
Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4%

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4%

How to use Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4%
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
DOPAMINUM HYDROCHLORICUM WZF 1%, 10 mg/ml, solution for infusion
DOPAMINUM HYDROCHLORICUM WZF 4%, 40 mg/ml, solution for infusion
Dopamine hydrochloride
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet, so that you can read it again if necessary.
- In case of any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if the symptoms of their illness are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%
- 3. How to use Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% and what is it used for
Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% contain dopamine as the active substance. Dopamine causes constriction of peripheral blood vessels, increased blood pressure, and stimulation of heart function. This action of dopamine is used when it is administered intravenously in life-threatening conditions called shock, when there is a sudden drop in blood pressure and decreased blood flow to the body's tissues. Shock may be caused by a heart attack, injury, blood infection, cardiac surgery, exacerbation of chronic heart failure (symptoms: shortness of breath, swelling of the lower limbs, fatigue, pain and pressure in the chest). Dopamine is also used in shock leading to kidney failure.
2. Important information before using Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%
When not to use Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%:
- if the patient is allergic to dopamine or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has a pheochromocytoma (a tumor located in the adrenal glands);
- if the patient has severe heart rhythm disorders, characterized by atrial fibrillation and very rapid heart action (called uncontrolled tachyarrhythmia).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%, the patient should discuss it with their doctor. Dopamine is administered by anesthesiologists or doctors specialized in intensive therapy. The doctor will exercise particular caution when using dopamine and will take appropriate action:
- if the patient has decreased blood volume in the body (hypovolemia);
- if the patient has diabetes;
- if the patient has kidney or liver failure;
- if the patient has or has had vascular diseases, characterized by cyanosis and feeling cold in the limbs (atherosclerosis, Raynaud's disease, arterial thrombosis, diabetic angiopathy, and Buerger's disease). Patients with these diseases should inform their doctor if their health condition allows.
During dopamine administration, the doctor will monitor the patient to detect side effects, especially those affecting the heart and kidneys. If the patient's blood pressure rises and their condition improves during dopamine administration, the doctor will gradually reduce the dose of dopamine to avoid suddenly lowering blood pressure. Dopamine can be used in children over 12 years old.
Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take, if possible and their health condition allows. The following medicines affect dopamine:
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (antidepressants), such as moclobemide, selegiline, especially if the patient has taken these medicines in the last 2 weeks;
- tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline;
- hypertension medicines from the beta-blocker group, such as propranolol or metoprolol;
- migraine medicines from the ergotamine derivative group;
- blood pressure lowering medicines, such as guanethidine;
- an antiepileptic medicine - phenytoin;
- diuretics, such as furosemide, amiloride, triamterene. Cyclopropane, isoflurane, or halothane (medicines used during surgery) should not be administered with dopamine.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
Dopamine is used in life-threatening conditions. The use of the medicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding will be decided by the doctor. There is no data available on the effect of dopamine on fertility in women and men.
Driving and using machines
This does not apply - the medicine is used in life-threatening conditions.
Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% contain sodium metabisulfite and sodium
Due to the presence of sodium metabisulfite, Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% may rarely cause severe hypersensitivity reactions and bronchospasm. Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% contains 3.17 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in each 5 ml ampoule. This corresponds to 0.16% of the maximum recommended daily dose of sodium in the diet for adults. Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% contains 12.27 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in each 5 ml ampoule. This corresponds to 0.61% of the maximum recommended daily dose of sodium in the diet for adults. Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% should be diluted before administration - see the section "Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals". The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, you should consult the product characteristics of the diluent used. In patients with reduced kidney function and in patients controlling their sodium intake, the sodium content in the final product should be considered.
3. How to use Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%
Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% are administered exclusively by medical personnel.
- The dose of the medicine is determined by the doctor. The applied dose depends on the patient's age, weight, and overall health.
- The medicine is administered by slow intravenous infusion (using appropriate equipment with controlled administration speed).
- During dopamine administration, medical personnel monitor the patient's heart function, blood pressure, and urine output to check how the patient reacts to the medicine.
Using a higher dose of Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% than recommended
Dopamine is administered by medical personnel, and therefore it is unlikely that the patient will receive more medicine than they should. After using a higher dose of dopamine than recommended, excessive blood pressure increase may occur. In such a case, the doctor will use appropriate treatment, i.e., reduce the dose or temporarily stop administering dopamine until the patient's condition improves. If there is no improvement, the doctor will administer a medicine called phentolamine.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. The most common ones are:
- headache;
- irregular, accelerated, or slowed heart rate, chest pain (so-called angina pectoris), palpitations, low blood pressure, vasoconstriction (may lead to limb ischemia or increased blood pressure);
- shortness of breath;
- nausea, vomiting.
Less common ones are:
- "goosebumps" causing hair standing on end;
- pupil dilation;
- very slow heart rate, changes in the electrocardiogram (ECG) recording, increased blood pressure;
- limb ischemia, which can cause gangrene, especially in patients with pre-existing vascular disease (symptoms: pain in the fingers of the hands or feet).
A high level of nitrogen in the blood (azotemia) may occur. Tissue necrosis caused by dopamine leakage into the tissues surrounding the vein into which the medicine is administered (called extravasation) may occur. In rare cases, ventricular arrhythmias have been reported, which were fatal.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%
Store the ampoules in the outer packaging to protect them from light, at a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze.
Medicines should be stored in a place that is out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the box and ampoule. The expiry date stated on the packaging is the last day of the given month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What does Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% contain?
- The active substance of the medicine is dopamine hydrochloride. Each ml contains 10 mg of dopamine hydrochloride.
- The other ingredients are: sodium metabisulfite, disodium edetate, water for injections.
What does Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% contain?
- The active substance of the medicine is dopamine hydrochloride. Each ml contains 40 mg of dopamine hydrochloride.
- The other ingredients are: sodium metabisulfite, disodium edetate, water for injections.
What does Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% look like and what does the packaging contain?
Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% are a colorless or slightly yellowish, clear liquid.
The medicines are packaged in cardboard boxes containing 10 ampoules of 5 ml each.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A.
Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
tel. +48 22 364 61 01
Date of the last update of the leaflet:
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
DOPAMINUM HYDROCHLORICUM WZF 1%, 10 mg/ml, solution for infusion
DOPAMINUM HYDROCHLORICUM WZF 4%, 40 mg/ml, solution for infusion
Dopamine hydrochloride
Preparation of Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4% for administration and method of administration
- The medicine should be administered by intravenous infusion, after prior dilution.
- Administer into a large vein or central venous system to minimize the risk of extravasation.
- The products should be diluted in controlled and validated aseptic conditions with 5% glucose solution or 0.9% NaCl solution. To obtain a solution for infusion, 100 mg - 800 mg of dopamine hydrochloride should be mixed with the diluent (5% glucose solution or 0.9% NaCl solution) to obtain a final volume of 250 ml. The resulting solution contains 400 micrograms - 3200 micrograms of dopamine hydrochloride per 1 ml. The dilution should be prepared in glass or polyethylene (LDPE) or polypropylene (PP) containers. After dilution with 0.9% NaCl solution or 5% glucose solution, chemical and physical stability has been demonstrated for 24 hours at 25°C. From a microbiological point of view, the prepared solution should be used immediately. If it is not used immediately, the user is responsible for the conditions and storage time. If necessary, the prepared solution can be stored for a maximum of 24 hours at 25°C, provided that the solution is prepared in controlled and validated aseptic conditions. Unused solution within 24 hours should be destroyed. The prepared solution does not require protection from light.
- Dopamine should not be mixed with alkaline solutions, such as sodium bicarbonate, as it loses its activity in such conditions.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to facilitate the flow of the solution.
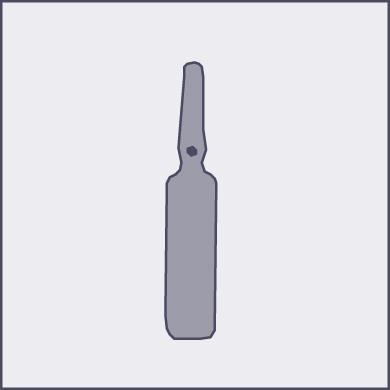
A colored dot has been placed on each ampoule (see figure 1) as a mark indicating the location of the break point below it.
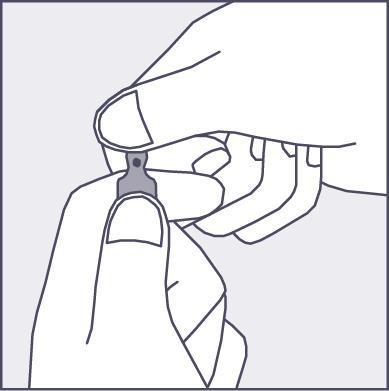
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, in both hands, with the colored dot facing you - see figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
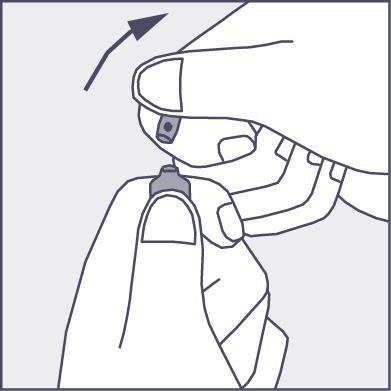
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused medicine should be destroyed in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Precautions for the use of Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 1% and Dopaminum hydrochloricum WZF 4%
- Before administering dopamine, hypovolemia should be corrected.
- The medicine should be administered after dilution into a large vein or into the central venous system to minimize the risk of extravasation. It should not be administered intra-arterially or as a bolus. In case of leakage of the medicine outside the blood vessel, the treatment of choice to limit necrotic changes is to inject a solution of phentolamine (from 5 mg to 10 mg in 10 to 15 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution) using a thin needle for subcutaneous injections.
- Discontinuation of the medicine infusion should be gradual to prevent hypotension.
- Patients with vascular diseases (such as atherosclerosis, Raynaud's disease, arterial thrombosis, diabetic angiopathy, and Buerger's disease) should be carefully monitored to detect changes in skin color or temperature of the limbs.
- In case of ischemia due to vasoconstriction, it should be considered to continue dopamine administration, due to the possibility of gangrene. This condition can be reversed by reducing the dose of dopamine or discontinuing its administration. To counteract ischemia, 5 mg to 10 mg of phentolamine can be administered intravenously.
- If symptoms occur, such as an increase in diastolic blood pressure, a significant decrease in systolic blood pressure (indicating vasoconstriction), the dose of dopamine should be reduced, and the patient should be carefully monitored.
- During dopamine administration, patients with kidney or liver failure should be carefully monitored.
- During dopamine administration, blood pressure, heart rate, and diuresis should be monitored.
Dosage
Adults, elderly, children over 12 years old:
Initially, an infusion of 1 μg/kg body weight/min to 5 μg/kg body weight/min.
Then, the dose can be increased every 10 to 30 minutes by 1 to 5 μg/kg body weight/min, up to a maximum of 20-50 μg/kg body weight/min. The average dose used in patients is 20 μg/kg body weight/min.
Doses above 50 μg/kg body weight/min are used in advanced circulatory failure.
In patients with severe, treatment-resistant chronic circulatory failure: treatment should be started at a dose of 0.5 μg/kg body weight/min to 2 μg/kg body weight/min, and then the dose should be increased by 1 to 3 μg/kg body weight/min to increase diuresis.
Children under 12 years old:
The safety and efficacy of dopamine in children have not been established.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4%Dosage form: Solution, 10 mg/mlActive substance: dopaminePrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 1 mg/10 mlActive substance: epinephrineManufacturer: Laboratoire AguettantPrescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 1 mg/mlActive substance: epinephrinePrescription required
Alternatives to Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4% in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4% in Hiszpania
Alternative to Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4% in Ukraina
Online doctors for Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4%
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Dopaminum hidrohloricum Vzf 4% – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










