
Disport

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Disport

How to use Disport
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET: USER INFORMATION
Dysport
300 units; 500 units of Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin complex,
powder for solution for injection
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for this person. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Dysport and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Dysport
- 3. How to use Dysport
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Dysport
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Dysport and what is it used for
Dysport contains Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin complex (commonly known as botulinum toxin) produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum (botulinum toxin rod). Its action is based on inhibiting muscle contraction by preventing the release of a chemical substance that causes physiological muscle contraction. This helps reduce abnormal muscle tension called muscle spasm.
Indications for use
- Symptomatic treatment of focal spasticity of the lower limbs in children with cerebral palsy aged 2 years or older
- Symptomatic treatment of focal spasticity of the upper limbs in children with cerebral palsy aged 2 years or older
- Urinary incontinence (urinary incontinence) due to problems with the urinary bladder related to spinal cord damage or multiple sclerosis in patients who regularly undergo clean intermittent catheterization
- Cervical dystonia in adults
- Blepharospasm in adults
- Hemifacial spasm in adults
- Upper limb spasticity in adults
- Lower limb spasticity in adults
- Excessive axillary sweating
2. Important information before using Dysport
When not to use Dysport
- if the patient is allergic (hypersensitive) to botulinum toxin or any of the other ingredients of Dysport (listed in section 6)
- if the patient has a urinary tract infection during treatment for urinary incontinence
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Dysport, discuss with your doctor:
- if there are any muscle-related complaints or diseases, e.g. myasthenia (a chronic disease characterized by rapid fatigue and weakness of skeletal muscles)
- if the muscles at the proposed injection site show signs of atrophy
- if there have been swallowing or breathing disorders in the past
- if there is significant muscle weakness
- if there are chronic respiratory disorders
- if there is a tendency to bleed
- if there is inflammation or infection at the proposed injection site
Dysport and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Children and adolescents
In the treatment of spasticity associated with cerebral palsy, Dysport should be used in children aged 2 years or older.
Driving and using machines
After injection of Dysport, temporary muscle weakness and vision disturbances may occur. In such cases, do not drive vehicles or operate machines.
This medicine contains human albumin, a protein derived from human blood.
The risk of transmitting infectious agents is very low, but it cannot be completely ruled out.
3. How to use Dysport
The injection will be performed by a doctor who will decide how often the medicine should be administered. This will depend on the type of symptoms found in the patient.
Dysport should only be used for one patient and only during one therapeutic session.
In the symptomatic treatment of focal spasticity of the lower limbs in children:
Children aged 2 years or older: the dose is determined by the doctor. Dysport is injected into the spastic muscles of the lower limbs.
The total dose of Dysport per therapeutic session should not exceed 1000 units or 30 units/kg. Injections will be performed approximately every 16-22 weeks or as needed, but no more frequently than every 12 weeks.
In the symptomatic treatment of focal spasticity of the upper limbs in children:
Children aged 2 years or older: the dose is determined by the doctor. Dysport is injected into the spastic muscles of the upper limb. In the case of injection into one upper limb, the dose during one therapeutic session should not exceed 640 units or 16 units/kg, whichever is smaller. In the case of injection into both upper limbs during one therapeutic session, the dose should not exceed 840 units or 21 units/kg, whichever is smaller. Usually, within a few weeks after the end of treatment, muscle spasms should subside, and the effect of treatment should last for about 16-28 weeks. The doctor will repeat the procedures approximately every 16-28 weeks or as needed, but no more frequently than every 16 weeks.
In the simultaneous treatment of focal spasticity of the upper and lower limbs in children:
If it is necessary to treat both the upper and lower limbs during the same therapeutic session, the doctor should determine the dose of Dysport to be injected into each limb, not exceeding the total dose administered during one therapeutic session of 1000 units or 30 units/kg, whichever is smaller. Re-treatment of both the upper and lower limbs should be considered no earlier than 12-16 weeks after the previous therapeutic session.
In the treatment of urinary incontinence:
The first dose administered into the urinary bladder muscle is 600 units. However, during subsequent injections, the doctor may decide to increase the dose to 800 units.
Dysport will be administered during cystoscopy. A tube with a light source at the end will be inserted into the urinary bladder through the opening through which urine is excreted (called the urethral orifice). This will allow the doctor performing the procedure to have insight into the inside of the urinary bladder, making it possible to administer Dysport into the urinary bladder wall. Dysport will only be administered to patients who undergo clean intermittent catheterization (CIC). CIC is a procedure in which a catheter (a soft, hollow tube inserted into the urethra to facilitate urine removal from the urinary bladder) is temporarily inserted into the urinary bladder and then removed after the bladder is emptied. For further details on the procedure, consult your doctor.
In order to prevent urinary tract infections, it will be necessary to take antibiotics. If you are taking a blood-thinning medicine, your doctor will modify the treatment before and after the injection with Dysport. Before the injection, the patient may receive local anesthesia, general anesthesia, or a sedative. The patient will be observed for at least 30 minutes after the injection. Usually, symptoms should subside within 2 weeks, and improvement may last up to 48 weeks. The doctor will decide whether to repeat the treatment as needed, but no more frequently than every 12 weeks.
In the treatment of cervical dystonia:
Typically, the first dose of Dysport is 500 units. The doctor may divide this dose, injecting it into several places on the neck, presumably into 2 or 3 of the most active muscles.
Patients with significant underweight or elderly patients may be given a smaller dose.
Relief of muscle spasms should usually occur within 1 week. Depending on how long the treatment effect lasts, additional doses (250-1000 units) can be administered approximately every 12-16 weeks.
In the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm:
The doctor will perform injections in the facial area affected by the disease. The first dose is 40 units per eye. Depending on how long the treatment effect lasts, injections can be performed approximately every 12 weeks. If a longer duration of treatment effect is needed, the dose of Dysport can be increased to 80 units per eye. The maximum dose administered should not exceed a total dose of 120 units per eye.
In the treatment of upper limb spasticity in adults:
Depending on the doctor's decision, Dysport will be injected at a dose of 500 to 1000 units. The doctor may divide this dose by injecting it into individual muscles of the arm and shoulder. Relief of muscle spasms should usually occur within a week. Injections will be performed approximately every 12-16 weeks.
In the treatment of lower limb spasticity in adults:
Dysport is usually administered at a dose of 1500 units. The doctor may divide this dose by injecting it into individual muscles of the lower limb. Injections will be performed approximately every 12-16 weeks.
In the treatment of upper and lower limb spasticity in adults:
If there is a need to administer the medicine to both the upper and lower limbs during one therapeutic session, the doctor may divide the dose of Dysport between the muscles of these two body parts. In this case, the total dose of the medicine should not exceed 1500 units.
In the treatment of excessive axillary sweating:
Dysport is usually administered at a dose of 100 units per axilla. The doctor will divide this dose by injecting it into 10 places in the axilla. The maximum effect should be visible about 2 weeks after administration. The maximum dose administered should not exceed 200 units per axilla.
Overdose of Dysport
In the event of administration of a higher dose of Dysport than recommended, the patient may experience muscle weakness other than those into which the medicine was injected. Symptoms of overdose may not occur immediately after injection. If they occur, contact your doctor immediately. If you experience difficulty breathing, swallowing, or speaking, go to the nearest medical facility.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Dysport can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
You should immediately inform your doctor if:
- the patient experiences swallowing, breathing, or speech difficulties
- the patient experiences breathing difficulties with or without facial swelling, mouth, tongue, and/or throat swelling, redness of the skin, or itchy, lumpy rash (hives). The occurrence of such symptoms may indicate that the patient is allergic to Dysport.
Frequency of side effects:
| Frequency of occurrence | |
| Very common | may occur in more than 1 in 10 people |
| Common | may occur in up to 1 in 10 people |
| Uncommon | may occur in up to 1 in 100 people |
| Rare | may occur in up to 1 in 1000 people |
| Frequency not known | frequency cannot be estimated from the available data |
Some side effects may occur in all patients treated with Dysport, while others may depend on the type of symptoms being treated. Please read the information related to the specific symptom.
The following side effects have been reported (regardless of indication):
Common:
- bruises and/or pain at the injection site
- general weakness
- fatigue
- flu-like symptoms
Uncommon:
- itching
Rare:
- rash, neuralgia with muscle atrophy
Frequency not known (frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
- numbness
- muscle atrophy
Other side effects related to the spread of the medicine beyond the injection site (increased muscle weakness, swallowing difficulties, or choking with a fatal outcome in very rare cases) have also been reported.
Symptomatic treatment of focal spasticity of the lower limbs in children with cerebral palsy
The following side effects have been reported:
Common:
- muscle pain
- weakness of the lower limb muscles
- urinary incontinence
- flu-like symptoms
- pain, redness, bruising at the injection site
- gait disturbance
- fatigue
- fall
Uncommon:
- decrease in strength and weakness
Symptomatic treatment of focal spasticity of the upper limbs in children with cerebral palsy
The following side effects have been reported:
Common:
- muscle weakness
- muscle pain
- flu-like symptoms
- fatigue
- itching, bruising, pain, swelling, and rash at the injection site
- rash
Uncommon:
- decrease in strength and weakness
Simultaneous treatment of focal spasticity of the upper and lower limbs in children with cerebral palsy
No additional side effects were reported during simultaneous treatment of the upper and lower limbs during the same therapeutic session compared to separate administration to the upper or lower limb.
Treatment of urinary incontinence due to neurogenic overactivity of the detrusor muscle
The following side effects have been reported:
Common:
- hematuria*
- constipation
- bacteriuria*
- erectile dysfunction, sometimes referred to as impotence
- urinary tract infection*
- headache
- fever
Uncommon:
- numbness
- muscle weakness
- urinary bladder pain*
- uncontrolled reflex reaction of the body (autonomic dysreflexia)*
- inability to empty the urinary bladder (urinary retention)
- bleeding from the urinary bladder or the urethra (the tube that carries urine out of the body)*
Treatment of cervical dystonia
The following side effects have been reported:
Very common:
- swallowing difficulties (dysphagia)
- dry mouth
- muscle weakness
Common:
- headache
- facial muscle weakness
- dizziness
- blurred vision
- visual acuity decreased
- shortness of breath
- neck pain
- musculoskeletal pain
- muscle pain
- arm and finger pain
- muscle stiffness
- change in voice (dysphonia)
Uncommon:
- double vision
- ptosis (drooping eyelid)
- muscle atrophy
- jaw muscle weakness
- nausea
Rare:
- aspiration (choking)
Treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm
The following side effects have been reported:
Very common:
- ptosis (drooping eyelid)
Common:
- dry eyes
- double vision
- increased tearing
- eyelid edema
- facial weakness
Uncommon:
- facial nerve palsy
Rare:
- eye muscle palsy (limitation of eye movement)
- eyelid inversion
Treatment of upper limb spasticity in adults
The following side effects have been reported:
Common:
- muscle weakness
- musculoskeletal pain
- hand and finger pain
- pain, redness, swelling at the injection site
- fatigue, weakness
- flu-like symptoms
Uncommon:
- swallowing difficulties
Treatment of lower limb spasticity in adults
The following side effects have been reported:
Common:
- fall
- muscle weakness
- muscle pain
- swallowing difficulties (dysphagia)
- weakness
- fatigue
- flu-like symptoms
- bruising, pain, rash, itching at the injection site
Treatment of excessive axillary sweating
The following side effects have been reported:
Common:
- shortness of breath
- compensatory sweating (increased sweating in areas other than the armpits)
- back, shoulder, and neck pain
- back and calf muscle pain
Uncommon:
- dizziness
- headache
- tingling or numbness of the hands or feet
- involuntary eyelid spasms
- facial flushing
- nasal bleeding
If any of the side effects get serious, or if you notice any side effects not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor or pharmacist.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, you should tell your doctor. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
5. How to store Dysport
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
Store Dysport in a refrigerator (2°C - 8°C). Do not freeze.
The solution should be used immediately after reconstitution. After reconstitution, the solution can be stored for up to 24 hours in a refrigerator (2°C – 8°C).
6. Package contents and other information
What Dysport contains
- The active substance is botulinum toxin type A, 300 or 500 units/vial
- The other ingredients are human albumin and lactose monohydrate. Clostridium botulinum type A neurotoxin complex
What Dysport looks like and contents of the pack
Dysport is a white powder for solution for injection. The packs contain 1 or 2 vials.
Marketing authorization holder
Ipsen Pharma, 65 Quai Georges Gorse, 92100 Boulogne-Billancourt, France
Importer
Ipsen Manufacturing Ireland Limited, Blanchardstown Industrial Park, Blanchardstown, Dublin 15, Ireland
Date of last revision of the leaflet:June 2022
Additional information or a leaflet in a format suitable for the blind or partially sighted can be obtained by contacting:
Ipsen Poland Sp. z o.o., ul. Chmielna 73, 00-801 Warsaw, tel.: 22 653 68 00, fax: 22 653 68 22
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
In order to improve the identification of biological medicinal products, the name and batch number of the administered product should be clearly recorded.
The units of Dysport are specific to this product and are not interchangeable with units of other botulinum toxin products.
Dysport should be used by appropriately trained doctors.
The uncovered rubber stopper should be wiped with alcohol immediately before puncture with a needle. Use sterile needles of size 23 or 25.
The following instructions describe the preparation of Dysport for injection. The volumes of diluent listed allow for the preparation of concentrations suitable for use in the indicated indications, with the exception of the indication for neurogenic detrusor overactivity, for which specific instructions exist (see below).
Spasticity of the lower limbs in children with cerebral palsy aged 2 years or older
Dosing
The maximum total dose of Dysport administered during one therapeutic session should not exceed 15 units/kg body weight if injected into one lower limb or 30 units/kg body weight if injected into both lower limbs. The total dose of Dysport administered during one therapeutic session should not exceed 1000 units or 30 units/kg body weight, whichever is smaller. The total dose should be divided among the spastic muscles of the lower limbs. If possible, the dose per muscle should be divided into more than one injection site. The maximum volume of the injection into one site should not exceed 0.5 ml. Recommended dosing is presented in the table below:
| Concentration in units/ml | Volume of diluent to be added to the 300 unit vial | Volume of diluent to be added to the 500 unit vial |
| 500 units 200 units 100 units | 0.6 ml 1.5 ml 3 ml | 1 ml 2.5 ml 5 ml |
| Muscle | Recommended dose range per muscle per lower limb (units/kg body weight) | Number of injection sites per muscle |
| Distal | ||
| Gastrocnemius | 5 to 15 units/kg | Up to 4 |
| Soleus | 4 to 6 units/kg | Up to 2 |
| Tibialis posterior | 3 to 5 units/kg | Up to 2 |
| Proximal | ||
| Hamstring muscles | 5 to 6 units/kg | Up to 2 |
| Hip adductor muscles | 3 to 10 units/kg | Up to 2 |
| Total dose per lower limb | Up to 15 units/kg/limb if only distal muscles are injected, only proximal muscles are injected, or both distal and proximal muscles are injected. | |
Spasticity of the upper limbs in children with cerebral palsy aged 2 years or older
Dosing
The maximum dose of Dysport administered during one therapeutic session for unilateral injection should not exceed 16 units/kg body weight or 640 units, whichever is smaller. For bilateral injection, the maximum dose of Dysport administered during one therapeutic session should not exceed 21 units/kg body weight or 840 units, whichever is smaller. The total dose administered should be divided among the spastic muscles of the upper limb(s). No more than 0.5 ml of Dysport should be injected into one site. Recommended dosing is presented in the table below:
Dysport dosing by muscle in children with upper limb spasticity
| Muscle | Recommended dose range per muscle per upper limb (units/kg body weight) | Number of injection sites per muscle |
| Biceps brachii | 3 to 6 units/kg | Up to 2 |
| Brachialis | 1.5 to 3 units/kg | 1 |
| Biceps brachii | 3 to 6 units/kg | Up to 2 |
| Pronator teres | 1 to 2 units/kg | 1 |
| Pronator quadratus | 0.5 to 1 unit/kg | 1 |
| Flexor carpi radialis | 2 to 4 units/kg | Up to 2 |
| Flexor carpi ulnaris | 1.5 to 3 units/kg | 1 |
| Flexor digitorum profundus | 1 to 2 units/kg | 1 |
| Flexor digitorum superficialis | 1.5 to 3 units/kg | Up to 4 |
| Thenar muscles/ Adductor pollicis | 0.5 to 1 unit/kg | 1 |
| Opponens pollicis | 0.5 to 1 unit/kg | 1 |
| Total dose | Up to 16 units/kg/upper limb (not to exceed 21 units/kg in the case of injection into both upper limbs) | |
Spasticity of the lower limbs and upper limbs in children with cerebral palsy aged 2 years or older
Dosing
In the case of simultaneous treatment of upper and lower limb spasticity in children, refer to the dosing section for the respective indication, i.e. treatment of focal spasticity of the upper limbs or treatment of focal spasticity of the lower limbs in children. In the case of simultaneous treatment, the dose of Dysport should not exceed the total dose administered during one therapeutic session of 30 units/kg body weight or 1000 units, whichever is smaller. Re-treatment of the upper and lower limbs should be considered when the effect of the previous injection has decreased, but no earlier than 12-16 weeks after the previous therapeutic session. The optimal time for re-treatment should be determined based on the progression of the disease and the response to treatment.
Administration
In the treatment of lower limb spasticity or upper limb spasticity associated with cerebral palsy, or in both indications, a solution of Dysport is used, which is prepared by reconstituting the product in 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride solution for injection, and administered intramuscularly as described above.
Urinary incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity
Dosing
The recommended dose is 600 units. In the case of an inadequate response to treatment or in patients with a severe form of the disease (depending on the severity of objective and subjective symptoms and/or urodynamic parameters), a dose of 800 units can be used.
Dysport should be administered to patients who regularly undergo clean intermittent catheterization (CIC).
The total dose should be divided into 30 injections into the detrusor muscle, evenly distributed throughout the muscle, avoiding the trigone area. Dysport is injected using a flexible or rigid cystoscope, with each injection performed at a depth of approximately 2 mm, administering 0.5 ml to each site. To ensure that the entire dose is administered, the last injection should include approximately 0.5 ml of sterile sodium chloride solution.
Instructions for preparing the solution for the indication of urinary incontinence due to neurogenic detrusor overactivity:
The goal is to achieve the required volume of 15 ml of Dysport solution for injection after reconstitution, evenly divided into two 10 ml syringes, each containing 7.5 ml of the reconstituted solution at the same concentration.
Instructions for preparing the solution using 500 unit vials
- For a dose of 600 units:each of the 2 vials containing 500 units should be reconstituted using 2.5 ml of 9 mg/ml sodium chloride solution for injection without preservatives per vial. For the first 10 ml syringe, withdraw 1.5 ml from the first vial and for the second 10 ml syringe, withdraw 1.5 ml from the second vial. Complete the reconstitution by withdrawing 6 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) without preservatives into each syringe and gently mix. This will result in a total of 600 units of Dysport solution in two 10 ml syringes, each containing 7.5 ml of solution.
- For a dose of 800 units:each of the 2 vials containing 500 units should be reconstituted using 2.5 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) for injection without preservatives per vial. For the first 10 ml syringe, withdraw 2 ml from the first vial and for the second 10 ml syringe, withdraw 2 ml from the second vial. Complete the reconstitution by withdrawing 5.5 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) without preservatives into each syringe and gently mix. This will result in a total of 800 units of Dysport solution in two 10 ml syringes, each containing 7.5 ml of solution.
Instructions for preparing the solution using 300 unit vials
- For a dose of 600 units:each of the 2 vials containing 300 units should be reconstituted using 1.5 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) for injection without preservatives per vial. For the first 10 ml syringe, withdraw the entire 1.5 ml from the first vial and for the second 10 ml syringe, withdraw the entire 1.5 ml from the second vial. Complete the reconstitution by withdrawing 6 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) without preservatives into each syringe and gently mix. This will result in a total of 600 units of Dysport solution in two 10 ml syringes, each containing 7.5 ml of solution.
- For a dose of 800 units:each of the 3 vials containing 300 units should be reconstituted using 1.5 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) for injection without preservatives per vial. For the first 10 ml syringe, withdraw the entire 1.5 ml from the first vial and 0.5 ml from the second vial. For the second 10 ml syringe, withdraw 0.5 ml from the second vial and the entire 1.5 ml from the third vial. Complete the reconstitution by withdrawing 5.5 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) without preservatives into each syringe and gently mix. This will result in a total of 800 units of Dysport solution in two 10 ml syringes, each containing 7.5 ml of solution.
Instructions for preparing the solution using a combination of 500 unit and 300 unit vials (only for the 800 unit dose)
- For a dose of 800 units:the vial containing 500 units should be reconstituted using 2.5 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) for injection without preservatives; the vial containing 300 units should be reconstituted using 1.5 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) for injection without preservatives. For the first 10 ml syringe, withdraw 2 ml from the vial containing 500 units. For the second 10 ml syringe, withdraw the remaining 0.5 ml from the vial containing 500 units and the entire 1.5 ml from the vial containing 300 units. Complete the reconstitution by withdrawing 5.5 ml of sodium chloride solution (9 mg/ml) without preservatives into each syringe and gently mix. This will result in a total of 800 units of Dysport solution in two 10 ml syringes, each containing 7.5 ml of solution.
Cervical dystonia
Dosing
The recommended doses for the treatment of cervical dystonia apply to adults of any age, with a normal body weight, in whom no muscle wasting of the neck muscles is observed. In patients with reduced muscle mass of the neck muscles, e.g. due to significant underweight, or in elderly patients, the dose may be reduced.
The initial dose recommended for the treatment of cervical dystonia is 500 units, administered in divided doses into two or three of the most active neck muscles.
In the case of continued treatment, doses may be adjusted according to the treatment effect and observed side effects. It is recommended to administer 250-1000 units, although the use of higher doses from this range may be associated with an increased frequency and severity of side effects, in particular swallowing difficulties. The maximum administered dose should not exceed 1000 units. Relief of cervical dystonia symptoms should usually occur within a week of the first injection. Injections should be repeated approximately every 16 weeks or as needed to maintain treatment, but no more frequently than every 12 weeks.
In the case of cervical dystonia with rotation, a total dose of 500 units should be used, administering 350 units to the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the side toward which the chin is turned/head is rotated, and 150 units to the contralateral trapezius muscle.
In the case of cervical dystonia with lateral deviation of the head, a total dose of 500 units is recommended, administering 350 units to the sternocleidomastoid muscle on the side toward which the head is tilted, and 150 units to the trapezius muscle on the same side.
In cases where there is also elevation of the shoulders, treatment of the rhomboid and levator scapulae muscles may also be required on the same side, if significant hypertrophy of these muscles is observed in the EMG examination. When injection into three muscles is necessary, 500 units of Dysport should be divided as follows: 300 units to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, 100 units to the trapezius muscle, and 100 units to the third muscle.
In the case of cervical dystonia with retrocollis, a total dose of 500 units should be administered, with 250 units to each of the sternocleidomastoid muscles. Injections into both sternocleidomastoid muscles may increase the risk of neck muscle weakness.
In all other forms of cervical dystonia, identification and treatment of the most active muscles depend on the specialist knowledge of doctors and the results of the EMG examination. EMG should be used in the diagnosis of all complex forms of cervical dystonia, for re-evaluation after ineffective injections in non-complicated cases, and to guide injections into deeply located muscles or in patients with obesity, in whom palpation of the neck muscles is difficult.
Administration
In the treatment of cervical dystonia, a solution containing 500 units in 1 ml is used, which is prepared by reconstituting Dysport 300 units in 0.6 ml or Dysport 500 units in 1 ml of 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride solution for injection. Dysport is administered intramuscularly as described above.
Blepharospasm and Hemifacial Spasm
Dosage
10 units (0.05 ml) of the medicinal product should be injected medially and 10 units (0.05 ml) laterally with respect to the junction of the eyelid and orbital parts of both the upper (3 and 4) and lower (5 and 6) parts of the orbicularis oculi muscle of each eye.
To minimize the risk of eyelid ptosis, injections should be avoided near the levator palpebrae superioris.
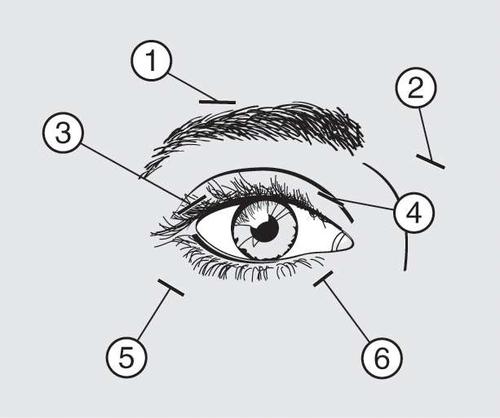
When injecting the product into the upper eyelid, the needle should be moved away from the center of the eyelid to avoid injecting the product into the levator palpebrae superioris muscle. The scheme above is intended to help with the proper distribution of the product injection. The onset of effect of the symptoms can be expected within two to four days after injection, but the maximum effect usually occurs after two weeks.
Injections should be repeated approximately every 12 weeks or as frequently as necessary to prevent the recurrence of symptoms, but no more frequently than every 12 weeks.
If the response to initial treatment is deemed insufficient, it may be necessary to increase the dose to 60 units during subsequent visits in the following manner: 10 units (0.05 ml) medially and 20 units (0.1 ml) laterally, 80 units: 20 units (0.1 ml) medially and 20 units (0.1 ml) laterally or up to 120 units: 20 units (0.1 ml) medially and 40 units (0.2 ml) laterally above and below each eye, using the injection technique described above. Additionally, Dysport can be injected into the procerus muscle above the eyebrow (1 and 2) if spasms in this area cause visual disturbances.
In cases of unilateral blepharospasm, injections should be limited to the affected eye. Patients with hemifacial spasm should be treated in the same way as those with unilateral blepharospasm. The recommended doses are used in adults of all ages, including the elderly.
Children: The efficacy and safety of this medicinal product for the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm in children have not been established.
Method of administration
In the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm, a solution containing 200 units in 1 ml is used, which is obtained after reconstitution of the Dysport 300 units in 1.5 ml or Dysport 500 units in 2.5 ml 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride injection solution. Dysport is administered by subcutaneous injections medially and laterally, with respect to the junction of the eyelid and orbital parts of both the upper and lower parts of the orbicularis oculi muscle of each eye.
Focal Spasticity of Upper and Lower Limbs in Adults
Upper Limb
Dosage
In clinical trials, doses of 500 and 1000 units were divided among selected muscles, in specified treatment sessions according to the scheme presented below.
No more than 1 ml of solution should be injected into one site.
Lower Limb
Dosage
The total dose of the medicinal product should not exceed 1500 units. No more than 1 ml of solution should be injected into one site.
| Muscles injected | Recommended dose of Dysport (units) |
| Flexor carpi radialis (FCR) muscle Flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU) muscle | 100-200 units 100-200 units |
| Flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) muscle Flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS) muscle Flexor pollicis longus muscle Flexor pollicis brevis muscle | 100-200 units 100-200 units 100-200 units 25-50 units |
| Biceps brachii muscle Brachioradialis muscle Biceps brachii (BB) muscle Supinator muscle | 200-400 units 100-200 units 200-400 units 100-200 units |
| Triceps brachii (long head) muscle Pectoralis major muscle Subscapularis muscle Latissimus dorsi muscle | 150-300 units 150-300 units 150-300 units 150-300 units |
| Muscles injected | Recommended dose of Dysport (units) | Number of injections per muscle |
| Distal | ||
| Pronator teres muscle | 300-550 units | 2-4 |
| Gastrocnemius muscle | ||
| Medial head | 100-450 units | 1-3 |
| Lateral head | 100-450 units | 1-3 |
| Tibialis posterior muscle | 100-250 units | 1-3 |
| Flexor digitorum longus muscle | 50-200 units | 1-2 |
| Flexor digitorum brevis muscle | 50-200 units | 1-2 |
| Flexor hallucis longus muscle | 50-200 units | 1-2 |
| Flexor hallucis brevis muscle | 50-100 units | 1-2 |
| Proximal | ||
| Rectus femoris muscle | 100-400 units | 1-3 |
| Hamstring muscles | 100-400 units | 1-3 |
| Adductor magnus muscle | 100-300 units | 1-3 |
| Adductor longus muscle | 50-150 units | 1-2 |
| Adductor brevis muscle | 50-150 units | 1-2 |
| Gracilis muscle | 100-200 units | 1-3 |
| Gluteus maximus muscle | 100-400 units | 1-2 |
The degree and form of muscle spasticity at the time of repeat injection may require a change in the dose of Dysport and the injection site.
Upper and Lower Limb
If during one therapeutic session there is a need to administer the product to both the upper and lower limb muscles, the dose of Dysport should be adjusted according to the patient's needs, remembering that the total dose should not exceed 1500 units.
Method of administration
In the treatment of focal spasticity of upper and lower limbs, a solution containing 100, 200 or 500 units in 1 ml is used, which is obtained after reconstitution of Dysport in 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride injection solution. Dysport is administered by intramuscular injections into the specified muscles above.
Axillary Hyperhidrosis
Dosage
The recommended initial dose for the treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis is 100 units per axilla. If the desired effect is not achieved, the dose can be increased to 200 units per axilla in the next administration. The maximum dose administered should not exceed 200 units per axilla.
The area to be injected must be previously tested with the iodine-starch test. Both axillae must be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected. Intra-dermal injections should be performed at ten sites. 10 units should be administered at each site, i.e. 100 units per axilla. The maximum effect should be visible about two weeks after the injection.
Method of administration
In the treatment of axillary hyperhidrosis, a solution containing 200 units in 1 ml is used, which is obtained after reconstitution of the Dysport 300 units in 1.5 ml or Dysport 500 units in 2.5 ml 0.9% (w/v) sodium chloride injection solution. Dysport is administered by intra-dermal injections as described above.
Detailed information on dosing and administration can be found in the Summary of Product Characteristics.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterIpsen Manufacturing Ireland Limited
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DisportDosage form: Solution, 200 U Speywood/mlActive substance: botulinum toxinPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 125 Speywood unitsActive substance: botulinum toxinPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 125 Speywood unitsActive substance: botulinum toxinPrescription required
Alternatives to Disport in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Disport in Ukraine
Alternative to Disport in Spain
Online doctors for Disport
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Disport – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














