
Biofazolin

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Biofazolin

How to use Biofazolin
Leaflet attached to the packaging: patient information
Biofazolin, 1 g, powder for solution for injection
Cefazolin
Read the leaflet carefully before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- In case of any doubts, consult a doctor or nurse.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person, even if their symptoms are the same.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or nurse. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
- 1. What is Biofazolin and what is it used for
- 2. Important information before using Biofazolin
- 3. How to use Biofazolin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Biofazolin
- 6. Contents of the packaging and other information
1. What is Biofazolin and what is it used for
Biofazolin contains the antibiotic cefazolin, which belongs to the group of first-generation cephalosporins.
The medicine is administered intramuscularly or intravenously (by injection or infusion) after dissolution and proper dilution.
Indications
Biofazolin is used to treat severe infections caused by susceptible bacteria:
- respiratory tract infections*,
- urinary tract infections,
- skin and soft tissue infections,
- biliary tract infections,
- bone and joint infections,
- septicaemia,
- endocarditis. *Biofazolin is effective in eliminating streptococci from the nose and throat. The drug of choice for the treatment and prevention of streptococcal infections, including the prevention of rheumatic fever, is penicillin.
There is no data confirming the effectiveness of Biofazolin in late prevention of rheumatic fever.
Before starting treatment, the doctor will recommend a bacterial culture and determination of susceptibility to cefazolin.
Biofazolin is used to preventsurgical site infections in patients undergoing surgical procedures with a high risk of infection, e.g. cholecystectomy in high-risk patients (especially after 70 years of age, in patients with acute cholecystitis, with obstructive jaundice, with stones) or after appendectomy or hysterectomy, or in patients where infection at the surgical site would be particularly dangerous (e.g. in cardiothoracic surgery, orthopaedic surgery, especially when implanting endoprostheses).
2. Important information before using Biofazolin
When not to use Biofazolin
- if the patient is allergic to cefazolin or other cephalosporin antibiotics.
Warnings and precautions
Before starting Biofazolin, the patient should discuss it with their doctor or nurse.
If the patient is allergic, especially to certain antibiotics (penicillins and cephalosporins), they should inform their doctor.
Patients allergic to penicillins may also be allergic to cephalosporins (cross-allergy).
A severe allergic reaction may occur after administration of Biofazolin.
Particular caution should be exercised in patients who have experienced allergic reactions to penicillins, especially anaphylactic shock (a severe, immediate allergic reaction characterized by flushing, swelling, itching, hives, and difficulty breathing).
If the patient experiences worrying allergic symptoms, they should inform their doctor.
It may be necessary to discontinue Biofazolin and administer appropriate treatment.
In case of a severe allergic reaction, adrenaline and other anti-shock medications (circulatory support medications, corticosteroids, and antihistamines) may be necessary.
If the patient experiences diarrhea, they should inform their doctor.
Pseudomembranous colitis, characterized by diarrhea, may occur during or after treatment with cefazolin.
In case of mild diarrhea, the doctor will recommend only discontinuing the medicine, while in more severe cases, they will recommend fluid and electrolyte replacement. The doctor may recommend oral metronidazole or vancomycin. Medications that slow down bowel movements or other constipating medications should not be administered.
Using Biofazolin, like other antibiotics, may cause fungal infections (candidiasis) of the mouth and genital organs or overgrowth of non-susceptible bacteria. The doctor will recommend appropriate treatment in such cases.
Using Biofazolin in patients with impaired renal function
If the patient has kidney problems, they should inform their doctor before using Biofazolin, as it may be necessary to adjust the dose of the medicine. The dosage is determined by the doctor based on renal function, see: Dosage in patients with renal impairment.
Biofazolin and other medicines
The patient should inform their doctor about all medicines they are currently taking or have recently taken, as well as any medicines they plan to take.
Powerful diuretics, such as furosemide, used concurrently with cefazolin, may cause adverse effects on the kidneys.
Concomitant use of cefazolin with anticoagulant medications may prolong blood clotting time and increase the risk of bleeding.
Probenecid delays the excretion of cefazolin in the urine.
Influence on laboratory test results
Cefazolin may cause:
- false-positive results of glucose tests in urine, performed using the reduction method,
- false-positive results of antiglobulin tests (Coombs test).
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
If the patient is pregnant or breastfeeding, suspects they may be pregnant, or plans to have a child, they should consult their doctor before using this medicine.
If the patient is pregnant or suspects they may be pregnant, this medicine can only be used if the doctor considers it absolutely necessary.
Caution should be exercised during breastfeeding, as cefazolin passes into breast milk in small amounts, which may cause diarrhea, fungal infections (candidiasis), or allergic reactions in the breastfed child.
Driving and operating machinery
Biofazolin does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery.
Biofazolin contains sodium
The medicine contains 52.8 mg of sodium (the main component of common salt) per vial (per 1 g of product).
This corresponds to 2.64% of the maximum recommended daily dose of sodium in the diet for adults.
The sodium content from the diluent should be taken into account when calculating the total sodium content in the prepared solution [see below: information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals (information on solution preparation)]. To obtain accurate information about the sodium content in the solution used to dilute the medicine, the patient should consult the leaflet of the diluent used.
3. How to use Biofazolin
This medicine should always be used in accordance with the doctor's recommendations. In case of doubts, the patient should consult their doctor or nurse.
Biofazolin is administered intravenously in a 3- to 5-minute injection or in a 20- to 30-minute infusion, or intramuscularly.
Adults
Cefazolin is usually administered in doses of 500 mg to 1.5 g, given every 6, 8, or 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection.
| Type of infection | Dosage |
| Mild infections caused by Gram-positive cocci | 250 mg or 500 mg every 8 hours |
| Pneumonia caused by S. pneumoniae | 500 mg every 12 hours |
| Acute, uncomplicated urinary tract infections | 1 g every 12 hours |
| Moderate to severe infections | 500 mg or 1 g every 6 or 8 hours |
| Severe, life-threatening infections, such as: septicaemia, endocarditis* | 1 g or 1.5 g every 6 hours |
* In very severe and life-threatening infections, the dose can be increased to 12 g per day.
Children
25 to 50 mg/kg body weight per day in divided doses every 6 or 8 hours.
In severe infections, the dose is increased to 100 mg/kg body weight per day in divided doses.
Cefazolin is not recommended for use in premature infants and newborns in the first month of life, as there is no data confirming the safety of the antibiotic in this patient group.
Dosage for surgical prophylaxis
Usually, 1 g of cefazolin is administered 30 to 60 minutes before surgery, and an additional 500 mg or 1 g during procedures lasting longer than 2 hours.
In cases of high-risk procedures, 500 mg or 1 g is administered every 6 or 8 hours for 24 hours after surgery.
In special cases (e.g. after implantation of joint prostheses, after open-heart surgery), the antibiotic is administered for 3 to 5 days.
Dosage in patients with renal impairment
After the first dose, appropriate for the type and severity of the infection, subsequent dosing should be adjusted according to the degree of renal impairment.
Adults
| Creatinine clearance | Serum creatinine concentration | Dosage |
| >55 ml/min | <1.5 mg% | no change |
| 35-54 ml/min | 1.6-3.0 mg% | 100% of the recommended daily dose in 3 divided doses every 8 hours |
| 11-34 ml/min | 3.1-4.5 mg% | 50% of the dose every 12 hours |
| <10 ml min< td> | >4.6 mg% | 50% of the dose every 18 or 24 hours |
Children
Using a higher than recommended dose of Biofazolin
Patients with renal impairment are particularly at risk of overdose; in these patients, the medicine may accumulate in the body due to poor excretion. After an overdose, headache, dizziness, drowsiness, sensory disturbances, and in severe cases, seizures may occur.
Excessive accumulation of the medicine in the body may cause increased creatinine, urea, liver enzymes, and bilirubin levels, as well as changes in blood composition (thrombocytosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia), decreased blood coagulability (prolonged prothrombin time), and a false-positive Coombs test result.
If an overdose is suspected, the patient should immediately inform their doctor, who will administer appropriate symptomatic treatment.
In case of seizures, it is recommended to discontinue the medicine, administer anticonvulsant medications, and ensure proper respiratory ventilation. The patient's circulation, gasometry, and electrolyte parameters should be monitored. Haemodialysis and haemoperfusion remove the medicine from the body.
Missing a dose of Biofazolin
The medicine should be used in accordance with the doctor's recommendations.
If an intravenous injection or infusion did not occur at the scheduled time, the missed dose should be administered as soon as possible. However, if the next dose is approaching, the missed dose should not be administered. The medicine should be continued to be used at the scheduled times.
A double dose should not be used to make up for a missed dose.
| Creatinine clearance | Dosage |
| 40-70 ml/min | 60% of the recommended daily dose in 2 divided doses every 12 hours |
| 20-40 ml/min | 25% of the recommended daily dose in 2 divided doses every 12 hours |
| 5-20 ml/min | 10% of the recommended daily dose once a day |
In case of further doubts regarding the use of this medicine, the patient should consult their doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Biofazolin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Based on available data, the frequency of side effects cannot be determined.
The patient should immediately contact their doctor or nurse if they experience:
- anaphylaxis (a severe, immediate allergic reaction characterized by flushing, swelling, itching, hives, and difficulty breathing);
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (a severe skin reaction characterized by blisters on the mucous membranes of the mouth and genital organs, fever, and joint pain);
- pseudomembranous colitis (inflammation of the intestines that can cause watery diarrhea, which may contain blood) during or after treatment with cefazolin;
- hepatitis, jaundice caused by bile stasis.
Other side effects:
- oral thrush;
- drug fever;
- loss of appetite, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting;
- rash;
- increased urea levels without clinical symptoms of renal impairment; isolated cases of interstitial nephritis and other renal function disorders have been reported in severely ill patients treated with multiple medications;
- genital and anal itching, vulvitis, vaginal yeast infections;
- pain and induration at the injection site, phlebitis after intravenous administration.
Side effects that may be revealed by laboratory tests:
- eosinophilia (increased white blood cell count in a blood smear), neutropenia (decreased granulocyte count), leukopenia (decreased white blood cell count), thrombocytopenia (decreased platelet count);
- increased liver enzyme activity (ASAT, ALAT, alkaline phosphatase), increased urea levels without clinical symptoms of renal impairment.
Reporting side effects
If the patient experiences any side effects, including those not listed in this leaflet, they should inform their doctor or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products
Al. Jerozolimskie 181C
02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301
Fax: +48 22 49 21 309
Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder.
By reporting side effects, more information can be collected on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Biofazolin
Store in a temperature below 30°C. Protect from light.
The prepared solution can be stored for 24 hours in a refrigerator, i.e. at a temperature between 2°C and 8°C.
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging. The expiry date refers to the last day of the given month.
The inscription on the packaging after the abbreviation EXP indicates the expiry date, and after the abbreviation Lot indicates the batch number.
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Biofazolin contains
- The active substance of the medicine is cefazolin. The vial contains 1 g of cefazolin (in the form of sodium salt). Biofazolin contains sodium - see section 2 "Biofazolin contains sodium ". The medicine does not contain excipients.
What Biofazolin looks like and what the packaging contains
Biofazolin is available in the form of a powder for solution for injection in a glass vial. The powder is white or almost white.
The glass vial is closed with a rubber stopper and protected with an aluminium cap or an aluminium cap with a hood, in a cardboard box.
Biofazolin is available in vials of 1 g.
The packaging contains 1 or 10 vials.
Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
phone: +48 22 364 61 01
Manufacturer
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
ul. Pelplińska 19, 83-200 Starogard Gdański
Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A.
Production Plant in Duchnice
ul. Ożarowska 28/30
05-850 Ożarów Mazowiecki
Date of the last update of the leaflet: ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Information intended exclusively for healthcare professionals:
Biofazolin, 1 g, powder for solution for injection
Cefazolin
Preparation of solutions for injection and infusion
Biofazolin is administered intravenously in a 3- to 5-minute injection or in a 20- to 30-minute infusion, or intramuscularly.
Preparation of the solution for injection
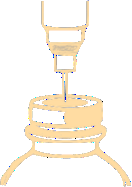
Pierce the stopper with a needle and inject the recommended volume of solvent into the vial. To pierce the stopper, a needle with a diameter not larger than 0.8 mm (21 G) should be used. The needle should be inserted into the centre of the stopper at a 90° angle, as shown in the following diagram:
Before administration, the solution should be checked for clarity and absence of insoluble particles.
Intravenous injection(3 to 5 minutes)
The contents of the vial should be dissolved in at least 10 ml of water for injection.
The medicine should be injected very slowly, not less than 3 minutes.
Intravenous infusion(20 to 30 minutes)
Cefazolin should be reconstituted and then diluted in 50 ml or 100 ml of one of the following solutions:
0.9% sodium chloride solution,
5% glucose solution,
10% glucose solution,
5% glucose solution with 0.9% sodium chloride solution,
5% glucose solution with 0.45% sodium chloride solution,
5% glucose solution with 0.2% sodium chloride solution,
Ringer's solution,
Ringer's solution with sodium lactate,
5% glucose solution with Ringer's solution and sodium lactate.
Intramuscular injection
The medicine should be administered deep into a large muscle. Intramuscular administration of cefazolin rarely causes pain.
The recommended volume of solvent should be added to the vial, and the contents should be shaken until completely dissolved. The solution may have a light yellow color.
Incompatibilities
Cefazolin solutions should not be mixed with aminoglycoside antibiotics or other medicines in the same syringe or infusion set.
| Dose | Recommended solvents | Volume of solvent | Volume of solution | Concentration of solution |
| 1 g | water for injection | 2.5 ml | 3 ml | 330 mg/ml |
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterZakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Zakłady Farmaceutyczne POLPHARMA S.A. Oddział Produkcyjny w Duchnicach
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BiofazolinDosage form: Powder, 1 gActive substance: cefazolinManufacturer: ACS Dobfar S.p.A ACS Dobfar S.p.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 1 gActive substance: cefazolinPrescription requiredDosage form: Powder, 2 gActive substance: cefazolinPrescription required
Alternatives to Biofazolin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Biofazolin in Ukraine
Alternative to Biofazolin in Spain
Online doctors for Biofazolin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Biofazolin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














