
Engerix B

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Engerix B

How to use Engerix B
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Engerix B 10 micrograms - suspension for injection
Vaccine against viral hepatitis B (rDNA)
Hepatitis B vaccine (rDNA)
Read the leaflet carefully before using the vaccine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This vaccine has been prescribed specifically for this person. Do not pass it on to others.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, tell the doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Engerix B vaccine and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Engerix B vaccine
- 3. How to use Engerix B vaccine
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Engerix B vaccine
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Engerix B vaccine and what is it used for
Engerix B is a vaccine used to prevent viral hepatitis B (HBV).
Engerix B 10 micrograms (pediatric dose) is indicated for use in newborns, infants, children, and adolescents up to 15 years of age.
In children from 11 to 15 years of age, Engerix B 20 micrograms (adult dose) can also be used, provided that the risk of HBV infection during the vaccination cycle is low and there is certainty that the 2-dose vaccination cycle will be completed. If these conditions cannot be met (e.g., hemodialysis patients, travelers to HBV-endemic areas, individuals in close contact with infected persons), the standard Engerix B 10 micrograms (pediatric dose) should be used. For more information, see the Engerix B 20 micrograms leaflet.
The vaccine causes the body to produce its own immunity by producing antibodies against the hepatitis B virus.
Viral hepatitis B (HBV): This disease is caused by the hepatitis B virus, which causes inflammatory swelling of the liver. The virus is found in bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal discharge, saliva (sputum) of an infected person. The disease may be asymptomatic for a period of 6 weeks to 6 months from infection. Some infected individuals may not have any symptoms or may have mild flu-like symptoms. Typically, infected individuals feel general malaise and fatigue. They may experience nausea, vomiting, dark urine, pale face, yellow skin and/or sclera (white of the eyes), and other symptoms that may require hospital treatment.
Most adults fully recover, but some individuals, especially children, despite the absence of symptoms, remain infected. These individuals are carriers of the hepatitis B virus. Carriers of the virus can infect others around them and are at risk of serious liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Vaccination is the best way to prevent the disease. None of the vaccine components are infectious.
2. Important information before using Engerix B vaccine
When not to use Engerix B vaccine
- if the patient is allergic to the active substance or any of the other components of this vaccine (listed in section 6). Allergy symptoms include itching skin rash, difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or tongue;
- if the patient has a high fever (body temperature above 38.0 ° C). A mild infection, such as a cold, should not be a contraindication to vaccination, but the doctor should be informed.
Warnings and precautions
Tell the doctor if the patient:
- has previously experienced health problems after vaccinations, especially against hepatitis B (including allergic reactions);
- has bleeding problems or bruises easily.
Fainting (especially in adolescents) may occur after or even before administration of each vaccine injection. Therefore, the doctor or nurse should be informed if the child has ever fainted during an injection.
Using Engerix B vaccine in patients with chronic liver disease or impaired immunity:
Patients with chronic liver disease, carriers of hepatitis C virus, can be vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Engerix B can also be used in individuals with impaired immunity, including those infected with HIV and with renal failure, including those on hemodialysis. It should be considered that they may not produce sufficient protection after a full vaccination cycle and may require additional doses of the vaccine.
It has also been observed that a number of factors can affect the reduced efficacy of hepatitis B vaccination. These include: male sex, obesity, smoking, route of vaccine administration, and certain chronic diseases.
In such cases, the need for additional doses of the vaccine may also arise.
In all these cases, the doctor will decide on the possible need for additional blood tests and the appropriate timing and method of vaccination.
As with other vaccines, it is possible that not all vaccinated individuals will develop a protective immune response.
Engerix B vaccine and other medicines
Tell the doctor about all medicines and vaccinations taken recently.
Engerix B can be given at the same time as vaccines against tuberculosis, Haemophilus influenzaetype b (Hib), hepatitis A, polio, measles, mumps, rubella, diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis, but the injection sites must be different.
Concomitant administration of Engerix B vaccine and standard dose of hepatitis B immunoglobulin at different sites does not affect the level of antibodies produced.
Engerix B vaccine can be given at the same time as the human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine. Concomitant administration of Engerix B vaccine with Cervarix (HPV vaccine) did not show a clinically significant effect on antibody production against HPV antigens.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Before taking any medicine during pregnancy or breastfeeding, consult a doctor.
The effect of the vaccine on fetal development has not been evaluated. It is believed that, like other inactivated viral vaccines, Engerix B does not pose a significant risk to the fetus.
Engerix B can be given to a pregnant woman only if there are clear indications for immunization and the benefits to the mother outweigh the potential risk to the fetus.
Clinical trials have not studied the effect of Engerix B vaccine administered to mothers on breastfed children. There is also no information on the excretion of hepatitis B virus antigen contained in the vaccine into breast milk. There is no contraindication to vaccinating breastfeeding mothers.
The doctor should discuss the benefits and potential risks associated with vaccination with Engerix B during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Driving and using machines
It is unlikely that Engerix B vaccine will have a significant impact on the ability to drive and use machines .However, if the patient feels unwell, they should not drive or operate machinery.
Other information
Due to the long incubation period of hepatitis B, it may happen that the vaccine is administered during the incubation period of the disease. In such cases, the vaccine may not prevent the development of infection.
Administration of Engerix B vaccine does not prevent liver infections caused by other pathogens.
This vaccine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per dose, which means the vaccine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to use Engerix B vaccine
Engerix B vaccine should be injected intramuscularly into the upper arm in children and adolescents or into the thigh in newborns, infants, and younger children.
Do not administer Engerix B vaccine into the buttock muscle or subcutaneously, as this may not provide sufficient protection.
Exceptionally, in patients with coagulation disorders due to the risk of bleeding after intramuscular administration, subcutaneous administration of the vaccine is allowed.
The vaccine should not be administered intravenously under any circumstances.
The following primary vaccination schedules are recommended:
The 3-dose schedule (0, 1, 6 months) results in a slower achievement of optimal immune response, but ensures a higher level of antibodies against hepatitis B virus.
- First dose: at any time
- Second dose: 1 month later
- Third dose: 6 months after the first dose
The accelerated schedule, when doses are given according to the 0, 1, 2 months schedule, allows for rapid achievement of optimal immune response and ensures better cooperation from the vaccinated person. A fourth dose is recommended 12 months after the first dose.
- First dose: at any time
- Second dose: 1 month later
- Third dose: 2 months after the first dose
- Fourth dose: 12 months after the first dose
In children from 11 to 15 years of age, Engerix B 20 micrograms (adult dose) can also be used according to a 2-dose vaccination schedule (0, 6 months) provided that the risk of hepatitis B virus infection during the vaccination cycle is low and there is certainty that the vaccination cycle will be completed. For more information, see the Engerix B 20 micrograms leaflet.
Make sure to receive the full vaccination consisting of three or four doses of the vaccine.
If all doses are not received, the vaccinated person may not be fully protected against the disease.
The doctor should inform about the possible need for additional doses and booster doses.
If the next dose of the vaccine is not received on time, it is necessary to talk to the doctor to schedule another visit.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Engerix B vaccine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects have been reported after vaccination:
♦ Very common (may occur in 1 in 10 doses of the vaccine or more often):
- headache
- pain and redness at the injection site, feeling of fatigue
- irritability
♦ Common (less than 1 in 10 doses of the vaccine):
- drowsiness
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain
- decreased appetite
- fever (37.5°C or higher), malaise, swelling at the injection site, other reactions at the injection site (such as induration)
♦ Uncommon (less than 1 in 100 doses of the vaccine):
- dizziness
- muscle pain
- flu-like symptoms
♦ Rare (less than 1 in 1,000 doses of the vaccine):
- generalized lymph node enlargement
- paresthesia (tingling sensation)
- hives, itching, rash
- joint pain
♦ Very rare (less than 1 in 10,000 doses of the vaccine):
- thrombocytopenia (bleeding or easier bruising due to a decrease in platelet count)
- encephalitis, encephalopathy, seizures, paralysis, neuritis, neuropathy, decreased sensation
- erythema multiforme, angioedema, lichen planus (skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders)
- arthritis, muscle weakness
- meningitis
- vasculitis, decreased blood pressure
- in very premature infants (born before or at 28 weeks of gestation), longer-than-normal pauses between breaths may occur within 2-3 days after vaccination
- allergic reactions, including anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions, and reactions similar to serum sickness. These may occur as local or generalized rash (which may be itchy or blistering), swelling of the eyelids and face, difficulty breathing or swallowing, sudden drop in blood pressure, or loss of consciousness. These reactions may occur even before leaving the doctor's office. In any case, immediate medical attention should be sought.
If the above events do not resolve or worsen, the doctor should be informed.
If other side effects occur that are not listed in this leaflet, the doctor should be informed.
Do not be concerned about this list of possible side effects. It is possible that no side effects will occur after vaccination.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, tell the doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: 22 49 21 301
Fax: 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects can help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Engerix B vaccine
Store in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
Do not freeze.
The vaccine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
The vaccine should be stored in its original packaging to protect it from light.
Do not use this vaccine after the expiration date stated on the packaging after "EXP". The expiration date refers to the last day of the given month.
The "Lot" abbreviation means the product batch number.
6. Package contents and other information
What Engerix B vaccine contains
- The active substance of Engerix B vaccine is:
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)
10 micrograms
adsorbed on aluminum hydroxide, hydrated
total: 0.25 milligrams Al
obtained from yeast cell culture ( Saccharomyces cerevisiae) using recombinant DNA technology
- The other ingredients are: sodium chloride, disodium phosphate dihydrate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate, water for injections.
What Engerix B vaccine looks like and what the pack contains
Engerix B (10 micrograms in 0.5 ml) is a suspension for injection in a vial or pre-filled syringe.
Pack sizes:
- 1-dose pre-filled syringes in packs of 1, 10, or 25,
- 1-dose vials in packs of 1, 10, or 100, with or without a syringe.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals S.A.
rue de l’Institut 89
1330 Rixensart, Belgium
To obtain more detailed information, contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
GSK Services Sp. z o.o.
ul. Rzymowskiego 53
02-697 Warsaw
phone: (22) 576-90-00
Date of last update of the leaflet:April 2023
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended only for healthcare professionals:
During storage, a white precipitate and a clear colorless liquid may form above.
Immediately before administration, the vaccine should be shaken vigorously to obtain a slightly cloudy suspension, and inspected for any particles or changes in appearance. If any of these abnormalities are found, the vaccine should not be administered.
Instructions for the pre-filled syringe
Hold the pre-filled syringe by the body, not by the plunger.
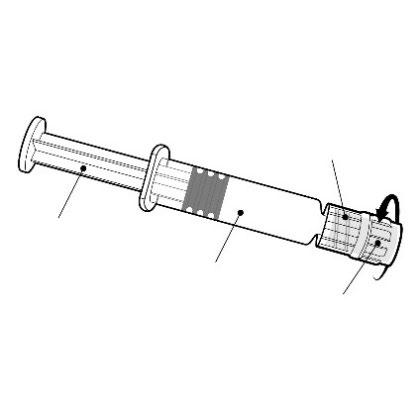
Luer Lock adapter
Plunger
Body
Attach the needle to the pre-filled syringe by connecting the needle cap to the Luer Lock adapter (LLA) and turning it a quarter turn in the direction of the arrow, until the needle is locked.
Do not pull the plunger out of the pre-filled syringe body. If this happens, do not administer the vaccine.
Disposal
Any unused product or waste should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Cap
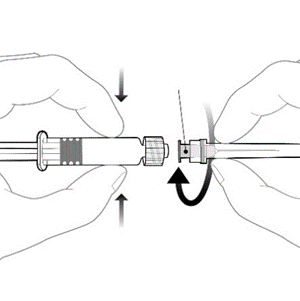
Needle cap
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterGlaxoSmithKline Biologicals S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Engerix BDosage form: Suspension, 20 mcg hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)/1 ml; 1 dose (1 ml)Active substance: hepatitis B, purified antigenManufacturer: GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Suspension, 20 mcg of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)/ml, 1-dose vaccine for adults; 1 dose (1 ml)Active substance: hepatitis B, purified antigenPrescription requiredDosage form: Suspension, 10 mcg of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg)/0.5 ml single-dose vaccine for children; 1 dose (0.5 ml)Active substance: hepatitis B, purified antigenPrescription required
Alternatives to Engerix B in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Engerix B in Spain
Alternative to Engerix B in Ukraine
Online doctors for Engerix B
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Engerix B – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














