
Cezarius

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Cezarius

How to use Cezarius
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
CEZARIUS 100 mg/ml oral solution
Levetiracetam
Read the contents of the leaflet carefully before taking the medicine or giving it to a child, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, so you can read it again if you need to.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for one person. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is CEZARIUS and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before taking CEZARIUS
- 3. How to take CEZARIUS
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store CEZARIUS
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is CEZARIUS and what is it used for
Levetiracetam is an antiepileptic medicine (used to treat seizures in epilepsy).
CEZARIUS is used:
- as monotherapy (using only CEZARIUS) in the treatment of certain types of epilepsy in adults and adolescents from 16 years of age with newly diagnosed epilepsy. Epilepsy is a condition where patients have recurring seizures. Levetiracetam is used to treat this type of epilepsy, where seizures initially occur in one part of the brain but may then spread to larger areas of both brain hemispheres (partial seizures with or without secondary generalization). The doctor has prescribed levetiracetam to reduce the number of seizures;
- as an adjunctive therapy (used in combination with other antiepileptic medicines):
- in the treatment of partial seizures or partial seizures with secondary generalization in adults, adolescents, children, and infants from 1 month of age,
- in the treatment of myoclonic seizures (short, shock-like muscle contractions) in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with juvenile myoclonic epilepsy,
- in the treatment of primary generalized tonic-clonic seizures (large seizures, including loss of consciousness) in adults and adolescents from 12 years of age with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (a type of epilepsy that is likely to have a genetic basis).
2. Important information before taking CEZARIUS
When not to take CEZARIUS
1/9
- If the patient is allergic to levetiracetam, pyrrolidine derivatives, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with CEZARIUS, discuss it with your doctor.
- If the patient has kidney disease, this medicine should be used as directed by the doctor. The doctor may decide to adjust the dosage.
- Contact the doctor if the child taking levetiracetam experiences slowed growth or unexpected changes in puberty.
- In some patients treated with antiepileptic medicines, such as CEZARIUS, thoughts of self-harm or suicidal thoughts have occurred. In case of symptoms of depression and/or suicidal thoughts, contact the doctor.
Children and adolescents
- CEZARIUS is not recommended as monotherapy (using only CEZARIUS) in children and adolescents under 16 years of age.
CEZARIUS and other medicines
Tell the doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the patient is taking, has recently taken, or plans to take.
Do not take macrogol (a medicine used for constipation) 1 hour before and 1 hour after taking levetiracetam, as it may prevent levetiracetam from working.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult a doctor or pharmacist before taking this medicine.
CEZARIUS should not be used during pregnancy unless it is absolutely necessary. It is not possible to completely rule out the risk of birth defects in the fetus. In animal studies, levetiracetam administered in doses higher than those used to control seizures in humans showed an adverse effect on fertility.
Breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment.
Driving and using machines
CEZARIUS may affect the ability to drive and use tools or machines, as it may cause drowsiness. This is more likely at the beginning of treatment or after increasing the dose. It is not recommended to drive or use machines until the effect of the medicine on the patient's ability to perform these activities is known.
CEZARIUS 100 mg/ml oral solution contains liquid maltitol(E965). If the patient has previously been diagnosed with intolerance to some sugars, they should consult a doctor before taking the medicine.
CEZARIUS 100 mg/ml oral solution contains methyl parahydroxybenzoate
(E218), which may cause (possibly delayed) allergic reactions.
3. How to take CEZARIUS
This medicine should always be taken as directed by the doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubts, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
2/9
CEZARIUS is taken twice a day, in the morning and evening, preferably at the same time of day. The amount of oral solution taken must be as directed by the doctor.
Monotherapy(treatment with only CEZARIUS oral solution)
Dosage for adults and adolescents from 16 years of age
For patients over 4 years of age, the appropriate dose should be measured using the 10 ml syringe provided with the packaging.
The usual dose of CEZARIUS is taken twice a day, in two equal doses; a single dose is between 5 ml (500 mg) and 15 ml (1500 mg).
Starting treatmentwith CEZARIUS begins with lower dosesfor the first two weeks, and then the dose is increased as directed by the doctor to achieve the recommended value.
Adjunctive therapy(treatment with CEZARIUS oral solution and other medicines prescribed by the doctor)
Dosage for adults and adolescents (from 12 to 17 years of age) with a body weight of 50 kg or more:
For patients over 4 years of age, the appropriate dose should be measured using the 10 ml syringe provided with the packaging.
The usual dose of CEZARIUS is taken twice a day, in two equal doses; a single dose is between 5 ml (500 mg) and 15 ml (1500 mg).
Dosage for children from 6 months of age and older:
The doctor will recommend the most suitable form of CEZARIUS, depending on the age, body weight, and dose.
For children from 6 months to 4 years of age, the appropriate dose should be measured using the 3 ml syringe provided with the packaging.
For children over 4 years of age, the appropriate dose should be measured using the 10 ml syringe provided with the packaging.
The usual dose of CEZARIUS is taken twice a day, in two equal doses; a single dose is between 0.1 ml (10 mg) and 0.3 ml (30 mg) per kilogram of the child's body weight. (Examples of doses are presented in the table below).
Dose for children from 6 months of age and older
| Body weight | Initial dose: 0.1 ml/kg body weight, twice a day | Maximum dose: 0.3 ml/kg body weight, twice a day |
| 6 kg |
|
|
| 8 kg |
|
|
| 10 kg | 1 ml twice a day | 3 ml twice a day |
| 15 kg |
|
|
| 20 kg | 2 ml twice a day | 6 ml twice a day |
3/9
| 25 kg |
|
|
| from 50 kg | 5 ml twice a day | 15 ml twice a day |
Dosage for infants (from 1 to less than 6 months of age):
For children from 1 month to less than 6 months of age, the appropriate dose should be measured using the 1 ml syringe provided with the packaging.
The usual dose of CEZARIUS is taken twice a day, in two equal doses; a single dose is between 0.07 ml (7 mg) and 0.21 ml (21 mg) per kilogram of the infant's body weight. (Examples of doses are presented in the table below).
| Dose for infants (from 1 month to less than 6 months of age) Body weight | Initial dose: 0.07 ml/kg body weight, twice a day | Maximum dose: 0.21 ml/kg body weight, twice a day |
| 4 kg | 0.3 ml twice a day | 0.85 ml twice a day |
| 5 kg | 0.35 ml twice a day | 1.05 ml twice a day |
| 6 kg | 0.45 ml twice a day | 1.25 ml twice a day |
| 7 kg | 0.5 ml twice a day | 1.5 ml twice a day |
Method of administration:
After measuring the correct dose using the appropriate syringe, CEZARIUS oral solution can be added to a glass of water or to the liquid given to the child to drink from a bottle.
Method of use:
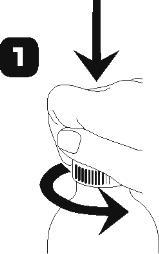
- Open the bottle: press the cap and turn it counterclockwise (figure 1)
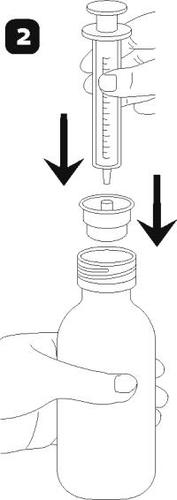
- Place the adapter on the bottle neck (figure 2), insert the dosing syringe into the adapter. Make sure it is properly secured.
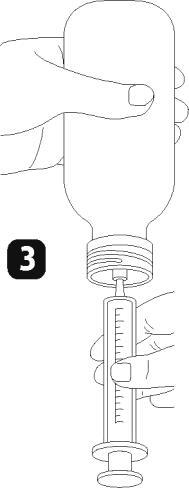
- Turn the bottle upside down (figure 3)
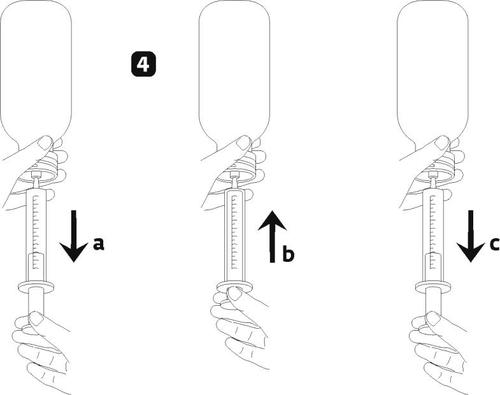
- Fill the dosing syringe with a small amount of solution by pulling the plunger down (figure 4a), press the plunger to remove air bubbles (figure 4b), then pull the plunger down to the mark corresponding to the dose of solution in milliliters (ml) prescribed by the doctor (figure 4c).
- Turn the bottle right side up. Remove the dosing syringe from the adapter.
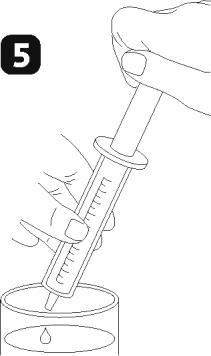
- Pressing the plunger, empty the syringe, pouring the measured dose of solution into a glass of water or into the bottle for the child (figure 5).
- Give the child the medicine mixed with water in the glass or bottle to drink.
- Close the plastic bottle with the cap.
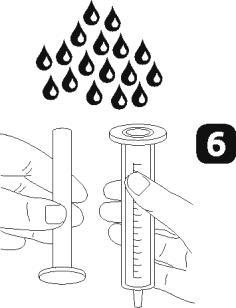
- Wash the dosing syringe with water (figure 6).
4/9
Duration of treatment:
- CEZARIUS is intended for long-term treatment. Treatment with CEZARIUS should be continued for as long as the doctor recommends.
- Do not stop treatment without consulting a doctor, as this may cause an increase in the frequency of seizures.
5/9
Using a higher dose of CEZARIUS than recommended:
After an overdose of levetiracetam, drowsiness, agitation, aggression, decreased consciousness, slowed breathing, and coma have been reported.
In case of taking a higher dose of CEZARIUS than recommended, consult a doctor immediately, who will recommend the most appropriate treatment for the overdose.
Missing a dose of CEZARIUS:
Consult a doctor if a dose of CEZARIUS has not been taken.
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping treatment with CEZARIUS:
If treatment with CEZARIUS is to be stopped, the medicine should be discontinued gradually to avoid an increase in the frequency of epileptic seizures. If the doctor decides to stop treatment, they will also inform how to gradually discontinue the medicine.
In case of any further doubts about taking the medicine, consult a doctor or pharmacist.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, CEZARIUS can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Inform your doctor or contact the nearest hospital emergency department immediately if you experience:
- weakness, dizziness, or difficulty breathing, as these symptoms may indicate a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis);
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat (Quincke's edema);
- flu-like symptoms and rash on the face and then on the whole body, high fever, increased liver enzyme activity in blood tests, increased number of certain white blood cells (eosinophilia), and swollen lymph nodes (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms - DRESS syndrome);
- symptoms such as reduced urine output, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, confusion, and swelling of the feet, ankles, or legs, as this may be a sign of sudden kidney function deterioration;
- a skin rash that may cause blisters and look like small targets (a dark spot surrounded by a lighter area and a dark ring around) (erythema multiforme);
- a widespread rash with blisters and peeling skin, mainly on the mouth, eyes, nose, and genitals (Stevens-Johnson syndrome);
- a severe form of rash causing skin peeling over more than 30% of the body surface (toxic epidermal necrolysis);
- signs of serious mental changes or noticing in the patient signs of disorientation, memory loss (amnesia), memory disturbances (forgetfulness), behavioral disturbances, or other neurological symptoms, including involuntary or uncontrolled movements. These may be symptoms of encephalopathy.
The most commonly reported side effects are: inflammation of the nasal passages and throat, drowsiness, headache, fatigue, and dizziness. At the beginning of treatment or when increasing the dose, side effects such as drowsiness, fatigue, or dizziness may occur more frequently. The intensity of these symptoms usually decreases over time.
6/9
Very common:may occur in more than 1 in 10 patients
- inflammation of the nasal passages and throat;
- drowsiness, headaches.
Common:may occur in 1 to 10 in 100 patients
- loss of appetite;
- depression, feelings of hostility or aggression, anxiety, insomnia, nervousness, or irritability;
- seizures, balance disturbances, dizziness (feeling of spinning), lethargy (lack of energy and enthusiasm), tremors (involuntary muscle tremors);
- dizziness (feeling of spinning);
- cough;
- abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia (indigestion), vomiting, nausea;
- rash;
- asthenia/fatigue (exhaustion).
Uncommon:may occur in 1 to 10 in 1,000 patients
- decreased platelet count; decreased white blood cell count;
- weight loss, weight gain;
- suicidal thoughts and attempts, mental disorders, abnormal behavior, hallucinations, anger, disorientation, panic attacks, mood swings;
- memory loss (amnesia), memory disturbances (forgetfulness), ataxia (coordination disturbances), paresthesia (tingling), attention disturbances;
- double vision, blurred vision;
- abnormal liver function tests;
- hair loss, rash, itching;
- muscle weakness, muscle pain;
- injuries.
Rare:may occur in 1 to 10 in 10,000 patients
- infection;
- decreased count of all blood cell types;
- severe allergic reactions (drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms - DRESS syndrome), Quincke's edema (swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and throat);
- decreased sodium levels in the blood;
- suicide, personality disorders (behavioral disturbances), thinking disturbances (slow thinking, inability to concentrate);
- involuntary muscle contractions of the head, trunk, and limbs, difficulty controlling movements, hyperkinesia (overactivity);
- pancreatitis;
- liver dysfunction, hepatitis;
- sudden kidney function deterioration;
- a skin rash that may cause blisters and look like small targets (a dark spot surrounded by a lighter area and a dark ring around) (erythema multiforme), a widespread rash with blisters and peeling skin, mainly on the mouth, eyes, nose, and genitals (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), and a severe form of rash causing skin peeling over more than 30% of the body surface (toxic epidermal necrolysis);
- rhabdomyolysis (breakdown of striated muscle) and associated increased creatine phosphokinase activity in the blood. The occurrence is significantly more frequent in Japanese patients compared to other patients (non-Japanese).
7/9
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, including those not listed in this leaflet, tell your doctor or pharmacist. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Drug Safety Monitoring of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products:
Aleje Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, tel.: +48 22 49 21 301, fax: +48 22 49 21 309, e-mail: [email protected].
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store CEZARIUS
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and bottle.
The expiry date refers to the last day of the month .
Do not use the medicine for more than 4 months after opening the bottle.
Store in the original packaging to protect from light.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What CEZARIUS contains
- The active substance of CEZARIUS is levetiracetam, each milliliter of oral solution contains 100 mg of levetiracetam.
- The other ingredients (excipients) are: sodium citrate (pH regulator), citric acid, methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E218), glycerol (E422), acesulfame potassium (E950), liquid maltitol (E965), raspberry flavor (a mixture of flavoring substances, propylene glycol E1520), purified water.
What CEZARIUS looks like and what the packaging contains
CEZARIUS oral solution 100 mg/ml is a clear liquid.
CEZARIUS oral solution (intended for use in children from 4 years of age, adolescents, and adults) is packaged in orange glass bottles containing 300 ml of liquid, placed in a cardboard box with a dosing syringe scaled every 0.25 ml, i.e., every 0.25 mg, and a bottle adapter.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
“PRZEDSIĘBIORSTWO PRODUKCJI FARMACEUTYCZNEJ HASCO-LEK” S.A.
51-131 Wrocław, ul. Żmigrodzka 242 E
8/9
Information about the medicine
tel. +48 (22) 742 00 22
e-mail: [email protected]
Date of last update of the leaflet:19.01.2018
9/9
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterPPF HASCO-LEK S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to CezariusDosage form: Tablets, 250 mgActive substance: levetiracetamPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 500 mgActive substance: levetiracetamPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 750 mgActive substance: levetiracetamPrescription required
Alternatives to Cezarius in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Cezarius in Spain
Alternative to Cezarius in Ukraine
Online doctors for Cezarius
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Cezarius – subject to medical assessment and local rules.







