

Bibloc

Ask a doctor about a prescription for Bibloc

How to use Bibloc
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Bibloc, 3.75 mg Film-Coated Tablets
Bisoprolol Fumarate
Read the Package Leaflet Carefully Before Taking the Medication, as it Contains Important Information for the Patient.
- Keep this Package Leaflet, as You May Need to Read it Again.
- In Case of Any Doubts, Consult a Doctor or Pharmacist.
- This Medication has been Prescribed Specifically for You. Do not Give it to Others. The Medication may Harm Another Person, even if their Symptoms are the Same.
- If the Patient Experiences any Adverse Reactions, including those not Listed in this Package Leaflet, they Should Inform their Doctor or Pharmacist. See Section 4.
Package Leaflet Contents:
- 1. What is Bibloc and What is it Used for
- 2. Important Information Before Taking Bibloc
- 3. How to Take Bibloc
- 4. Possible Adverse Reactions
- 5. How to Store Bibloc
- 6. Package Contents and Other Information
1. What is Bibloc and What is it Used for
Bibloc belongs to a Group of Medications called Beta-Adrenergic Blockers. They Protect the Heart from Excessive Activity.
Bibloc is Used to Treat:
- Heart Failure, Characterized by Shortness of Breath During Exercise or Fluid Retention in the Body. In this Case, Bibloc may be Used as Additional Treatment for Heart Failure, which is Already being Treated with Other Medications.
2. Important Information Before Taking Bibloc
When not to Take Bibloc
If the Patient is Allergic to Bisoprolol Fumarate or any of the Other Ingredients of this Medication (Listed in Section 6).
If the Patient has been Diagnosed with Cardiogenic Shock - a Severe Heart Disorder with Rapid, Weak Pulse, Low Blood Pressure, Cold, Sweaty Skin, Weakness, and Fainting.
If the Patient has Ever Experienced Wheezing or Severe Asthma, as Breathing Difficulties may Occur.
If the Patient has a Slow Heart Rate (Less than 60 Beats per Minute). In Case of Doubt, Consult a Doctor.
If the Patient has Very Low Blood Pressure.
If the Patient has Severe Circulatory Disorders (which may Cause Tingling in the Fingers and Toes or their Pallor or Cyanosis).
If the Patient has Severe Heart Rhythm Disorders.
If the Patient has Sudden Heart Failure or Existing Heart Failure that is not Controlled and Requires Hospital Treatment.
If the Patient has a Build-up of Acids in the Body, Diagnosed as Metabolic Acidosis. The Doctor will Provide Information on this.
If the Patient has a Pheochromocytoma (a Tumor of the Adrenal Gland) that is not being Treated.
In Case of Any Doubts, Consult a Doctor.
Warnings and Precautions
Before Starting to Take Bibloc, Consult a Doctor:
If the Patient has Wheezing or Difficulty Breathing (Asthma), they Should also Use Medications that Dilate the Airways. A Higher Dose of Beta-2-Mimetic may be Necessary.
If the Patient has Diabetes. Bibloc Tablets may Mask the Symptoms of Low Blood Sugar (such as Rapid Heart Rate, Palpitations, or Excessive Sweating).
If the Patient does not Consume Foods with a Stable Consistency.
If the Patient is being Treated for Allergies. Bibloc may Increase Sensitivity to Allergens and Exacerbate the Severity of Allergic Reactions. Treatment with Adrenaline may not be Effective and may Require a Higher Dose.
If the Patient has a First-Degree Atrioventricular Block (Conduction Disorder in the Heart).
If the Patient has Prinzmetal's Angina (Chest Pains Caused by Spasm of the Coronary Arteries that Supply Blood to the Heart Muscle).
If the Patient has Circulatory Disorders in the Hands and Feet.
If the Patient is to Undergo Surgery under Anesthesia, they Should Inform their Doctor, Hospital Staff, or Dentist about the Medications they are Taking.
If the Patient has (or has had) Psoriasis (a Recurring Disease Characterized by Skin Peeling and Dry Skin Rash).
If the Patient has a Pheochromocytoma (a Tumor of the Adrenal Gland). Before Prescribing Bibloc, the Doctor will Need to Initiate Appropriate Treatment.
If the Patient has Thyroid Function Disorders. Bisoprolol Tablets may Mask the Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism.
There is Currently no Therapeutic Experience with the Use of Bibloc in Heart Failure in the Following Patients:
- With Type 1 Diabetes, Treated with Insulin
- With Severe Kidney Disease
- With Severe Liver Disease
- With Certain Heart Diseases
- Who have had a Heart Attack in the Last 3 Months.
Treatment of Heart Failure with Bibloc Requires Regular Medical Supervision. This is Absolutely Necessary, Especially at the Beginning of Treatment and after its Completion.
Do not Stop Taking Bibloc Suddenly without a Valid Reason.
Consult a Doctor if any of the Described Warnings Apply to the Patient or have Applied in the Past.
Bibloc and Other Medications
Inform the Doctor or Pharmacist about all Medications Currently being Taken or Recently Taken, as well as those Planned to be Taken. This also Applies to Medications that are Available without a Prescription. Certain Medications should not be Taken at the Same Time as Bibloc, and Others may Require Changes, such as Dose Adjustments.
In any Case, Inform the Doctor about Taking or Receiving the Following Medications in Addition to Bibloc:
Medications Used to Control Blood Pressure or Heart Function Disorders (such as Amiodarone, Amlodipine, Clonidine, Digitalis Glycosides, Diltiazem, Disopyramide, Felodipine, Flecainide, Lidocaine, Methyldopa, Moxonidine, Phenytoin, Propafenone, Quinidine, Rilmenidine, Verapamil);
Sedatives and Medications Used to Treat Psychosis (a Mental Disorder), such as Barbiturates (also Used to Treat Epilepsy), Phenothiazines (also Used to Treat Nausea and Vomiting);
Medications Used to Treat Depression, such as Tricyclic Antidepressants, MAO-A Inhibitors;
Medications Used for Anesthesia during Surgery (see also "Warnings and Precautions");
Certain Pain Relievers (such as Acetylsalicylic Acid, Diclofenac, Indomethacin, Ibuprofen, Naproxen);
Medications Used to Treat Asthma, Nasal Congestion, or Certain Eye Diseases, such as Glaucoma (Increased Pressure in the Eye) or Pupil Dilation;
Certain Medications Used to Treat Shock (such as Adrenaline, Dobutamine, Noradrenaline);
Mefloquine (a Medication Used to Treat Malaria);
Rifampicin (an Antibiotic);
Ergotamine Derivatives (Used to Treat Migraines).
All these Medications and Bibloc may Affect Blood Pressure and (or) Heart Function.
Insulin or Other Antidiabetic Medications. There is a Risk of Enhanced Hypoglycemic Effect and Masking of Hypoglycemic Symptoms.
Bibloc and Alcohol
Alcohol may Enhance the Dizziness and Drowsiness Caused by Bibloc. In this Case, it is Recommended to Avoid Drinking Alcohol.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
If the Patient is Pregnant or Breastfeeding, Thinks they may be Pregnant, or Plans to have a Child, they Should Consult a Doctor before Taking this Medication. Bibloc may have a Harmful Effect on the Course of Pregnancy and (or) the Fetus. The Risk of Premature Birth, Miscarriage, Low Blood Sugar in the Newborn, and Slowed Heart Rate Increases. The Medication may also Affect the Development of the Child. Therefore, Bibloc should not be Used during Pregnancy.
It is not Known whether Bisoprolol Passes into Breast Milk, so it is not Recommended to Take Bibloc during Breastfeeding.
Driving and Operating Machines
The Medication may Cause Fatigue, Drowsiness, or Dizziness. If these Symptoms Occur, the Patient should not Drive or Operate Machines. It should be Noted that such Symptoms may Occur, Especially at the Beginning of Treatment, during Dose Changes, or when Consuming Alcohol.
Bibloc Contains Lactose and Sodium
If the Patient has Previously been Diagnosed with Intolerance to Certain Sugars, they Should Consult a Doctor before Taking the Medication.
This Medication Contains Less than 1 mmol (23 mg) of Sodium per Film-Coated Tablet, which means it is Considered "Sodium-Free".
3. How to Take Bibloc
This Medication should Always be Taken as Directed by the Doctor or Pharmacist. In Case of Doubts, Consult a Doctor or Pharmacist.
The Doctor will Inform the Patient about the Number of Tablets to Take. The Medication should be Taken in the Morning, before, during, or after Breakfast. The Tablet(s) should be Swallowed with a Small Amount of Water. The Tablets should not be Chewed or Crushed.
The Usual Dose is:
Heart Failure (Reduced Heart Contractility):
Before Starting Bibloc, the Patient is Usually Already Taking an ACE Inhibitor, Diuretic, or Digitalis Glycoside (a Heart Medication and Antihypertensive).
The Dose of Bibloc will be Gradually Increased until the Optimal Dose is Reached for the Patient:
1.25 mg once a Day for 1 Week. If this Dose is Well Tolerated, it can be Increased to:
2.5 mg once a Day for the Next Week. If this Dose is Well Tolerated, it can be Increased to:
3.75 mg once a Day for the Next Week. If this Dose is Well Tolerated, it can be Increased to:
5 mg once a Day for 4 Consecutive Weeks. If this Dose is Well Tolerated, it can be Increased to:
7.5 mg once a Day for 4 Consecutive Weeks. If this Dose is Well Tolerated, it can be Increased to:
10 mg once a Day (Maintenance Dose).
The Maximum Dose is 10 mg once a Day.
The Doctor will Determine the Optimal Dose for the Patient Based on, among Other Things, Adverse Reactions.
After the First Dose of 1.25 mg, the Doctor will Check the Patient's Blood Pressure, Heart Rate, and Heart Function.
Liver or Kidney Function Disorders
The Doctor will Increase the Dose of Bibloc with Particular Caution.
Elderly Patients
Dose Adjustment is Usually not Necessary.
If the Patient Feels that the Effect of Bibloc is too Strong or too Weak, they Should Inform their Doctor or Pharmacist.
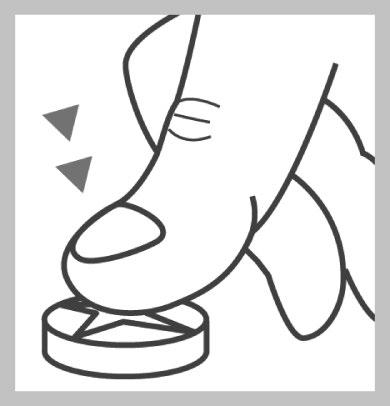
Place the Tablet on a Hard, Flat Surface, with the Notch Facing Upwards.
Press the Thumb on the Center of the Tablet. The Tablet will Break into 3 Equal Parts.
Duration of Treatment
Bibloc is Usually Taken Long-Term.
Use in Children and Adolescents
Due to the Lack of Studies on the Effect of Bibloc in Children and Adolescents, its Use is not Recommended in this Age Group.
Accidental Overdose of Bibloc
In Case of Unintentional Overdose, Immediately Consult a Doctor or Pharmacist.
Bring any Remaining Tablets or this Package Leafletso that Medical Personnel Know which Medication was Taken. Symptoms of Overdose may Include Dizziness, Drowsiness, Fatigue, Shortness of Breath and (or) Wheezing. Slow Heart Rate, Low Blood Pressure, Insufficient Heart Contractions, and Low Blood Sugar (which may Cause Hunger, Excessive Sweating, and Palpitations) may also Occur.
Missed Dose of Bibloc
Do not Take a Double Dose to Make up for a Missed Dose. Take the Usual Dose as Soon as Possible, and the Next Day Return to the Normal Dosage Schedule.
Stopping Treatment with Bibloc
Do not Stop Taking Bibloc Suddenly. If Treatment is Stopped Suddenly, the Disease may Worsen. The Dose of Bibloc should be Gradually Reduced over Several Weeks, as Directed by the Doctor.
In Case of Any Further Doubts about Taking this Medication, Consult a Doctor or Pharmacist.
4. Possible Adverse Reactions
Like all Medications, Bibloc can Cause Adverse Reactions, although not Everyone will Experience them.
If an Adverse Reaction is Severe, Occurs Suddenly, or Rapidly Worsens, Consult a Doctor Immediately to Prevent Serious Reactions.
The Most Severe Adverse Reactions are Related to Heart Function:
Slow Heart Rate (may Occur more Frequently than in 1 in 10 People)
Worsening of Existing Heart Failure (may Occur less Frequently than in 1 in 10 People)
Slow or Irregular Heart Rate (may Occur less Frequently than in 1 in 100 People)
If the Patient Experiences Dizziness, Weakness, or Difficulty Breathing, they Should Consult a Doctor as Soon as Possible.
If the Patient Experiences Severe Allergic Reactions, which may Include Swelling of the Face, Neck, Tongue, Lips, or Throat, or Difficulty Breathing, they Should Immediately Consult a Doctor.
The Following Adverse Reactions are Listed below by Frequency of Occurrence:
Common (may Occur less Frequently than in 1 in 10 People):
Fatigue, Exhaustion
Dizziness
Headache
Feeling of Coldness or Numbness in the Fingers or Toes, Ears, and Nose; more Frequent Occurrence of Cramping Pain in the Legs while Walking
Very Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension), especially in Patients with Heart Failure
Nausea, Vomiting
Diarrhea
Constipation
Uncommon (may Occur less Frequently than in 1 in 100 People):
Decrease in Blood Pressure when Standing, which may Cause Dizziness, Drowsiness, or Fainting
Sleep Disorders
Depression
Irregular Heart Rate
Breathing Difficulties in Patients with Asthma or a History of Breathing Disorders
Muscle Weakness and Cramps
Rare (may Occur less Frequently than in 1 in 1000 People):
Nightmares
Hallucinations
Fainting
Hearing Impairment
Rhinitis (Inflammation of the Nasal Mucosa), Causing a Runny Nose with Irritation
Skin Allergic Reactions (such as Itching, Sudden Redness of the Skin, Rash)
Dryness of the Eyes due to Reduced Tear Secretion (which can be Very Troublesome for Contact Lens Wearers)
Hepatitis (Inflammation of the Liver), Causing Abdominal Pain, Loss of Appetite, and Sometimes Jaundice with Yellowing of the Eyes and Skin, as well as Dark Urine
Decreased Sexual Performance (Impotence)
Increased Levels of Lipids in the Blood (Triglycerides) and Increased Activity of Liver Enzymes
Very Rare (may Occur less Frequently than in 1 in 10,000 People):
Exacerbation of Psoriasis or Occurrence of a Similar, Dry, Flaky Skin Rash, as well as Hair Loss
Itching or Redness of the Eyes (Conjunctivitis)
Reporting Adverse Reactions
If any Adverse Reactions Occur, including those not Listed in this Package Leaflet, Inform a Doctor, Pharmacist, or Nurse. Adverse Reactions can be Reported Directly to the Department for Monitoring of Adverse Reactions to Medicinal Products of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw
Phone: +48 22 49 21 301/Fax: +48 22 49 21 309/Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl
Adverse Reactions can also be Reported to the Marketing Authorization Holder.
Reporting Adverse Reactions will Help to Gather more Information on the Safety of the Medication.
5. How to Store Bibloc
Store the Medication in a Place that is Inaccessible to Children.
Do not Use this Medication after the Expiration Date Stated on the Packaging after EXP.
The Expiration Date Refers to the Last Day of the Specified Month.
Do not Use the Medication in the Bottle after 6 Months from the First Opening.
Blister: No Special Precautions for Storage.
Bottle: No Special Precautions for Storage.
After First Opening: Do not Store above 25°C.
Medications should not be Disposed of in Sewers or Household Waste. Ask a Pharmacist how to Dispose of Unused Medications. This will Help Protect the Environment.
6. Package Contents and Other Information
What Bibloc Contains
- The Active Substance is Bisoprolol Fumarate. Each Film-Coated Tablet Contains 3.75 mg of Bisoprolol Fumarate.
- Other Ingredients are: Calcium Hydrogen Phosphate Anhydrous, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Maize Starch, Cross-Linked Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium, Colloidal Anhydrous Silica, Magnesium Stearate, Lactose Monohydrate, Hypromellose, Titanium Dioxide (E 171), Macrogol 4000, Yellow Iron Oxide (E 172).
What Bibloc Looks Like and What the Package Contains
Yellow-White, Round, Film-Coated Tablets with a Notch, Marked "BIS 3,75" on one Side.
The Tablets can be Divided into Three Equal Doses.
The Film-Coated Tablets are Packaged in Blisters made of OPA/Aluminum/PVC/Aluminum Foil or in HDPE Bottles and Placed in a Cardboard Box.
Blisters Contain 30, 60, or 90 Tablets.
Bottles Contain 100 Tablets.
Not all Package Sizes may be Marketed.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Marketing Authorization Holder
Sandoz GmbH
Biochemiestrasse 10
6250 Kundl, Austria
Manufacturer
Lek Pharmaceuticals d.d.
Verovškova 57
1526 Ljubljana, Slovenia
Lek S.A.
ul. Domaniewska 50 C
02-672 Warsaw
Rowa Pharmaceuticals Ltd.
Newtown, Bantry, Co. Cork, Ireland
Salutas Pharma GmbH
Otto-von-Guericke-Allee 1
D-39179 Barleben, Germany
Lek S.A.
ul. Podlipie 16
95-010 Stryków
To Obtain more Detailed Information about the Medication and its Names in other European Economic Area Member States, Contact:
Sandoz Polska Sp. z o.o.
ul. Domaniewska 50 C
02-672 Warsaw
Phone: 22 209 70 00
Date of Last Update of the Package Leaflet:03/2022
Sandoz Logo
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterLek Pharmaceuticals d.d. LEK S.A. LEK S.A. Rowa Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Salutas Pharma GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to BiblocDosage form: Tablets, 1.25 mgActive substance: bisoprololManufacturer: Lek Pharmaceuticals d.d. LEK S.A. LEK S.A. Rowa Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Salutas Pharma GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 2.5 mgActive substance: bisoprololManufacturer: Lek Pharmaceuticals d.d. LEK S.A. LEK S.A. Rowa Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Salutas Pharma GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 5 mgActive substance: bisoprololManufacturer: Lek Pharmaceuticals d.d. LEK S.A. LEK S.A. Rowa Pharmaceuticals Ltd. Salutas Pharma GmbHPrescription required
Alternatives to Bibloc in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Bibloc in Spain
Alternative to Bibloc in Ukraine
Online doctors for Bibloc
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Bibloc – subject to medical assessment and local rules.










