

Durogesic

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Durogesic

How to use Durogesic
B. PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Durogesic, 12 µg/h, transdermal system, patch
Durogesic, 25 µg/h, transdermal system, patch
Durogesic, 50 µg/h, transdermal system, patch
Durogesic, 75 µg/h, transdermal system, patch
Durogesic, 100 µg/h, transdermal system, patch
fentanyl
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Durogesic and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Durogesic
- 3. How to use Durogesic
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Durogesic
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Durogesic and what is it used for
The name of this medicine is Durogesic.
Durogesic is indicated for the treatment of severe chronic pain:
- in adults who require continuous opioid treatment
- in children over 2 years of age who have already used opioid medications and require continuous opioid treatment.
Durogesic contains the active substance fentanyl, which is a strong pain reliever belonging to the opioid group.
2. Important information before using Durogesic
When not to use Durogesic
- if the patient is allergic to the active substance or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6),
- for short-term, sudden, or post-operative pain,
- if the patient has severe respiratory depression (significant slowing and shallowing of breathing). Do not use this medicine if any of the above situations apply to the patient. In case of doubt, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using Durogesic.
Warnings and precautions
- Durogesic may cause life-threatening side effects in people who do not regularly use opioid medications.
- Durogesic is a medicine that can be life-threatening to children. This also applies to used patches. It should be considered that the appearance of the patch (used or not) may encourage a child to touch it, stick it to their body, put it in their mouth, etc., which can lead to death.
- This medicine should be stored in a safe and protected place, inaccessible to other people - more information on this can be found in section 5.
In case of accidental attachment of the Durogesic patch to another person's skin
Patches should only be applied to the skin of the person they have been prescribed for. Several cases of accidental attachment of a patch to another person's skin have been reported during close physical contact or while sleeping in the same bed with the person using the patches. Accidental attachment of a patch to another person's skin (especially a child) can cause the medicine to be absorbed through the skin and lead to severe side effects, such as respiratory disorders with slow and shallow breathing, which can be life-threatening. If such a situation occurs, the patch should be removed immediately and a doctor should be consulted.
Special caution is required when using Durogesic
Consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine if
any of the following situations apply- closer monitoring of the patient may be necessary, when:
- the patient has had lung disease or breathing difficulties,
- the patient has had heart, liver, kidney, or low blood pressure problems,
- the patient has had a brain tumor,
- the patient has had persistent headaches or head injuries,
- the patient is elderly - they may be more sensitive to the effects of this medicine,
- the patient has myasthenia gravis, a disease that causes muscle weakness and fatigue.
If any of the above situations apply to the patient (or the patient is unsure), they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using Durogesic.
During treatment with patches, inform your doctor if the patient experiences
breathing problems during sleep.Opioids, such as Durogesic, can cause breathing disorders during sleep, such as sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep) and nocturnal hypoxemia (low oxygen levels in the blood). Inform your doctor if the patient, their partner, or caregiver notices any of the following symptoms:
- pauses in breathing during sleep
- nighttime awakenings due to shortness of breath
- difficulty maintaining sleep
- excessive daytime sleepiness. The doctor may decide to change the dose of the medicine.
During treatment with patches, inform your doctor if the patient notices a change in
pain perception.If the patient feels that:
- the pain is no longer relieved after applying the patch
- the pain is worsening
- there is a change in the way the pain is perceived (e.g., the patient feels pain in a different part of the body)
- there is pain upon touch, which should not be present. Do not change the dose yourself. The doctor may decide to change the dose or treatment.
Durogesic side effects
- Durogesic may cause unnatural fatigue and slowed or shallow breathing. Very rarely, these breathing disorders can be life-threatening or lead to death, especially in people who have not previously used opioid pain medications (such as Durogesic or morphine). If the patient, partner, or caregiver notices that the person using the patches is excessively sleepy and has slow or shallow breathing, they should:
- remove the patch
- call a doctor or go to the nearest hospital immediately
- encourage the patient to move and talk as much as possible.
- If the patient develops a fever while using Durogesic, they should consult their doctor - an increase in body temperature can significantly increase the absorption of the medicine through the skin.
- Durogesic may cause constipation; consult your doctor or pharmacist on how to prevent or alleviate constipation. A full list of side effects can be found in section 4.
Durogesic, like other opioids, may affect the normal production of hormones in the body, such as cortisol, prolactin, or sex hormones, especially with long-term use. The effects of these hormonal changes may include malaise (including nausea), loss of appetite, fatigue, weakness, dizziness, low blood pressure, infertility, or decreased sex drive. Additionally, women may experience changes in their menstrual cycle, and men may experience impotence or breast enlargement. If the patient notices any of these symptoms, they should consult their doctor.
Do not heat the patch application site with external heat sources, such as heated pads, electric blankets, hot water bottles, heated beds, heat lamps, or tanning lamps. Do not sunbathe or use prolonged warming baths, saunas, or whirlpool baths. In these situations, there is a risk of increased release of the medicine from the patch.
Long-term use and tolerance
This medicine contains fentanyl, which is an opioid pain reliever. Repeated use of opioid pain relievers can lead to decreased effectiveness of the medicine (the patient becomes accustomed to it, which is known as tolerance to the medicine). During treatment with Durogesic, the patient's sensitivity to pain may also increase. This phenomenon is known as hyperalgesia.
Increasing the dose of the patches may temporarily reduce the pain, but it can also be harmful. If the patient notices a decrease in the effectiveness of the medicine, they should consult their doctor. The doctor will decide whether it is better for the patient to increase the dose or gradually reduce the use of Durogesic.
Dependence and addictive use
Repeated use of Durogesic can also lead to dependence, abuse, and addictive use, which can result in life-threatening overdose. The risk of these side effects may increase with increasing dose and duration of use. Dependence or addictive use can cause the patient to feel a loss of control over the amount of medicine they use or how often they use it. The patient may feel the need to continue using the medicine, even if it no longer helps to relieve their pain.
The risk of dependence or addictive use varies from person to person. The risk of dependence on Durogesic or its addictive use may be higher if:
- the patient or someone in their family has ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medications, or illegal substances (addiction);
- the patient smokes tobacco;
- the patient has ever had mood disorders (depression, anxiety disorders, or personality disorders) or has been treated by a psychiatrist for other mental illnesses.
If the patient experiences any of the following symptoms while using Durogesic, it may indicate dependence or addictive use.
- The patient must use the medicine for a longer period than prescribed by the doctor.
- The patient must use a higher dose than recommended.
- The patient uses the medicine for reasons other than those for which the doctor prescribed it, such as "to calm down" or "to fall asleep".
- The patient has repeatedly tried to stop or control the use of the medicine but has been unable to do so.
- After stopping the use of the medicine, the patient feels unwell and experiences improvement in their condition when they start using the medicine again (withdrawal symptoms).
If the patient notices any of these symptoms, they should discuss the best treatment strategy with their doctor, including determining when it is appropriate to stop treatment and how to safely stop using the medicine.
Withdrawal symptoms after stopping Durogesic
Do not stop using this medicine suddenly. Withdrawal symptoms may occur, such as anxiety, difficulty sleeping, irritability, restlessness, anxiety, rapid heartbeat (palpitations), increased blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loss of appetite, tremors, chills, or sweating. If the patient wants to stop using this medicine, they should first consult their doctor. The doctor will inform them how to do it; usually, it is done by gradually reducing the dose, so that any unpleasant withdrawal symptoms are minimized. See also section 2 "Withdrawal symptoms after stopping Durogesic".
Durogesic and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the patient is currently taking or has recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take. This includes all over-the-counter medicines and herbal medicines.
When buying other medicines at a pharmacy, tell the pharmacist that you are using Durogesic.
The doctor knows which medicines can be safely used with Durogesic. The patient will require close monitoring if they use certain medicines listed below or if they stop using certain medicines listed below, as it may affect the required strength of Durogesic.
In particular, tell your doctor or pharmacist if the patient is taking:
- Other opioid pain relievers (such as buprenorphine, nalbuphine, or pentazocine) and certain pain relievers used for neuropathic pain (gabapentin and pregabalin).
- Sleeping pills (such as temazepam, zaleplon, or zolpidem).
- Calmatives (such as alprazolam, clonazepam, diazepam, hydroxyzine, or lorazepam) and antipsychotic medicines (such as aripiprazole, haloperidol, olanzapine, risperidone, or phenothiazines).
- Muscle relaxants (such as cyclobenzaprine or diazepam).
- Certain antidepressants called SSRI or SNRI (such as citalopram, duloxetine, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, or venlafaxine) - see below.
- Certain antidepressants or medicines used to treat Parkinson's disease called IMAO (such as isocarboxazid, phenelzine, selegiline, or tranylcypromine). Do not use Durogesic for 14 days after stopping these medicines - see below.
- Certain antihistamines, especially those that cause drowsiness (such as chlorpheniramine, clemastine, cyproheptadine, diphenhydramine, or hydroxyzine).
- Certain antibiotics (such as erythromycin or clarithromycin).
- Antifungal medicines (such as itraconazole, ketoconazole, fluconazole, or voriconazole).
- Medicines used to treat HIV infection (such as ritonavir).
- Anti-arrhythmic medicines (such as amiodarone, diltiazem, or verapamil).
- Antitubercular medicines (such as rifampicin).
- Certain antiepileptic medicines (such as carbamazepine, phenobarbital, or phenytoin).
- Certain medicines used to treat nausea and motion sickness (such as phenothiazines).
- Certain medicines used to treat heartburn and stomach ulcers (such as cimetidine).
- Certain medicines used to treat coronary artery disease (angina pectoris) or high blood pressure (such as nicardipine).
- Certain medicines used to treat blood cancers (such as idelalisib).
Using Durogesic with antidepressants
The risk of side effects increases when used with certain antidepressants. There may be an interaction between Durogesic and these medicines, and the patient may experience changes in their mental state, such as agitation, hallucinations, and other effects, such as changes in blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, high temperature, excessive reflexes, coordination disorders, muscle stiffness, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea (these may be symptoms of serotonin syndrome). In the case of concomitant use, the doctor may want to closely monitor the patient for such side effects, especially when starting treatment or when changing the dose of the medicine.
Using Durogesic with centrally acting depressants, including alcohol and certain narcotics
Concomitant use of Durogesic and calmatives, such as benzodiazepines or derivatives, increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma, and can be life-threatening. Therefore, concomitant use should only be considered when other treatment options are not possible.
If the doctor prescribes Durogesic with calmatives, the dose and duration of concomitant treatment should be limited by the doctor.
Inform your doctor about all calmatives you are taking and strictly follow the doctor's dosage recommendations. It may be helpful to inform friends or relatives to be aware of the above symptoms. If such symptoms occur, consult a doctor.
Do not drink alcohol while using Durogesic until you have discussed it with your doctor.
Surgical procedures
If the patient suspects they may undergo anesthesia, they should tell their doctor or dentist that they are using Durogesic.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Durogesic should not be used during pregnancy, unless discussed with a doctor.
Durogesic should not be used during the perinatal period, as it may cause respiratory disorders in the newborn.
Long-term use of Durogesic during pregnancy may cause withdrawal symptoms in the newborn (such as loud crying, tremors, seizures, inadequate food intake, and diarrhea), which can be life-threatening if not recognized and treated. If withdrawal symptoms are suspected in the child, consult a doctor immediately.
Durogesic should not be used during breastfeeding. Do not breastfeed for 3 days after removing the Durogesic patch. The medicine may pass into breast milk.
Driving and using machines
Durogesic may affect the ability to drive and use machines or tools, as it can cause drowsiness and dizziness. If these symptoms occur, do not drive or operate any machines or tools. Do not drive until you know how the medicine affects you.
Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you are unsure whether you can drive safely while using this medicine.
3. How to use Durogesic
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you. If you are not sure, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
The doctor will decide which strength of Durogesic is suitable for the patient, based on the severity of the pain, the patient's overall condition, and the pain treatment used so far.
Before starting and regularly during treatment, the doctor will also discuss with the patient what to expect from using Durogesic, when and for how long to use it, when to consult a doctor, and when to stop using the medicine (see also section 2 "Withdrawal symptoms after stopping Durogesic").
Using and changing patches
- Each patch contains enough medicine for 3 days (72 hours).
- Change the patch every third day, unless your doctor tells you otherwise.
- Always remove the old patch beforeapplying a new one.
- Always change the patch at the same timeevery 3 days (72 hours).
- If the patient uses more than 1 patch, change all patches at the same time.
- Write down the day, date, and time you applied the patch to remember when to change it.
- The following table shows when to change the patch:
Patch applied on: Patch change on:
Monday
Thursday
Tuesday
Friday
Wednesday
Saturday
Thursday
Sunday
Friday
Monday
Saturday
Tuesday
Sunday
Wednesday
Where to apply the patch
Adults
- Apply patches to a flat area of the upper body or arm (avoiding joints).
Children
- To minimize the risk of the child touching or removing the patch, apply it to the upper back.
- Check frequently to ensure the patch is properly attached to the skin.
- It is essential to ensure the child does not remove the patch and put it in their mouth, as this can be life-threatening or fatal.
- Monitor the child closely for 48 hours after:
- applying the first patch
- applying a patch with a higher dose.
- The effect of the patch may be delayed after the first dose is applied. During this time, the child may receive additional pain relievers. The doctor will inform you about this.
Adults and children
Do not apply the patch:
- to the same spot twice in a row
- to moving areas (joints), irritated, or damaged skin
- to very hairy skin. If there is hair, do not shave it (shaving irritates the skin). Instead, cut the hair as close to the skin as possible.
Applying the patch
Step 1: Preparing the skin
- Make sure the skin is completely dry, clean, and cool before applying the patch
- If the skin needs to be cleaned, do so with cold water
- Do not use soap or other cleaning products, oils, creams, lotions, or talcum powder before applying the patch
- Do not apply the patch immediately after a hot bath or shower.
Step 2: Opening the pouch
- Each patch is in an individual pouch
- Tear the pouch at the notch marked with an arrow
- Gently, completely tear or cut off one edge of the pouch (if using scissors, cut close to the edge to avoid damaging the patch)
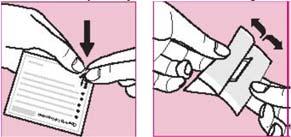
- Hold the open pouch by both edges and stretch
- Remove the patch and apply it immediately
- Keep the empty pouch to use later to dispose of the used patch
- Each patch can only be used once
- Do not remove the patch from the pouch until you are ready to apply it
- Check the patch for damage
- Do not use patches that are cut, broken, or damaged in any way
- Never divide or cut patches.
Step 3: Removing the protective layer and applying the patch to the skin
- Make sure the clothing in the area where the patch will be applied is loose; do not wear tight, elastic bands or bandages
- Carefully peel off one half of the protective layer from the center of the patch. Avoid touching the adhesive layer of the patch
- Apply the adhesive layer of the patch to the skin
- Remove the second part of the protective layer and press the entire patch firmly onto the skin with your hand
- Hold for at least 30 seconds. Make sure the patch is fully attached, especially at the edges.
Step 4: Removing the patch
- Immediately after removing the patch, fold it in half, with the adhesive layers together
- Put it back in the original pouch and dispose of it according to the pharmacist's instructions
- Keep used patches in a place that is out of sight and inaccessible to children - even used patches still contain medicine that can be harmful to children and life-threatening.
Step 5: Washing hands
- Always wash your hands with clean water after applying or removing a patch.
Additional information about using Durogesic
Daily activities while using patches
- Patches are waterproof
- You can take a shower or bath, but do not rub the patch
- You can exercise or play sports while wearing a patch, with your doctor's permission
- You can also swim while wearing a patch, but:
- Do not use prolonged warming baths or saunas
- Do not wear tight, elastic bands or bandages over the patch
- While using the patch, do not heat the patch application site with external heat sources, such as heated pads, electric blankets, hot water bottles, heated beds, heat lamps, or tanning lamps. Do not sunbathe or use prolonged warming baths, saunas, or whirlpool baths. In these situations, there is a risk of increased release of the medicine from the patch.
How quickly will the patch work?
- The maximum effect of the first patch may be delayed.
- During the initial treatment period, the doctor may prescribe additional pain relievers
- After the initial treatment period, the patch should provide constant pain relief, so you can stop taking other pain relievers. However, the doctor may occasionally recommend using additional pain relievers.
How long will the patient use the patches?
- Durogesic patches are used to treat chronic pain. The doctor will inform the patient about the expected duration of treatment.
If the pain worsens
- If the pain suddenly worsens after applying the last patch, check the patch. If it is no longer attached well or has fallen off, replace it (see also the section "If the patch comes off").
- If the pain worsens over time while using the patches, the doctor may prescribe a patch with a higher dose and (or) administer additional pain relievers
- If increasing the dose of the patches does not improve the pain, the doctor may decide to stop using the patches.
If more patches than recommended are used or a patch with the wrong dose is used
If too many patches are used or a patch with the wrong dose is used, remove the patches immediately and consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Overdose symptoms include breathing disorders or shallow breathing, fatigue, extreme drowsiness, inability to think clearly, difficulty walking or talking, and feelings of fainting, dizziness, or confusion. Overdose can also cause brain disorders called toxic leukoencephalopathy.
If the patient forgets to change the patch
- Change the patch as soon as you remember and make a note of the day and time. The next patch should be changed after the standard 3 days (72 hours).
- If it has been longer than the scheduled patch change, consult your doctor, as additional pain relievers may be necessary, but do notapply an extra patch.
If the patch comes off
- If the patch comes off before the scheduled change, apply a new one in its place and make a note of the day and time. Apply the patch to a different area:
- on the upper body or arm
- on the upper back - in children
- Inform your doctor and leave the patch on for 3 days (72 hours)or as directed by your doctor, until the next scheduled patch change
- If the patch comes off repeatedly, consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
Stopping treatment with patches
- Do not stop using this medicine suddenly. If the patient wants to stop using this medicine, they should first consult their doctor. The doctor will inform them how to do it; usually, it is done by gradually reducing the dose, so that any unpleasant withdrawal symptoms are minimized. See also section 2 "Withdrawal symptoms after stopping Durogesic".
- When stopping treatment with patches, do not restart treatment without consulting a doctor. In this situation, a different dose than before may be required.
If you have any further doubts about using the medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
If the patient, partner, or caregiver notices any of the following symptoms in the person using the patches, they should remove the patch and consult a doctor or go to the hospital immediately. Intensive medical care may be necessary.
Medical care.
- Feeling excessively sleepy, slow, or having shallow breathing. Very rarely, these breathing disorders can be life-threatening or lead to death, especially in people who have not previously used strong opioid pain relievers (such as Durogesic or morphine). Follow the above advice and encourage the patient to move and talk as much as possible. (Uncommon, may occur in less than 1 in 100 people)
- Sudden swelling of the face or throat, severe irritation, redness, or blisters on the skin. These may be symptoms of a severe allergic reaction. (Frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- Seizures (Uncommon, may occur in less than 1 in 100 people)
- Decreased consciousness or loss of consciousness (Uncommon, may occur in less than 1 in 100 people).
The following side effects have also been reported
Very common side effects (may occur in more than 1 in 10 people):
- nausea, vomiting, constipation
- drowsiness
- feeling dizzy
- headache.
Common side effects (may occur in less than 1 in 10 people):
- allergic reaction
- loss of appetite
- insomnia
- depression
- feeling anxious or confused
- seeing, feeling, hearing, smelling things that do not exist (hallucinations)
- tremors or muscle spasms
- disorders of sensation, tingling, burning skin (paresthesia)
- dizziness
- rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- high blood pressure
- shortness of breath
- diarrhea
- dry mouth
- stomach pain or indigestion
- excessive sweating
- itching, rash, redness of the skin
- inability to urinate or fully empty the bladder
- feeling tired, weak, unwell
- feeling cold
- peripheral edema on the limbs.
Uncommon side effects (may occur in less than 1 in 100 people):
- agitation or disorientation
- unusual state of happiness and increased activity (euphoria)
- decreased sensation, especially skin (hypoesthesia)
- memory loss
- blurred vision
- slow heartbeat or low blood pressure
- hypoxia (cyanosis)
- intestinal obstruction (ileus)
- itchy rash, allergic reaction, or other skin disorders at the patch application site
- flu-like symptoms
- feeling changes in body temperature
- fever
- muscle tremors
- erectile dysfunction or sexual function disorders
- difficulty swallowing.
Rare side effects (may occur in less than 1 in 1000 people):
- pupil constriction
- periodic breathing pauses (apnea)
The following side effects have also been reported, but their frequency is unknown:
- male sex hormone deficiency (androgen deficiency)
- delirium (symptoms may include agitation, anxiety, disorientation, confusion, fear, seeing or hearing things that do not exist, sleep disturbances, nightmares)
- the patient may become dependent on Durogesic (see section 2).
A rash, redness, or mild itching may occur at the patch application site on the skin. These reactions are usually mild and disappear after removing the patch. If they do not disappear or the patch causes significant skin irritation, tell your doctor.
Repeated use of patches may lead to decreased effectiveness of the medicine (tolerance to the medicine may develop) or the patient may become dependent on it.
After switching from other pain relievers to Durogesic or suddenly stopping Durogesic, the patient may experience withdrawal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, and chills. Inform your doctor immediately if such symptoms occur.
In newborns whose mothers have used Durogesic for a long time during pregnancy, cases of withdrawal symptoms have been observed.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety, Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Durogesic
Where to store patches
Unused and used Durogesic patches should be stored in a place that is out of sight and inaccessible to children.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light.
There are no special storage temperature requirements for this medicine.
The medicine should be stored in a safe and protected place, inaccessible to other people. It can cause serious harm and lead to death if used accidentally or intentionally by people who have not been prescribed it.
How long can Durogesic be stored
Do not use this medicine after the expiration date stated on the protective pouch of the patch and the outer packaging after: EXP. The expiration date refers to the last day of the specified month.
If the expiration date has passed, return unused patches to a pharmacy.
The medicine should be stored in closed pouches in the original packaging, without special requirements.
How to dispose of used and unused patches
Accidental attachment of a used or unused patch to another person's skin, especially a child, can be fatal.
A used patch should be folded in half, with the adhesive layers together, placed in the original pouch, and disposed of in a place that is out of sight and inaccessible to others, especially children, until disposal. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed.
Do not throw medicines down the drain or into household waste. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Durogesic contains
- The active substance of Durogesic is fentanyl. Durogesic, transdermal system, patch 12 µg/h contains 2.1 mg of fentanyl and releases the medicine at a dose of 12 micrograms per hour. Durogesic, transdermal system, patch 25 µg/h contains 4.2 mg of fentanyl and releases the medicine at a dose of 25 micrograms per hour. Durogesic, transdermal system, patch 50 µg/h contains 8.4 mg of fentanyl and releases the medicine at a dose of 50 micrograms per hour. Durogesic, transdermal system, patch 75 µg/h contains 12.6 mg of fentanyl and releases the medicine at a dose of 75 micrograms per hour. Durogesic, transdermal system, patch 100 µg/h contains 16.8 mg of fentanyl and releases the medicine at a dose of 100 micrograms per hour.
Other ingredients (excipients) of the patch are:
The outer layer, film: polyester and ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer.
The protective layer, film: siliconized polyester.
The layer containing the active substance: acrylic adhesive.
Printing inks (on the outer layer):
Durogesic 12 µg/h also contains orange printing ink.
Durogesic 25 µg/h also contains red printing ink.
Durogesic 50 µg/h also contains green printing ink.
Durogesic 75 µg/h also contains blue printing ink.
Durogesic 100 µg/h also contains gray printing ink.
What Durogesic looks like and contents of the pack
Durogesic 12 µg/h
Durogesic is a semi-transparent, rectangular patch with rounded corners. Each patch has an area of 5.25 cm and has an orange border printed with "DUROGESIC 12 µg fentanyl/h".
Durogesic 25 µg/h
Durogesic is a semi-transparent, rectangular patch with rounded corners. Each patch has an area of 10.5 cm and has a red border printed with "DUROGESIC 25 µg fentanyl/h".
Durogesic 50 µg/h
Durogesic is a semi-transparent, rectangular patch with rounded corners. Each patch has an area of 21.0 cm and has a green border printed with "DUROGESIC 50 µg fentanyl/h".
Durogesic 75 µg/h
Durogesic is a semi-transparent, rectangular patch with rounded corners. Each patch has an area of 31.5 cm and has a blue border printed with "DUROGESIC 75 µg fentanyl/h".
Durogesic 100 µg/h
Durogesic is a semi-transparent, rectangular patch with rounded corners. Each patch has an area of 42.0 cm and has a gray border printed with "DUROGESIC 100 µg fentanyl/h".
The medicine is supplied in cardboard boxes containing 5 individually packaged patches in heat-sealed pouches (made of acrylonitrile or cyclic olefin copolymer).
Marketing authorization holder:
Janssen-Cilag International NV
Turnhoutseweg 30
B-2340 Beerse
Belgium
Manufacturer:
Janssen-Pharmaceutica NV
Turnhoutseweg 30
B-2340 Beerse
Belgium
To obtain more detailed information on this medicine, please contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Janssen-Cilag Polska Sp. z o.o.
phone: +48 22 237 60 00
This medicine is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area
Economically and in the United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) under the following names:
| Austria, Belgium, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Finland, France, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovenia, Sweden | Durogesic |
| Germany | Durogesic SMAT |
| Ireland, United Kingdom (Northern Ireland) | Durogesic DTrans |
| Spain | Duogesic Matrix |
Date of the last update of the leaflet: 10/2024
Other sources of information
Detailed information about this medicinal product is available on the website of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products www.urpl.gov.pl
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterJanssen Pharmaceutica N.V.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DurogesicDosage form: Tablets, 200 mcgActive substance: fentanylPrescription required
Alternatives to Durogesic in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Durogesic in Spain
Alternative to Durogesic in Ukraine
Online doctors for Durogesic
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Durogesic – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














