
How to use Desferal
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Warning! Keep the leaflet! Information on the immediate packaging in a foreign language.
Desferal, 500 mg, powder for solution for injection
Deferoxamine mesylate
It is essential to carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient
- The leaflet should be kept, so that it can be re-read if necessary.
- In case of any doubts, the doctor or pharmacist should be consulted.
- This medicine has been prescribed to a specific person. It should not be given to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if the symptoms of their illness are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, the doctor or pharmacist should be informed. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is Desferal and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Desferal
- 3. How to use Desferal
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Desferal
- 6. Package contents and other information
1. What is Desferal and what is it used for
What is Desferal
Desferal contains the active substance - deferoxamine mesylate, also known as a "chelator". The medicine removes excess iron or aluminum from the body.
What is Desferal used for
Desferal is used to treat chronic excessive iron accumulation in the body, for example:
- in patients being treated for various types of anemia, such as thalassemia, sideroblastic anemia, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, or other chronic forms of anemia, in which multiple blood transfusions are necessary. Multiple transfusions can lead to excessive iron accumulation in the body;
- in patients with primary (hereditary) hemochromatosis;
- in patients with late-stage porphyria cutanea tarda.
Desferal can be used in adults, adolescents, and children.
It can also be used for:
- treatment of acute iron poisoning;
- treatment of chronic excessive aluminum accumulation in patients with end-stage renal failure requiring regular dialysis. In some cases, dialysis can lead to excessive aluminum accumulation in the body;
- diagnosis of excessive iron or aluminum accumulation in the body.
The doctor's instructions should be followed strictly. They may differ from the general information contained in this leaflet.
2. Important information before using Desferal
When not to use Desferal
- if the patient is allergic to deferoxamine mesylate - the active substance of Desferal, except in situations where a successfully completed desensitization procedure allows the administration of Desferal.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting Desferal, the doctor or pharmacist should be consulted. Before using Desferal, the doctor should be informed if:
- the patient suspects that they may be allergic to Desferal;
- in the past, after using Desferal, allergic reactions (skin rash, shortness of breath or difficulty breathing) have occurred;
- the patient has any kidney function disorders.
The doctor should be informed immediatelyif, during treatment with Desferal, the patient experiences any of the following symptoms:
- high body temperature, sore throat, shortness of breath, abdominal pain, severe diarrhea, or general feeling of discomfort (symptoms of fungal or bacterial infections);
- significantly reduced urine output (symptom of kidney function disorders);
- vision and hearing disorders;
- dizziness, feeling of emptiness in the head (symptoms of low blood pressure), shortness of breath, which may occur if Desferal is administered too quickly by intravenous infusion. See also section 3 "Administration of a higher dose of Desferal than recommended";
- heart rhythm disorders, possible symptoms that may occur in patients taking Desferal and also taking high doses of vitamin C. If the doctor also recommends taking vitamin C supplements, it should be ensured that Desferal has been used regularly for at least one month before starting vitamin C. The recommended doses of vitamin C should be strictly followed. The daily dose of vitamin C should not exceed 200 mg.
Monitoring the patient's health during Desferal treatment
- It may be necessary to perform certain blood and urine tests on the patient before starting and during treatment.
- In patients with excessive iron accumulation in the body, the iron concentration (ferritin) will be monitored to assess the effectiveness of Desferal. It will also be necessary to perform vision and hearing tests. In children and adolescents, growth and body weight will be regularly monitored. The doctor will take into account the results of these tests when selecting the appropriate dose of Desferal for the patient.
- If the patient is taking vitamin C during Desferal treatment, the doctor will also assess heart function.
During Desferal treatment, the urine may turn reddish-brown due to the excretion of the iron complex. This is usually not a cause for concern, but if the change in urine color causes concern, the doctor or nurse should be contacted.
The doctor should be consulted in case of any questions about the action of Desferal or the reasons for its prescription.
Children and adolescents
The doctor should be informed if it is noticed that the growth rate of a child treated with Desferal has slowed down.
Desferal and other medicines
The doctor or pharmacist should be told about all medicines currently being taken by the patient, as well as any medicines that the patient plans to take. This is especially true for the following medicines:
- medicines containing prochlorperazine (a neuroleptic medicine used to treat neurological disorders);
- vitamin C. Vitamin C should not be taken in a dose higher than 200 mg per day (see "Warnings and precautions" above);
- gallium isotope (Ga), administered before imaging tests (X-rays) in the diagnosis of certain diseases. It may be necessary to change the dosage or even discontinue one of the medicines.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, or thinks they may be pregnant or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
Desferal should not be used during pregnancy unless the doctor decides that it is necessary to use this medicine. The doctor will inform the patient about the risks of using Desferal during pregnancy.
Breastfeeding
Desferal should not be used during breastfeeding. The doctor will decide whether to stop breastfeeding or discontinue Desferal, taking into account the importance of the medicine for the mother.
Fertility
There is no data on the effect of deferoxamine on fertility, but studies conducted on animals have shown that Desferal may harm the fetus. Sexually active women of childbearing age are advised to use effective contraception during Desferal treatment and for 1 month after stopping treatment.
Driving and using machines
Using Desferal may cause vision and hearing disorders, as well as dizziness or other nervous system disorders. The patient should not drive a vehicle or operate machinery until these symptoms have resolved.
3. How to use Desferal
This medicine should always be used as directed by the doctor. In case of doubts, the doctor should be consulted.
Dosage and administration method
The doctor will determine the appropriate dose and administration method, individually for each patient. Depending on how the patient responds to treatment, the doctor may reduce or increase the dose of Desferal.
Desferal is intended for injection in the form of an aqueous solution. The powder should be dissolved in water for injection. The resulting solution with a recommended concentration of 95 mg/ml (for subcutaneous and intravenous administration) should be clear, colorless to slightly yellow. Only clear solutions should be used. Opalescent or cloudy solutions should not be used.
The Desferal solution with a concentration of 95 mg/ml can be diluted with fluids commonly used for infusion (0.9% NaCl solution, 5% glucose solution, Ringer's solution, lactated Ringer's solution, peritoneal dialysis fluids, such as Dianeal 137 Glucose 2.27%, Dianeal PD4 Glucose 2.27%, and CAPD/DPCA 2 Glucose 1.5%).
Treatment of chronic excessive iron accumulation
The dosage is determined by the doctor, depending on the patient's condition. For most patients, a dose of 20-60 mg per kilogram of body weight per day is sufficient.
Desferal can be administered by slow subcutaneous infusion (subcutaneous injection using an infusion pump), intravenous infusion, or intramuscular injections.
The doctor or nurse may prepare a ready-to-use solution for the patient or inform the patient how to prepare the solution themselves. In long-term treatment of patients with excessive iron accumulation in the body, it is very practical and convenient to administer Desferal by slow subcutaneous infusion, lasting from 8 to 12 hours (e.g., at night). For this purpose, a lightweight, portable infusion pump is used. With the help of the pump, Desferal is usually administered 5-7 times a week. The pump should be used carefully, in aseptic conditions.
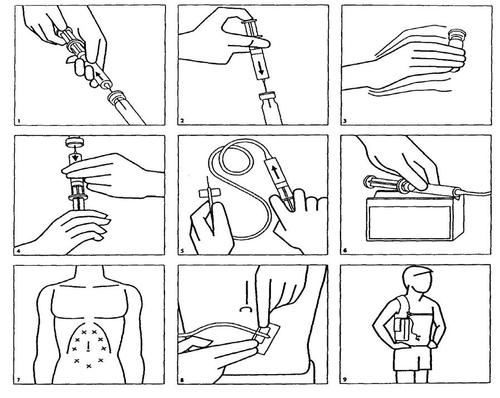
The following is the method of preparing the solution for subcutaneous infusion:
- 1. Draw water for injection into a syringe.
- 2. After rubbing the rubber stopper of the Desferal vial with alcohol, inject the contents of the syringe into the vial.
- 3. Shake the vial thoroughly until the powder is dissolved.
- 4. Draw the resulting solution into the syringe.
- 5. Attach the needle with a winged tip to the syringe and connect it to the infusion set.
- 6. Place the syringe in the pump.
- 7. The needle with a winged tip can be inserted under the skin of the abdomen, arm, or upper leg (thigh). It is essential to clean the skin with alcohol before inserting the needle. Then, with one hand, create a skin fold, and with the other hand, insert the needle until the "wings" are felt. The tip of the needle should move freely under the skin. If the tip of the needle does not move freely, it may be inserted too superficially under the skin. In this case, try to insert the needle in a new location, after cleaning the skin with alcohol.
- 8. Secure the needle with a plaster.
- 9. The pump is usually worn on the body on a belt or in a special case attached to the arm. Many patients find it most convenient to use it at night.
Elderly patients
Desferal can be used in elderly patients.
The doctor will select the appropriate dose for the elderly patient, usually starting with the lowest value in the dose range, due to the higher frequency of impaired liver, kidney, or heart function, as well as concomitant diseases and the use of other medicines.
Concomitant use of vitamin C
After at least one month of regular Desferal treatment, the doctor may recommend concurrent administration of vitamin C. The maximum daily dose of vitamin C for adults is 200 mg, divided into smaller doses taken throughout the day.
For children under 10 years of age, a dose of 50 mg of vitamin C per day is usually appropriate, while for older children, a dose of 100 mg is recommended.
Treatment of acute iron poisoning
- Desferal can be used in cases of iron preparation poisoning.
Treatment of chronic excessive aluminum accumulation in patients with end-stage renal failure
- Depending on the aluminum concentration in the patient's blood, Desferal is usually administered once a week by slow intravenous infusion, during the last 60 minutes of dialysis or 5 hours before the start of dialysis.
- In patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis or continuous cyclic peritoneal dialysis, Desferal should be administered before the last exchange of dialysis fluid on a given day.
- The dose of Desferal is 5 mg per kilogram of body weight.
- The duration of treatment depends on the test results recommended by the doctor.
Iron and aluminum overload test
- In the case of a test for excessive iron accumulation in the body, Desferal is administered intramuscularly in a dose of 500 mg. Urine is collected for 6 hours, and then the iron content is determined.
- In the case of patients requiring determination of aluminum overload, Desferal is administered by slow intravenous infusion during dialysis, in a dose of 5 mg/kg body weight. The aluminum content is determined in blood samples taken immediately before and after dialysis.
How long to use Desferal
The medicine should be used regularly and strictly according to the doctor's instructions. This will bring the best results and reduce the risk of side effects. In case of any questions or doubts related to treatment, the doctor should be consulted.
If there are any questions about how long to use Desferal, the doctor should be consulted.
Administration of a higher dose of Desferal than recommended
A higher dose or concentration of the medicine than recommended by the doctor should not be used, as this may cause local side effects at the injection site and other general side effects, such as dizziness, feeling of emptiness in the head (symptoms of low blood pressure), rapid or slow heart rate, gastrointestinal disorders (nausea), significantly reduced urine output (symptom of acute kidney failure), nervous system disorders (e.g., agitation, loss of speech, headaches), shortness of breath (symptom of respiratory function disorder), vision and hearing disorders.
In case of administration of a higher dose of Desferal than recommended, the doctor or hospital staff should be contacted immediately. It may be necessary to use appropriate treatment.
Missing a dose of Desferal
In case of a missed dose, the doctor should be informed immediately.
Stopping Desferal treatment
Desferal treatment should not be stopped unless the doctor decides to do so. If the patient stops treatment, the ability to remove excess iron from the body will be lost (see "How long to use Desferal").
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Desferal can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Too rapid intravenous administration of Desferal may cause side effects, and even collapse. If side effects occur, the doctor's help may be necessary. Some side effects can be serious.
The doctor should be informed immediately if the patient experiences any of the following side effects:
hearing disorders, vision disorders, severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, dizziness, feeling of emptiness in the head (symptoms of low blood pressure), rapid heart rate, shock (occurring when the medicine is administered too quickly), bleeding, fever, sore throat or mouth ulcers, rash, itching, hives, difficulty breathing or swallowing, feeling of pressure in the chest with wheezing or coughing, swelling, mainly of the face, tongue, and throat, nervous system disorders, significantly reduced urine output, seizures.
If any of the following side effects occur, the doctor should be told.
Very common(these side effects may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
joint pain, muscle pain, reactions at the injection site, including pain, swelling, redness, itching, and scabbing.
Common(these side effects may affect less than 1 in 10 people):
headache, nausea, hives, delayed growth, bone disorders (metaphyseal dysplasia), fever.
Uncommon(these side effects may affect less than 1 in 100 people):
neurosensorial hearing loss, tinnitus, asthma, vomiting, abdominal pain, reactions at the injection site, including blisters, swelling, burning.
Rare(these side effects may affect less than 1 in 1000 people):
fungal infections (mucormycosis/zygomycosis), vision loss, eye disorders (loss of visual field, retinal degeneration, optic neuritis, cataract, reduced visual acuity, blurred vision, night blindness, visual field disorders, color vision disorder), hypotension, rapid heart rate (tachycardia) and shock (occurring when the medicine is administered too quickly).
Very rare(these side effects may affect less than 1 in 10,000 people):
gastrointestinal inflammation (caused by Yersinia bacteria), blood disorders (including low platelet count, low white blood cell count), severe allergic reactions, such as anaphylactic shock, anaphylactic reaction, angioedema (symptoms may include rash, itching, hives, difficulty breathing or swallowing; feeling of pressure in the chest with wheezing or coughing; dizziness; swelling, mainly of the face, tongue, and throat), neurological disorders (including dizziness, brain cell damage, peripheral neuropathy, numbness and tingling), shortness of breath, lung infiltrates, diarrhea, generalized rash.
Frequency not known(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data):
seizures, muscle spasms, acute kidney failure (significantly reduced urine output), kidney function disorders, increased creatinine levels in the blood.
At the injection site, very common side effects include pain, swelling, redness, itching, and scabbing, while blisters, local swelling, and burning are uncommon. Local reactions may be associated with general reactions, such as joint pain or muscle pain (very common), headache (common), hives (common), nausea (common), fever (common), vomiting (uncommon), abdominal pain (uncommon), or asthma (uncommon).
There have been rare reports of increased aminotransferase activity in patients treated with Desferal. The use of Desferal in the treatment of aluminum overload may decrease serum calcium levels and exacerbate hyperparathyroidism.
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, the doctor or pharmacist should be informed. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products,
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309,
website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Desferal
This medicine should not be used after the expiry date stated on the packaging.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated.
Do not store above 25°C.
Each vial is for single use only. The solution should be used immediately after preparation, i.e., administration should be started within 3 hours. If the solution is prepared under validated aseptic conditions, it can be stored at room temperature for a maximum of 24 hours before administration. Opalescent or cloudy solutions should not be used.
The medicine should be stored out of the sight and reach of children.
Any unused vials should be returned to the pharmacy.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The pharmacist should be asked how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Desferal contains
The active substance of Desferal is deferoxamine mesylate.
Each vial contains 500 mg of deferoxamine mesylate.
What Desferal looks like and what the package contains
Desferal is available as a powder in vials, in a cardboard box.
Each package contains 10 vials.
For more detailed information, the marketing authorization holder or parallel importer should be consulted.
Marketing authorization holder in Bulgaria, the country of export:
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25
90429 Nuremberg, Germany
Manufacturer:
Novartis Pharma GmbH
Roonstrasse 25
90429 Nuremberg
Germany
Novartis Farmacéutica SA
Gran Via de les Corts Catalanes, 764
Barcelona, 08013 Barcelona
Spain
Parallel importer:
InPharm Sp. z o.o.
ul. Strumykowa 28/11
03-138 Warsaw
Repackaged by:
InPharm Sp. z o.o. Services sp. k.
ul. Chełmżyńska 249
04-458 Warsaw
Marketing authorization number in Bulgaria, the country of export:9800063
Parallel import authorization number: 424/24
Date of leaflet approval: 02.12.2024
[Information about the trademark]
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Marketing authorisation holder (MAH)Novartis Pharma GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to DesferalDosage form: Powder, 500 mgActive substance: deferoxaminePrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 500 mgActive substance: deferoxaminePrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 500 mgActive substance: deferoxaminePrescription required
Alternatives to Desferal in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.







