
Cernevit

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Cernevit

How to use Cernevit
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: information for the user
CERNEVIT, powder for solution for injection and infusion
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains
important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet:
- 1. What is CERNEVIT and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using CERNEVIT
- 3. How to use CERNEVIT
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store CERNEVIT
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is CERNEVIT and what is it used for
CERNEVIT is a powder for solution for injection and infusion.
It contains 12 vitamins:
| Active substances | Equivalent to | ||
| retinol palmitate | 3500 IU | vitamin A | 3500 IU |
| cholecalciferol | 220 IU | vitamin D3 | 220 IU |
| DL-α-tocopherol | 10.20 mg | vitamin E | 11.20 IU |
| ascorbic acid | 125 mg | vitamin C | 125 mg |
| co-carboxylase tetrahydrate | 5.80 mg | vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 3.51 mg |
| sodium phosphate riboflavin | 5.67 mg | vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 4.14 mg |
| pyridoxine hydrochloride | 5.50 mg | vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 4.53 mg |
| cyanocobalamin | 6 µg | vitamin B12 | 6 µg |
| folic acid | 414 µg | folic acid | 414 µg |
| dexpanthenol | 16.15 mg | pantothenic acid | 17.25 mg |
| biotin | 69 µg | biotin | 69 µg |
| niacinamide | 46 mg | vitamin PP | 46 mg |
CERNEVIT provides vitamins to patients receiving parenteral nutrition (through an IV).
2. Important information before using CERNEVIT
When not to use CERNEVIT
- if the patient is allergic (hypersensitive) to the active substances or any of the other ingredients of this medicine, especially vitamin B or any of the excipients, including soy protein and peanut products (see section 6. Contents of the packaging and other information)
- in patients under 11 years of age
- if the patient has hypervitaminosis of any of the vitamins contained in the CERNEVIT preparation
Warnings and precautions
Before starting CERNEVIT, tell your doctor, pharmacist or nurse:
- if the patient has liver disease
- if the patient has kidney disease
- if the patient has epilepsy
- if the patient has Parkinson's disease
CERNEVIT and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines the patient is taking now or recently, and about medicines the patient plans to take, including those available without a prescription.
Be especially careful if the patient is taking any of the following types of medicines:
- L-Dopa (used to treat Parkinson's disease)
- phenobarbital, phenytoin and/or primidone (used to treat epilepsy) The doctor may monitor the levels of these medicines in the patient's blood and adjust their doses when the patient starts or stops taking CERNEVIT.
Laboratory test disturbances
Cernevit contains 69 micrograms of biotin per 5 ml. If the patient is to undergo laboratory tests, they must inform their doctor or laboratory staff that they have recently taken Cernevit, as biotin may interfere with the results of such tests. Depending on the test, the results may be falsely elevated or falsely low due to biotin. The doctor may order the patient to stop taking Cernevit before undergoing laboratory tests. It should also be remembered that other products that may be taken, such as multivitamin preparations or dietary supplements used to improve hair, skin and nails, may also contain biotin and affect laboratory test results. If the patient is taking such products, they should inform their doctor or laboratory staff.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding and fertility
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, thinks they may be pregnant or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Pregnancy
If necessary, this medicine may be given to a pregnant woman under strict adherence to indications and dosage to avoid overdose of vitamins.
Breastfeeding
Administration of CERNEVIT during breastfeeding is not recommended.
If the patient is breastfeeding and also receiving CERNEVIT, there is a risk of vitamin A overdose in the child.
Fertility
There is no available data on the effect of CERNEVIT on fertility in men or women.
3. How to use CERNEVIT
CERNEVIT will be administered by medical staff. It is usually given as an intravenous infusion.
The recommended dose is 1 vial per day.
Overdose of CERNEVIT
In this case, the symptoms of CERNEVIT overdose are mainly symptoms related to vitamin A overdose:
- symptoms of acute vitamin A overdose include:
- gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting)
- nervous system disorders (headache, optic nerve edema, seizures) caused by increased intracranial pressure in the patient
- psychiatric disorders (irritability)
- skin disorders (delayed skin peeling)
- symptoms of chronic vitamin A overdose include:
- headache caused by increased intracranial pressure in the patient
- bony diseases (sensitivity or painful swelling at the ends of the limbs)
If any of the above overdose symptoms are observed, the doctor should be informed. The doctor may discontinue the CERNEVIT infusion.
In case of any further doubts related to the use of this medicine, the doctor, pharmacist or nurse should be consulted.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
The following side effects are common and occur in 1 to 10 out of 100 patients:
- pain at the injection site.
The following side effects are rare and occur in 1 to 10 out of 1000 patients:
- nausea (nausea), vomiting.
The following side effects occur with an unknown frequency:
- allergic reactions, with respiratory disorders, chest pain, throat swelling, urticaria, rash, skin redness, abdominal discomfort, as well as cardiac arrest
- increased levels of vitamin A and vitamin A transport proteins in the blood
- taste disorders (metallic taste in the mouth)
- rapid heartbeat
- rapid breathing
- diarrhea
- increased levels of liver enzymes and bile acids
- itching
- fever, generalized pain, infusion site reactions such as burning sensation, rash
The doctor should be informed immediately if symptoms of an allergic reaction occur, such as respiratory disorders, chest pain, throat swelling, urticaria, rash, skin redness, abdominal discomfort. The doctor will discontinue the infusion and take necessary measures.
Reporting side effects
If side effects occur, the doctor or nurse should be consulted.
This includes any side effects not listed in this leaflet.
Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices and Biocidal Products
Jerozolimskie Avenue 181C
PL 02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
email: [email protected]
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects can help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store CERNEVIT
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Store at room temperature, i.e. between 15°C and 25°C. Protect from light.
Store in the outer carton.
After reconstitution, the product retains chemical and physical stability for 24 hours at 25°C.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately after reconstitution.
Otherwise, the time and conditions of storage until use are the responsibility of the person administering the product, and storage should not exceed 24 hours at 2-8°C, unless reconstitution was performed under controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging after "Expiry date". The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What CERNEVIT contains
- The active substances of the medicine are:
1 vial of 5 ml contains:
| Active substances | Equivalent to | ||
| retinol palmitate | 3500 IU | vitamin A | 3500 IU |
| cholecalciferol | 220 IU | vitamin D3 | 220 IU |
| DL-α-tocopherol | 10.20 mg | vitamin E | 11.20 IU |
| ascorbic acid | 125 mg | vitamin C | 125 mg |
| co-carboxylase tetrahydrate | 5.80 mg | vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 3.51 mg |
| sodium phosphate riboflavin | 5.67 mg | vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 4.14 mg |
| pyridoxine hydrochloride | 5.50 mg | vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 4.53 mg |
| cyanocobalamin | 6 µg | vitamin B12 | 6 µg |
| folic acid | 414 µg | folic acid | 414 µg |
| dexpanthenol | 16.15 mg | pantothenic acid | 17.25 mg |
| biotin | 69 µg | biotin | 69 µg |
| niacinamide | 46 mg | vitamin PP | 46 mg |
IU = International Units
mg = milligrams
The other ingredients are: glycine, soy phospholipids, glycocholic acid, sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid.
CERNEVIT contains 24 mg of sodium (1 mmol) per vial. This should be taken into account in patients on a controlled sodium diet.
What CERNEVIT looks like and contents of the pack
CERNEVIT is supplied in brown glass vials. To prepare the infusion solution, medical staff may use the BIO-SET system, which facilitates the dissolution of CERNEVIT.
CERNEVIT is available in packs of 10 or 20 vials, with or without the BIO-SET system.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Baxter Polska Sp. z o.o.
Kruczkowskiego 8
00-380 Warsaw
Manufacturer
Baxter SA
Boulevard René Branquart 80
7860 Lessines, Belgium
To obtain more detailed information, please contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder.
Baxter Polska Sp. z o.o.
Kruczkowskiego 8
00-380 Warsaw
phone: (22) 488 37 77
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 26.03.2019
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The following information is intended for healthcare professionals only
Qualitative and quantitative composition
1 vial of 5 ml contains:
| Active substances | Equivalent to | ||
| retinol palmitate | 3500 IU | vitamin A | 3500 IU |
| cholecalciferol | 220 IU | vitamin D3 | 220 IU |
| DL-α-tocopherol | 10.20 mg | vitamin E | 11.20 IU |
| ascorbic acid | 125 mg | vitamin C | 125 mg |
| co-carboxylase tetrahydrate | 5.80 mg | vitamin B1 (thiamine) | 3.51 mg |
| sodium phosphate riboflavin | 5.67 mg | vitamin B2 (riboflavin) | 4.14 mg |
| pyridoxine hydrochloride | 5.50 mg | vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) | 4.53 mg |
| cyanocobalamin | 6 µg | vitamin B12 | 6 µg |
| folic acid | 414 µg | folic acid | 414 µg |
| dexpanthenol | 16.15 mg | pantothenic acid | 17.25 mg |
| biotin | 69 µg | biotin | 69 µg |
| niacinamide | 46 mg | vitamin PP | 46 mg |
The excipients are: glycine, soy phospholipids, glycocholic acid, sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid
Appearance of the solution
After reconstitution, the resulting solution is yellow-orange in color.
Dosage and administration
Only for adults and children over 11 years old
1 vial per day.
Administer by slow intramuscular or intravenous injection, or intravenously in the form of infusions.
Method of administration
- intravenous administrationMethod of reconstitution: see below instructions for use and preparation.
After reconstitution: Inject slowly (at least 10 minutes; see section Warnings) intravenously or as an intravenous infusion in a solution of physiological saline or 5% glucose.
Administration can be continued throughout the period of parenteral nutrition. To meet nutritional needs and prevent deficiencies and potential complications arising from them
CERNEVIT can be added to nutritional mixtures containing carbohydrates, fats, amino acids and electrolytes, provided that compatibility and stability have been previously established for each preparation in the nutritional mixture.
- intramuscular administrationMethod of reconstitution: see below instructions for use and preparation.
Consider the total amount of vitamins from all sources, such as other forms of nutrition, administration of other vitamins or medicines containing vitamins as inactive ingredients (see section Interactions).
The patient's clinical condition and vitamin levels should be monitored to maintain their appropriate levels.
It should be taken into account that some vitamins, especially A, B and B, are sensitive to ultraviolet light (e.g. direct and indirect sunlight). Additionally, high oxygen content in the solution may increase the loss of vitamins A, B, C and E. These factors should be considered if appropriate vitamin levels are not achieved.
Contraindications
CERNEVIT should not be used:
- in hypersensitivity to any active substance, especially vitamin B or any excipient, including soy protein and soy products (lecithin in micelle mixtures comes from soy) or peanut protein and peanut products
- in newborns, infants and children under 11 years of age
- in hypervitaminosis of any of the vitamins contained in this product
Special warnings and precautions for use
Warnings
Allergic reactions
- For CERNEVIT and other multivitamin products, as well as single vitamins (especially B, B, B and folic acid), severe systemic allergic reactions have been reported. For CERNEVIT and other parenteral vitamin products, fatal reactions have been reported.
- Cross-allergies have been observed between soy and peanut proteins
- In some cases, the occurrence of an allergic reaction after intravenous administration of multivitamin products may be related to the rate of administration. In the case of intravenous infusion, CERNEVIT should be administered slowly. In the case of intravenous injection, it should be administered slowly (the injection should last at least 10 minutes).
If symptoms of an allergic reaction occur, the infusion or injection must be stopped immediately.
- Vitamin toxicity
- The patient's clinical condition and vitamin levels in the blood should be monitored to avoid overdose and toxic effects, especially of vitamins A, D and E, and in particular in patients who also receive vitamins from other sources or use other factors that increase the risk of toxic effects of vitamins.
- Monitoring is especially important in patients receiving long-term parenteral multivitamin supplementation.
Vitamin A hypervitaminosis
- The risk of vitamin A hypervitaminosis and toxic effects (e.g. skin and bone disorders, double vision, liver cirrhosis) is increased, for example:
- in patients with protein deficiency
- in patients with renal failure (even in the absence of vitamin A supplementation)
- in patients with liver failure
- in patients with low body mass (e.g. pediatric patients)
- and in patients undergoing long-term treatment.
- Acute liver disease in patients with high vitamin A stores in the liver can lead to the occurrence of symptoms of vitamin A toxicity.
Refeeding syndrome in patients receiving parenteral nutrition
Supplementation of nutrients in severely malnourished patients can cause a syndrome of related symptoms, characterized by the transfer of potassium, phosphorus and magnesium to the intracellular space, as anabolic processes predominate in the patient. There may also be a deficiency of thiamine and fluid retention in the body. Close monitoring and gradual increase in nutrient intake, avoiding overfeeding, can prevent these complications. In case of nutritional deficiencies, appropriate supplementation may be justified.
Sediment in patients receiving parenteral nutrition
Sedimentation in pulmonary vessels has been reported in patients receiving parenteral nutrition, including parenteral nutrition with vitamin supplementation. Some cases were fatal. Excessive addition of calcium and phosphate increases the risk of calcium phosphate sediment formation. Sedimentation has been reported even in the absence of phosphate salts in the solution. Sediment formation at a distance from the filter on the infusion line and the suspicion of sediment formation in the bloodstream have also been reported.
In addition to checking the solution, the infusion set and catheter should also be periodically checked for the presence of sediment.
If symptoms of respiratory function disorders occur, the infusion should be discontinued and the patient's clinical condition should be assessed.
Check if the container is damaged.
Work in aseptic conditions.
Do not store partially used vials; do not use if the color of the product after reconstitution is improper.
Special precautions for use
Liver
- In patients receiving CERNEVIT, it is recommended to monitor liver function parameters. Special monitoring is recommended in patients with jaundice of hepatic origin or other signs of cholestasis. In patients receiving CERNEVIT, cases of increased liver enzyme activity, including isolated increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT) activity in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, have been reported. Additionally, increased bile acid levels (all and individual bile acids, including glycocholic acid) have been observed in patients receiving CERNEVIT.
- In some patients receiving parenteral nutrition (including parenteral nutrition with vitamin supplementation), liver and biliary disorders, including cholestasis, steatosis, fibrosis and cirrhosis, leading to liver failure, as well as cholecystitis and cholelithiasis, have been reported. The etiology of these disorders is considered to be multifactorial and may vary between patients. Patients who develop abnormal laboratory test results or other signs of liver and biliary disorders should be evaluated by a doctor with knowledge of liver diseases to identify possible causal and contributing factors and to take possible therapeutic and preventive measures.
Use in patients with impaired liver function
Patients with impaired liver function may require individual vitamin supplementation.
Particular attention should be paid to preventing vitamin A toxicity, as liver disease is associated with increased susceptibility to toxic effects of vitamin A, especially in combination with chronic excessive alcohol consumption (see also "Vitamin A hypervitaminosis" and "Liver" above).
Use in patients with impaired renal function
Patients with impaired renal function may require individual vitamin supplementation, depending on the degree of renal impairment and the presence of concomitant diseases. In patients with severe renal failure, particular attention should be paid to maintaining adequate vitamin D levels and preventing toxic effects of vitamin A, which may occur in such patients even with low-dose vitamin A supplementation or in the absence of supplementation.
Vitamin B hypervitaminosis and toxicity (peripheral neuropathy, involuntary movements) have been reported in patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis who received parenteral multivitamin products containing 4 mg of pyridoxine administered three times a week.
General monitoring
In patients receiving parenteral multivitamin products for a long time as the only source of vitamins, the clinical condition and vitamin levels should be monitored to ensure proper supplementation, e.g.:
- vitamin A in patients with decubitus ulcers, wounds, burns, short bowel syndrome or cystic fibrosis
- vitamin B in dialyzed patients
- vitamin B in patients with cancer
- vitamin B in patients with renal failure
- individual vitamins whose requirements may be increased due to interactions with other medicines (see section Interactions)
Deficiencies of one or more vitamins should be corrected through specific supplementation.
CERNEVIT does not contain vitamin K, which should be administered separately if necessary.
Use in patients with vitamin B deficiency
Before starting supplementation with CERNEVIT in patients at risk of vitamin B deficiency and when planning to administer CERNEVIT for several weeks, it is recommended to assess the vitamin B status.
After a few days of administration, both the level of cyanocobalamin (vitamin B) and folic acid in the product may be sufficient to cause an increase in red blood cells, reticulocytes and hemoglobin in some patients with vitamin B deficiency with megaloblastic anemia. This may mask a vitamin B deficiency.
Effective treatment of vitamin B deficiency requires higher doses of cyanocobalamin than are provided in CERNEVIT.
Supplementation with folic acid in patients with vitamin B deficiency who are not receiving vitamin B may not prevent the development or progression of neurological changes associated with vitamin B deficiency. It is even suggested that the patient's neurological condition may worsen.
When interpreting vitamin B levels, it should be taken into account that recent intake of vitamin B may result in a normal level despite a deficiency in tissues.
Disturbances of laboratory tests
Biotin may interfere with laboratory tests based on the interaction of biotin and streptavidin, leading to falsely lowered or elevated test results, depending on the test. The risk of interference is higher in children and patients with impaired renal function, and increases with higher doses. When interpreting laboratory test results, possible biotin interference should be taken into account, especially if there is a lack of consistency with the clinical presentation (e.g. thyroid test results mimicking those indicating Graves' disease in patients taking biotin without symptoms of this disease, or falsely negative troponin test results in patients taking biotin with myocardial infarction). In cases where interference is suspected, alternative tests that are not susceptible to biotin interference should be performed, if available. If laboratory tests are ordered for patients taking biotin, consultation with laboratory staff is recommended.
The presence of ascorbic acid in serum and urine may cause falsely high or low readings of glucose levels in some glucose measurement systems, including portable test strips and portable glucose meters. The technical data for each laboratory test should be consulted to determine potential disturbances caused by vitamins.
Concomitant use with antiepileptic drugs:
Due to the presence of folic acid, concomitant administration of CERNEVIT with antiepileptic drugs containing phenobarbital, phenytoin or primidone requires special caution.
Concomitant use with levodopa:
Due to the presence of pyridoxine in CERNEVIT, concomitant use with levodopa requires caution, as it may reduce the effectiveness of L-dopa. To prevent this interaction, a decarboxylase inhibitor, such as carbidopa, can be added.
Medicines that bind to acidic alpha-1-glycoprotein (AAG):
In an in vitro study using human serum, a concentration of glycocholic acid about 4 times higher than the concentration of glycocholic acid in serum, which could result from the injection of a bolus of CERNEVIT in an adult, increased the fraction of certain medicines binding to acidic alpha-1-glycoprotein (AAG) by 50-80%.
It is not known whether this effect is clinically significant if the amount of glycocholic acid contained in a standard dose of CERNEVIT (as a component of mixed micelles) is administered in a slow intravenous injection, slow intramuscular injection or infusion over a longer period.
Patients receiving CERNEVIT and medicines binding to AAG should be closely monitored for increased effects of these medicines. These include propranolol, prazosin and many others.
Interactions related to supplementation with other vitamins:
Certain medicines may interact with certain vitamins in doses significantly exceeding those contained in CERNEVIT. This should be taken into account in patients taking vitamins from multiple sources, and when this occurs, patients should be monitored for these interactions and appropriate action should be taken.
Overdose
Acute or chronic overdose of vitamins (especially A, D and E) can cause symptomatic hypervitaminosis.
The risk of overdose is particularly high if the patient receives vitamins from multiple sources, and overall vitamin supplementation does not meet the individual needs of the patient, and in patients with increased susceptibility to hypervitaminosis (see section Special precautions for use).
The symptoms of CERNEVIT overdose are mainly due to vitamin A overdose.
Clinical symptoms of acute vitamin A overdose (doses exceeding 150,000 IU)
- gastrointestinal disturbances, headache, increased intracranial pressure, optic nerve edema, psychiatric disorders, excessive irritability and even seizures. As a late symptom of the body's reaction to overdose, generalized skin peeling has been observed.
Clinical symptoms of chronic vitamin A overdose (long-term administration of higher than physiological doses of vitamin A in patients who do not require supplementation of vitamin deficiency)
- increased intracranial pressure, excessive growth of the cortical layer of long bones and premature closure of the epiphyseal plates of bones. The diagnosis is based on the presence of tender or painful subcutaneous swellings in the limbs. On X-ray, there are thickening of the periosteum of the shaft of the ulna, radius, clavicle and ribs.
Treatment of vitamin overdose usually involves discontinuing vitamin supplementation and other actions in accordance with clinical indications (such as limiting calcium intake, increasing diuresis and hydration).
Pharmaceutical particulars
Shelf life
2 years
Special precautions for storage
Store at room temperature, i.e. between 15°C and 25°C, protected from light.
Store in the outer carton.
After reconstitution, the product retains chemical and physical stability for 24 hours at 25°C.
From a microbiological point of view, the product should be used immediately after reconstitution.
Otherwise, the time and conditions of storage until use are the responsibility of the person administering the product, and storage should not exceed 24 hours at 2-8°C, unless reconstitution was performed under controlled and validated aseptic conditions.
Type and content of packaging
Brown glass vials containing 750 mg of powder, in a carton. Packs of 10 and 20 vials.
Brown glass vials containing 750 mg of powder, with the BIO-SET system, in a carton. Packs of 10 and 20 vials.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Incompatibilities, instructions for disposal and preparation of the medicinal product for use (if applicable)
- During preparation of the solution and addition of the component to the parenteral nutrition mixture, aseptic conditions should be observed.
- Gently mix to dissolve the lyophilized powder.
- CERNEVIT must be completely dissolved before it is transferred from the vial.
- Do not use the product if the reconstituted solution is not clear and the original seal is broken.
- After adding CERNEVIT to the parenteral nutrition solution, check for any abnormal color change and/or presence of insoluble complex or crystal precipitates.
- The final solution should be thoroughly mixed if CERNEVIT is used as a component of the parenteral nutrition mixture.
- Unused reconstituted CERNEVIT should be discarded and not stored for later use.
- Medicines for parenteral administration should be inspected visually for particulate matter and abnormal coloration prior to administration, whenever the solution and container permit.
- It is recommended to use a filter at the end of the line when administering all types of parenteral nutrition.
If necessary, refer to relevant references on compatibility and guidelines. This medicinal product must not be mixed with other medicinal products, except for those that have been shown to be compatible and stable. For further information, contact the marketing authorization holder.
Check the compatibility of solutions administered simultaneously through the same line.
CERNEVIT (vials without BIO-SET)
Intravenous administration
Using a syringe, inject 5 ml of water for injections or glucose 5% or 0.9% sodium chloride solution into the vial.
Gently mix to dissolve the powder.
The resulting solution is yellow-orange in color.
Subcutaneous Administration
Dissolve the powder in 2.5 ml of water for injection as described above.
CERNEVIT BIO-SET
CERNEVIT with the BIO-SET system allows for direct dissolution of the preparation in bags (single and multi-chamber) with an injection port.
Single-chamber bag:
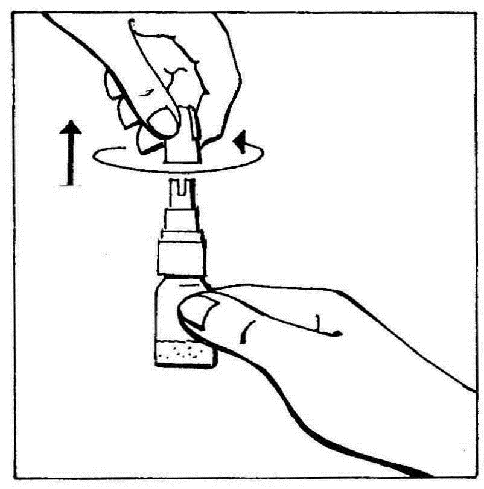
- 1. Remove the cap by twisting and then pulling to break the protective ring.
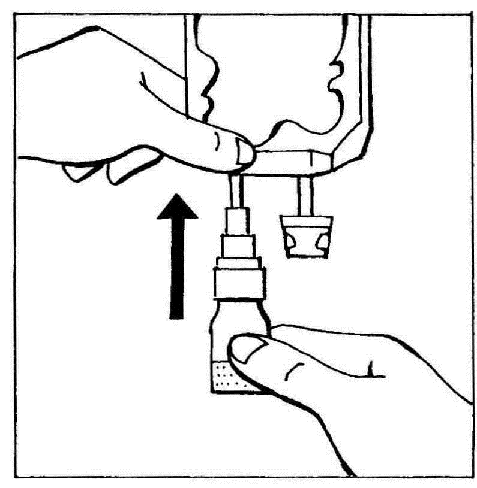
- 2. Connect the BIO-SET directly to the injection port of the bag.
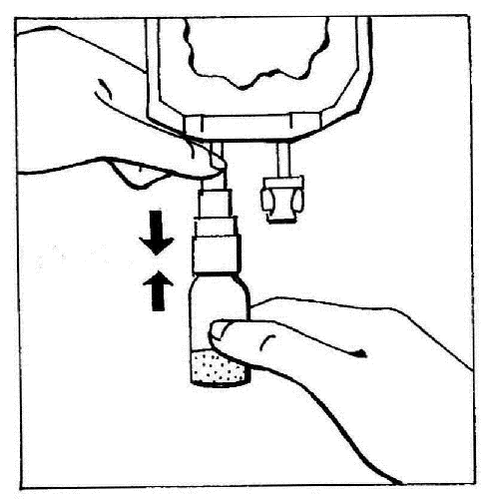
- 3. Activate the BIO-SET by pressing the transparent, movable part. This allows the rubber stopper of the vial to be pierced.
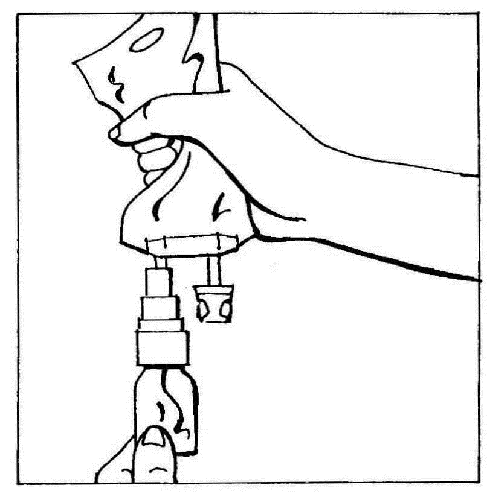
- 4. Position the connected elements (CERNEVIT with BIO-SET and the bag with infusion fluid) vertically, holding the bag on top. Gently squeeze the bag several times to cause the fluid to flow into the vial (approx. 5 ml). Shake the vial to dissolve the powder.
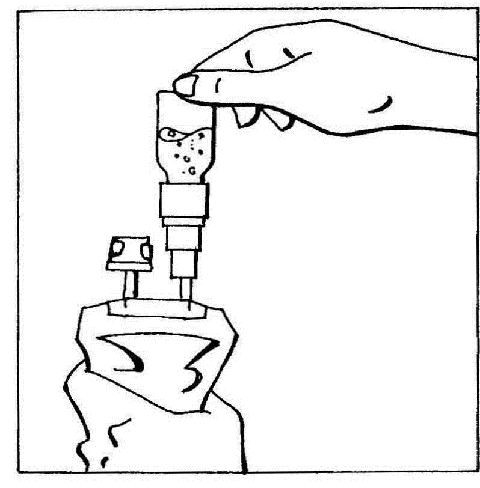
- 5. Invert the connected elements and hold them vertically with the vial on top. Gently squeeze the bag several times to move the air from the bag into the vial. This will cause the fluid to flow back into the bag.
- 6. Repeat steps 4 and 5 until the vial is empty.
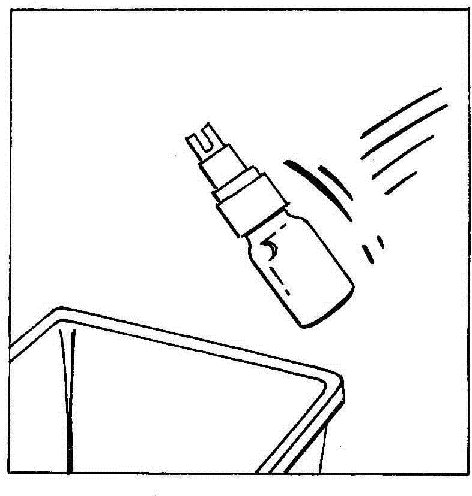
- 7. Disconnect and discard the vial with the BIO-SET.
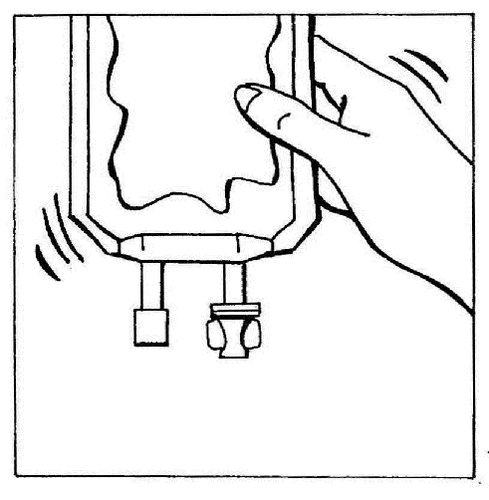
- 8. Gently mix the contents of the bag.
Multi-chamber bag:
The CERNEVIT preparation with the BIO-SET should be dissolved before activating the multi-chamber bag (before opening the breakable welds and before mixing all the chambers).
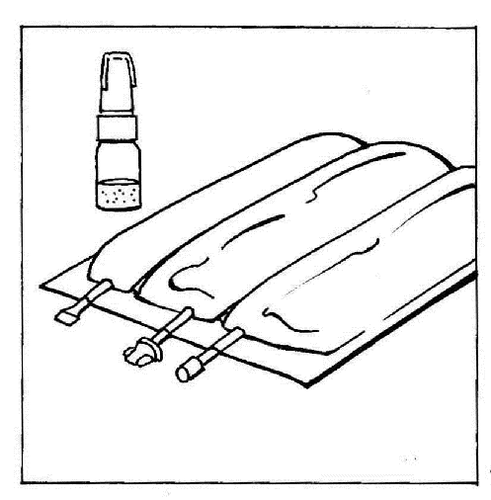
- 1. Place the multi-chamber bag on a table.
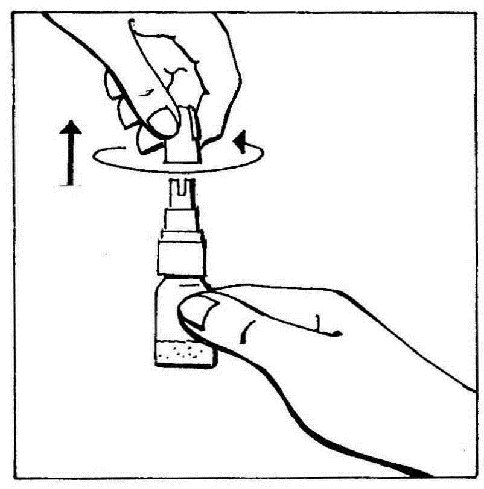
- 2. Remove the cap by twisting and then pulling to break the protective ring.
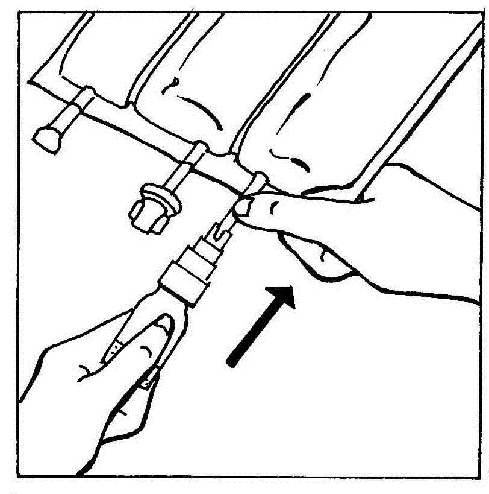
- 3. Connect the BIO-SET directly to the injection port of the bag.
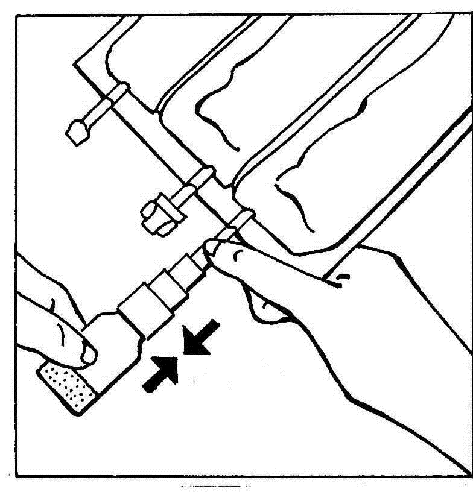
- 4. Activate the BIO-SET by pressing the transparent, movable part. This allows the rubber stopper of the vial to be pierced.
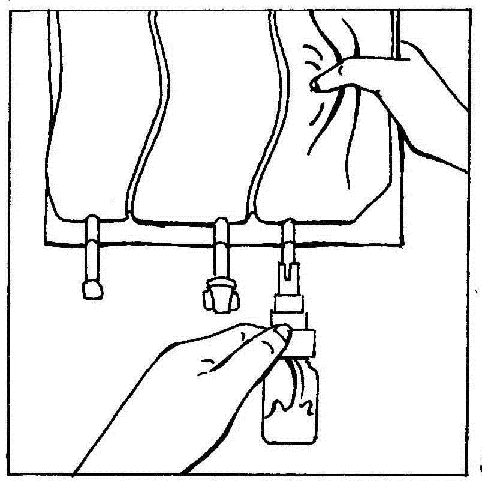
- 5. Hold the vial vertically. Gently squeeze the bag chamber several times to cause the fluid to flow into the vial (approx. 5 ml). Shake the vial to dissolve the powder.
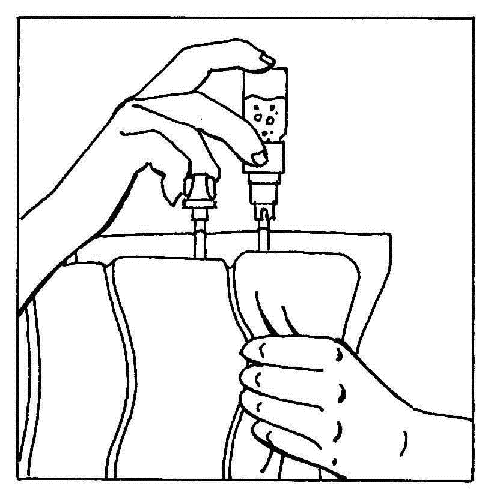
- 6. Invert the connected elements and hold them vertically with the vial on top. Gently squeeze the bag chamber several times to move the air from the bag into the vial. This will cause the fluid to flow back into the bag.
- 7. Repeat steps 5 and 6 until the vial is empty.
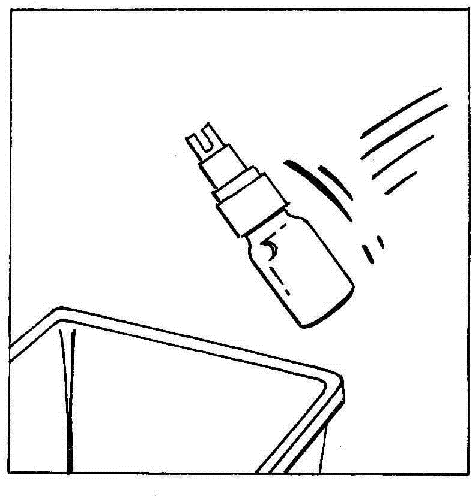
- 8. Disconnect and discard the vial with the CERNEVIT BIO-SET.
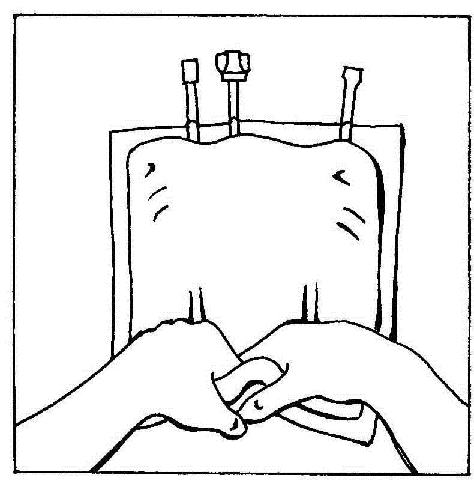
- 9. Break the welds of the bag chambers. Finally, activate the multi-chamber bag.
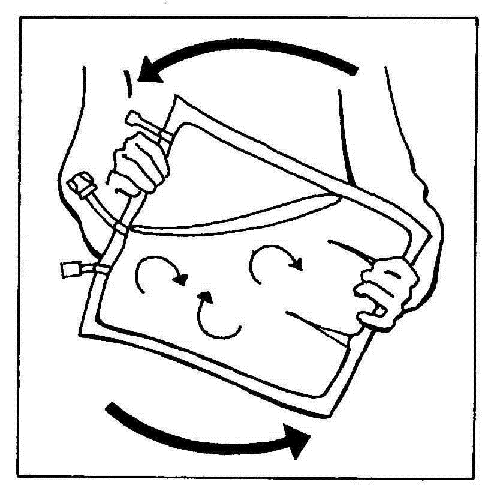
- 10. Gently mix the contents of the bag by turning it at least 3 times.
WARNING:
Be careful not to disconnect the BIO-SET from the injection port of the bag during the dissolution of the preparation.
- Country of registration
- Prescription requiredNo
- Manufacturer
- ImporterBaxter S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to CernevitDosage form: Concentrate, -Active substance: electrolytes in combination with other drugsManufacturer: Fresenius Kabi Norge ASPrescription not requiredDosage form: Concentrate, (170.1 mg + 133.5 mg + 14 mg)/mlActive substance: electrolytes in combination with other drugsPrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 1 g/10 mlActive substance: calcium chlorideManufacturer: Demo S.A.Prescription required
Alternatives to Cernevit in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Cernevit in Ukraine
Alternative to Cernevit in Spain
Online doctors for Cernevit
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Cernevit – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














