
Bunondol

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Bunondol

How to use Bunondol
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
BUNONDOL, 0.3 mg/ml, Solution for Injection
Buprenorphine
Read the package leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- Ask your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse if you have any further questions.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Leaflet
- 1. What is Bunondol and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Bunondol
- 3. How to use Bunondol
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Bunondol
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Bunondol and what is it used for
Bunondol contains buprenorphine, a strong pain-relieving medicine.
Buprenorphine belongs to a group of medicines called opioid analgesics.
Bunondol is intended for intramuscular and intravenous administration.
Bunondol is used for acute and chronic pain of moderate to severe intensity.
Buprenorphine is used for post-operative and chronic pain, most often of cancer origin.
2. Important information before using Bunondol
When not to use Bunondol:
- if you are allergic to buprenorphine, other opioid medicines, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Bunondol, discuss with your doctor if you have:
- depression or other diseases treated with antidepressant medicines. Using these medicines together with Bunondol may lead to serotonin syndrome, a life-threatening disease (see "Bunondol and other medicines").
Your doctor will exercise special caution when using buprenorphine and will take appropriate action in patients:
- with reduced thyroid function (hypothyroidism);
- with reduced adrenal gland function (insufficient hormone production);
- with asthma or other breathing problems, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD);
- with an enlarged prostate or difficulty urinating;
- with muscle weakness (myasthenia gravis);
- who are weakened or exhausted by disease;
- with bile duct disorders;
- with liver function disorders;
- with kidney function disorders;
- who are elderly;
- who are children;
- who have had head injuries;
- with increased intracranial pressure (symptoms such as headache, changes in consciousness and balance, vision problems);
- with nervous system disorders, psychoses;
- with alcoholism;
- with scoliosis.
Tolerance, dependence, and addiction
This medicine contains buprenorphine, an opioid medicine. Repeated use of opioids can lead to the medicine becoming less effective (getting used to the medicine, known as tolerance). Repeated use of Bunondol may also lead to dependence, abuse, and addiction, which can result in life-threatening overdose. The risk of these side effects may increase with increasing dose and longer treatment duration.
Dependence or addiction can cause the patient to lose control over the amount of medicine taken and the frequency of administration.
The risk of dependence on Bunondol may vary depending on the individual. The risk of dependence on Bunondol may be higher if:
- the patient or someone in their family has ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines, or illegal substances (addiction);
- the patient is a smoker or uses nicotine products;
- the patient has ever had mood problems (depression, anxiety, or personality disorders) or has been treated by a psychiatrist for other mental illnesses.
If any of the following symptoms occur while taking Bunondol, it may indicate dependence:
- need to take the medicine for longer than prescribed by the doctor;
- need to take a higher dose than prescribed;
- need to continue taking the medicine even if it does not relieve pain;
- taking the medicine for reasons other than prescribed, such as "to calm down" or "to sleep better";
- repeatedly attempting to stop or control the use of the medicine;
- feeling unwell after stopping the medicine, and feeling better after taking it again (withdrawal symptoms). If any of these symptoms occur, consult a doctor to discuss the best treatment option, including when to stop taking the medicine and how to do it safely (see section 3, Stopping Bunondol).
Breathing difficulties during sleep
Bunondol may cause breathing difficulties during sleep, such as sleep apnea (pauses in breathing during sleep) and hypoxemia (low oxygen level in the blood). Symptoms may include pauses in breathing during sleep, nighttime awakenings due to shortness of breath, difficulty staying asleep, or excessive daytime sleepiness. If the patient or another person notices these symptoms, they should contact a doctor. The doctor may consider reducing the dose.
Children and adolescents
Bunondol can be used intramuscularly or intravenously in children over 6 months of age for pain relief (see section 3 "How to use Bunondol"). If you have any doubts, consult a doctor.
Bunondol and other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist about all medicines you are taking, have recently taken, or plan to take.
Some medicines may increase the side effects of Bunondol, and sometimes cause very serious reactions. While taking Bunondol, do not take other medicines without first consulting your doctor, especially:
- medicines used to treat depression, such as moclobemide, tranylcypromine, citalopram, escitalopram, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, paroxetine, sertraline, duloxetine, venlafaxine, amitriptyline, doxepin, or trimipramine. These medicines may interact with Bunondol and cause symptoms such as involuntary, rhythmic muscle contractions, including those that control eye movements, agitation, hallucinations, coma, excessive sweating, tremors, increased reflexes, muscle tension, and body temperature above 38°C. If such symptoms occur, consult a doctor.
- medicines used to treat allergies, motion sickness, or nausea (antihistamines or antiemetics);
- medicines used to treat mental disorders (antipsychotics or neuroleptics);
- muscle relaxants;
- medicines used to treat Parkinson's disease;
- sleeping medicines, such as phenobarbital;
- calming medicines, such as diazepam;
- phenothiazine derivatives, such as promazine or chlorpromazine;
- rifampicin, troleandomycin (antibiotics);
- phenytoin, gabapentin, or pregabalin used to treat epilepsy or nerve pain (neuropathic pain);
- contraceptives containing gestodene;
- antifungal medicines (ketoconazole);
- HIV/AIDS medicines, such as ritonavir.
Taking Bunondol and sedative medicines, such as benzodiazepines or their derivatives, increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), or coma, which can be life-threatening. Therefore, combined treatment should only be considered when other treatment options are not available.
If Bunondol is used with sedative medicines, the doctor should limit the dose and duration of treatment.
The patient should inform the doctor about all sedative medicines being taken and strictly follow the prescribed dose. It may be helpful to inform a family member or close friend of the patient about the possibility of the above symptoms. If these symptoms occur, consult a doctor.
Bunondol and alcohol
Alcohol should be avoided while taking buprenorphine.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using this medicine.
Buprenorphine should not be used during pregnancy. Buprenorphine may reduce milk production. The use of buprenorphine during pregnancy and breastfeeding will be decided by your doctor.
Driving and using machines
Buprenorphine may cause drowsiness and affect physical and mental performance. While taking Bunondol, do not drive vehicles or operate machines.
3. How to use Bunondol
Bunondol is administered by medical personnel.
Before starting treatment and regularly during treatment, the doctor will discuss with the patient what to expect from Bunondol, when and how long to take it, when to contact the doctor, and when to stop the medicine (see also: Stopping Bunondol).
- The dose of buprenorphine is determined by the doctor individually for each patient.
- Bunondol is administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
- Bunondol can be used in children over 6 months of age for pain relief.
- Bunondol should be used according to the scheme prescribed by the doctor.
Using a higher dose of Bunondol than recommended
Since Bunondol is administered by medical personnel, it is unlikely that the patient will receive more medicine than they should.
After using a higher dose of the medicine than recommended, the following symptoms may occur: drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, very severe narrowing of the pupils ("pinpoint pupils"), increased breathing difficulties.
If such symptoms occur, immediately inform the medical personnel. They will take appropriate action.
Missing a dose of Bunondol
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
Stopping Bunondol
In case of sudden discontinuation of buprenorphine, withdrawal symptoms occur rarely and are mild, as the medicine has a low potential for dependence.
Withdrawal symptoms include: nausea, diarrhea, cough, mood changes, tearing, dilated pupils, runny nose, insomnia with persistent yawning, sweating, increased blood pressure, muscle tremors, "goosebumps", loss of appetite, slight increase in respiratory rate, feeling of widespread pain in the body, strong craving for the medicine, and hallucinations.
If you have any further doubts about using this medicine, consult your doctor or pharmacist, or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Stop using the medicine and immediately consult a doctor or nurse if you experience the first symptoms of an allergic reaction (e.g., swelling of the face, lips, tongue, throat, causing difficulty breathing or swallowing). Such symptoms are rare after intravenous administration of buprenorphine. The doctor will decide on further action.
The following side effects are very common:
- nausea, vomiting;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness.
These side effects occur more frequently in patients treated on an outpatient basis.
The following side effects may occur:
- low blood pressure (leading to fainting);
- anxiety, mood changes, hallucinations.
The following side effects occur rarely:
- rash;
- headache;
- difficulty urinating;
- vision problems;
- breathing difficulties.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, please inform your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
Reporting side effects will help to gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Bunondol
Store the ampoules in the outer packaging to protect from light, at a temperature below 25°C. Do not freeze.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
This medicine should be stored in a safe place, out of the reach of other people. The medicine can cause serious harm or even death if taken by someone who has not been prescribed it, either accidentally or intentionally.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the carton and ampoule. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP means the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot means the batch number.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines that are no longer needed. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Bunondol contains
- The active substance of the medicine is buprenorphine hydrochloride. Each ml of solution contains 0.3 mg of buprenorphine.
- The other ingredients are: glucose, 10% hydrochloric acid (to adjust pH), water for injections.
What Bunondol looks like and contents of the pack
Bunondol is a colorless or almost colorless, clear liquid.
The medicine is packed in a cardboard box containing 5 ampoules made of colorless glass with a capacity of 1 ml.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Date of last revision of the leaflet:
Information intended for healthcare professionals only:
Please refer to the current Summary of Product Characteristics for Bunondol.
BUNONDOL, 0.3 mg/ml, Solution for Injection
Buprenorphine
Method of administration of Bunondol
- The dose is determined by the doctor individually for each patient.
- Bunondol can be administered intramuscularly or as a slow intravenous injection (see "Dosage").
- The medicine should not be mixed or administered simultaneously through the same intravenous access with solutions having an alkaline reaction.
Instructions for opening the ampoule
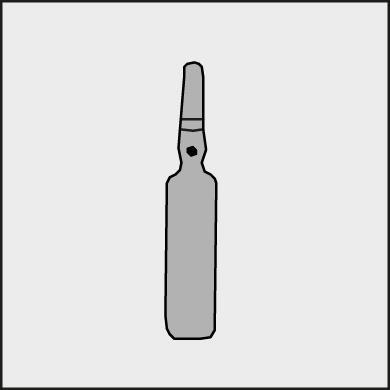
- Before opening the ampoule, make sure the entire solution is in the lower part of the ampoule. You can gently shake the ampoule or tap it with your finger to help the solution flow down.
- Each ampoule has a colored dot (see Figure 1) as a mark indicating the break point below it.
Figure 1.
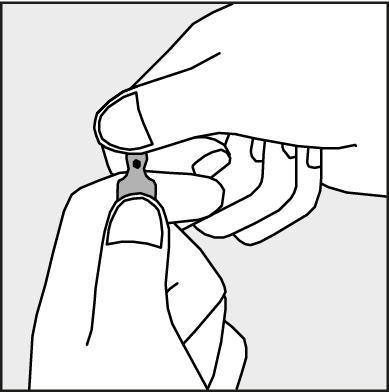
- To open the ampoule, hold it vertically, with both hands, with the colored dot facing you
- see Figure 2. Hold the upper part of the ampoule so that your thumb is above the colored dot.
Figure 2.
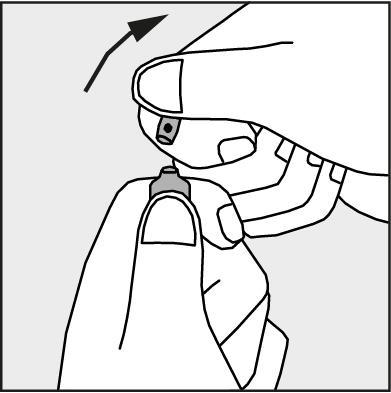
- Press in the direction of the arrow shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
The ampoules are intended for single use only and should be opened immediately before use. Any unused product or waste should be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
Precautions for using Bunondol
- As with other potent opioids, buprenorphine may cause respiratory depression after administration of the recommended doses. Therefore, buprenorphine should be used with caution in patients with respiratory function disorders, such as asthma, respiratory failure, right heart failure, reduced respiratory reserve, hypoxemia, hypercapnia, or previous respiratory depression.
- Although studies in healthy volunteers have shown that opioid receptor antagonists may not completely reverse the effects of buprenorphine, clinical experience suggests that naloxone is beneficial in counteracting respiratory depression. Respiratory stimulants, such as doxapram, are also effective.
- Special caution is recommended when administering buprenorphine to patients receiving medicines that depress the activity of the central nervous system, such as general anesthetics, antihistamines, phenothiazine derivatives, sedatives, or sleeping medicines. When using such combined treatment, it is recommended to reduce the dose of one or both medicines.
- Concomitant use of Bunondol with gabapentinoids (gabapentin and pregabalin) may lead to respiratory depression, hypotension, deep sedation, coma, or death.
- Buprenorphine hydrochloride, like other opioid analgesics, may cause an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure and should be administered with caution to patients with head injuries, intracranial lesions, and other conditions that may lead to an increase in cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
- Buprenorphine may cause pupil constriction and changes in consciousness, which may make it difficult to assess the patient's condition.
- Buprenorphine hydrochloride should be administered with caution to elderly patients, weakened patients, children, and patients with kidney or liver function disorders. Since buprenorphine is metabolized in the liver, its effects may be increased in patients with liver function disorders, so it should be used with caution in these patients.
- Buprenorphine, like other opioids, causes an increase in bile duct pressure, so it should be used with caution in patients with diseases that make it difficult to drain bile.
- Use with caution in patients with hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency (e.g., Addison's disease), myasthenia gravis, central nervous system depression, psychoses, coma, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture, alcoholism, delirium tremens, or kyphoscoliosis.
- Studies in humans and animals have shown that buprenorphine has a lower potential for dependence compared to so-called pure opioid receptor agonists.
- Repeated use of Bunondol, even in therapeutic doses, may lead to dependence on the medicine. The risk of dependence on opioid medicines may vary depending on individual risk factors in the patient, dose, and duration of treatment with opioids.
- It has been shown that in opioid-dependent individuals, administration of small doses of buprenorphine prevents the occurrence of withdrawal symptoms. Rarely, in opioid-dependent individuals, buprenorphine has been observed to cause euphoria. Therefore, buprenorphine should be administered with caution to patients who are dependent on or suspected of being dependent on opioids.
- Concomitant administration of Bunondol and other serotonergic medicines, such as MAO inhibitors, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), or tricyclic antidepressants, may lead to serotonin syndrome, a life-threatening disease. If concomitant use of other serotonergic medicines is clinically justified, the patient should be closely monitored, especially in the initial phase of treatment and during dose increases. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome may include changes in mental status, autonomic instability, neuromuscular disorders, or gastrointestinal symptoms. If serotonin syndrome is suspected, consider reducing the dose or stopping treatment, depending on the severity of the symptoms.
Dosage
- In pain of various origins Adults and adolescents over 12 years of ageUsually 1 to 2 ml (0.3 to 0.6 mg) every 6 to 8 hours.
Children under 12 years of age
3 to 6 μg/kg body weight every 6 to 8 hours. Do not exceed a dose of 9 μg/kg body weight.
The safety of buprenorphine in children under 6 months of age has not been established.
- In premedication in adults or as a supplementary analgesic
- premedication: 1 ml (0.3 mg) intramuscularly 1 hour before the procedure;
- as a supplementary analgesic: intravenously 1 ml to 1.5 ml (0.3 mg to 0.45 mg).
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterKrka Polska Sp. z o.o. Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BunondolDosage form: Tablets, 0.2 mgActive substance: buprenorphinePrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 0.4 mgActive substance: buprenorphinePrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 2 mgActive substance: buprenorphineManufacturer: Fine Foods & Pharmaceuticals N.T.M. S.p.A L.Molteni & C. dei F.lli Alitti Societa di Esercizio S.p.A.Prescription required
Alternatives to Bunondol in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Bunondol in España
Alternative to Bunondol in Ucrania
Online doctors for Bunondol
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Bunondol – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














