

Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% Heavi

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% Heavi

How to use Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% Heavi
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: patient information
BUPIVACAINE WZF SPINAL 0.5% HEAVY, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Bupivacaine hydrochloride
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor, pharmacist, or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy
- 3. How to use Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy and what is it used for
The medicine contains bupivacaine, which belongs to a group of local anesthetics with an amide structure. It has a long-acting anesthetic effect. Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy is used for anesthesia of parts of the body during surgery in adults and children of all ages. After administration of the medicine, certain parts of the body are anesthetized, so the patient does not feel pain. The medicine is used:
- in subarachnoid anesthesia during urological operations, on the lower limbs, and in the abdominal cavity. Subarachnoid anesthesia involves administering the medicine into the spinal canal in the spine.
2. Important information before using Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy
When not to use Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy
- If the patient is allergic (symptoms, e.g., rash, swelling of the face and throat, shortness of breath) to bupivacaine, other local anesthetics with an amide structure, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If the patient has diseases such as meningitis, encephalitis, intracranial hemorrhage, or brain and spinal cord tumors.
- If the patient has spinal canal stenosis, inflammatory conditions, spinal tuberculosis, or injuries.
- If the patient has a blood infection (sepsis).
- If the patient has changes in the spinal cord caused by a specific type of anemia resulting from a lack of vitamin B (subacute combined degeneration of the spinal cord in pernicious anemia).
- If the patient has a skin infection at the site of anesthesia or in its vicinity.
- If the patient has experienced cardiogenic shock (sudden drop in blood pressure and reduced blood flow through the body's tissues).
- If the patient has experienced hypovolemic shock (resulting from a decrease in circulating blood volume due to, e.g., dehydration, bleeding).
- If the patient has coagulation disorders or is taking anticoagulant medications (to "thin" the blood).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with the medicine, discuss it with your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy is administered by anesthesiologists. During treatment with the medicine, they will provide the patient with proper care and, in case of problems, will administer oxygen therapy (oxygen administration) and take other appropriate actions to maintain vital functions. Therefore, it is very important to tell your doctor about all health problems, especially:
- if the patient has hypovolemia (reduced circulating blood volume due to, e.g., dehydration, bleeding);
- if the patient has serious heart problems, such as heart block (the heart does not beat rhythmically, there is significant slowing and disorganization of heart function);
- if the patient has had or has kidney or liver function disorders (severe kidney or liver failure);
- if the patient has neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, neuromuscular disorders. Elderly patients, in poor general condition, should be under special medical care. In elderly patients or women in advanced pregnancy, after using Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy, there is a greater risk of total spinal anesthesia (manifested by respiratory arrest). In these patients, the doctor will use a smaller dose of the medicine to reduce the risk of total spinal anesthesia. Subarachnoid anesthesia may cause paralysis of the intercostal muscles, and in patients with pleural effusion, respiratory disorders may occur. Blood infection can increase the risk of developing an intraspinal abscess in the postoperative period.
Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy and other medicines
Tell your doctor about all medicines you are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as medicines you plan to take. In particular, tell your doctor if you are taking medicines for arrhythmias, such as amiodarone, mexiletine. Concomitant use of other medicines with a similar structure to bupivacaine (e.g., lidocaine - a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic agent) and bupivacaine may increase the toxic effects of each of these medicines on the human body.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine. The use of the medicine during pregnancy and breastfeeding will be decided by your doctor.
Driving and using machines
Depending on the dose used, local anesthetics may have a slight effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. Therefore, it is not recommended to perform these activities on the day of anesthesia.
Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy contains glucose and sodium
The medicine contains 72.72 mg of glucose (equivalent to 80 mg of anhydrous glucose) per 1 ml of solution for injection. This should be taken into account in patients with diabetes. The medicine contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of sodium per dose, which means the medicine is considered "sodium-free".
3. How to use Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy
- The medicine is administered by a doctor, usually an anesthesiologist.
- The dose of the medicine may vary from patient to patient. The dose will be determined by the doctor based on the patient's age, weight, health status, and the duration of the operation. The doctor will provide detailed information on the dosing of the medicine.
- Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy is intended for subarachnoid anesthesia.
Use in children and adolescents
Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy is injected slowly into the spinal canal (part of the spine) by an anesthesiologist experienced in techniques for anesthesia in children. The dose depends on the patient's age and weight and will be determined by the anesthesiologist.
Use of a higher dose of Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy than recommended
The medicine is administered by a doctor, so it is unlikely that the patient will receive more medicine than they should. If symptoms of overdose occur, the doctor will administer appropriate treatment. Initially, the following symptoms of overdose are observed:
- numbness of the tongue;
- a feeling of emptiness in the head;
- dizziness;
- muscle tremors. Severe symptoms of overdose (which occur very rarely) include: seizures and circulatory failure (the heart cannot ensure proper blood circulation and supply oxygen to meet the body's needs), significant lowering of blood pressure, respiratory arrest.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. If the patient experiences the first symptoms of hypersensitivity (e.g., swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, causing difficulty breathing or swallowing), they should immediately tell their doctor.Such symptoms are rare. The doctor will then assess the severity of the symptoms and decide on further action.Very common (occurring in more than 1 in 10 patients):
- hypotension (significant lowering of blood pressure), bradycardia;
- nausea.
Common (occurring in 1 to 10 in 100 patients):
- headache;
- vomiting;
- urinary retention, incontinence.
Uncommon (occurring in 1 to 10 in 1,000 patients):
- paresthesia (tingling, pricking, burning);
- weakness;
- abnormal sensation (dysesthesia);
- muscle weakness, back pain.
Rare (occurring in less than 1 in 1,000 patients):
- cardiac arrest;
- allergic reactions, anaphylactic shock - see the information provided at the beginning of section 4.
- unintentional total spinal anesthesia (manifested by respiratory arrest), paralysis (e.g., of the lower limbs);
- neuropathy (symptoms: tingling, numbness, weakness of the innervated muscle);
- arachnoiditis (one of the meninges);
- respiratory depression (severe breathing difficulties).
Side effects in children and adolescents
Side effects in children are similar to those that occur in adults.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, you should tell your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products Al. Jerozolimskie 181C 02-222 Warsaw Tel.: +48 22 49 21 301 Fax: +48 22 49 21 309 Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy
There are no special precautions for storing the medicine. The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the ampoule and carton. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month stated. The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number. The medicine does not contain preservatives. The solution should be used immediately after opening the ampoule. The remaining, unused solution should be destroyed. It is not recommended to re-sterilize the solution. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. You should ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy contains
- The active substance of the medicine is bupivacaine hydrochloride. Each 1 ml of solution for injection contains 5 mg of bupivacaine hydrochloride.
- The other ingredients are: glucose 72.72 mg (equivalent to 80 mg of anhydrous glucose), sodium hydroxide (to adjust the pH), water for injections.
What Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy looks like and what the pack contains
Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy is a colorless, clear liquid. The carton contains 5 ampoules of 4 ml each.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Polpharma S.A. ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański tel. +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
INFORMATION INTENDED EXCLUSIVELY FOR MEDICAL PROFESSIONALS
Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy, 5 mg/ml, solution for injection
Bupivacaine hydrochloride
Preparation of Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy for administration and method of administration
- Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy is intended for subarachnoid administration in adults and children of all ages.
- The medicine does not contain preservatives. The solution should be used immediately after opening the ampoule.
- It is not recommended to re-sterilize the solution.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
Before opening the ampoule, make sure that the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule. You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down. Each ampoule has a colored dot (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the location of the break point below it.
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, in both hands, with the colored dot facing you - see Figure 2. The upper part of the ampoule should be grasped in such a way that the thumb is above the colored dot.
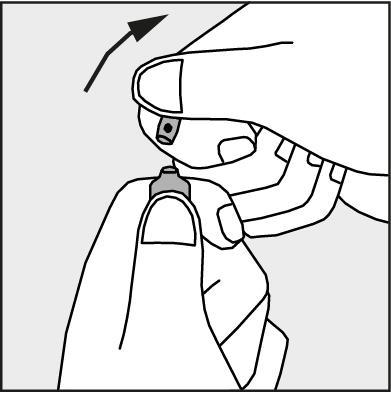
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3. The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. The remaining contents of the unused product should be destroyed in accordance with applicable regulations.
Figure 1.
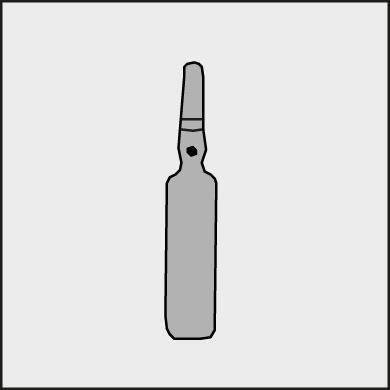
Figure 2.
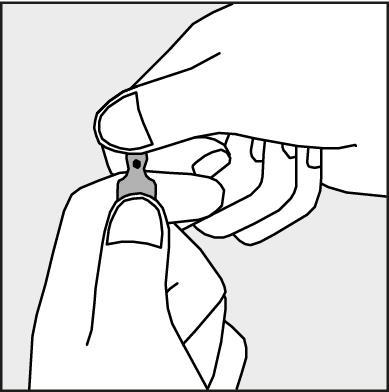
Figure 3.
Warnings and precautions
Subarachnoid anesthesia should be performed in centers employing appropriately trained and experienced personnel. During the use of local anesthetics, it is necessary to ensure the possibility of oxygen therapy and cardiopulmonary resuscitation. The equipment used during resuscitation and the medicines administered during resuscitation should be available. Before starting subarachnoid anesthesia, an intravenous cannula should be inserted. The anesthesiologist performing the anesthesia should pay particular attention to not administering the product into a blood vessel. The anesthesiologist performing the anesthesia should be properly trained and familiar with the methods of diagnosing and managing symptoms of toxicity and other complications. In case of acute symptoms of toxicity or symptoms of total spinal anesthesia, the administration of the medicine should be stopped immediately (see below "Procedure in case of symptoms of overdose"). If the concentration of bupivacaine in the serum increases during regional anesthesia, symptoms of acute toxicity from the cardiovascular and central nervous systems may occur. Similar symptoms may occur with other local anesthetics. An increase in the concentration of the local anesthetic in the serum is most often caused by unintentional intravascular administration or injection into a highly vascularized area of the body. Cases of ventricular arrhythmia, ventricular fibrillation, sudden cardiovascular collapse, and death have been reported due to increased bupivacaine concentration in the general circulation. In case of cardiac arrest, achieving a successful resuscitation result may require prolonged cardiopulmonary resuscitation. No increased bupivacaine concentration in the serum has been observed after using the recommended doses of bupivacaine during subarachnoid anesthesia. The risk of high or total spinal anesthesia is greater in elderly patients or in women in advanced pregnancy - in these patients, the dose of the local anesthetic should be reduced. Very high or total spinal anesthesia is a rare but serious side effect that can occur after subarachnoid anesthesia. The consequence of spinal anesthesia is cardiovascular and respiratory failure. It should be remembered that subarachnoid anesthesia can sometimes cause total spinal anesthesia, including paralysis of the intercostal muscles and diaphragm, especially in pregnant women. Before performing subarachnoid anesthesia, regardless of the local anesthetic used, the potential risk and benefit for the patient should be considered. Particular attention is required for elderly patients, in poor general condition, or with, e.g., partial atrioventricular block II or III degree, advanced liver disease, or severe kidney failure. Regional anesthesia is often indicated in this group of patients. It is recommended to exercise caution in patients with neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis, hemiplegia, transverse myelitis, neuromuscular disorders, although after performing subarachnoid anesthesia, no worsening of these disorders has been observed. Patients taking antiarrhythmic drugs of class III (e.g., amiodarone) who are using bupivacaine should be under close observation, and it is recommended to consider monitoring their ECG. The effect of bupivacaine and class III antiarrhythmic drugs may be additive.
Dosage
Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy is intended for subarachnoid administration. The density of the solution at 20°C is 1.026 g/ml (at 37°C it is 1.021 g/ml).
Newborns, infants, and children with a body weight of up to 40 kg
Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy may be used in children. One of the differences between small children and adults is the relatively large volume of cerebrospinal fluid in infants and newborns, which requires the administration of relatively larger doses per kilogram of body weight to achieve the same level of blockade as in adults. Regional anesthesia procedures in children should be performed by qualified clinicians who are well acquainted with this group of patients and the technique of performing anesthesia. The doses listed in the table should be considered as recommended for use in children. There are individual differences. Factors affecting specific blockade techniques and individual patient requirements are described in anesthesia textbooks. The smallest required dose should be used to achieve adequate anesthesia. Table: Recommended dosing in newborns, infants, and children
Adults and children over 12 years
The experience of the anesthesiologist and knowledge of the patient's physical condition are important when determining the dose of the medicinal product. Various factors that may affect individual blockade techniques and patient requirements should be taken into account. The smallest required dose should be used to achieve adequate anesthesia. There are individual differences in patients regarding the onset and duration of anesthesia, and the extent of anesthesia may be difficult to predict, but it will depend on the volume of the administered medicine, especially the isobaric solution (ordinary). The doses listed below refer to adult patients with a standard body build. In elderly patients and women in advanced pregnancy, the dose of the product should be reduced. Subarachnoid anesthesia for surgical procedures on the lower limbs and hip joint, as well as in the abdominal cavity (also for cesarean section) 2 to 4 ml of Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy (10 to 20 mg of bupivacaine hydrochloride). The anesthetic effect occurs within 5 to 8 minutes after administration of the product and lasts for 2 to 3 hours in the lower limbs and hip joint, and 45 to 60 minutes in the abdominal cavity. Subarachnoid anesthesia for urological procedures The recommended dose is 1.5 to 3 ml of Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy (7.5 to 15 mg of bupivacaine hydrochloride). The anesthetic effect occurs within 5 to 8 minutes after administration of the product and lasts for 2 to 3 hours.
| Body weight (kg) | Dose (mg/kg body weight) |
| <5 | 0.40-0.50 mg/kg body weight |
| 5 to 15 | 0.30-0.40 mg/kg body weight |
| 15 to 40 | 0.25-0.30 mg/kg body weight |
The extent of anesthesia after using the product depends on many factors, such as the volume of the administered medicine, the patient's position during anesthesia, and the patient's position after administration of the medicine. After administering 3 ml of the solution into the subarachnoid space between L2 and L3, different levels of anesthesia can be achieved, depending on the patient's position. If the patient is sitting during anesthesia, all segments below the level of Th10-Th12 will be blocked. If the product is administered to the patient in a lateral position, and after the injection, the patient is placed on their back, all segments below the level of Th10-Th12 will be blocked. It should be emphasized that regardless of the type of local anesthetic used, the extent of the blocked segments is individual and in some clinical cases, it is impossible to predict before performing anesthesia. It is recommended to administer the solution into the subarachnoid space below L2. No studies have been conducted on the use of Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy in volumes greater than 4 ml, so it is not recommended to administer a dose greater than 4 ml of the product. In case of anesthesia failure, a new attempt to perform anesthesia should be made by puncturing at a different level of the spine and using a smaller volume of the product. One of the reasons for the lack of anesthetic effect may be poor distribution of the product in the subarachnoid space (it may improve with a change in the patient's position).
Procedure in case of symptoms of overdose
In case of symptoms of toxicity or symptoms of total spinal anesthesia, the administration of the local anesthetic should be stopped immediately. Procedure in case of total spinal anesthesiaSymptoms of high or total spinal anesthesia may include respiratory arrest and (or) hypotension. In these cases, proper ventilation and oxygenation of the blood should be ensured by administering oxygen and using assisted or controlled breathing. In case of hypotension, vasoconstrictor drugs, such as ephedrine, should be administered intravenously in a dose of 10 to 15 mg, and if necessary, the injections should be repeated until the blood pressure increases to the desired value. To increase blood pressure, a rapid intravenous infusion of multi-electrolyte fluids or colloids can also be used. Procedure in case of general toxicity symptomsIn case of milder general symptoms of toxicity, treatment does not need to be started. It should be started immediately when seizures occur. The goal of treatment is primarily to stop the seizure and ensure proper oxygenation of the blood; oxygen should be administered, and if necessary, assisted or controlled ventilation should be used. If seizures do not stop spontaneously within 15 to 30 seconds, thiopental should be administered intravenously in a dose of 100 to 150 mg or diazepam in a dose of 5 to 10 mg. Alternatively, succinylcholine can be administered intravenously in a dose of 50 to 100 mg, but in this case, the patient should be intubated and full treatment should be started as for a patient after muscle relaxation. Proper oxygenation, breathing, and circulation should always be ensured, and treatment of acidosis should be started. The doses of medicines used in the treatment of overdose of Bupivacaine WZF Spinal 0.5% Heavy in children should be adjusted according to their age and body weight.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredNo
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% HeaviDosage form: Solution, 5 mg/mlActive substance: bupivacainePrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 5 mg/mlActive substance: bupivacaineManufacturer: JSC GrindexPrescription not requiredDosage form: Solution, 5 mg/mlActive substance: bupivacaineManufacturer: AS GrindeksPrescription not required
Alternatives to Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% Heavi in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% Heavi in Spain
Alternative to Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% Heavi in Ukraine
Online doctors for Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% Heavi
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Bupivacaine Vzf Spinal 0,5% Heavi – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














