

Dolcontral

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Dolcontral

How to use Dolcontral
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
DOLCONTRAL, 50 mg/ml, solution for injection
Pethidine hydrochloride
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, consult your doctor.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Dolcontral and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Dolcontral
- 3. How to use Dolcontral
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Dolcontral
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Dolcontral and what is it used for
Dolcontral contains pethidine, which is a strong pain reliever. Pethidine belongs to a group of pain relievers called opioids.
Dolcontral is intended for subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous administration.
Dolcontral is used for severe pain. Pethidine is used for pain associated with surgery, postoperative pain, and pain caused by biliary and renal colic.
2. Important information before using Dolcontral
When not to use Dolcontral:
- if the patient is allergic to pethidine, other opioids, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has breathing difficulties (severe respiratory failure);
- if the patient is taking or has taken within the last 2 weeks medicines for depression called monoamine oxidase inhibitors;
- in children under one year of age.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Dolcontral, the patient should discuss it with their doctor.
Dolcontral should not be used to treat chronic pain; it should only be used to treat acute episodes of severe pain.
The doctor will exercise special caution when using pethidine and will take appropriate action in patients:
- with reduced thyroid function (hypothyroidism) or hyperthyroidism;
- with opioid or other substance dependence (e.g., alcohol, drugs);
- with impaired consciousness;
- with head or brain injuries, or patients with increased intracranial pressure;
- with reduced adrenal gland function, Addison's disease (insufficient production of hormones by the adrenal gland);
- with asthma or other breathing problems, e.g., chronic obstructive pulmonary disease;
- with prostate or urethral problems, or difficulty urinating;
- with low blood pressure (hypotension);
- with acute abdominal problems (e.g., inflammatory bowel disease or impaired bowel motility);
- with liver function disorders (e.g., liver cirrhosis);
- with kidney function disorders;
- with seizure disorders, including epilepsy (Dolcontral may be given to patients with epilepsy only with antiepileptic drugs);
- with heart rhythm disorders called supraventricular tachycardia;
- in children and adolescents under 16 years of age.
If the patient develops dependence, sudden cessation of pethidine may lead to withdrawal symptoms - see section 3, subsection: "Discontinuation of Dolcontral".
Older patients should be given lower doses of pethidine, as pethidine may cause hypotension, even at recommended doses.
Dolcontral may affect the results of doping tests. Using Dolcontral for doping purposes can be hazardous to health.
Pethidine should not be used concomitantly with monoamine oxidase inhibitors, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors, or products containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum), due to the risk of serotonin syndrome. The symptoms of this syndrome are: agitation, high fever, diarrhea, accelerated heart rate, sweating, tremors, and impaired consciousness, coma, severe respiratory depression, and hypotension.
Children
Dolcontral can be used in children over one year of age (see section 3). If in doubt, consult your doctor.
Dolcontral and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
The following medicines may affect the action of pethidine:
- monoamine oxidase inhibitors (antidepressants), especially if the patient has taken them within the last 2 weeks. These medicines should not be used with pethidine - see section 2, subsection: "When not to use Dolcontral";
- sleeping pills, e.g., phenobarbital;
- tranquilizers, anxiolytics, e.g., diazepam;
- phenothiazine derivatives, e.g., promazine, chlorpromazine;
- cimetidine (a medicine for stomach or duodenal ulcers);
- an antiepileptic drug (phenytoin);
- ritonavir (used to treat HIV infections);
- strong painkillers (e.g., pentazocine, buprenorphine, nalbuphine, morphine);
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, serotonin and noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors - see section "Warnings and precautions";
- products containing St. John's Wort (Hypericum perforatum) - see section "Warnings and precautions".
Using Dolcontral with barbiturates, morphine, and other central nervous system depressants may lead to reduced consciousness or respiratory depression. The patient should tell their doctor about all medicines they are taking and strictly follow the prescribed dose. If these symptoms occur, the patient should consult their doctor.
Concomitant use of Dolcontral and sedatives, e.g., benzodiazepines or derivatives, increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), or coma, which can be life-threatening. Therefore, combined treatment should only be considered when other treatment options are not available.
If Dolcontral is used with sedatives, the doctor should limit the dose and duration of concomitant use.
The patient should tell their doctor about all sedatives they are taking and strictly follow the prescribed dose. It may be helpful to inform a family member or close friend of the patient about the possibility of these symptoms. If these symptoms occur, the patient should consult their doctor.
Dolcontral and alcohol
Concomitant use of opioids, including this medicine, and alcohol may lead to excessive sedation, respiratory depression, coma, and death.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
- Dolcontral should not be used in pregnant women and during childbirth. Newborns born to mothers who have been given pethidine may experience breathing difficulties, slowed heart rate, and feeding difficulties.
- The decision to use Dolcontral during breastfeeding will be made by the doctor. There is no data on the effect of pethidine hydrochloride on fertility.
Driving and using machines
Pethidine impairs psychophysical performance. During treatment with this medicine, the patient should not drive vehicles or operate machines.
3. How to use Dolcontral
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. If in doubt, consult your doctor.
Dolcontral is administered by medical personnel.
- The dose of pethidine is determined by the doctor individually for each patient.
- Dolcontral is administered subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously.
- Dolcontral can be used in children over one year of age before and during surgery and for pain treatment.
- Dolcontral should be used according to the scheme prescribed by the doctor.
Using a higher dose of Dolcontral than recommended
- Since Dolcontral is administered by medical personnel, it is unlikely that the patient will receive more medicine than they should.
- After using a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, the following symptoms may occur: pinpoint pupils and slowed breathing to respiratory arrest. Additionally, overdose may lead to impaired consciousness up to coma, low blood pressure, accelerated heart rate, dizziness, muscle spasms, elevated body temperature, hallucinations, and dilated pupils. Severe overdose, especially after intravenous administration of pethidine, may lead to respiratory and circulatory depression and death.
- If such symptoms occur, the patient should immediately inform the medical personnel, who will take appropriate action.
Missing a dose of Dolcontral
The patient should not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Discontinuation of Dolcontral
In case of sudden cessation of pethidine, especially in dependent individuals, withdrawal symptoms occur. These are: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, cough, mood changes, depression, irritability, restlessness, agitation, lacrimation, dilated pupils, rhinorrhea, insomnia with persistent yawning, sweating, increased blood pressure, circulatory failure, muscle tremors, "goosebumps", loss of appetite, slight increase in respiratory rate, feeling of widespread pain in many parts of the body, abdominal cramps, very strong craving for the drug, and hallucinations. The severity of symptoms depends on the patient's condition, the size and frequency of doses, and the duration of pethidine use.
If the patient has any further doubts about using this medicine, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The patient should stop using the medicine and immediately consult their doctor or nurse if they experience the first symptoms of an allergic reaction (e.g., facial swelling, lip swelling, tongue swelling, throat swelling, causing breathing or swallowing difficulties). The doctor will decide on further action.
Common (less than 1 in 10 patients) side effects include:
- confusion, mood changes (from deep sadness to unnatural cheerfulness), changes in cognitive abilities, difficulty making decisions, and perception disorders; excitement, hallucinations, delusions; the type and severity of these symptoms depend on the patient's personality type and the duration of treatment;
- sedation, dizziness;
- respiratory depression.
Frequency not known (cannot be estimated from available data):
- hypersensitivity reactions, including severe ones (see information at the beginning of this section), hypotension and/or tachycardia, flushing, sweating, and itching;
- disorientation, hallucinations, dependence, withdrawal symptoms (listed in section 3, subsection: "Discontinuation of Dolcontral");
- tremors, involuntary muscle movements, seizures;
- pupil constriction, especially after rapid intravenous administration;
- myocardial infarction (in the course of an allergic reaction - Kounis syndrome);
- accelerated heart rate, slowed heart rate;
- very low blood pressure (hypotension);
- bronchospasm, hiccups (mainly after rapid intravenous administration);
- nausea, vomiting (especially after rapid intravenous administration), constipation (due to increased muscle tone in the gastrointestinal tract, especially during prolonged use of the medicine), dry mouth;
- biliary spasm;
- difficulty urinating (due to increased muscle tone in the urinary tract, especially during prolonged use of the medicine);
- rapid loss of the body's sensitivity to the medicine in case of frequent administration (development of tachyphylaxis);
- pain, redness, urticaria, swelling along the affected vein (in case of intravenous administration);
- muscle necrosis, nerve damage (in case of repeated intramuscular administration).
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
e-mail: [email protected]
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Dolcontral
Store at a temperature below 25°C. Protect from light. Do not freeze.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation "EXP" means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation "Lot" means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Dolcontral contains
- The active substance of the medicine is pethidine hydrochloride. Each ml of solution contains 50 mg of pethidine hydrochloride.
- The other ingredient is: water for injections.
What Dolcontral looks like and contents of the pack
Dolcontral is a colorless, clear liquid.
The medicine is packaged in cardboard boxes containing 10 ampoules of 1 ml or 10 ampoules of 2 ml.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Warsaw Pharmaceutical Works Polfa S.A.
ul. Karolkowa 22/24; 01-207 Warsaw
To obtain more detailed information, the patient should contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Warsaw Pharmaceutical Works Polfa S.A.
ul. Karolkowa 22/24; 01-207 Warsaw
phone: 22 691 39 00
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
_________________________________________________________________________________
Information intended for healthcare professionals only
The patient should read the current Summary of Product Characteristics of this medicinal product available on the website of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products.
DOLCONTRAL, 50 mg/ml, solution for injection
Pethidine hydrochloride
Method of administration of Dolcontral
- The dose is determined by the doctor individually for each patient.
- The medicine can be administered intramuscularly, subcutaneously, or as a slow intravenous injection (see "Dosage").
- Before intravenous administration, the contents of the ampoule can be diluted to 10 ml with 10% glucose solution, 0.9% sodium chloride solution, or water for injections, resulting in a solution with a concentration of 5 mg/ml (after dilution of the contents of a 1 ml ampoule) or 10 mg/ml (after dilution of the contents of a 2 ml ampoule).
- The patient should consider the sodium content from the diluent in the prepared dilution of the medicine. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, the patient should read the Summary of Product Characteristics of the diluent used.
- Physical and chemical incompatibilities have been observed with solutions containing: aminophylline, barbiturates (especially thiopental solution - an inactive pharmacological complex is formed), sodium heparin, sodium hydrocortisone succinate, methylprednisolone succinate, morphine sulfate, phenytoin sodium, sodium bicarbonate, sodium iodide, sulfadiazine sodium.
After mixing pethidine with sodium cefoperazone or mezlocillin, a precipitate forms.
Incompatibilities have also been observed with sodium acyclovir, imipenem, furosemide, doxorubicin hydrochloride liposomal, idarubicin, and solutions containing potassium iodide.
Before mixing the medicine with another medicine in the same syringe, the patient should always read the information leaflet of the other medicine to exclude pharmaceutical incompatibilities.
The ampoules are for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused product should be destroyed in accordance with applicable regulations.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, the patient should make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule.
The patient can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with their finger to facilitate the flow of the solution.
A colored dot (see Figure 1) is placed on each ampoule as a mark indicating the location of the break point below it.
- To open the ampoule, the patient should hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing them - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
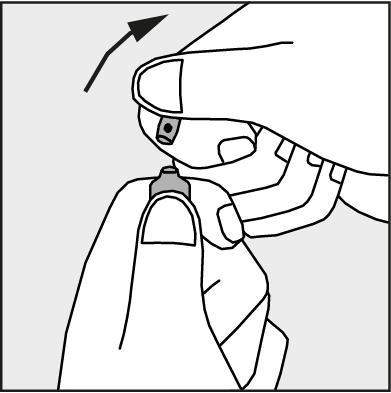
- Press according to the arrow on Figure 3.
Figure 1.

Figure 2.
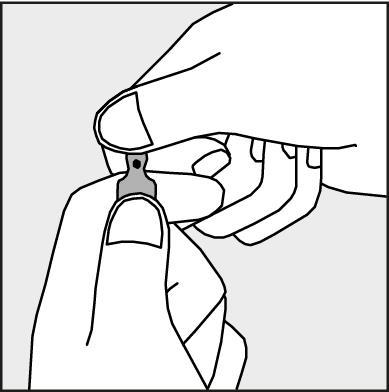
Figure 3.
Precautions for using Dolcontral
- Repeated administration of pethidine may lead to the development of tolerance. Sudden cessation of the medicine in patients with developed tolerance may cause withdrawal symptoms.
- Pethidine used for a long time may cause opioid-type dependence. It should be used with caution in individuals who abuse drugs or have a tendency to abuse drugs.
- Dolcontral should not be used to treat chronic pain.
- The medicine should be used with caution in patients with impaired consciousness, respiratory or respiratory center disorders, or conditions where respiratory depression should be avoided, with head or brain injuries, or increased intracranial pressure, with hypotension, hypovolemia, severe liver function disorders (e.g., liver cirrhosis), kidney function disorders, a history of seizures, hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, adrenal insufficiency (e.g., Addison's disease), supraventricular tachycardia, prostate or urethral problems (e.g., prostate hypertrophy and urethral stricture), acute abdominal problems, children and adolescents under 16 years of age, and elderly patients (a dose reduction is recommended).
Dosage
- In premedication (administered 30 to 90 minutes before surgery) Adults and elderly patients: 50 mg to 100 mg intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Elderly patients are more sensitive to pethidine.
Children: 1 mg/kg body weight to 2 mg/kg body weight intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
- In maintenance of anesthesia Small repeated doses of diluted medicine (e.g., 10 mg/ml) should be administered slowly intravenously or the medicine should be administered as a continuous infusion (e.g., diluted to 1 mg/ml). The dose of the medicine should be adjusted according to the patient's condition, the type of premedication and anesthesia used, the type and duration of the surgical procedure.
- Treatment of severe pain, e.g., pain in acute myocardial infarction, biliary and renal colic, postoperative pain Adults: 25 mg to 100 mg intramuscularly or subcutaneously. Doses can be repeated every 4 hours. If necessary, the medicine can be administered slowly intravenously in a dose of 25 mg to 50 mg, preferably after prior dilution. The daily dose should not exceed 500 mg of pethidine hydrochloride.
Elderly patients: in elderly patients who are more sensitive to pethidine, the initial dose should not exceed 25 mg. When administered repeatedly, the total daily dose should be reduced.
Children: 0.5 mg/kg body weight to 2 mg/kg body weight intramuscularly or subcutaneously every 4 hours.
Patients with liver or kidney function disorders
Using the medicine in patients with liver function disorders may lead to increased pethidine concentrations in the blood; therefore, the dose should be reduced accordingly. In case of kidney function disorders, the intervals between doses should be increased or the dose of the medicine should be reduced to avoid accumulation of active pethidine metabolites.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterWarszawskie Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLFA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DolcontralDosage form: Tablets, 200 mcgActive substance: fentanylPrescription required
Alternatives to Dolcontral in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Dolcontral in Іспанія
Online doctors for Dolcontral
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Dolcontral – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














