
NEVIRAPINA TEVA 400 MG COMPRIMIDOS DE LIBERACION PROLONGADA EFG

Cómo usar NEVIRAPINA TEVA 400 MG COMPRIMIDOS DE LIBERACION PROLONGADA EFG
Traducción generada por IA
Este contenido ha sido traducido automáticamente y se ofrece solo con fines informativos. No sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
Ver originalContenido del prospecto
- Introducción
- Qué es Nevirapina Teva 400mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada EFG y para qué se utiliza
- Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
- Cómo tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
- Posibles efectos adversos
- Conservación de Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
- Contenido del envase e información adicional
Introducción
Prospecto:información para el usuario
Nevirapina Teva 400 mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada EFG
Lea todo el prospecto detenidamente antes de empezar a tomar este medicamento,porque contiene información importante para usted.
- Conserve este prospecto, ya que puede tener que volver a leerlo.
- Si tiene alguna duda, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico, o enfermero.
- Este medicamento se le ha recetado solamente a usted, y no debe dárselo a otras personas aunque tengan los mismos síntomas que usted, ya que puede perjudicarles.
- Si experimenta efectos adversos, consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero, incluso si se trata de efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. Ver sección 4.
Contenido del prospecto
- Qué es Nevirapina Teva 400 mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada EFG y para qué se utiliza
- Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
- Cómo tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
- Posibles efectos adversos
- Conservación de Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
- Contenido del envase e información adicional
1. Qué es Nevirapina Teva 400mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada EFG y para qué se utiliza
Nevirapina pertenece a un grupo de medicamentos denominados antirretrovirales, que se utilizan en el tratamiento de la infección por el Virus de la Inmunodeficiencia Humana (VIH).
El principio activo de este medicamento se llama nevirapina. Nevirapina pertenece a una clase de medicamentos anti-VIH llamados inhibidores no nucleósidos de la transcriptasa inversa (INNTIs). La transcriptasa inversa es un enzima que el VIH necesita para multiplicarse. Nevirapina impide el funcionamiento de la transcriptasa inversa. Bloqueando la acción de la transcriptasa inversa, Nevirapina ayuda a controlar la infección por VIH-1.
Nevirapina está indicado en el tratamiento de adultos, adolescentes y niños de tres años de edad o mayores capaces de tragar comprimidos, infectados por VIH-1. Debe tomar Nevirapina junto con otros medicamentos antirretrovirales. Su médico le indicará los medicamentos adecuados para usted.
Nevirapina comprimidos de liberación prolongada únicamente debe usarse después de un tratamiento de dos semanas con otro tipo de medicamento que contenga nevirapina (suspensión o comprimidos de liberación inmediata) a menos que usted esté actualmente en tratamiento con Nevirapina y esté cambiando a la forma de liberación prolongada.
2. Qué necesita saber antes de empezar a tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
NO tomeNevirapina Teva 400 mg
- si es alérgico a nevirapina o a cualquiera de los demás componentes de este medicamento (incluidos en la sección 6 “Composición de Nevirapina Teva”).
- si ha tomado nevirapina con anterioridad y tuvo que interrumpir el tratamiento porque padeció:
- erupción grave en la piel
- erupción en la piel con otros síntomas como por ejemplo:
- fiebre
- formación de ampollas
- llagas en la boca
- inflamación del ojo
- hinchazón de la cara
- hinchazón general
- dificultad para respirar
- dolor muscular o de las articulaciones
- malestar general
- dolor abdominal
- reacciones de hipersensibilidad (alergia)
- inflamación del hígado (hepatitis)
- si padece enfermedad grave del hígado
- si ha tenido que interrumpir el tratamiento con nevirapina en el pasado debido a cambios en la función de su hígado
- si está utilizando algún medicamento que contenga hipérico o hierba de San Juan (Hypericum perforatum). Este producto puede producir que nevirapina deje de funcionar adecuadamente.
Advertencias y precauciones
Consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de empezar a tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg.
Durante las primeras 18 semanas de tratamiento con nevirapina es muy importante que usted y su médico vigilen la aparición de reacciones hepáticas o cutáneas. Estas reacciones pueden llegar a ser graves e incluso suponer un riesgo para la vida. El riesgo de padecer estas reacciones es mayor durante las primeras 6 semanas de tratamiento.
Si experimenta erupción grave o hipersensibilidad (reacciones alérgicas que pueden aparecer en forma de erupción) junto con otros efectos adversos como:
DEBE DEJAR DE TOMAR NEVIRAPINA Y PONERSE EN CONTACTO con su médico INMEDIATAMENTE, ya que estas reacciones pueden suponer un riesgo para la vida o producir la muerte. Si alguna vez experimenta solamente síntomas de erupción leve sin ninguna otra reacción, informe a su médico inmediatamente, quien le indicará si debe dejar de tomar nevirapina. Si experimenta síntomas que sugieran daño en el hígado, tales como:
debe dejar de tomar nevirapina y debe contactar con su médico inmediatamente. Si padece reacciones hepáticas, cutáneas o de hipersensibilidad graves mientras está tomando nevirapina, NO VUELVA A TOMAR NEVIRAPINA sin antes haber consultado a su médico. Debe tomar su dosis de nevirapina tal y como le ha indicado su médico. Esto es especialmente importante durante los primeros 14 días de tratamiento (ver más información en “Cómo tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg”). |
Los siguientes pacientes presentan mayor riesgo de desarrollar problemas en el hígado:
- mujeres
- pacientes infectados de hepatitis B o C
- anomalías en las pruebas de función hepática
- pacientes naïve con mayores recuentos de células CD4 al principio del tratamiento con
nevirapina (mujeres con más de 250 células/mm³, hombres con más de 400 células/mm³)
- pacientes pretratados con carga viral de VIH-1 detectable en plasma y contajes de células CD4
mayores al inicio del tratamiento con nevirapina (mujeres con más de 250 células/mm³,
hombres con más de 400 células/mm³)
En algunos pacientes con infección por VIH (SIDA) avanzada y antecedentes de infección oportunista (enfermedad definitoria de SIDA) pueden aparecer signos y síntomas de inflamación de infeccionespreviaspoco después de iniciar el tratamiento anti-VIH. Se cree que estos síntomas son debidos a una mejoría en la respuesta inmune del organismo, permitiéndole combatir infecciones que estaban presentes sin ningún síntoma aparente. Si usted observa cualquier síntoma de infección, por favor informe a su médico inmediatamente.
Además de las infecciones oportunistas, también pueden aparecer trastornos autoinmunitarios(una afección que ocurre cuando el sistema inmunitario ataca tejido corporal sano) después de que usted haya empezado a tomar medicamentos para el tratamiento de su infección por VIH. Los trastornos autoinmunitarios pueden aparecer muchos meses después del inicio del tratamiento. Si observa cualquier síntoma de infección u otros síntomas como por ejemplo debilidad muscular, debilidad que empieza en las manos y pies y que asciende hacia el tronco del cuerpo, palpitaciones, temblor o hiperactividad, informe a su médico inmediatamentepara recibir el tratamiento necesario.
Pueden producirse cambios en la grasa corporal en pacientes que están recibiendo tratamiento antirretroviral combinado. Consulte a su médico si observa cambios en la grasa corporal (ver sección 4. “Posibles efectos adversos”).
En algunos pacientes que reciben tratamiento antirretroviral combinado puede desarrollarse una
enfermedad de los huesos llamada osteonecrosis(la muerte de tejido óseo causada por la pérdida de aporte de sangre en el hueso). La duración del tratamiento antirretroviral combinado, el uso de corticosteroides, el consumo de alcohol, la debilidad grave del sistema inmune y el índice de masa corporal elevado pueden ser algunos de los numerosos factores de riesgo para desarrollar esta enfermedad. Los síntomas de la osteonecrosis son: rigidez en las articulaciones, dolor y molestias especialmente en cadera, rodilla y hombro, y dificultad de movimiento. Si usted nota cualquiera de estos síntomas, comuníqueselo a su médico.
Si está tomando nevirapina y zidovudina de forma conjunta, informe a su médico porque puede que deba comprobar sus glóbulos blancos.
Notome Nevirapina después de una exposición a VIH a menos que se le haya diagnosticado VIH y su médico le haya indicado hacerlo.
No se debe utilizar prednisona para tratar erupciones asociadas a Nevirapina.
Si está tomando anticonceptivos orales(p. ej. “la píldora”) u otros métodos hormonales de control de la natalidad mientras está en tratamiento con Nevirapina, debe utilizar adicionalmente un método anticonceptivo de barrera (p. ej. preservativos) para prevenir el embarazo y la transmisión del VIH.
Si está recibiendo terapia hormonal post-menopáusica, consulte a su médico antes de tomar este
medicamento.
Si está tomando o si se le receta rifampicina para tratar la tuberculosis, informe a su médico antes de tomar este medicamento con nevirapina.
Los comprimidos de liberación prolongada de nevirapina o partes de los comprimidos se pueden eliminar y ver de forma ocasional en las heces. Estos pueden parecer comprimidos enteros, pero no se ha visto que afecten a la eficacia de nevirapina.
Niños y adolescentes
Nevirapina Teva 400 mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada puede utilizarse en niños si:
- tienen ≥ 8 años de edad y pesan 43,8 kg o más
- tienen más de 3 años de edad y menos de 8 años de edad y pesan 25 kg o más
- tienen una superficie corporal de 1,17 metros cuadrados o superior
Para niños más pequeños está disponible una forma líquida en suspensión oral.
Uso deNevirapina Teva 400 mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada EFGcon otros medicamentos
Informe a su médico o farmacéutico si está utilizando, ha utilizado recientemente o podría tener que utilizar cualquier otro medicamento. Antes de iniciar el tratamiento con nevirapina informe a su médico de todos los demás medicamentos que esté tomando. Es posible que su médico necesite controlar si sus otros medicamentos todavía funcionan y realizar ajustes de dosis. Lea atentamente el prospecto de todos los otros medicamentos anti-VIH que toma en combinación con nevirapina.
Es especialmente importante que informe a su médico si está utilizando o ha utilizado recientemente:
- hipérico o hierba de San Juan (Hypericum perforatum, planta medicinal para el tratamiento de
la depresión)
- rifampicina (medicamento para el tratamiento de la tuberculosis)
- rifabutina (medicamento para el tratamiento de la tuberculosis)
- macrólidos p.ej. claritromicina (medicamento para el tratamiento de infecciones bacterianas)
- fluconazol (medicamento para el tratamiento de infecciones por hongos)
- ketoconazol (medicamento para el tratamiento de infecciones por hongos)
- itraconazol (medicamento para el tratamiento de infecciones por hongos)
- metadona (medicamento utilizado para el tratamiento de la adicción a los opiáceos)
- warfarina (medicamento para reducir la formación de coágulos en sangre)
- anticonceptivos hormonales (p. ej. “la píldora”)
- atazanavir (otro medicamento para el tratamiento de la infección por VIH)
- lopinavir/ritonavir (otro medicamento para el tratamiento de la infección por VIH)
- fosamprenavir (otro medicamento para el tratamiento de la infección por VIH)
- efavirenz (otro medicamento para el tratamiento de la infección por VIH)
- etravirina (otro medicamento para el tratamiento de la infección por VIH)
- rilpivirina (otro medicamento para el tratamiento de la infección por VIH)
- zidovudina (otro medicamento para el tratamiento de la infección por VIH)
- elvitegravir/cobicitstat (otro medicamento para el tratamiento de la infección por VIH)
Su médico controlará cuidadosamente el efecto de nevirapina y de cualquiera de estos medicamentos si los está utilizando a la vez.
Toma deNevirapina Teva 400 mgcon los alimentos y bebidas
No existen restricciones para la toma de nevirapina con los alimentos y bebidas.
Embarazo y lactancia
Si está embarazada, cree que podría estar embarazada o tiene intención de quedarse embarazada, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de utilizar este medicamento.
No se recomiendaque las mujeres que conviven con el VIH den el pecho porque la infección por VIH puede transmitirse al bebé a través de la leche materna.
Si está dando el pecho o piensa en dar el pecho, debe consultarcon su médico lo antes posible.
Conducción y uso de máquinas
Cuando tome nevirapina puede experimentar fatiga. Vaya con precaución cuando participe en
actividades tales como conducir o utilizar herramientas o máquinas. Si experimenta fatiga debe evitar trabajos potencialmente peligrosos como conducir y utilizar herramientas o máquinas.
3. Cómo tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
No debe utilizar nevirapina por su cuenta. Debe utilizarlo con al menos otros dosmedicamentos antirretrovirales. Su médico le recomendará los medicamentos adecuados para usted.
Siga exactamente las instrucciones de administración de este medicamento indicadas por su médico. En caso de duda, consulte de nuevo a su médico o farmacéutico.
Dosis:
Adultos:
La dosis es de un comprimido de nevirapina de 200 mg al día durante los primeros 14 días de tratamiento (periodo “inicial”). Hay otras formulaciones disponibles para este periodo inicial. Después de 14 días, la dosis habitual es de un comprimido de liberación prolongada de 400 mg una vez al día.
Es muy importante que tome solamente un comprimido al día de nevirapina 200 mg durante los primeros 14 días (periodo “inicial”). Si tiene alguna erupción durante este periodo, no empiece a tomar Nevirapina Teva 400 mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada y consulte a su médico. |
Se ha demostrado que el periodo “inicial” de 14 días disminuye el riesgo de padecer erupción en la piel.
Aquellos pacientes que ya estén en tratamiento con comprimidos de liberación inmediata o suspensión oral pueden cambiarse a comprimidos de liberación prolongada sin periodo inicial.
Como Nevirapina siempre debe tomarse en combinación con otros medicamentos antirretrovirales, debe seguir las instrucciones de sus otros medicamentos cuidadosamente. Éstas se proporcionan en los prospectos de estos medicamentos.
Su médico comprobará, si es necesario, la disponibilidad de otras formulaciones de nevirapina, por ejemplo una suspensión oral (para todos los grupos de edad, peso y superficie corporal).
Debe seguir tomando nevirapina todo el tiempo que le indique su médico.
Como se ha explicado anteriormente, en la sección ‘Advertencias y precauciones’, su médico le controlará con pruebas hepáticas y vigilando la aparición de efectos adversos como erupción. Es posible que dependiendo de los resultados, su médico decida interrumpir o suprimir el tratamiento con nevirapina. Asimismo, su médico podría decidir reiniciar el tratamiento a dosis inferiores.
Si padece insuficiencia renalo hepáticade cualquier grado, únicamente tome nevirapina 200 mg comprimidos o nevirapina 50 mg/ 5 ml suspensión oral. Si lo necesitara, su médico valorará estas formulaciones adicionales.
Sólo tome nevirapina comprimidos de liberación prolongada por vía oral. No mastique los comprimidos de liberación prolongada. Puede tomar nevirapina con o sin alimentos.
Si toma másNevirapina Teva 400 mgdel que debe
No tome más nevirapina de lo que le ha prescrito su médico y de lo que está descrito en este prospecto. Actualmente hay poca información sobre los efectos de una sobredosis de nevirapina. Consulte a su médico si ha tomado más nevirapina del que debiera. En caso de sobredosis o ingestión accidental consultar al Servicio de Información Toxicológica, teléfono: 91 562 04 20 e indicar la cantidad ingerida.
Si olvidó tomarNevirapina Teva 400 mg
Procure no olvidar ninguna dosis. Si se da cuenta de que se ha olvidado una dosis dentro de las 12 horas posteriores a la hora programada, tome la dosis olvidada tan pronto como le sea posible. Si han pasado más de 12 horas de la hora programada, solamente tome la próxima dosis en su horario habitual.
Si interrumpe el tratamiento conNevirapina Teva 400 mg
Tomar las dosis a las horas indicadas:
- aumenta en gran manera la eficacia de su combinación de medicamentos antirretrovirales
- disminuye las posibilidades de que la infección por VIH se vuelva resistente a los medicamentos antirretrovirales
Es importante que continúe tomando nevirapina de forma correcta, tal como se ha descrito anteriormente salvo que su médico le indique que debe interrumpir el tratamiento.
Si interrumpe la administración de nevirapina durante más de 7 días, su médico le indicará que comience otra vez con el periodo “inicial” de 14 días con nevirapina comprimidos (como se ha descritonanteriormente), antes de volver a la toma de una dosis diaria con nevirapina comprimidos de liberación prolongada.
Si tiene cualquier otra duda sobre el uso de este medicamento, pregunte a su médico o farmacéutico.
4. Posibles efectos adversos
Durante el tratamiento del VIH puede haber un aumento en el peso corporal y en los niveles de
glucosa y lípidos en la sangre. Esto puede estar en parte relacionado con la recuperación de la salud y con el estilo de vida y en el caso del aumento de los lípidos en la sangre, algunas veces puede ser debido a los medicamentos para el VIH por sí mismos. Su médico le controlará estos cambios.
Al igual que todos los medicamentos, este medicamento puede producir efectos adversos, aunque no todas las personas los sufran.
Como se ha mencionado ya en ‘Advertencias y precauciones’, los efectos adversos más importantes de nevirapina son reacciones cutáneas graves y que suponen un riesgo para la vida y daños graves del hígado. Estas reacciones se producen principalmente durante las primeras 18 semanas de tratamiento con nevirapina. Este es, por lo tanto, un periodo importante que requiere la estrecha monitorización de su médico.
Si observa algún síntoma de erupción, informe a su médico inmediatamente.
Cuando la erupción se produce, normalmente es de leve a moderada. Sin embargo, en algunos pacientes aparece una erupción en forma de reacción cutánea vesicular que puede ser grave o suponer un riesgo para la vida (síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y necrólisis epidérmica tóxica), habiéndose registrado víctimas mortales. La mayoría de los casos de erupción tanto grave como leve/moderada, se producen durante las primeras seis semanas de tratamiento.
Si aparece la erupción y además siente malestar general, debe interrumpir el tratamiento y acudir inmediatamente a su médico.
Pueden producirse reacciones de hipersensibilidad (alergia). Tales reacciones pueden aparecer en forma de anafilaxis (un tipo grave de reacción alérgica) con síntomas como:
- erupción
- hinchazón de la cara
- dificultad para respirar (espasmo bronquial)
- shock anafiláctico
Las reacciones de hipersensibilidad también pueden presentarse como una erupción con otros efectos adversos como:
- fiebre
- formación de ampollas en la piel
- llagas en la boca
- inflamación del ojo
- hinchazón de la cara
- hinchazón general
- dificultad para respirar
- dolor muscular o de las articulaciones
- disminución del número de glóbulos blancos de la sangre (granulocitopenia)
- malestar general
- problemas graves del hígado o los riñones (fallo del hígado o los riñones)
Si experimenta erupción y cualquiera de los demás efectos adversos de una reacción de hipersensibilidad (alergia), informe a su médico inmediatamente. Estas reacciones pueden producir la muerte.
Se han descrito anomalías de la función hepática con el uso de Nevirapina. Esto incluye algunos casos de inflamación del hígado (hepatitis), que puede ser repentina e intensa (hepatitis fulminante) y fallo hepático, pudiendo ambas ser mortales.
Informe a su médico si experimenta cualquiera de los siguientes síntomas clínicos de daño en el hígado:
- pérdida de apetito
- malestar general (náuseas)
- vómitos
- coloración amarilla de la piel (ictericia)
- dolor abdominal
Los efectos adversos descritos a continuación se han presentado en pacientes a los que se administró nevirapina 200 mg comprimidos durante la fase inicial de 14 días:
Frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 10 personas):
- erupción
- fiebre
- dolor de cabeza
- dolor abdominal
- malestar general (náuseas)
- diarrea
- sensación de cansancio (fatiga)
Poco frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 personas):
- reacciones alérgicas (hipersensibilidad)
- reacciones alérgicas caracterizadas por erupción, inflamación de la cara, dificultad para
respirar (espasmo bronquial) o shock anafiláctico
- reacción medicamentosa con síntomas sistémicos (reacción medicamentosa con eosinofilia y
síntomas sistémicos)
- inflamación del hígado intensa y repentina (hepatitis fulminante)
- erupciones de la piel graves y potencialmente mortales (Síndrome de Stevens-Johnson
/necrólisis epidérmica tóxica)
- coloración amarilla de la piel (ictericia)
- urticaria
- líquido bajo la piel (angioedema)
- vómitos
- dolor muscular (mialgia)
- dolor articular (artralgia)
- disminución del número de células blancas de la sangre (granulocitopenia)
- anomalías en las pruebas de función del hígado
- disminución del fósforo en sangre
- aumento de la presión arterial
Raros (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas):
- inflamación del hígado (hepatitis)
- disminución del número de células rojas de la sangre (anemia)
Los efectos adversos descritos a continuación se han presentado en pacientes a los que se administró nevirapina comprimidos de liberación prolongada una vez al día en la fase de mantenimiento:
Frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 10 personas):
- erupción
- dolor de cabeza
- dolor abdominal
- malestar general (náuseas)
- inflamación del hígado (hepatitis)
- sensación de cansancio (fatiga)
- anomalías en las pruebas de función del hígado
- disminución del fósforo en sangre
- aumento de la presión arterial
- vómitos
- heces blandas (diarrea)
Poco frecuentes (pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 personas):
- reacciones alérgicas (hipersensibilidad)
- reacciones alérgicas caracterizadas por erupción, inflamación de la cara, dificultad para
respirar (espasmo bronquial) o shock anafiláctico
- reacción medicamentosa con síntomas sistémicos (reacción medicamentosa con eosinofilia y
síntomas sistémicos)
- inflamación del hígado intensa y repentina (hepatitis fulminante)
- erupciones de la piel graves y potencialmente mortales (Síndrome de Stevens-Johnson
/necrólisis epidérmica tóxica)
- disminución del número de células rojas de la sangre (anemia)
- disminución del número de células blancas de la sangre (granulocitopenia)
- coloración amarilla de la piel (ictericia)
- urticaria
- líquido bajo la piel (angioedema)
- dolor muscular (mialgia)
- dolor articular (artralgia)
- fiebre
Cuando se ha utilizado nevirapina en asociación con otros medicamentos antirretrovirales, se han registrado también los siguientes acontecimientos:
- disminución del número de glóbulos rojos o plaquetas
- inflamación del páncreas
- disminución o anomalías en las sensaciones cutáneas
Estos efectos están generalmente asociados con otros agentes antirretrovirales y pueden producirse cuando nevirapina se usa en asociación con otros agentes; sin embargo, es poco probable que estos efectos se deban al tratamiento con nevirapina.
Otros efectos adversos en niños y adolescentes
Puede producirse una disminución de los glóbulos blancos (granulocitopenia), más frecuentemente en niños. La disminución de los glóbulos rojos (anemia), que puede estar relacionada con el tratamiento con nevirapina, también es más frecuente en niños. Al igual que ocurre con los síntomas de erupción, informe a su médico de cualquier efecto adverso.
Comunicación de efectos adversos
Si experimenta cualquier tipo de efecto adverso, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de posibles efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. También puede comunicarlos directamente a través del sistema nacional de farmacovigilancia de medicamentos de Uso Humano www.notificaRAM.es Mediante la comunicación de efectos adversos usted puede contribuir a proporcionar más información sobre la seguridad de este medicamento.
5. Conservación de Nevirapina Teva 400 mg
Mantenereste medicamentofuera de la vista y del alcance de los niños.
No utilice este medicamento después de la fecha de caducidad que aparece en la caja y el blíster o la etiqueta del frasco después de “CAD”. La fecha de caducidad es el último día del mes que se indica.
Este medicamento no requiere condiciones especiales de conservación
Los medicamentos no se deben tirar por los desagües ni a la basura. Deposite los envases y los medicamentos que no necesita en el punto SIGRE de la farmacia. En caso de duda pregunte a su farmacéutico cómo deshacerse de los envases y de los medicamentos que no necesita. De esta forma ayudará a proteger el medio ambiente.
6. Contenido del envase e información adicional
Composición deNevirapina Teva 400 mg
- El principio activo es nevirapina.
Cada comprimido de liberación prolongada contiene 400 mg de nevirapina
- Los demás componentes son celulosa microcristalina, povidona, óxido de polietileno, sílice coloidal anhidra y estearato de magnesio.
Aspecto del producto y contenido del envase
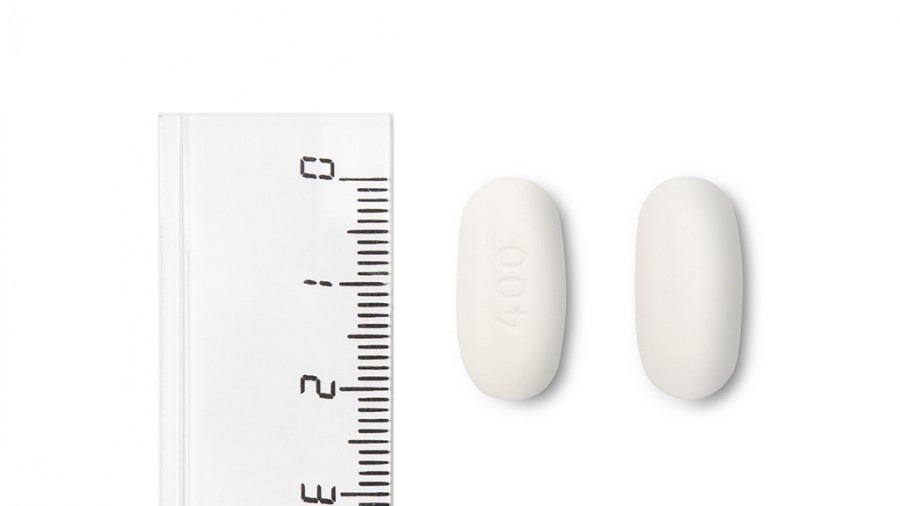
Nevirapina Teva 400 mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada EFG son comprimidos de color blanco a blanquecino, ovalados y biconvexos, de aproximadamente 20,5 mm de largo y 10 mm de ancho, grabadas con “400” en una cara y plana en la otra.
Blísters de aluminio conteniendo 10, 10x1, 30, 30x1, 60, 60x1, 90, 90x1, 100 y 100x1 comprimidos de liberación prolongada y frasco de polietileno de alta densidad (HDPE) que contiene 30 comprimidos de liberación prolongada.
Puede que solamente estén comercializados algunos tamaños de envases.
Titular de la autorización de comercialización
TEVA PHARMA, S.L.U.
C/ Anabel Segura, 11, Edificio Albatros B, 1ª planta,
Alcobendas, Madrid
28108 España
Responsables de la fabricación
TEVA Gyógyszergyár Zrt.
Pallagi út 13, Debrecen,
4042 Hungría
ó
Teva Operations Poland Sp. z.o.o
ul. Mogilska 80. , Kraków
31-546 Polonia
Este medicamento está autorizado en los estados miembros del Espacio Económico Europeo con los siguientes nombres:
DENevirapin-ratiopharm 400 mg Retardtabletten
DKNevirapine Teva B.V.
ESNevirapina Teva 400mg comprimidos de liberación prolongada EFG
FRNevirapine Teva LP 400mg, comprimé à liberation prolongée
ITNevirapina Teva Italia
NLNevirapine retard Teva 400 mg, tabletten met verlengde afgifte
PTNevirapina Teva
Fecha de la última revisión de esteprospecto:Abril 2023
Otras fuentes de información
La información detallada de este medicamento está disponible en la página web de la Agencia Española de Medicamentos y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
- País de registro
- Principio activo
- Requiere recetaSí
- Fabricante
- Esta información es de carácter general y no sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
- Alternativas a NEVIRAPINA TEVA 400 MG COMPRIMIDOS DE LIBERACION PROLONGADA EFGForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO LIBERACION MODIFICADA, 400 mgPrincipio activo: NevirapinaFabricante: Aurovitas Spain, S.A.U.Requiere recetaForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO, 200 mgPrincipio activo: NevirapinaFabricante: Kern Pharma S.L.Requiere recetaForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO, 200 mgPrincipio activo: NevirapinaFabricante: Laboratorios Normon S.A.Requiere receta
Médicos online para NEVIRAPINA TEVA 400 MG COMPRIMIDOS DE LIBERACION PROLONGADA EFG
Comenta la dosis, los posibles efectos secundarios, interacciones, contraindicaciones o la revisión de receta de NEVIRAPINA TEVA 400 MG COMPRIMIDOS DE LIBERACION PROLONGADA EFG, sujeto a valoración médica y a la normativa local.
Preguntas frecuentes















