
Dicloberl 50

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Dicloberl 50

How to use Dicloberl 50
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
Dicloberl 50
50 mg, suppositories
Diclofenac sodium
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- If you have any doubts, consult your doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Dicloberl 50 and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Dicloberl 50
- 3. How to use Dicloberl 50
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Dicloberl 50
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Dicloberl 50 and what is it used for
Dicloberl 50 is a pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory medicine (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug).
Symptomatic treatment of pain and inflammation in:
- acute joint inflammation (including gout attacks);
- chronic joint inflammation, especially rheumatoid arthritis (chronic polyarthritis);
- Bechterew's disease (ankylosing spondylitis) and other rheumatic inflammatory conditions of the spine;
- exacerbations of degenerative joint disease and degenerative spinal disease;
- soft tissue inflammation in rheumatic disorders;
- painful swelling or inflammation after injuries.
If there is no improvement or the patient feels worse, they should consult their doctor.
2. Important information before using Dicloberl 50
When not to use Dicloberl 50
- if the patient is allergic to diclofenac or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6);
- if the patient has a history of breathing problems (bronchospasm), asthma attacks, chest pain, nasal mucosal swelling or skin reactions after taking acetylsalicylic acid or another non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug;
- if the patient has non-specific blood disorders;
- if the patient currently has stomach or intestinal ulcers, bleeding or perforation (which may include bloody vomiting, bleeding during bowel movements, fresh blood in the stool or black stool color, tarry stools);
- if the patient has a history of active or recurrent peptic ulcer disease or bleeding (two or more separate cases of confirmed ulcers or bleeding);
- if the patient has a history of gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation related to previous use of NSAIDs;
- if the patient has cerebral bleeding or any other active bleeding;
- if the patient has severe renal or hepatic impairment;
- if the patient has heart disease and/or cerebrovascular disease, e.g. after a heart attack, stroke, transient ischemic attack (mini-stroke) or vascular occlusion of the heart or brain, or after a procedure to clear blocked vessels;
- if the patient has circulatory disorders (peripheral arterial disease);
- in the last three months of pregnancy;
- if the patient has proctitis or anal inflammation
- in children and adolescents under 18 years of age due to the high content of the active substance.
Warnings and precautions
The following cases concern situations in which Dicloberl 50 may only be used under certain conditions (e.g. with longer intervals between doses or with smaller doses under medical supervision). The patient should consult their doctor. This also applies to situations that have occurred in the past.
Before starting to use Dicloberl 50, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or pharmacist.
General information
The patient should avoid taking Dicloberl 50 with other NSAIDs, including so-called COX-2 inhibitors (selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors), due to the lack of evidence of better therapeutic effect and the possibility of more frequent or more severe side effects.
Taking the medicine in the smallest effective dose for the shortest period necessary to alleviate symptoms may reduce the risk of side effects (see section 3 "How to use Dicloberl 50").
Gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcer disease and perforation
There have been reports of gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcer disease and perforation with fatal outcomes in patients taking all NSAIDs, occurring at various times during treatment, with and without warning symptoms or without previous severe adverse reactions affecting the gastrointestinal tract.
The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcer disease or perforation increases with increasing doses of NSAIDs and is higher in patients with a history of peptic ulcer disease, especially if it was complicated by bleeding or perforation, as well as in the elderly. In such patients, treatment should be started and continued with the smallest available dose.
In such patients, as well as in patients requiring concurrent administration of low-dose acetylsalicylic acid or other drugs that may increase the risk of adverse reactions affecting the gastrointestinal tract, it is recommended to consider concurrent administration of drugs with a protective effect on the gastric mucosa (e.g. misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors).
Patients with a history of adverse reactions affecting the gastrointestinal tract, especially the elderly, should report all abnormal abdominal symptoms (especially gastrointestinal bleeding), especially at the beginning of treatment.
Caution is recommended when taking drugs that may increase the risk of peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding, such as systemic corticosteroids, anticoagulant drugs (e.g. warfarin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (used to treat depression) or antiplatelet drugs (e.g. acetylsalicylic acid) (see section 2 "Dicloberl 50 and other medicines").
In case of gastrointestinal bleeding or peptic ulcer disease during treatment with Dicloberl 50, the medicine should be discontinued. The patient should be instructed to discontinue the medicine and consult a doctor in case of sudden abdominal pain, tarry stools or bloody vomiting (see section 4 "Possible side effects").
NSAIDs should be used with caution and under close medical supervision in patients with symptoms indicating gastrointestinal disease, peptic ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding in their history, as they may exacerbate these conditions (see section 4 "Possible side effects").
Before using Dicloberl 50, the patient should tell their doctor if they have recently undergone or are scheduled to undergo stomach or gastrointestinal surgery, as Dicloberl 50 may sometimes cause impaired wound healing in the intestines after surgery.
Effect on the cardiovascular system
Taking such medicines as Dicloberl 50 may be associated with an increased risk of heart attack ("myocardial infarction") or stroke.
Before using Dicloberl 50, the patient should inform their doctor
- if they smoke
- if they have diabetes
- if they have angina pectoris, thrombosis, hypertension, high cholesterol or high triglycerides.
Taking the medicine in the smallest effective dose for the shortest period necessary to alleviate symptoms reduces the risk of side effects.
In case of heart disease or a history of stroke, the patient should discuss the treatment with their doctor or pharmacist.
Skin reactions
Very rarely, severe skin reactions with redness and blisters have been reported in association with the use of NSAIDs, some of which were fatal (exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis/Lyell's syndrome) (see section 4 "Possible side effects"). It appears that the greatest risk of these reactions occurs at the beginning of treatment: in most cases, the onset of such a reaction occurs during the first month of treatment. In case of the first signs of skin rash, mucosal lesions (e.g. in the mouth or nose) or other symptoms of hypersensitivity, Dicloberl 50 should be discontinued immediately and the patient should consult a doctor.
Effect on the liver
Before deciding to start treatment with diclofenac in patients with liver function disorders, caution should be exercised (discuss with a doctor or pharmacist), as they may experience worsening of the disease. As with other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), including diclofenac, the activity of one or more liver enzymes may increase. If diclofenac is to be used for a long time or repeatedly, it is recommended to regularly monitor liver function parameters as a precaution. Dicloberl 50 should be discontinued immediately in case of clinical symptoms of liver function disorders.
Hepatitis may occur without warning signs.
Caution should be exercised when using Dicloberl 50 in patients with porphyria (a blood disorder), as the product may exacerbate the disease.
Effect on the kidneys
Due to reports of fluid retention and edema associated with NSAID treatment, including diclofenac, caution should be exercised in patients with renal impairment, a history of hypertension, the elderly, patients taking diuretics or drugs that significantly affect kidney function, and patients with significantly reduced extracellular fluid volume for any reason, e.g. before or after major surgery. In these cases, the doctor will monitor kidney function as a precaution.
Discontinuation of treatment usually leads to a return to the pre-treatment state.
Other
Dicloberl 50 can only be used after careful assessment of the benefit-risk ratio:
- in certain congenital blood disorders (e.g. acute intermittent porphyria),
- in certain autoimmune diseases (in systemic lupus erythematosus and mixed connective tissue disease).
Dicloberl 50 50 mg can only be used under close medical supervision:
- in patients with allergies (e.g. skin reactions to other medicines, asthma, hay fever), chronic nasal mucosal swelling or chronic respiratory diseases with airway obstruction or chronic respiratory infections, as they are at increased risk of allergic reactions.
Rarely, severe acute hypersensitivity reactions (e.g. anaphylactic shock) may occur. If the first symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction occur after taking Dicloberl 50, the patient should discontinue the medicine. Medical personnel will provide appropriate symptomatic treatment.
Diclofenac may periodically inhibit platelet aggregation. Therefore, patients with coagulation disorders should be closely monitored.
Like other NSAIDs, diclofenac may mask signs of infection. If signs of infection (e.g. redness, swelling, overheating, pain, fever) occur or worsen while taking Dicloberl 50, the patient should contact their doctor immediately.
If the patient is taking blood-thinning or blood-sugar-lowering medicines, it is recommended to monitor blood clotting parameters or blood sugar levels as a precaution.
During long-term use of Dicloberl 50, regular monitoring of liver function parameters, kidney function and blood morphology is required.
The patient should inform their doctor or dentist about taking Dicloberl 50 before surgical procedures.
During long-term use of painkillers, headaches may occur, which should not be treated by increasing the dose of these medicines. The patient should consult their doctor if they experience frequent headaches despite taking Dicloberl 50.
Generally, habitual use of painkillers, especially combinations of several active substances with analgesic effects, may cause irreversible kidney damage, associated with the risk of kidney failure (analgesic nephropathy).
Children and adolescents
Dicloberl 50 is not suitable for use in children and adolescents under 18 years of age due to the lack of sufficient data on the use of diclofenac in rheumatic diseases in children.
Elderly
Due to the possibility of side effects in elderly patients, they should be monitored closely. Caution is recommended in elderly patients with concomitant diseases.
In particular, in frail elderly patients or those with low body weight, it is recommended to use the smallest effective dose. The frequency of side effects during NSAID treatment, especially gastrointestinal bleeding, peptic ulcer disease and perforation, which can be fatal, is higher in the elderly. These gastrointestinal reactions usually have more serious consequences in the elderly and can lead to death.
Dicloberl 50 and other medicines
The patient should tell their doctor or pharmacist about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Other NSAIDs (including acetylsalicylic acid) and corticosteroids
Taking Dicloberl 50 with other anti-inflammatory and analgesic medicines from the NSAID group or corticosteroids (anti-inflammatory or hormone replacement therapy) increases the risk of peptic ulcer disease and gastrointestinal bleeding. The patient should not take diclofenac with other NSAIDs.
Digoxin, phenytoin and lithium
Concurrent use of Dicloberl 50 with digoxin (a medicine used to treat heart rhythm disorders), phenytoin (a medicine used to treat seizures) or lithium (a medicine used to treat mental disorders) may increase the levels of these medicines in the blood. Monitoring of lithium levels in the blood is necessary. Monitoring of digoxin and phenytoin levels in serum is recommended.
Diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II antagonists
Dicloberl 50 may reduce the effect of diuretics and antihypertensive drugs (e.g. beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II antagonists). Therefore, blood pressure should be monitored periodically.
Dicloberl 50 may reduce the effect of ACE inhibitors and angiotensin II antagonists (medicines used to treat heart disease and lower blood pressure). Taking these medicines concurrently with Dicloberl 50 may increase the risk of kidney function disorders. Patients should be properly hydrated and their kidney function should be monitored periodically after starting treatment and at appropriate intervals thereafter.
Concurrent use of Dicloberl 50 with potassium-sparing diuretics (some diuretics) may lead to increased potassium levels in the blood. Therefore, regular monitoring of potassium levels is recommended.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
Certain antidepressants (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors [SSRIs]) may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers.
Methotrexate
Taking Dicloberl 50 within 24 hours before or after methotrexate administration (a medicine used to treat inflammatory diseases and certain types of cancer) may increase methotrexate levels in the blood and increase the risk of side effects.
Cyclosporin
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including diclofenac) may increase the toxic effect of cyclosporin on the kidneys (a medicine used to prevent transplant rejection and treat rheumatic diseases). The patient should take a lower dose of diclofenac.
Anticoagulant and antiplatelet drugs
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may increase the effect of antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs (used to prevent blood clotting), such as warfarin. More frequent visits to the doctor may be necessary.
Probenecid
Drugs containing probenecid (used to treat gout) may slow down the excretion of diclofenac. This may increase the risk of side effects.
Antidiabetic drugs
When taking blood-sugar-lowering medicines (antidiabetic drugs), there have been reports of diclofenac affecting blood sugar levels, which may require adjustment of the antidiabetic drug dose. Therefore, as a precaution, it is recommended to monitor blood sugar levels at the same times.
Quinolone antibacterials
Quinolones (a type of antibiotic) may cause seizures when used concurrently with NSAIDs.
Cholestyramine and colestipol
These drugs (used to lower blood lipid levels) may slow down or reduce the absorption of diclofenac. Therefore, it is recommended to take Dicloberl 50 at least 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours after taking cholestyramine or colestipol.
Strong CYP2C9 inhibitors
Voriconazole (a medicine used to treat severe fungal infections) and sulfinpyrazone (a medicine used to treat gout) may increase diclofenac levels in the blood when used concurrently. This may lead to accumulation of diclofenac in the body and increase the risk of side effects.
Tenofovir
Taking tenofovir (a medicine used to treat hepatitis B and to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS) at the same time as NSAIDs (such as diclofenac) may increase the levels of urea and creatinine (kidney function parameters) in the blood. Therefore, kidney function should be monitored to check for possible increases in these parameters.
Deferasirox
Taking deferasirox (a medicine used in patients undergoing multiple blood transfusions due to various types of anemia) at the same time as NSAIDs (such as diclofenac) may increase the risk of side effects affecting the stomach and intestines. Therefore, the doctor should closely monitor patients taking deferasirox with NSAIDs.
Mifepristone
Used to terminate pregnancy. NSAIDs should not be taken for 8-12 days after mifepristone administration due to the theoretical risk that prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors may alter the effectiveness of mifepristone.
Pemetrexed
Concurrent administration of pemetrexed and NSAIDs may increase the effect of pemetrexed, so caution should be exercised when administering high doses of NSAIDs.
Dicloberl 50 and alcohol
The patient should not drink alcohol while being treated with Dicloberl 50.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
The patient should inform their doctor if they become pregnant during treatment with Dicloberl 50.
Dicloberl 50 may be used in the first and second trimester of pregnancy only after consulting a doctor.
The patient should not take Dicloberl 50 if they are in the last three months of pregnancy, as it may harm the unborn child or cause complications during delivery. Dicloberl 50 may cause kidney and heart disorders in the unborn child. It may also increase the risk of bleeding in the mother and child and cause delayed or prolonged labor. In the first six months of pregnancy, Dicloberl 50 should not be used unless the doctor considers it absolutely necessary. If treatment is necessary during this period or when trying to conceive, the smallest possible dose should be used for the shortest possible time.
From the 20th week of pregnancy, Dicloberl 50, if taken for more than a few days, may cause kidney disorders in the unborn child - this may lead to a decrease in the amount of amniotic fluid surrounding the child (oligohydramnios) or narrowing of the blood vessels (ductus arteriosus) in the child's heart. If treatment is necessary for a longer period, the doctor may recommend additional monitoring.
Breastfeeding
Like other NSAIDs, diclofenac passes into breast milk in small amounts. Therefore, to avoid side effects in the infant, diclofenac should not be used during breastfeeding.
Fertility
Like other prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors, Dicloberl 50 may make it more difficult to conceive. If the patient plans to conceive or has problems conceiving, they should inform their doctor.
Driving and using machines
When taking high doses of Dicloberl 50, side effects affecting the central nervous system, such as fatigue and dizziness, may occur, which may limit the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. This applies especially to situations where the medicine is taken with alcohol. The patient may have limited ability to react quickly and appropriately to unexpected and sudden events. If such symptoms occur, the patient should not drive vehicles or operate machinery. They should not use tools or operate machinery and should not work without proper foot support.
3. How to use Dicloberl 50
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
Dosage
If the doctor has not prescribed otherwise, the medicine should be used as follows:
Diclofenac is dosed depending on the severity of the disease. The recommended daily dose for adults is 50 to 150 mg of diclofenac sodium, divided into 1 to 3 doses.
Method of administration
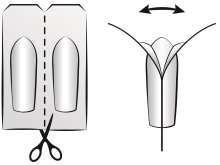
To remove the suppository from the packaging, the patient should tear off one suppository from the rest of the blister pack by repeatedly bending it at the perforation or cut the suppository along the perforation line using scissors.
Then, holding the free ends of the foil at the top of the suppository between their thumbs and index fingers, the patient should carefully tear open both foil flaps until they can remove the suppository (see diagram).
The patient should insert Dicloberl 50 deeply into the rectum, preferably after bowel movements.
To improve the sliding properties, the suppository can be warmed in the hand or briefly immersed in hot water.
Duration of treatment
The treating doctor will decide on the duration of treatment.
In rheumatic diseases, long-term use of Dicloberl 50 may be necessary.
Taking the medicine in the smallest effective dose for the shortest period necessary to alleviate symptoms reduces the risk of side effects (see "Warnings and precautions").
If the patient feels that the effect of Dicloberl 50 is too strong or too weak, they should consult their doctor.
Use in children and adolescents
Dicloberl 50 is not recommended for use in children and adolescents.
Using a higher than recommended dose of Dicloberl 50
| Age: | Single dose: | Total daily dose: |
| Adults | 1 suppository (equivalent to 50 mg of diclofenac sodium) | 1 to 3 suppositories (equivalent to 50 mg to 150 mg of diclofenac sodium) |
The patient should use Dicloberl 50 as directed by their doctor or according to the dosage information in the leaflet. If the patient feels that the analgesic effect of the medicine is insufficient, they should not increase the dose, but consult their doctor.
There are no characteristic clinical symptoms of diclofenac overdose. Overdose symptoms may include central nervous system disorders, such as headache, dizziness, feeling of emptiness in the head, restlessness (agitation), irritability or fatigue, as well as abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and gastrointestinal bleeding. Additionally, kidney or liver function disorders may occur. Sudden decrease in blood pressure, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression) and blue discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes (cyanosis) may also occur. There is no specific antidote.
In case of suspected overdose, the patient should inform their doctor.
Depending on the severity of the poisoning, the doctor will decide on the appropriate treatment.
Missing a dose of Dicloberl 50
The patient should not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
In case of any further doubts about using this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Dicloberl 50 can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Some side effects can be serious. If the patient experiences any side effects, they should tell their doctor, who will decide on further action.
The occurrence of the following side effects of the medicine depends mainly on the dose used and varies individually.
The most common side effects are gastrointestinal disorders. Peptic ulcer disease (gastric or duodenal ulcers) and gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation may occur, sometimes leading to death, especially in the elderly (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions"). Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, bloating, constipation, indigestion, abdominal pain, black stool or bloody vomiting have been reported (see section 2 "Warnings and precautions"). The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding is dose-dependent and duration-dependent.
The patient should stop using Dicloberl 50 and consult their doctor immediately if they notice:
- mild painful abdominal cramps and tenderness, starting soon after starting to use Dicloberl 50, followed by rectal bleeding or bloody diarrhea, usually within 24 hours of abdominal pain (frequency not known - cannot be estimated from available data).
The patient should tell their doctor immediately if they experience any of the following symptoms:
- chest pain, which may be a sign of a potentially serious allergic reaction called Kounis syndrome.
Reports have been made of edema (fluid accumulation in tissues), hypertension and heart failure associated with NSAID treatment.
Taking such medicines as Dicloberl 50 may be associated with an increased risk of arterial thrombotic events, e.g. heart attack or stroke (see section 2 "When not to use Dicloberl 50" and "Warnings and precautions").
Frequent:may affect up to 1 in 10 patients
- gastrointestinal disorders, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, as well as minor gastrointestinal bleeding, which may rarely cause anemia.
- hypersensitivity reactions, such as rash and itching.
- central nervous system disorders, such as headache, dizziness, feeling of emptiness in the head, restlessness (agitation), irritability or fatigue.
- digestive disorders (indigestion), bloating, stomach cramps (abdominal pain), loss of appetite, as well as peptic ulcer disease (with a risk of bleeding or perforation).
- increased liver enzyme activity in the blood.
- vertigo of labyrinthine origin.
- local irritation, discharge of blood or painful defecation may occur frequently after suppository administration.
Uncommon:may affect up to 1 in 100 patients
- hives. In such a case, the medicine should be discontinued immediately and the patient should consult a doctor.
- bloody vomiting, blood in the stool or bloody diarrhea.
- liver damage (especially during long-term treatment), hepatitis with or without jaundice (which may have a fulminant course in individual cases, even without preceding symptoms).
- hair loss.
- edema (fluid accumulation in tissues), especially in patients with hypertension or kidney function disorders.
Rare:may affect up to 1 in 1000 patients
- hypersensitivity, anaphylactic and pseudoanaphylactic reactions (which may manifest as bronchospasm, dyspnea [respiratory failure], tachycardia, hypotension [low blood pressure] and shock).
- gastritis (gastric mucosal inflammation), gastrointestinal bleeding.
- kidney function disorders.
- asthma, including breathing difficulties (dyspnea).
Very rare:may affect up to 1 in 10,000 patients
- worsening of infections (e.g. development of necrotizing fasciitis) in temporal relation to systemic use of NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, to which Dicloberl 50 also belongs). In case of signs of infection (e.g. redness, swelling, overheating, pain, fever) or their worsening while taking Dicloberl 50, the patient should contact their doctor immediately. The doctor will decide whether to administer other medicines used to treat infections or antibiotics.
- symptoms of meningitis (e.g. headache, nausea, vomiting, fever, stiff neck or changes in consciousness) have occurred during diclofenac treatment. It appears that patients with concomitant autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, mixed connective tissue disease) are more likely to experience these side effects.
- blood disorders [anemia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, pancytopenia, agranulocytosis (a serious condition associated with a significant decrease in neutrophil count in the blood), hemolytic anemia and aplastic anemia (lack of red blood cells due to their rapid breakdown)]. The first symptoms of these disorders may be fever, sore throat, mouth ulcers, flu-like symptoms, significant fatigue, nosebleeds and skin bleeding. In such cases, the medicine should be discontinued immediately and the patient should consult a doctor. The patient should not take painkillers or antipyretics on their own.
- angioedema (angioedema). In case of any of these symptoms, which may occur even after a single dose of the medicine, the patient should discontinue diclofenac and seek medical attention immediately.
- allergic vasculitis and pneumonitis.
- psychotic reactions, depression, anxiety, insomnia, nightmares.
- disorders of sensation, taste disorders, memory disorders, disorientation, seizures, tremors, stroke.
- vision disorders (blurred and double vision).
- tinnitus, hearing disorders.
- palpitations, chest pain, heart failure (heart failure), heart attack (myocardial infarction).
- hypertension (high blood pressure).
- Oral mucosal inflammation, including ulcerative stomatitis, glossitis, esophageal lesions as well as lower abdominal symptoms such as colitis (including bloody colitis), or exacerbation of Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis (inflammatory bowel diseases with accompanying ulcers), pancreatitis, intestinal stricture. In case of sudden abdominal pain, bloody vomiting, black stool or blood in the stool, the patient should discontinue Dicloberl 50 and consult their doctor immediately.
- Liver necrosis, liver failure. During long-term treatment, liver function parameters should be monitored at regular intervals.
- Severe skin reactions, such as skin rash with redness (exanthema, rash, erythema, erythema multiforme), skin rash with blisters (e.g. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis/Lyell's syndrome) or skin peeling (exfoliative dermatitis), photosensitivity (reactions to sunlight), local skin bleeding (purpura), which may be allergic in nature.
- kidney damage (interstitial nephritis), which may be accompanied by acute kidney failure, proteinuria (excess protein in the urine) and/or hematuria (blood in the urine), nephrotic syndrome (edema and increased protein in the urine). Therefore, kidney function should be monitored at regular intervals. Decreased urine output, fluid accumulation in the body (edema) as well as general malaise may be symptoms of kidney function disorders, including kidney failure. In case of these symptoms or their worsening while taking Dicloberl 50, the patient should discontinue the medicine and consult their doctor immediately.
Frequency not known:frequency cannot be estimated from available data
- ischemic colitis.
The patient should follow the instructions above regarding certain side effects!
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety, Urząd Rejestracji Produktów Leczniczych, Wyrobów Medycznych i Produktów Biobójczych
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Dicloberl 50
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Dicloberl 50 should not be used after the expiry date stated on the carton after EXP (abbreviation used to describe the expiry date). The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
The medicine should not be stored above 25°C. The medicine should be stored in its original packaging to protect it from light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of medicines they no longer need. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Dicloberl 50 contains
- The active substance of the medicine is diclofenac sodium. Each suppository contains 50 mg of diclofenac sodium.
- The other ingredients are: propyl gallate, ethanol 96%, cornstarch, solid fat (Witepsol H 15).
What Dicloberl 50 looks like and what the package contains
Almost white to light yellow, elongated suppositories in blisters of non-transparent composite PVC/PE film with the batch number embossed.
Packaging containing 5 or 10 suppositories.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Berlin-Chemie AG
Glienicker Weg 125
12489 Berlin, Germany
To obtain more detailed information about this medicine, the patient should contact the local representative of the marketing authorization holder:
Berlin-Chemie/Menarini Polska Sp. z o.o.
Phone: +48 22 566 21 00
Fax: +48 22 566 21 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterBerlin-Chemie AG
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Dicloberl 50Dosage form: Solution, 25 mg/mlActive substance: diclofenacManufacturer: IBSA Farmaceutici Italia S.r.l.Prescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 50 mg/mlActive substance: diclofenacManufacturer: IBSA Farmaceutici Italia S.r.l.Prescription requiredDosage form: Solution, 75 mg/mlActive substance: diclofenacManufacturer: IBSA Farmaceutici Italia S.r.l.Prescription required
Alternatives to Dicloberl 50 in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Dicloberl 50 in Ukraina
Alternative to Dicloberl 50 in Hiszpania
Online doctors for Dicloberl 50
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Dicloberl 50 – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














