How to use Adaring
Leaflet accompanying the packaging: user information
Adaring, (0.120 mg + 0.015 mg)/24 h, intrauterine therapeutic system
Etonogestrel + Ethinylestradiol
Important information about combined hormonal contraceptives:
- If used correctly, they are one of the most reliable, reversible methods of contraception.
- They slightly increase the risk of blood clots in veins and arteries, especially in the first year of use or after resuming use after a break of 4 weeks or more.
- Caution should be exercised and a doctor should be consulted if the patient suspects that blood clot symptoms have occurred (see section 2 "Blood clots").
You should carefully read the contents of the leaflet before using the medicine, as it contains important information for the patient.
- You should keep this leaflet so that you can read it again if necessary.
- In case of any doubts, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
- This medicine has been prescribed specifically for you. Do not pass it on to others. The medicine may harm another person.
- If the patient experiences any side effects, including any side effects not listed in this leaflet, they should tell their doctor or pharmacist. See section 4.
Table of contents of the leaflet
1. What is Adaring and what is it used for
2. Important information before using Adaring
- 2.1 When not to use Adaring
- 2.2 Warnings and precautions Blood clots Cancer
- 2.3 Children and adolescents
- 2.4 Adaring and other medicines Diagnostic tests
- 2.5 Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- 2.6 Driving and using machines
3. How to use Adaring
- 3.1 Insertion and removal of Adaring
- 3.2 Three weeks of use, one week of break
- 3.3 When to insert the first Adaring intrauterine system
- 3.4 What to do if… Procedure in case of accidental expulsion of the system from the vaginaProcedure when the system has been out of the vagina for some timeProcedure in case of damage to the intrauterine systemProcedure in case of insertion of more than one intrauterine systemProcedure when, after a one-week break, the patient forgets to insert a new systemintrauterineProcedure when the patient wants to stop using Adaring
Procedure when the patient forgets to remove the intrauterine system on time
Procedure in case of absence of bleeding
Procedure in case of unexpected bleeding
Procedure in case of change in the day of bleeding
Procedure in case of desire to delay the onset of bleeding
- 3.5 Procedure when the patient wants to stop using Adaring
4. Possible side effects
5. How to store Adaring
6. Contents of the packaging and other information
What Adaring contains
What Adaring looks like and what the packaging contains
Responsible entity and manufacturer
1. What is Adaring and what is it used for
Adaring is a contraceptive in the form of an intrauterine therapeutic system, preventing pregnancy. Each intrauterine system contains a small amount of two female sex hormones - etonogestrel and ethinylestradiol. These hormones are slowly released from the system into the bloodstream. Due to the small dose of hormones released, Adaring is classified as a low-dose hormonal contraceptive. Since Adaring releases two different hormones, it is also a combined contraceptive.
Adaring works like a combined oral contraceptive pill, but unlike a pill that must be taken every day, Adaring is used for 3 weeks in a row.
Adaring releases two female sex hormones that inhibit the release of egg cells from the ovaries. Since egg cells are not released, the patient cannot become pregnant.
2. Important information before using Adaring
General notes
Before starting to take Adaring, you should read the information about blood clots in section 2. It is especially important to read about the symptoms of blood clots (see section 2 "Blood clots").
This leaflet describes situations in which you should stop using Adaring or in which its effectiveness may be reduced. In these situations, you should abstain from sexual intercourse or use an additional non-hormonal contraceptive method, such as a condom or another mechanical method. You should notuse methods based on a calendar or body temperature measurement. They may be ineffective because Adaring affects changes in body temperature and cervical mucus consistency throughout the month.
Adaring, like other hormonal contraceptives, does not protect against HIV (AIDS) or other sexually transmitted diseases.
2.1 When not to use Adaring
You should not use Adaring if you have any of the following conditions. If you have any of the following conditions, you should inform your doctor. The doctor will discuss with you which other contraceptive method will be more suitable.
if you currently have (or have ever had) a blood clot in the veins of the legs (deep vein thrombosis), in the lungs (pulmonary embolism), or in other organs,
if you know you have blood coagulation disorders - such as protein C deficiency, protein S deficiency, antithrombin III deficiency, factor V Leiden, or antiphospholipid antibodies,
if you need to have surgery or will be immobilized for a long time (see "Blood clots"),
if you have had a heart attack or stroke,
if you have (or have had in the past) angina pectoris (a disease that causes severe chest pain and can be the first symptom of a heart attack) or transient ischemic attack (transient stroke symptoms),
if you have any of the following diseases that may increase the risk of arterial thrombosis:
severe diabetes with blood vessel damage
very high blood pressure
very high levels of fats in the blood (cholesterol or triglycerides)
hyperhomocysteinemia
if you have (or have had in the past) a type of migraine called "migraine with aura",
if you have (or have had in the past) pancreatitis associated with high levels of fats in the blood,
if you have (or have had in the past) severe liver disease, and liver function has not returned to normal,
if you have (or have had in the past) a benign or malignant liver tumor,
if you have (or have had in the past) breast cancer or genital cancer, or if there is a suspicion of these cancers,
if you have unexplained vaginal bleeding,
if you are allergic to ethinylestradiol or etonogestrel, or any of the other ingredients of this medicine (listed in section 6).
If any of the above symptoms occur for the first time during the use of Adaring, you should immediately remove the system from the vagina and consult a doctor, and in the meantime, use a non-hormonal contraceptive method.
You should not use Adaring in patients with hepatitis C and taking medicinal products containing ombitasvir with paritaprevir and ritonavir, dasabuvir, glecaprevir with pibrentasvir, or sofosbuvir with velpatasvir and voxilaprevir (see also section 2.4 "Adaring and other medicines").
2.2 Warnings and precautions
When should you contact a doctor?
You should immediately contact a doctor
if you notice possible symptoms of blood clots, which may indicate that you have blood clots in your leg (deep vein thrombosis), blood clots in your lungs (pulmonary embolism), a heart attack, or a stroke (see below "Blood clots (thrombosis)").
To get a description of the serious side effects listed, see "How to recognize blood clots".
You should tell your doctor if you have any of the following conditions.
If these symptoms occur or worsen during the use of Adaring, you should also tell your doctor.
- if breast cancer is present or has occurred in close relatives;
- if you have epilepsy (see section 2.4 "Adaring and other medicines");
- if you have liver disease (e.g., jaundice) or gallbladder disease (e.g., gallstones);
- if you have Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis (chronic inflammatory bowel diseases);
- if you have systemic lupus erythematosus (a disease that affects the body's natural defense system);
- if you have hemolytic uremic syndrome (a blood clotting disorder that causes kidney failure);
- if you have sickle cell anemia (a hereditary disease of red blood cells);
- if you or a close relative have been diagnosed with high levels of fats in the blood (hypertriglyceridemia). Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with an increased risk of developing pancreatitis;
- if you need to have surgery or will be immobilized for a long time (see "Blood clots");
- if you are immediately after childbirth, then you are at increased risk of blood clots. You should consult a doctor to find out how soon you can start taking Adaring after childbirth;
- if you have superficial thrombophlebitis (blood clots in the veins under the skin);
- if you have varicose veins;
- if you have diseases that occurred for the first time or worsened during pregnancy or previous use of sex hormones (e.g., hearing loss, porphyria [a blood disease], herpes gestationis [a blistering skin rash during pregnancy], Sydenham's chorea [a neurological disorder in which there are involuntary, sudden movements of the body]),
- if you experience symptoms of angioedema, such as swelling of the face, tongue, and/or throat, and/or difficulty swallowing or shortness of breath, you should contact your doctor immediately. Products containing estrogens may cause or worsen symptoms of hereditary or acquired angioedema;
- if you currently have or have had chloasma (brownish-yellow pigmentation spots, so-called "pregnancy spots", especially on the face). If they occur, you should avoid excessive sun exposure and ultraviolet radiation;
ultraviolet radiation;
- if you have conditions that make it difficult to use Adaring, such as frequent constipation, cervical prolapse, pain during intercourse.
- if you experience sudden, frequent need to urinate with a burning sensation and/or pain, and if you cannot locate the intrauterine system in the vagina. These symptoms may indicate that the intrauterine system has been accidentally inserted into the bladder.
BLOOD CLOTS
The use of combined hormonal contraceptives, such as the Adaring intrauterine system, is associated with an increased risk of blood clots, compared to not using the therapy. In rare cases, a blood clot can block a blood vessel and cause serious complications.
Blood clots can occur
- in veins (hereinafter referred to as "venous thromboembolism" or "venous thromboembolic disease")
- in arteries (hereinafter referred to as "arterial thromboembolism" or "arterial thromboembolic disease").
Not everyone recovers fully after a blood clot. In rare cases, the effects of a blood clot can be permanent or, very rarely, fatal.
Remember that the overall risk of harmful blood clots caused by Adaring is small.
HOW TO RECOGNIZE BLOOD CLOTS
You should immediately contact a doctor if you notice any of the following symptoms.
What might the patient be suffering from?
- swelling of the leg or swelling along a vein in the leg or foot,
Is the patient experiencing any of these symptoms?
Deep vein thrombosis
especially if it is accompanied by:
o pain or tenderness in the leg, which can only be felt when standing or walking,
o increased temperature in the affected leg,
o change in the color of the leg skin, e.g., pallor, redness, or cyanosis.
- sudden unexplained shortness of breath or rapid breathing;
- sudden unexplained cough, which may be accompanied by coughing up blood;
- sharp chest pain, which may worsen with deep breathing;
- severe dizziness or fainting;
- rapid or irregular heartbeat;
- severe abdominal pain.
If the patient is unsure, they should contact a doctor,
| because some of these symptoms, such as cough or shortness of breath, can be mistaken for milder conditions, such as a respiratory infection (e.g., a cold). | |
Symptoms usually occur in one eye:
| Retinal vein thrombosis (blood clot in the eye) |
| Heart attack |
| Stroke |
| Blood clots blocking other blood vessels |
BLOOD CLOTS IN VEINS
What can happen if blood clots form in a vein?
- The use of combined hormonal contraceptives is associated with an increased risk of blood clots in the veins (venous thromboembolism). Although these side effects are rare, they can occur most often in the first year of using combined hormonal contraceptives.
- If blood clots form in the veins in the leg or foot, it can lead to the development of deep vein thrombosis.
- If a blood clot moves from the leg and settles in the lungs, it can cause pulmonary embolism.
- In very rare cases, a blood clot can form in another organ, such as the eye (retinal vein thrombosis).
eye (retinal vein thrombosis).
When is the risk of blood clots in a vein the highest?
The risk of forming blood clots in a vein is highest during the first year of using combined hormonal contraceptives for the first time. The risk may also be higher when resuming the use of combined hormonal contraceptives (the same or a different medicine) after a break of 4 weeks or more.
After the first year, the risk decreases, but it is always higher compared to not using combined hormonal contraceptives.
If you stop using Adaring, the risk of blood clots returns to normal within a few weeks.
What affects the risk of blood clots?
The risk depends on the natural risk of venous thromboembolism and the type of combined hormonal contraceptive used.
The overall risk of blood clots in the legs or lungs associated with Adaring is small.
- During the year, about 2 out of 10,000 women who do not use combined hormonal contraceptives and are not pregnant will develop blood clots.
- During the year, about 5-7 out of 10,000 women using combined hormonal contraceptives containing levonorgestrel, norethisterone, or norgestimate will develop blood clots.
- During the year, about 6 to 12 out of 10,000 women using combined hormonal contraceptives containing ethinylestradiol or etonogestrel, such as the Adaring intrauterine system, will develop blood clots.
- The risk of blood clots depends on the patient's individual medical history (see "Factors that increase the risk of blood clots", below).
| Risk of blood clots in a year | |
| Women who do not use combined hormonal pills/patches/systems and are not pregnant | About 2 out of 10,000 women |
| Women using combined hormonal contraceptive pills containing levonorgestrel, norethisterone, or norgestimate | About 5-7 out of 10,000 women |
| Women using the Adaring intrauterine system | About 6-12 out of 10,000 women |
Factors that increase the risk of blood clots in veins
The risk of blood clots associated with Adaring is small, but some factors can increase this risk.
The risk is higher:
- if you are severely overweight (body mass index (BMI) over 30 kg/m 2);
- if someone in your immediate family has had blood clots in their legs, lungs, or other organs at a young age (e.g., under 50). In this case, you may have hereditary blood coagulation disorders;
- if you need to have surgery or will be immobilized for a long time due to injury or illness or have a leg in a cast. It may be necessary to stop using Adaring for a few weeks before surgery or immobilization. If you need to stop using Adaring, you should ask your doctor when you can resume using it;
- with age (especially over 35 years);
- if you have given birth in the last few weeks.
The risk of blood clots increases with the number of risk factors present in the patient.
Long-distance air travel (>4 hours) may temporarily increase the risk of blood clots, especially if you have other risk factors.
It is essential to tell your doctor if any of these factors apply to you, even if you are not sure. Your doctor may decide to stop using Adaring.
You should inform your doctor if any of the above conditions change during the use of Adaring, e.g., if someone in your immediate family is diagnosed with a blood clot without a known cause or if you gain weight significantly.
BLOOD CLOTS IN ARTERIES
What can happen if blood clots form in an artery?
Similarly to blood clots in veins, blood clots in arteries can have serious consequences, such as a heart attack or stroke.
Factors that increase the risk of blood clots in arteries
It is essential to note that the risk of a heart attack or stroke associated with Adaring is very small, but it may increase:
- with age (over about 35 years);
- if you smoke.While using a hormonal contraceptive like Adaring, it is recommended to quit smoking. If you are unable to quit smoking and are over 35 years old, your doctor may recommend using a different type of contraception;
- if you are overweight;
- if you have high blood pressure;
- if someone in your immediate family has had a heart attack or stroke at a young age (under 50). In this case, you may also be at increased risk of having a heart attack or stroke;
- if you or a close relative have been diagnosed with high levels of fats in the blood (cholesterol or triglycerides);
- if you have migraines, especially migraines with aura;
- if you have heart disease (valve damage, arrhythmia called atrial fibrillation);
- if you have diabetes.
If you have more than one of the above conditions or if any of them are severe, the risk of blood clots may be even higher.
You should inform your doctor if any of the above conditions change during the use of Adaring, e.g., if you start smoking, if someone in your immediate family is diagnosed with a blood clot without a known cause, or if you gain weight significantly.
CANCER
The following information is based on studies using combined hormonal contraceptives and may also apply to Adaring. Information on the intrauterine use of hormonal contraceptives (as with Adaring) is not yet available.
Among women using combined hormonal contraceptives, breast cancer has been found to occur slightly more often, although it is not known whether this is caused by the medicines used. It is possible that women using combined hormonal contraceptives are more likely to have their breasts examined, which can lead to the detection of more cases of breast cancer. The increased incidence of breast cancer gradually decreases after stopping the use of combined hormonal contraceptives.
Regular breast examination is very important. If a lump is detected, you should contact your doctor. You should also inform your doctor if breast cancer has occurred or is suspected in close relatives (see section 2.2 "Warnings and precautions").
In rare cases, women using combined hormonal contraceptives have been found to have benign liver tumors, and very rarely, malignant liver tumors as well. If you experience unusual, severe abdominal pain, you should contact your doctor.
There are reports that women using combined hormonal contraceptives are less likely to develop endometrial cancer (cancer of the uterine lining) and ovarian cancer. It is possible that this also applies to Adaring, but this has not been confirmed yet.
PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS
Some women using hormonal contraceptives, including Adaring, have reported depression or low mood. Depression can be severe and sometimes lead to suicidal thoughts. If mood changes and symptoms of depression occur, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible for further medical advice.
2.3 Children and adolescents
No safety and efficacy studies have been conducted on the use of Adaring in adolescents under the age of 18.
2.4 Adaring and other medicines
You should always inform your doctor about the use of other medicines and herbal products. You should also inform your doctor or another specialist (or pharmacist) about the use of Adaring when prescribing other medicines (or pharmacist who dispenses medicines). They may inform you about the need to use an additional contraceptive method (e.g., a condom for men), how long to use it, or the need to change the medicine you are taking.
Some medicines:
- may affect the level of Adaring in the blood
- may reduce the effectiveness of Adaring in preventing pregnancy
- may cause unexpected bleeding. This includes medicines used to treat:
- epilepsy (e.g., primidone, phenytoin, barbiturates, carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, felbamate);
- tuberculosis (e.g., rifampicin);
- HIV infection (e.g., ritonavir, nelfinavir, nevirapine, efavirenz);
- hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection (e.g., boceprevir, telaprevir)
- other infectious diseases (e.g., griseofulvin)
- high blood pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs (bosentan);
- depression (herbal products containing St. John's Wort ) .
If you are taking medicines or herbal products that may reduce the effectiveness of Adaring, you should use an additional mechanical contraceptive method (such as a condom for men). Since the effect of another medicine on Adaring may persist for up to 28 days after stopping its use, it is necessary to use a mechanical contraceptive method for such a long period. Note: You should not use Adaring with a diaphragm, cervical cap, or female condom, as Adaring may interfere with the proper placement and positioning of these contraceptive methods. However, you can use a condom for men as an additional mechanical contraceptive method.
Adaring may affect the action of other medicines, such as:
- medicines containing cyclosporine;
- the antiepileptic medicine lamotrigine (the effect may be an increased frequency of seizures).
You should not use Adaring in patients with hepatitis C and taking medicinal products containing ombitasvir with paritaprevir and ritonavir, dasabuvir, glecaprevir with pibrentasvir, or sofosbuvir with velpatasvir and voxilaprevir, as they may cause abnormal liver function test results (elevated liver enzyme activity).
Before starting to take these medicines, your doctor will prescribe a different type of contraception.
You can start taking Adaring again after about 2 weeks from the end of the above-mentioned treatment. See section 2.1 "When not to use Adaring".
Before using any medicine, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
During the use of Adaring, you can use tampons at the same time. You should insert Adaring before inserting a tampon. You should be careful when removing a tampon to avoid accidentally removing Adaring as well. If Adaring is expelled, it is enough to wash the intrauterine system with cold or warm water and insert it back as soon as possible.
Damage to the intrauterine system has occurred during the use of vaginal products, such as moisturizers or treatments for infections (see section 3.4. "Procedure in case of damage to the intrauterine system").
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS
If laboratory tests of blood or urine are performed, you should inform the persons performing the tests about the use of Adaring, as the use of the intrauterine system may affect the results of some laboratory tests.
2.5 Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Adaring should not be used during pregnancy or if pregnancy is suspected. If you become pregnant while using Adaring, you should remove the intrauterine system and contact your doctor.
If you want to stop using Adaring because you want to become pregnant, you should read section 3.5 "Procedure when the patient wants to stop using Adaring".
It is not recommended to use Adaring during breastfeeding. If you want to use Adaring during breastfeeding, you should consult your doctor first.
2.6 Driving and using machines
Adaring does not affect the ability to drive or use machines.
3. How to use Adaring
This medicine should always be used as directed by your doctor or pharmacist. In case of doubt, you should consult a doctor or pharmacist.
Adaring can be inserted and removed by yourself. Your doctor will instruct you on when to start using Adaring. The intrauterine system should be inserted on the appropriate day of your cycle (see section 3.3 "When to insert the first Adaring intrauterine system") and left in place for 3 weeks. It is a good idea to regularly check that the intrauterine system is in place. After 3 weeks, you should remove the system and take a one-week break. Usually, withdrawal bleeding occurs during this break.
You should not use certain mechanical contraceptive methods for women, such as a diaphragm, cervical cap, or female condom, while using Adaring. You should not use these mechanical contraceptive methods as an additional method of contraception, as Adaring may interfere with the proper placement and positioning of these contraceptive methods. However, you can use a condom for men as an additional mechanical contraceptive method.
3.1 Insertion and removal of Adaring
- 1. Before insertion, check the expiration date (see section 5 "How to store Adaring").
- 2. Before insertion or removal, wash your hands.
- 3. Choose the most comfortable position for insertion, such as standing with one leg raised, squatting, or lying down.
- 4. Remove Adaring from the pouch. Keep the pouch for later use.
- 5. Holding the system with your thumb and index finger, squeeze it and insert it into the vagina (see figures 1-4). The correct position of Adaring is one in which you do not feel it. If the system is uncomfortable, you should gently push it further into the vagina. The exact position of the system in the vagina does not affect its contraceptive effectiveness.
- 6. After 3 weeks, remove the system from the vagina. You can do this by hooking your index finger under the edge of the system or by grasping it with your index and middle fingers and pulling it out (figure 5). If you are unable to locate the system in the vagina but cannot remove it, you should contact your doctor.
- 7. Dispose of the used system with household waste, preferably in a closed pouch in which it was originally packaged. Do not flush Adaring down the toilet.
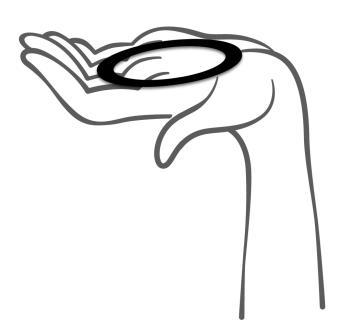
Figure 1
Remove the system from the pouch
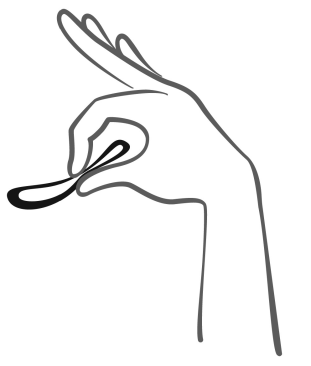
Figure 2
Squeeze the system
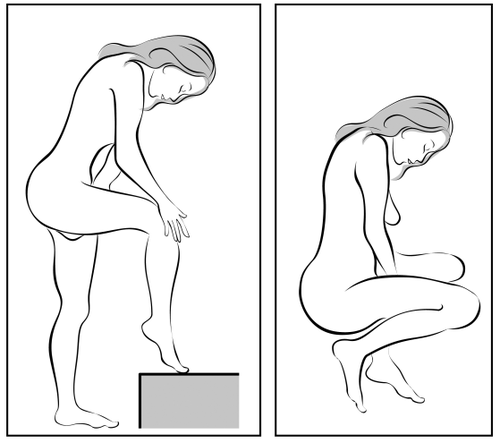
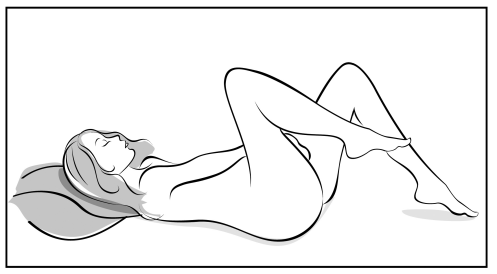
Figure 3
Choose the most comfortable position
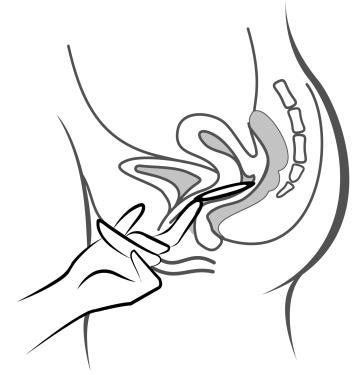
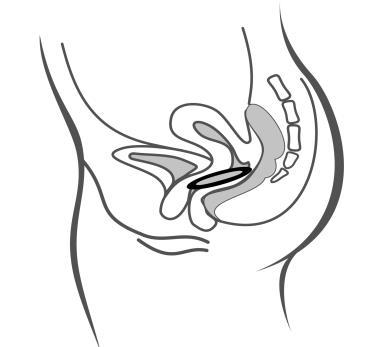
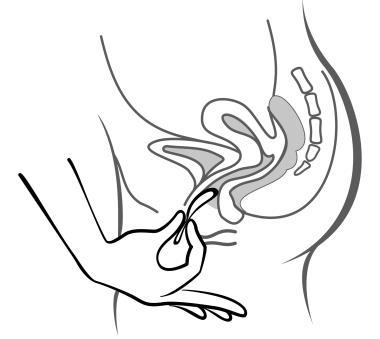
Figure 4A
Figure 4B
Figure 4C
Insert the system into the vagina with one hand (figure 4A), if necessary, with the other hand spreading the labia. Place it inside the vagina so that it does not cause discomfort (figure 4B). Leave the system in the vagina for 3 weeks (figure 4C).
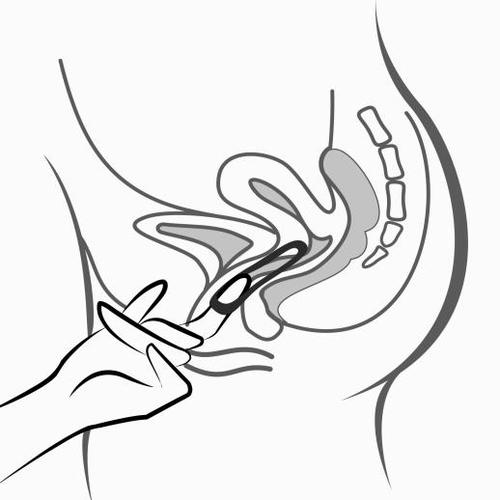
Figure 5
Remove the system from the vagina by hooking your index finger under the edge of the system or by grasping it with your index and middle fingers and pulling it out.
3.2 Three weeks of use, one week of break
- 1. The system should be in the vagina for three weeks without interruption, counting from the day of insertion.
- 2. After three weeks, you should remove it on the same day of the week that it was inserted and at about the same time. For example, if Adaring was inserted on a Wednesday at around 10:00 PM, it should be removed on the Wednesday three weeks later, at around 10:00 PM.
- 3. After removing the system, you should take a one-week break. During this time, you may experience bleeding. It usually starts 2-3 days after removal.
- 4. You should insert a new system exactly one week after the break (on the same day of the week as usual and at about the same time), even if bleeding is still present.
If you delay inserting a new system by more than 3 hours, its contraceptive effectiveness may be reduced. In such a case, you should follow the instructions in section 3.4 "Procedure when, after a one-week break, the patient forgets to insert a new intrauterine system".
If you use Adaring according to the above instructions, subsequent bleedings will occur at approximately the same days of the week.
3.3 When to insert the first Adaring intrauterine system
- The previous cycle did not involve the use of a hormonal contraceptiveInsert Adaring on the first day of your natural cycle (i.e., the first day of your period). Adaring is effective from the moment of insertion. There is no need to use any additional contraceptive methods. You can also start using Adaring between the 2nd and 5th day of your period, but in this case, you should use an additional contraceptive method (such as a condom) during the first 7 days of using Adaring. This recommendation only applies to the first use of Adaring.
- The previous month you used combined hormonal contraceptive pillsYou should start using Adaring no later than the day after the break in taking your current medicine. If your current medicine also has pills that do not contain active substances, you should start using Adaring no later than the day after taking the last pill that does not contain active substances. If you are unsure which pill this is, you should ask your doctor or pharmacist. You should not extend the break in taking your current pills beyond the recommended period. If you have been taking your pills regularly and are sure you are not pregnant, you can stop taking the pills on any day and start using Adaring immediately.
- The previous month you used a transdermal system (patch)You should start using Adaring no later than the day after the break in using the transdermal system. You should not extend the break in using the transdermal system beyond the recommended period. If you have been using the transdermal system regularly and are sure you are not pregnant, you can stop using the transdermal system on any day and start using Adaring immediately.
- The previous month you used a progestogen-only contraceptive (minipill)You can stop taking the minipill on any day and start using Adaring the next day at the same time you would have taken the minipill. During the first 7 days of using Adaring, you should use an additional contraceptive method (such as a condom).
- The previous month you used an implant, injections, or an intrauterine system releasing progestogen [IUS]You should start using Adaring on the day of the next scheduled injection or on the day the implant or intrauterine system releasing progestogen is removed. During the first 7 days of using Adaring, you should use an additional contraceptive method (such as a condom).
- After giving birthAfter giving birth, your doctor may recommend using Adaring only after your first period. Sometimes, you can start using Adaring earlier. Your doctor will advise you when. If you are breastfeeding and want to use Adaring, you should discuss this with your doctor.
doctor.
- After a miscarriageAs advised by your doctor.
3.4 What to do if…
Procedure in case of accidental expulsion of the system from the vagina
Adaring may be accidentally expelled from the vagina, e.g., if it was not inserted correctly, during tampon removal, during intercourse, due to constipation, or due to cervical prolapse. Therefore, you should regularly check that the system is in the vagina (e.g., before and after intercourse).
3.5 Procedure when the patient wants to stop using Adaring
See section 2.5 "Pregnancy and breastfeeding".
3.5 Procedure for stopping the use of Adaring
Adaring can be stopped at any time. If the patient does not want to become pregnant, they should ask their doctor about other contraceptive methods. If they stop using Adaring because they want to become pregnant, they should wait until the first menstruation and then try to conceive. This will help determine the date of birth.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, Adaring can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them. If side effects occur, especially severe and persistent ones, or changes in health that the patient considers related to the use of Adaring, they should consult a doctor. All women using combined hormonal contraceptives have an increased risk of blood clots in the veins (venous thromboembolism) or blood clots in the arteries (arterial thrombosis). For more information on the risk factors associated with the use of combined hormonal contraceptives, see section 2 "Important information before using Adaring". The patient should contact a doctor immediately if they experience any of the following symptoms of angioedema: swelling of the face, tongue, and/or throat, and/or difficulty swallowing. Women using Adaring have reported the following side effects:
- Frequent:may occur in up to 1 in 10 women
- abdominal pain, nausea
- vaginal infections caused by fungi (such as "thrush"); discomfort caused by the presence of the system in the vagina; itching of the genitals; discharge
- headache or migraine; depressive mood; decreased libido
- breast pain; pelvic pain; painful menstruation
- acne
- weight gain
- expulsion of the system.
Uncommon:may occur in up to 1 in 100 women
- vision disorders; dizziness
- bloating; vomiting, diarrhea, or constipation
- fatigue, malaise, or irritability; mood changes; sudden mood changes
- edema (fluid retention in the body)
- urinary tract infections
- problems or pain during urination; urgency to urinate or need to urinate frequently
- discomfort during intercourse, including pain, bleeding, or inconvenience caused by the presence of the system, felt by the partner
- increased blood pressure
- increased appetite
- back pain; muscle cramps; pain in the lower or upper limbs
- decreased skin sensitivity
- breast tenderness or enlargement; fibrocystic breast disease (lumps that can cause swelling or pain in the breast)
- cervicitis; cervical polyps; cervical eversion
- changes in menstrual bleeding (e.g. heavy, prolonged, irregular, or complete absence of menstruation); pelvic discomfort; premenstrual syndrome; uterine cramps
- vaginal infections (fungal or bacterial); burning sensation, unpleasant odor, pain, discomfort, or dryness of the vagina or vulva
- hair loss, rash, itching, or hives
- urticaria
Rare:may occur in up to 1 in 1000 women
- harmful blood clots in a vein or artery, for example: in the leg or foot (e.g. deep vein thrombosis);
in the lungs (e.g. pulmonary embolism); heart attack; stroke; transient ischemic attack or "mini-stroke"; blood clots in the liver, stomach, intestine, kidney, or eye. The risk of blood clots may be higher if the patient has other risk factors (see section 2 for more information on risk factors and symptoms of blood clots).
- galactorrhea (spontaneous flow of milk from the breast, not associated with childbirth or nursing).
Unknown:(frequency cannot be estimated from the available data)
- chloasma (brownish spots on the skin, especially on the face)
- penile disorders in the partner (such as irritation, rash, itching)
- difficulty removing the intrauterine therapeutic system without medical assistance (e.g. due to the system adhering to the vaginal wall)
- vaginal wall damage associated with damage to the intrauterine therapeutic system
Women using combined hormonal contraceptives have reported breast cancer and liver tumors. For more information, see section 2.2 "Warnings and precautions", "Tumors". Adaring may be damaged. For more information, see section 3.4 "Procedure in case of damage to the intrauterine therapeutic system".
Reporting side effects
If any side effects occur, including any side effects not listed in the leaflet, the patient should tell their doctor, pharmacist, or nurse. Side effects can be reported directly to the Department of Adverse Reaction Monitoring of Medicinal Products, Medical Devices, and Biocidal Products, Al. Jerozolimskie 181C, PL: 02-222 Warsaw, Tel: +48 22 49 21 301, Fax: +48 22 49 21 309, website: https://smz.ezdrowie.gov.pl. Side effects can also be reported to the marketing authorization holder. Reporting side effects will help gather more information on the safety of the medicine.
5. How to store Adaring
The medicine should be stored out of sight and reach of children. The patient should contact a doctor if they suspect that a child has been exposed to the hormones in Adaring. There are no special storage temperature recommendations. The medicine should be stored in its original packaging to protect it from light. Adaring should be used (inserted) no later than one month before the expiration date stated on the box and sachet after EXP. The expiration date refers to the last day of the specified month. The batch number is stated on the packaging after the abbreviation "Lot". After opening, the sachet should be kept for later use, e.g. during temporary storage of the intrauterine therapeutic system after removal from the vagina and for its disposal. Adaring should not be used if it has changed color or if there are any signs of deterioration. This medicinal product may pose a risk to the environment. After removing the Adaring intrauterine therapeutic system from the vagina, it should be placed in the sachet, and the sachet should be tightly closed. The closed sachet should then be carefully disposed of in accordance with local requirements (i.e. disposed of with other household waste or taken to a pharmacy for proper disposal) in a way that avoids exposing others. The Adaring intrauterine therapeutic system should not be flushed down the toilet or disposed of in the sewage system. The patient should ask their pharmacist how to dispose of unused medicines. This will help protect the environment.
6. Package contents and other information
What Adaring contains
- The active substances of Adaring are: etonogestrel and ethinylestradiol. Adaring contains 8.25 mg of etonogestrel and 2.60 mg of ethinylestradiol. Etonogestrel and ethinylestradiol are released from the intrauterine therapeutic system at a rate of 0.120 mg and 0.015 mg per day for 3 weeks.
- The other ingredients are: ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer 28% vinyl acetate and polyurethane (a type of plastic that does not dissolve in the body).
What Adaring looks like and what the package contains
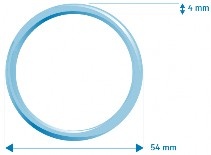
Intrauterine therapeutic system. Adaring is a flexible, transparent, colorless or almost colorless ring with an outer diameter of 54 mm and a cross-sectional diameter of 4 mm. Each intrauterine therapeutic system is packaged in a foil sachet. The sachet is placed in a cardboard box with a leaflet and calendar stickers to help the patient remember when to insert and remove the intrauterine therapeutic system. The package contains: 1 intrauterine therapeutic system, 3 intrauterine therapeutic systems, or 6 intrauterine therapeutic systems. Not all pack sizes may be marketed.
Marketing authorization holder and manufacturer
Marketing authorization holder
Adamed Pharma S.A. Pieńków, ul. M. Adamkiewicza 6A 05-152 Czosnów Tel: +48 22 732 77 00
Manufacturer
Adamed Pharma S.A. Pieńków, ul. M. Adamkiewicza 6A 05-152 Czosnów Laboratorios León Farma, S.A. c/La Vallina s/n, Poligono Industrial Navatejera 24193 - Villaquilambre, León Spain
- Orion Corporation Orion Pharma Orionintie 1 FI-02200 Espoo Finland
This medicinal product is authorized in the Member States of the European Economic Area under the following names:
Netherlands: Nilho 0,120 mg / 0,015 mg per 24 hours, aid for vaginal use Czech Republic: Teyla Finland: Vagiprev 0,120 mg / 0,015 mg per 24 hours, depot preparation for vaginal use Denmark: Vagiprev 0.120 / 0.015 mg per 24 hours Ireland: Etonogestrel / Ethinylestradiol 0,120 / 0,015 mg per 24 hours, vaginal delivery system United Kingdom: SyreniRing 0,120mg / 0,015mg per 24 hours Hungary: Ringinel 0,120 mg / 0,015 mg / 24 hours vaginal drug delivery system Norway: Etonogestrel / Ethinylestradiol Chemo 0,120 mg / 0,015 mg per 24 hours vaginal insert Slovakia: Teyla 0,120 mg / 0,015 mg per 24 hours vaginal insert Romania: Teyla 0,120mg / 0,015 mg / 24 hours vaginal delivery system Poland: Adaring
Date of last revision of the leaflet: 12.2024
- Country of registration
- Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- ImporterAdamed Pharma S.A. Laboratorios Leon Farma, S.A. Orion Corporation
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a licensed doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to AdaringDosage form: System, (0.120 mg + 0.015 mg)/24 hActive substance: vaginal ring with progestogen and estrogenManufacturer: N.V. OrganonPrescription requiredDosage form: System, (0.12 mg + 0.015 mg)/24 hActive substance: vaginal ring with progestogen and estrogenPrescription requiredDosage form: System, (0.120 mg + 0.015 mg)/24 hActive substance: vaginal ring with progestogen and estrogenPrescription not required
Alternatives to Adaring in other countries
The best alternatives with the same active ingredient and therapeutic effect.
Alternative to Adaring in Ukraine
Alternative to Adaring in Spain
Online doctors for Adaring
Discuss dosage, side effects, interactions, contraindications, and prescription renewal for Adaring – subject to medical assessment and local rules.