
Estradiol
Fem 7 and FemSete 50 are different trade names for the same medicine.
Before using the medicine, the patient should carefully read the leaflet, as it contains important information.
- The leaflet should be kept so that it can be re-read if necessary.
- In case of any further doubts, the patient should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for one person. It should not be given to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if the symptoms of their illness are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet:
- 1. What is Fem 7 and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Fem 7
- 3. How to use Fem 7
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Fem 7
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Fem 7 and what is it used for
Fem 7 is a transdermal system, a patch containing estradiol as the active substance. The estradiol in Fem 7 is 17β (beta) estradiol, a hormone identical to natural estradiol. Estradiol belongs to the group of sex hormones, estrogens, and is mainly produced in the granulosa cells of the ovarian follicle. In smaller amounts, estrogens are also produced in the corpus luteum, placenta, and adrenal glands. After menopause (when menstruation completely stops), ovarian function decreases, and the body produces only a small amount of estradiol. The lack of estrogens is the cause of various disorders in many women: hot flashes, sleep disturbances, thinning of the mucous membrane of the uterus and other tissues of the urogenital system, and osteoporosis. Fem 7 is available as a transdermal system, a patch. This means that the estrogen that the body needs to supplement is slowly delivered to the body through the skin using a self-adhesive patch. The estradiol in this patch alleviates the unpleasant symptoms of menopause. It can also be used to prevent osteoporosis (reduced bone strength) if the patient cannot take other medicines for this purpose. Experience with the use of the medicine in women over 65 years of age is limited.
Fem 7 is not a contraceptive.
2. Important information before using Fem 7
When not to use Fem 7
- if the patient is allergic to estradiol or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has or is suspected of having breast cancer (see below regarding breast cancer);
Page 1 11
- if the patient has or is suspected of having endometrial cancer (endometrium - mucous membrane of the uterus) or any other estrogen-dependent malignant tumor (see below regarding endometrial cancer and ovarian cancer);
- if the patient has untreated endometrial hyperplasia (an increase in the number of cells of the mucous membrane lining the uterus);
- if the patient has vaginal bleeding of unknown cause;
- if the patient has or has had deep vein thrombosis (thrombosis of deep veins) or moving blood clots to the lungs or other parts of the body (see below regarding blood clots);
- if the patient has blood coagulation disorders(such as protein C, protein S, or antithrombin deficiency);
- if the patient has or has recently had a heart attack, stroke, or angina pectoris (see below regarding heart disease and stroke);
- if the patient has acute liver disease or liver disease that has occurred in the past, until liver function test results normalize;
- if the patient has porphyria.
Children and adolescents
The use of Fem 7 in children is contraindicated.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting to use Fem 7, the patient should discuss it with their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Medical examination / control examinations Before starting or re-introducing hormone replacement therapy, the doctor will conduct a thorough medical interview, including a family interview. The physical examination (including examination of the pelvic organs and breasts) should take into account the data from the interview and contraindications and warnings regarding the use of HRT. During treatment, the doctor will perform periodic control examinations, the frequency and type of which should be adapted to the needs of the individual patient. HRT should be used for as long as the benefits of its use outweigh the risks. If the patient notices changes in their breasts corresponding to breast lumps (see "Breast cancer" below), they should report it to their doctor, who may refer them for a mammogram. Conditions requiring special control If any of the following situations or conditions occur, have occurred in the past, or have significantly worsened during pregnancy or previous hormone replacement therapy, the patient's health should be closely monitored by a doctor. It should be considered that the listed disorders may recur or worsen during the use of Fem 7. This applies in particular to diseases such as:
- benign tumors of the uterus (uterine fibroids / uterine leiomyomas) or endometriosis (the presence of fragments of the uterine mucous membrane in various locations within the pelvis);
- previous thromboembolic disorders or risk factors for them (see below);
- risk factors for estrogen-dependent tumors, e.g., breast cancer in close relatives;
- hypertension;
- liver disease (e.g., liver adenoma);
- diabetes with vascular changes or without vascular changes;
- gallstones;
- migraine or (severe) headaches;
- systemic lupus erythematosus (an autoimmune disease);
- endometrial hyperplasia in the past (see below);
- epilepsy;
- asthma;
- otosclerosis (a disease affecting the bony labyrinth leading to hearing impairment);
- hereditary and acquired angioedema.
Page 2 11
Indications for immediate discontinuation of treatment. Treatment should be discontinued immediately if any of the conditions listed in the "When not to use Fem 7" section occur or if:
- jaundice or worsening of liver function;
- significant increase in blood pressure;
- appearance of migraines;
- pregnancy;
- swelling of the face, tongue, and (or) throat and (or) difficulty swallowing or hives, in combination with difficulty breathing, which suggests angioedema.
Safety of HRT
Besides the benefits, HRT is associated with certain risks that the patient should consider when deciding on this type of treatment or its continuation.
Endometrial cancer (cancer of the uterine mucous membrane)
Long-term administration of estrogens alone increases the risk of endometrial cancer. The addition of progestogen significantly reduces this risk.
- Patient with an intact uterus is usually prescribed progestogen and estrogen therapy. These substances may be prescribed separately or in the form of a combined drug as part of HRT.
- In the case of patients who have had a hysterectomy, the doctor will discuss with the patient the safety of using only estrogen without progestogen.
- In the case of patients who have had a hysterectomy due to endometriosis, in whom residual endometriosis foci exist, the risk may apply to any remaining fragments of the uterine mucous membrane in the body. Therefore, the doctor may prescribe HRT consisting of progestogen and estrogen.
Comparison:
Comparing women with an intact uterus who do not use HRT- in about 5 out of 1,000of them, the doctor will diagnose endometrial cancer between the ages of 50 and 65.
In the case of women using HRT with only estrogens, this number will be 2 to 12 times higher, depending on the dose and duration of HRT.
Adding progestogen to HRT with only estrogens significantly reduces the risk of endometrial cancer.
If the patient experiencesintermenstrual bleeding or spotting, it is usually not a cause for concern, especially during the first few months of HRT use.
If, however, bleeding or spotting:
- lasts longer than the first few months
- occurs for the first time some time after starting HRT
- persists even after discontinuing HRT, the patient should inform their doctor. This may indicate that the uterine mucous membrane has thickened.
Breast cancer
Women with current or past breast cancer should not use HRT.
Data confirm that taking hormone replacement therapy (HRT) in the form of combined estrogen and progestogen or only estrogen increases the risk of breast cancer. The additional risk depends on how long the patient uses HRT. This additional risk becomes apparent after 3 years of HRT use. After stopping HRT, the additional risk will decrease over time, but the risk may persist for 10 years or longer if HRT lasted more than 5 years.
The risk of breast cancer is also higher:
- in patients whose close relatives (mother, sister, or grandmother) had breast cancer
- in patients with significant overweight.
Comparison:
In the case of women between the ages of 50 and 54 who do not use HRT, breast cancer will be diagnosed in about 13 to 17 out of 1,000 womenover a period of 5 years.
In the case of women aged 50 who start 5-year estrogen-only HRT, the number of cases will be 16-17 per 1,000 patients(i.e., 0 to 3 additional cases).
In the case of women aged 50 who start 5-year estrogen-progestogen HRT, the number of cases will be 21 per 1,000 patients(i.e., 4 to 8 additional cases).
In the case of women between the ages of 50 and 59 who do not use HRT, breast cancer will be diagnosed in about 27 out of 1,000 womenover a period of 10 years.
In the case of women aged 50 who start 10-year estrogen-only HRT, the number of cases will be 34 per 1,000 patients(i.e., 7 additional cases).
In the case of women aged 50 who start 10-year estrogen-progestogen HRT, the number of cases will be 48 per 1,000 patients(i.e., 21 additional cases).
If the patient noticesany changes in the breasts, such as:
- dimples in the breast skin
- changes in the nipples
- any visible or palpable lumps should report to their doctor as soon as possible. Blood clots
HRT is associated with a higher risk of venous thrombosis (deep vein thrombosis), especially in the first year of HRT use.
These blood clots are not always life-threatening if, however, one of them moves to the lungs, it can cause chest pain, shortness of breath, collapse, and even death. This condition is called pulmonary embolism.
Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism are examples of venous thromboembolic disease(VTE).
Blood clots are more likely to occur:
- in patients with significant overweight
- in patients with a history of blood clots
- if there have been blood clots in the patient's close family
- if the patient has had at least one miscarriage
- if the patient has coagulation disorders that require treatment with anticoagulant drugs
- in patients who are immobilized for a longer period due to major surgery, injury, or illness
- in patients with a rare disease called systemic lupus erythematosus.
If any of these conditions occur in the patient, they should consult their doctor about whether it is possible to start HRT.
Comparison:
In women between the ages of 50 and 59 who do not use HRT, the number of blood clot cases over 5 years is estimated to be 4 to 7 per 1,000 women. In women between the ages of 50 and 59 using estrogen-progestogen HRT, the number of blood clot cases over 5 years will be 9 to 12 per 1,000 women(i.e., 5 additional cases). In women between the ages of 50 and 59 with a hysterectomy using only estrogen HRT, the number of blood clot cases over 5 years will be 5 to 8 per 1,000 women(i.e., 1 additional case).
If the patient experiences:
Page 4 11
- painful swelling of the leg
- sudden chest pain
- difficulty breathing should report to their doctor as soon as possible and not use HRT until the doctor agrees. These may be symptoms of thrombosis.
If the patient is scheduled for surgery, they should inform their doctor. It may be necessary to discontinue HRT 4 to 6 weeks before surgery to reduce the risk of blood clots. The doctor will inform the patient when they can resume HRT.
Ischemic heart disease
HRT is not recommended for women with current or recent heart disease.
If the patient has ever had heart disease, they should consult their doctor about whether it is possible to use HRT.
HRT does not support the prevention of heart disease.
Studies with one type of HRT (conjugated estrogens and medroxyprogesterone) have shown that the risk of heart disease may be slightly higher during the first year of treatment. In the case of other HRTs, it is likely that the risk will be similar, but this is not certain.
If the patient experiences:
- chest pain radiating to the arm and neck should report to their doctor as soon as possible and not use HRT until the doctor agrees. These may be symptoms of heart disease.
Stroke
Recent studies suggest that HRT slightly increases the risk of stroke. Other factors that may increase the risk of stroke include:
- aging
- high blood pressure
- smoking
- excessive alcohol consumption
- irregular heartbeat
If the patient has any of the above factors that increase the risk of stroke, or if the patient has had a stroke in the past, they should consult their doctor about whether they can use HRT.
Comparison:
In women between the ages of 50 and 59 who do not use HRT, about 8 out of 1,000 womenwill experience a stroke over 5 years. In women between the ages of 50 and 59 using HRT, the number of stroke cases over 5 years will be 11 cases per 1,000 women(i.e., 3 additional cases).
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is rare - much rarer than breast cancer. The use of HRT containing only estrogens or a combination of estrogens and progestogens is associated with a slightly increased risk of ovarian cancer.
The risk of ovarian cancer depends on age. For example, in women between the ages of 50 and 54 who do not use HRT, ovarian cancer will be diagnosed over 5 years in about 2 out of 2,000 women. In women who have taken HRT for 5 years, it will occur in about 3 out of 2,000 women(i.e., about 1 additional case).
Other disorders
Page 5 11
Estrogens can cause fluid retention, so patients with heart or kidney disorders should be closely monitored. Patients with end-stage renal failure should be closely monitored, as it can be expected that the concentration of the active substances of Fem 7 will increase in the bloodstream.
Patients with previously occurring hypertriglyceridemia should be closely monitored during estrogen therapy or other hormone replacement therapy, as rare cases have been reported where increased triglyceride levels in the blood led to pancreatitis when using estrogen therapy.
Estrogens affect the levels of other hormones and proteins.
HRT does not improve cognitive function (memory loss, perception disorders, attention). There is evidence of an increased risk of dementia in women who started HRT at the age of 65 or older.
Fem 7 and other medicines
The metabolism of estrogens and progestogens may be increased during concurrent use of substances that induce the activity of enzymes that metabolize drugs (mainly cytochrome P-450 enzymes), such as antiepileptic drugs (e.g., phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine) and anti-infective drugs (rifampicin, rifabutin, nevirapine, efavirenz).
Ritonavir and nelfinavir, although known as strong enzyme inhibitors, have enzyme-inducing properties when used concomitantly with steroid hormones.
Herbal products containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) may induce estrogen metabolism.
When administered transdermally, the so-called "first-pass effect" in the liver does not occur, so substances that induce enzymes have a smaller effect on estrogens and progestogens administered in this way than on hormones taken orally.
Clinically, accelerated metabolism of estrogens and progestogens may lead to a weakening of their action and disturbances in the menstrual bleeding profile.
Warning!This also applies to medicines taken recently.
Hormone replacement therapy may affect the action of other medicines:
- anti-epileptic drugs (lamotrigine), as it may affect the frequency of seizures;
- drugs used to treat hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (such as the treatment regimen using ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir with dasabuvir or without dasabuvir, and the treatment regimen using glecaprevir/pibrentasvir) as it may cause increased liver function test results in the blood (increased ALT enzyme activity) in women using combined hormonal contraceptives containing ethinyl estradiol. Fem 7 contains estradiol instead of ethinyl estradiol. It is not known whether increased ALT enzyme activity may occur when using Fem 7 concomitantly with this type of HCV treatment regimen.
The patient should tell their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take. The doctor will provide the patient with appropriate instructions.
Laboratory tests
If a blood test is necessary, the patient should inform their doctor or laboratory staff that they are taking Fem 7, as this medicine may affect the results of some tests.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Fem 7 is not indicated for use during pregnancy. If the patient becomes pregnant during treatment with Fem 7, the medicine should be discontinued immediately.
Most epidemiological studies to date on accidental exposure of the fetus to estrogens have not shown harmful effects on the embryo and fetus.
Page 6 11
Breastfeeding
Fem 7 is not indicated for use during breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
No effects of Fem 7 on the ability to drive and use machines have been reported.
3. How to use Fem 7
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. In case of doubt, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
Dosage for adults
- Fem 7 is used once a week, i.e., the used patch should be replaced immediately with a new one every 7 days (always on the same day of the week).
- Treatment should be started with one patch.
- If there is no alleviation of menopausal symptoms, the dose can be increased to two patches per week.
- No more than two patches should be used per week.
- If symptoms of overdose occur, e.g., breast tenderness, the dose should be reduced accordingly.
- Fem 7 should be used cyclically (3 weeks of treatment, 1 week without patching) or continuously.
- In the case of using the Fem 7 patch in women with an intact uterus, a progestogen hormone must also be administered for at least 12 days of the cycle. After completion of progestogen administration, regular withdrawal bleeding may occur.
In women who have had a hysterectomy and are not using hormone replacement therapy or are switching from another product to HRT, the use of Fem 7 can be started at any time.
In women with an intact uterus who are not using hormone replacement therapy, the use of Fem 7 can be started at any time.
In women with an intact uterus using sequential HRT, the use of Fem 7 can be started after the end of the previous treatment cycle.
The use of Fem 7 in children is contraindicated.
Method of administration
The procedure is illustrated by the following figures.
The patch consists of a thin, transparent foil, octagonal in shape, connected to a two-part, stronger protective foil.
The octagonal part of the patch is the actual, active patch. The inner adhesive side contains the hormone estradiol, which is continuously released into the skin.
Each Fem 7 patch is packaged in a separate, tightly closed sachet.
Page 7 11
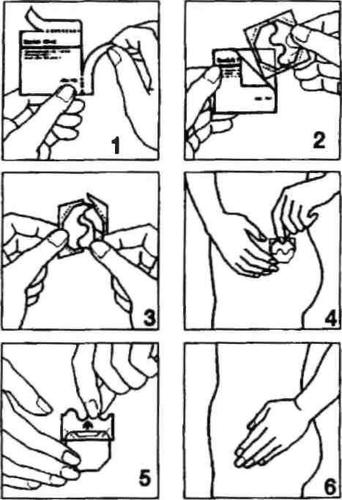
- Open one of the sachets along the side notches (do not use scissors), and then remove the patch. (Fig. 1 and 2).
- The patch should be applied to the skin immediately after removal from the packaging.
- Remove half of the two-part protective layer. Do not touch the adhesive part of the patch with your fingers. Apply the adhesive part of the patch to the skin. (Fig. 3 and 4).
- Remove the second half of the protective layer. Press the patch with your hand and hold for 30 seconds. The patch will warm up to body temperature, ensuring its optimal adhesion to the skin. (Fig. 5 and 6). Make sure the entire patch adheres to the skin, especially at the edges.
- The patch application site should be changed each time, i.e., a new patch can be applied to the same site after two weeks.
- The skin at the selected site should be healthy, degreased, dry, and undamaged.
- The best places to apply the patch are the hips, upper buttocks, and lower abdomen, as the skin is relatively smooth in these areas. The Fem 7 patch should not be applied to the breasts or their immediate vicinity! The patch should not be applied to the waist!
- The patch adheres well to the skin. Bathing in a bathtub, showering, and exercising should not affect the patch's action.
- Avoid rubbing the patch with a sponge or towel, as this may cause the patch to detach.
- Avoid wearing tight clothing that may cause the patch to detach.
- If the patch detaches completely before 7 days, simply apply a new patch.
- Each patch should be used for 7 days. It is recommended to change the patch always on the same day of the week.
- The next patch should be applied according to the original treatment plan. Avoid exposing the patch to direct sunlight. If some adhesive remains on the skin after removing the patch, it can be gently wiped off with a cream or cosmetic milk.
How long can Fem 7 be used
Page 8 11
Each patch should be used for 7 days.
HRT should be continued for as long as the benefits of alleviating menopausal symptoms outweigh the risks associated with HRT use.
Using more than the recommended dose of Fem 7
Due to the route of administration, significant overdose of estradiol when using Fem 7 is unlikely, and the effects of overdose can be immediately eliminated by removing the patch.
Overdose symptoms are mainly: breast tenderness, swelling, nausea, and vaginal bleeding.
In case of overdose, the dose of the medicine should be reduced accordingly.
Missing a dose of Fem 7
Also, in the case of missing a patch change after 7 days, it should be replaced immediately, and the next patch change should be performed on the scheduled day, at the usual time.
A double dose should not be used to make up for a missed patch.
Stopping the use of Fem 7
The duration of the entire treatment is determined by the doctor. The need for continued treatment should be regularly assessed (e.g., every 6 months). In case of early termination of treatment or if side effects occur, the patient should consult their doctor.
In case of any further doubts regarding the use of this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Fem 7 can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects are possible during hormone replacement therapy in the menopause:
Very common side effects (which may occur in more than 1 in 10 patients):
- Skin reaction at the patch application site, including itching, redness of the skin (erythema), rash, hives, swelling of the skin, and changes in skin pigmentation. These reactions usually resolve within 2-3 days after removing the patch.
Common side effects (which may occur in less than 1 in 10 patients):
- weight gain or loss
- headaches,
- abdominal pain, nausea,
- rash, itching,
- vaginal bleeding or spotting.
Uncommon side effects (which may occur in less than 1 in 100 patients):
- allergic reaction,
- depressed mood,
- vision disturbances,
- palpitations,
- erythema multiforme, hives,
- breast pain, breast tenderness,
- dizziness,
- nausea,
- edema.
Rare side effects (which may occur in less than 1 in 1,000 patients):
- nervousness,
- decreased or increased libido,
- migraine,
- intolerance to contact lenses,
- bloating and vomiting,
- hirsutism, acne,
- muscle cramps,
- painful menstruation, discharge, premenstrual syndrome, breast enlargement,
- fatigue,
- uterine fibroids.
If any of these symptoms occur, the patient should inform their doctor, who will adjust the dosage of the medicine.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Fem 7
- The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
- Store at a temperature below 30°C.
- Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the specified month.
- Used patches should be folded in half with the adhesive side inward and then discarded.
- Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Fem 7 contains
The active substance of Fem 7 is estradiol (in the form of estradiol hemihydrate).
1 transdermal system, patch contains:
active substance:
estradiol (in the form of estradiol hemihydrate 1.5 mg).
The active surface area of the system is 15 cm².
The estradiol release rate is 50 μg/24 h for 7 days.
other ingredients are:
Adhesive layer: styrene-isoprene copolymer, glycerin esters of hydrogenated rosin acids.
Outer protective layer: poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET).
Protective layer (to be removed): poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) coated with silicone.
What Fem 7 looks like and contents of the pack
Fem 7 is an octagonal, transparent, elastic transdermal system, a patch with rounded edges, placed on a removable protective foil larger than the system.
Page 10 11
4 transdermal systems, patches, and 12 transdermal systems, patches.
For more detailed information, please contact the marketing authorization holder or parallel importer.
Marketing authorization holder in Portugal, the country of export:
Theramex Ireland Limited, 3rd Floor, Kilmore House, Park Lane, Spencer Dock, D01 YE64 - Dublin 1, Ireland
Manufacturer:
LTS Lohmann Therapie-Systeme AG, Lohmannstr. 2, 56626 Andernach, Germany
Parallel importer:
Delfarma Sp. z o.o., ul. Św. Teresy od Dzieciątka Jezus 111, 91-222 Łódź
Repackaged by:
Delfarma Sp. z o.o., ul. Św. Teresy od Dzieciątka Jezus 111, 91-222 Łódź
Portuguese marketing authorization number: 2638682
2638781
Parallel import authorization number: 160/25
Date of leaflet approval: 30.04.2025
[Information about the trademark]
Page 11 11
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Marketing authorisation holder (MAH)Theramex Ireland Limited
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Fem 7Dosage form: Gel, 0.5 mgActive substance: estradiolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription requiredDosage form: Gel, 1 mgActive substance: estradiolManufacturer: Orion CorporationPrescription requiredDosage form: Gel, 1 mg/gActive substance: estradiolPrescription required
Alternatives to Fem 7 in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Fem 7 in Spain
Alternative to Fem 7 in Ukraine
Online doctors for Fem 7
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Fem 7 – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










