
Adin
Ask a doctor about a prescription for Adin

How to use Adin
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
ADIN, 60 micrograms, oral lyophilisate
ADIN, 120 micrograms, oral lyophilisate
ADIN, 240 micrograms, oral lyophilisate
Desmopressin
Read the package leaflet carefully before taking the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- Keep this package leaflet, you may need to read it again.
- If you have any further questions, ask your doctor.
- This medicine has been prescribed for you only. Do not pass it on to others. It may harm them, even if their symptoms are the same as yours.
- If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor. See section 4.
Table of Contents of the Package Leaflet:
- 1. What Adin is and what it is used for
- 2. Important information before taking Adin
- 3. How to take Adin
- 4. Possible side effects
- 5. How to store Adin
- 6. Contents of the pack and other information
1. What Adin is and what it is used for
Adin contains desmopressin, which acts similarly to the natural hormone produced by the pituitary gland, arginine vasopressin. Desmopressin is characterized by a significantly prolonged antidiuretic effect (reducing urine production) and a complete lack of vasoconstrictive effect at therapeutic doses. Adin is used to treat:
- central diabetes insipidus;
- primary nocturnal enuresis in children over 6 years of age with normal urine concentrating ability;
- nocturia in adults associated with nocturnal polyuria (the volume of urine produced at night exceeds the bladder capacity).
2. Important information before taking Adin
When not to take Adin
Warnings and precautions
Before starting treatment with Adin, discuss it with your doctor. Your doctor will exercise caution in the following cases:
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to rule out severe urinary bladder disorders and bladder outlet obstruction. Special precautions should be taken in patients with renal impairment and cardiovascular disease. In the event of acute illnesses with water and electrolyte disorders, such as generalized infection, feverish diseases, gastroenteritis, Adin should be discontinued and the doctor consulted.
Children
Adin is used to treat central diabetes insipidus and primary nocturnal enuresis in children over 6 years of age with normal urine concentrating ability.
Adin and other medicines
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you are taking now or have taken recently, as well as any medicines you plan to take. In particular, inform your doctor about taking:
- tricyclic antidepressants;
- selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors;
- chlorpromazine;
- carbamazepine;
- oral hypoglycemic agents from the sulfonylurea group, e.g. chlorpropamide;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- loperamide.
The above-mentioned medicines may lead to excessive water retention in the body or a decrease in sodium levels in the blood.
Adin with food and drink
During treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis in children and nocturia in adults, fluid intake should be limited to a minimum from 1 hour before taking the medicine to 8 hours after taking it. Taking Adin without restricting fluid intake may lead to excessive water retention in the body or a decrease in sodium levels in the blood, which may, but does not have to, manifest as headaches, nausea, vomiting, weight gain, or in severe cases, convulsions. The above warning does not apply to patients taking Adin for the treatment of central diabetes insipidus. Taking the medicine with food may reduce the strength and duration of its action.
Adin in patients with renal and/or hepatic impairment
Before taking the medicine, consult your doctor.
Adin in elderly patients
It is not recommended to start treatment for nocturia in patients over 65 years old.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, think you may be pregnant, or plan to have a child, consult your doctor before taking this medicine.
Driving and using machines
Adin has no influence or negligible influence on the ability to drive and use machines.
3. How to take Adin
This medicine should always be taken exactly as prescribed by your doctor. If you are unsure, consult your doctor. Adin should be placed under the tongue, where the medicine dissolves without the need for water. Treatment of central diabetes insipidus with Adin: The doctor determines the dosage individually for each patient, but the total daily dose is usually within the range of 120 to 720 micrograms sublingually. Treatment of children and adults usually starts with 60 micrograms of desmopressin sublingually 3 times a day. Subsequent doses are determined by the doctor based on the patient's response. In most patients, the maintenance dose is 60 to 120 micrograms of desmopressin sublingually 3 times a day. Treatment of primary nocturnal enuresis in children with Adin: Treatment usually starts with a dose of 120 micrograms. The medicine is given sublingually once a day before bedtime. If this dose is insufficient, the doctor may order an increase in the dose to 240 micrograms. Fluid intake should be limited to a minimum from 1 hour before taking the medicine to 8 hours after taking it. After three months of treatment, the doctor should order the discontinuation of the medicine for at least one week and assess whether further treatment is necessary. Treatment of nocturia in adults with Adin: Treatment usually starts with a dose of 60 micrograms. The medicine is given sublingually once a day before bedtime. If this dose is not sufficiently effective after one week of use, the doctor may order an increase in the dose to 120 micrograms and then to 240 micrograms, with weekly intervals when increasing the dose. Fluid intake should be limited to a minimum from 1 hour before taking the medicine to 8 hours after taking it.
Overdose of Adin
Taking a higher dose than recommended increases the risk of excessive water retention in the body or a decrease in sodium levels in the blood, which may, but does not have to, manifest as headaches, nausea, vomiting, weight gain, or in severe cases, convulsions. If you take more Adin than recommended, consult your doctor immediately.
Missed dose of Adin
Do not take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Adin can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
In adults:
The following very common side effectsaffect more than 1 in 10 people taking the medicine:
- headache.
The following common side effectsaffect between 1 and 10 in 100 people taking the medicine:
- hyponatremia (low sodium levels in the blood);
- dizziness;
- hypertension;
- nausea;
- abdominal pain;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- vomiting;
- symptoms related to the urinary bladder and urethra;
- edema;
- fatigue.
The following uncommon side effectsaffect between 1 and 10 in 1,000 people taking the medicine:
- insomnia;
- drowsiness;
- paresthesia (tingling, prickling, or numbness);
- visual disturbances;
- balance disorders;
- palpitations;
- orthostatic hypotension (decrease in blood pressure when changing position from lying to standing);
- shortness of breath;
- indigestion;
- flatulence;
- bloating;
- sweating;
- itching;
- rash;
- urticaria;
- muscle cramps;
- muscle pain;
- malaise;
- chest pain;
- flu-like symptoms;
- weight gain;
- increased liver enzyme levels;
- hypokalemia (low potassium levels in the blood).
The following rare side effectsaffect between 1 and 10 in 10,000 people taking the medicine:
- confusion;
- allergic skin rash.
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from available data):
- anaphylactic reactions;
- dehydration;
- hypernatremia (high sodium levels in the blood);
- seizures;
- weakness;
- coma.
In children and adolescents:
The following common side effectsaffect between 1 and 10 in 100 people taking the medicine:
- headache.
The following uncommon side effectsaffect between 1 and 10 in 1,000 people taking the medicine:
- emotional instability;
- aggression;
- abdominal pain;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- diarrhea;
- symptoms related to the urinary bladder and urethra;
- peripheral edema;
- fatigue.
The following rare side effectsaffect between 1 and 10 in 10,000 people taking the medicine:
- restlessness;
- nightmares;
- mood swings;
- drowsiness;
- hypertension;
- irritability.
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from available data)
- anaphylactic reactions;
- hyponatremia;
- abnormal behavior;
- emotional disorders;
- depression;
- hallucinations;
- insomnia;
- attention disorders;
- psychomotor hyperactivity;
- seizures;
- nasal bleeding;
- allergic skin rashes;
- rash;
- sweating;
- urticaria.
Reporting side effects
If you experience any side effects, including any not listed in this leaflet, please tell your doctor. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Pharmacovigilance of the Office for Registration of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products: Aleje Jerozolimskie 181C, 02-222 Warsaw, Tel: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, Website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. How to store Adin
Keep the medicine out of the sight and reach of children. Store in the original package to protect from moisture and light. Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the packaging after the EXP label. The expiry date refers to the last day of the month. Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. Ask your pharmacist how to dispose of medicines no longer required. This will help protect the environment.
6. Contents of the pack and other information
What Adin contains
- The active substance is desmopressin in a dose of 60, 120, or 240 micrograms.
- The other ingredients are: gelatin, mannitol, anhydrous citric acid.
What Adin looks like and contents of the pack
Adin 60 micrograms is a white tablet with a drop-shaped marking on one side. Adin 120 micrograms is a white tablet with a marking of two drops on one side. Adin 240 micrograms is a white tablet with a marking of three drops on one side. One pack of Adin contains 30 or 100 oral lyophilisates.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder: Ferring-Léčiva, a.s., K Rybníku 475, 252-42 Jesenice u Prahy, Czech Republic. Manufacturer: Ferring GmbH, Wittland 11, D-24109 Kiel, Germany. Date of last revision of the leaflet:10/2020. For more detailed information, please contact the representative of the marketing authorization holder. Ferring Pharmaceuticals Poland Sp. z o.o., ul. Szamocka 8, 01-748 Warsaw, Tel.: +48 22 246 06 80, Fax: +48 22 246 06 81.
Instructions for removing lyophilisates from the blister pack
Lyophilisates are fragile. Do not push them through the blister pack foil, as this may cause them to crumble. Lyophilisates should be removed from the blister pack after first removing the aluminum foil, as shown in the diagrams below:
- 1.Completely tear off the end strip of the blister pack, starting from the corner with the printed hand symbol.
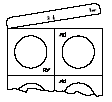
- 2.Tear off the blister pack unit along the perforation.
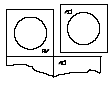
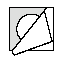
- 3.Pull back the foil, starting from the corner with the printed arrow, and gently remove the lyophilisate.
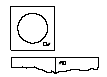
- 4.By repeating steps 2 and 3, you can access the next lyophilisate.
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- ImporterFerring GmbH
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to AdinDosage form: Lyophilizate, 60 mcgActive substance: desmopressinManufacturer: Ferring GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Lyophilizate, 240 mcgActive substance: desmopressinManufacturer: Ferring GmbHPrescription requiredDosage form: Tablets, 60 mcgActive substance: desmopressinPrescription required
Alternatives to Adin in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Adin in Spain
Alternative to Adin in Ukraine
Online doctors for Adin
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Adin – subject to medical assessment and local rules.














