KALETRA (80 MG + 20 MG)/ML SOLUCION ORAL

Cómo usar KALETRA (80 MG + 20 MG)/ML SOLUCION ORAL
Traducción generada por IA
Este contenido ha sido traducido automáticamente y se ofrece solo con fines informativos. No sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
Ver originalContenido del prospecto
Introducción
Prospecto: información para el usuario
Kaletra (80 mg+ 20 mg)/ml solución oral
(lopinavir + ritonavir)
Lea todo el prospecto detenidamente antes de empezar a tomar este medicamento, porque contiene información importante para usted o para su hijo.
- Conserve este prospecto, ya que puede tener que volver a leerlo.
- Si tiene alguna duda, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico.
- Este medicamento se le ha recetado solamente a usted o a su hijo y no debe dárselo a otras personas aunque tengan los mismos síntomas que usted, ya que puede perjudicarles.
- Si experimenta efectos adversos, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico incluso si se trata de efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto.Ver sección 4.
Contenido del prospecto
- Qué es Kaletra y para qué se utiliza
- Qué necesita saber antes de que usted o su hijo tomen Kaletra
- Cómo tomar Kaletra
- Posibles efectos adversos
- Conservación de Kaletra
- Contenido del envase e información adicional
1. Qué es Kaletra y para qué se utiliza
- Su médico le ha recetado Kaletra para ayudar a controlar su infección por el virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH). Esto es posible ya que Kaletra actúa impidiendo que la infección se extienda rápidamente.
- Kaletra no es una cura para la infección por VIH o el SIDA.
- Kaletra se utiliza en niños de 14 días de edad y mayores, en adolescentes y adultos infectados con el VIH, el virus causante del SIDA.
- Kaletra contiene los principios activos lopinavir y ritonavir. Kaletra es un medicamento antirretroviral que pertenece al grupo de los llamados inhibidores de la proteasa.
- Kaletra se receta para el uso en combinación con otros medicamentos antivirales. Su médico le informará y decidirá qué medicamentos son mejores en su caso.
2. Qué necesita saber antes de que usted o su hijo tomen Kaletra
No tome Kaletra:
- si es alérgico a lopinavir, ritonavir o a alguno de los demás componentes de este medicamento (incluidos en la sección 6).
- si tiene problemas graves de hígado.
No tome Kaletra con ninguno de los siguientes medicamentos:
- astemizol o terfenadina (normalmente utilizados para tratar los síntomas de la alergia – estos medicamentos pueden no requerir receta médica);
- midazolam oral (tomado por la boca), triazolam (usados para aliviar la ansiedad y/o los problemas del sueño);
- pimozida (usado para tratar la esquizofrenia);
- quetiapina (utilizado para tratar la esquizofrenia, el trastorno bipolar y el trastorno depresivo mayor);
- lurasidona (utilizado para tratar la depresión);
- ranolazina (utilizado para tratar el dolor crónico en el pecho [angina de pecho]);
- cisaprida (usado para aliviar ciertos problemas de estómago);
- ergotamina, dihidroergotamina, ergonovina y metilergonovina (usados para tratar los dolores de cabeza);
- amiodarona, dronedarona (usados para tratar alteraciones del ritmo cardiaco);
- lovastatina, simvastatina (usadas para disminuir el colesterol en sangre);
- lomitapida (usado para disminuir el colesterol en sangre);
- alfuzosina (usada en hombres para tratar los síntomas del agrandamiento de próstata (hiperplasia prostática benigna (HPB));
- ácido fusídico (usado para tratar infecciones de la piel causadas por la bacteria Staphylococcus como impétigo y dermatitis infectada). El ácido fusídico se usa también para tratar infecciones a largo plazo de los huesos y las articulaciones llevadas bajo supervisión médica (ver Uso de Kaletra con otros medicamentos);
- colchicina (medicamento utilizado para tratar la gota). Si usted tiene problemas de hígado o riñón (ver sección Otros medicamentos y Kaletra);
- elbasvir/grazoprevir (utilizados para tratar la hepatitis crónica por virus C [VHC]);
- ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir con o sin dasabuvir (utilizados para tratar la hepatitis crónica por virus C [VHC]);
- neratinib (utilizado para tratar el cáncer de mama);
- avanafilo o vardenafilo (utilizado para tratar la impotencia);
- sildenafilo usado para el tratamiento de la hipertensión pulmonar (presión arterial elevada en la arteria pulmonar). Se puede usar el sildenafilo para el tratamiento de la disfunción eréctil bajo supervisión médica (ver sección Otros medicamentos y Kaletra);
- productos que contienen hierba de San Juan (Hypericum perforatum).
Para más información sobre otros medicamentos que requieren precauciones especiales consulte la lista de medicamentos abajo incluida en“Otros medicamentos y Kaletra”.
Si actualmente está tomando cualquiera de estos medicamentos, consulte a su médico por si es necesario cambiar su tratamiento de las otras patologías o su tratamiento antirretroviral.
Advertencias y precauciones
Consulte a su médico o farmacéutico antes de empezar a tomar Kaletra.
Información importante
- Las personas que toman Kaletra pueden aún desarrollar infecciones u otras enfermedades asociadas con el VIH y el SIDA. Por lo tanto, es importante que permanezca bajo la supervisión de su médico mientras está tomando Kaletra.
- A pesar de que el tratamiento antirretroviral efectivo reduzca el riesgo de transmisión, mientras esté tomando este medicamento aún puede transmitir el VIH a los demás. Consulte a su médico sobre qué precauciones son necesarias para evitar infectar a otras personas.
Informe a su médico si usted o su hijo padecen o han padecido
- Hemofiliatipo A y B, ya que Kaletra puede incrementar el riesgo de hemorragia.
- Diabetesya que se han notificado aumentos de azúcar en sangre en pacientes que estaban tomando Kaletra.
- Antecedentes de problemas de hígado, ya que los pacientes con antecedentes de enfermedad de hígado, incluyendo hepatitis B o C crónica, tienen un riesgo mayor de sufrir efectos adversos hepáticos graves y potencialmente mortales.
Informe a su médico si usted o su hijo sufren
- Náuseas, vómitos, dolor abdominal, dificultad para respirar y debilidad grave de los músculos en las piernas y en los brazos, ya que estos pueden ser síntomas de niveles de ácido láctico incrementado.
- Sed, orina frecuente, visión borrosa o pérdida de peso, ya que esto puede ser indicativo de elevados niveles de azúcar en sangre.
- Náuseas, vómitos, dolor abdominal ya que grandes aumentos en la cantidad de triglicéridos (grasas en sangre) se consideran un factor de riesgo para la pancreatitis (inflamación del páncreas) y los síntomas descritos pueden sugerir esta condición.
- En algunos pacientes con infección por VIH avanzada y antecedentes de infecciones oportunistas, se pueden presentar signos y síntomas de inflamación de infecciones previas poco después de iniciar el tratamiento anti-VIH. Se cree que estos síntomas son debidos a una mejoría en la respuesta inmune del organismo, permitiéndole combatir infecciones que estaban presentes sin síntomas aparentes.
- Además de las infecciones oportunistas, puede sufrir también transtornos autoinmunes (un problema que ocurre cuando el sistema inmune ataca el tejido de un cuerpo sano) después de que empiece a tomar medicamentos para el tratamiento de su infección por VIH. Los trastornos autoinmunes pueden aparecer varios meses después del comienzo del tratamiento. Si usted observa cualquier síntoma de infección u otros síntomas como debilidad muscular, debilidad que empieza por las manos y los pies y que va subiendo por el tronco, palpitaciones, temblor o hiperactividad, por favor informe a su médico de inmediato para buscar el tratamiento necesario.
- Rigidez en las articulaciones, dolor y molestias(especialmente en cadera, rodilla y hombro) y dificultad de movimiento, ya que algunos pacientes que toman estos medicamentos pueden desarrollar una enfermedad de los huesos llamada osteonecrosis (muerte del tejido oseo provocada por la pérdida de aporte de sangre al hueso). Entre los numerosos factores de riesgo para desarrollar esta enfermedad se encuentran la duración del tratamiento antirretroviral combinado, el uso de corticosteroides, el consumo de alcohol, la inmunodepresión grave (disminución en la actividad del sistema inmune) y el índice de masa corporal elevado.
- Dolor muscular, molestias o debilidad, particularmente en combinación con estos medicamentos. En raras ocasiones estas alteraciones musculares han sido graves.
- Síntomas de mareo, sensación de mareo, desmayos o sensación de latidos anormales del corazón. Kaletra puede provocar cambios en el ritmo cardíaco y la actividad eléctrica de su corazón. Estos cambios pueden verse en un ECG (electrocardiograma).
Otros medicamentos y Kaletra
Informe a su médico o farmacéutico si usted o su hijo están tomando, han tomado recientemente o pudieran tener que tomar cualquier otro medicamento.
- antibióticos (ej. rifampicina, rifabutina, claritromicina);
- medicamentos anticancerígenos (ej. abemaciclib, afatinib, apalutamida, ceritinib, encorafenib, ibrutinib, venetoclax, la mayoría de los inhibidores de la tirosina quinasa como dasatinib y nilotinib, y también la vincristina y la vinblastina);
- anticoagulantes (ej. warfarina, rivaroxaban, vorapaxar);
- antidepresivos (ej. trazodona, bupropión);
- medicamentos antiepilépticos (ej. carbamazepina, fenítoina, fenobarbital, lamotrigina y valproato);
- medicamentos para tratar infecciones por hongos (ej. ketoconazol, itraconazol, voriconazol);
- medicamentos contra la gota (ej. colchicina). Usted no debe tomar Kaletra con colchicina si tiene problemas de hígado o riñón ( ver también “No tome Kaletra” más arriba);
- medicamentos para tratar la turbeculosis (ej. bedaquilina, delamanida);
- medicamentos antivirales usados en el tratamiento de la infección crónica por el virus de la hepatitis C (VHC) en adultos (ej. glecaprevir/pibrentasvir, simeprevir y sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir);
- medicamentos para la disfunción eréctil (ej. sildenafilo y tadalafilo);
- ácido fusídico usado en el tratamiento a largo plazo de infecciones de los huesos y las articulaciones (ej. osteomielitis);
- medicamentos para el corazón incluyendo:
- digoxina;
- antagonistas de los canales del calcio (ej. felodipino, nifedipino, nicardipino);
- medicamentos usados para corregir el ritmo cardíaco (ej. bepridil, lidocaína sistémica, quinidina);
- antagonista HIV CCR5 (ej. maraviroc)
- inhibidor integrasa HIV-1 (ej. raltegravir)
- levotiroxina (usado para tratar problemas de tiroides);
- medicamentos utilizados para disminuir el colesterol en sangre (ej. atorvastatina, lovastatina, rosuvastatina o simvastatina);
- medicamentos usados para tratar el asma y otros problemas relacionados con los pulmones, como la enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) (ej. salmeterol);
- medicamentos usados para tratar la hipertensión pulmonar arterial (alta presión sanguínea en la arteria pulmonar) (ej.bosentan, riociguat, sildenafilo, tadalafilo);
- medicamentos que afectan al sistema immunológico (ej. ciclosporina, sirolimus (rapamicina), tacrolimus);
- medicamentos usados para dejar de fumar (ej. bupropión);
- analgésicos (ej. fentanilo);
- medicamentos similares a la morfina (ej. metadona);
- anticonceptivos orales o uso de parches anticonceptivos para evitar el embarazo (ver sección “Anticonceptivos” más abajo);
- inhibidores de la proteasa (ej. fosamprenavir, indinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, tripanavir);
- sedantes (ej. midazolam inyectable);
- esteroides (ej. budesonida, dexametasona, propionato de fluticasona, etinilestradiol, triamcinolona);
- medicamentos que interaccionan con el alcohol (ej. disulfiram).
Para más información sobre otros medicamentos que no debe tomar si está tomando Kaletra consulte la lista de medicamentos arriba incluida en“No tome Kaletra con ninguno de los siguientes medicamentos”.
Informe a su médico o farmacéutico si usted o su hijo están tomando, han tomado recientemente o pudieran tener que tomar otros medicamentos, incluso los adquiridos sin receta.
Medicamentos para la disfunción eréctil (ej. avanafilo, vardenafilo, sildenafilo y tadalafilo)
- No tome Kaletrasi está tomando actualmente avanafilo o vardenafilo.
- No debe tomar Kaletra junto con sildenafilo cuando se usa para el tratamiento de la hipertensión pulmonar (alta presión sanguínea en la arteria pulmonar) (ver también la sección de arriba No tome Kaletra).
- Si está tomando sildenafilo o tadalafilo y Kaletra juntos, podría tener el riesgo de reacciones adversas como una disminución de la presión sanguínea, desmayos, cambios de la visión y una erección del pene que dure más de 4 horas. Si la erección del pene durase más de 4 horas, debe acudir inmediatamenteal médico para evitar un daño permanente del pene. Su médico puede explicarle estos síntomas.
Anticonceptivos
- Si está tomando anticonceptivos orales o un parche anticonceptivo para evitar un embarazo, debe utilizar un tipo de contracepción adicional o diferente (p. ej. preservativo), ya que Kaletra puede reducir la eficacia de los anticonceptivos orales y los parches.
- Kaletra no reduce el riesgo de transmisión del VIH a otros. Debe usar las precauciones apropiadas (p. ej. usando un preservativo) para prevenir la transmisión de la enfermedad por contacto sexual.
Embarazo y lactancia
- Si está embarazada o en periodo de lactancia, cree que podría estar embarazada o tiene intención de quedarse embarazada, consulte a su médico inmediatamenteantes de utilizar este medicamento.
- Si usted está embarazada o en periodo de lactancia, consulte con su médico o farmacéutico antes de tomar este medicamento porque contiene propilenglicol y alcohol. Las embarazadas o las madres en período de lactancia no deben tomar Kaletra solución oral a no ser que específicamente se lo recomiende el médico.
- Se recomienda que las mujeres infectadas por VIH no den el pecho a sus hijos ya que existe la posibilidad de que el niño pueda infectarse con el VIH por la leche materna.
Conducción y uso de máquinas
No se han realizado estudios específicos de los posibles efectos de Kaletra sobre la capacidad para conducir y utilizar máquinas. No conduzca ni utilice máquinas si experimenta algún efecto adverso (p. ej. náuseas) que pueda afectar a su capacidad para hacerlo de forma segura. Consulte a su médico.
Kaletra contiene 42% v/v de etanol. La cantidad de alcohol en este medicamento puede afectar a su capacidad para conducir o usar máquinas y puede afectar a su juicio y tiempos de reacción.
Información importante sobre algunos de los componentes de Kaletra
Kaletra contiene 42% v/v de alcohol y 15% de propilenglicol p/v. Cada ml de Kaletra solución oral contiene 356,3 mg de alcohol y 152,7 mg de propilenglicol. El alcohol y el propilenglicol son potencialmente dañinos para aquellos que padecen enfermedades hepáticas, enfermedades renales, alcoholismo, epilepsia, enfermedad o daño cerebral, así como para embarazadas y niños. Estos pueden modificar o aumentar los efectos de otros medicamentos.
En la(s) dosis recomendada(s) para adultos de este medicamento, la concentración estimada de alcohol en sangre en su cuerpo es de aproximadamente 0,002 - 0,01 g/dL. Esto es similar a un adulto que ha bebido 4-22 ml de cerveza o 1-4 ml de vino.
Otros medicamentos también pueden contener alcohol y el alcohol se puede consumir en alimentos y bebidas. Los efectos combinados pueden conducir a un aumento de los niveles de alcohol en la sangre y aumentar los efectos secundarios del alcohol.
Este medicamento contiene hasta 0,8 g de fructosa por dosis cuando se administra según las dosis recomendadas. Esto puede no ser adecuado en intolerancia hereditaria a la fructosa. Debido a que puede existir la posibilidad de intolerancia no detectada a la fructosa, el medicamento debería administrarse a bebés y niños solamente después de consultar con el médico.
Kaletra contiene glicerol que es dañino en dosis altas. Puede producir dolor de cabeza y molestias gastrointestinales y diarrea.
Kaletra contiene aceite de ricino polioxil 40 hidrogenado. A dosis altas puede producir náusea, vómito, cólicos y purga grave. No se debe administrar cuando existe obstrucción intestinal.
Kaletra contiene potasio como acesulfame potásico que puede ser dañino en personas con una dieta baja en potasio. Un contenido alto de potasio en sangre puede producir molestias en el estómago y diarrea.
Kaletra contiene sodio como sacarina sódica, cloruro sódico y citrato sódico, que puede ser dañino en personas con una dieta baja en sodio.
3. Cómo tomar Kaletra
Kaletra está recomendado para su uso en adultos y niños de 14 días de edad y mayores, que estén infectados por VIH.
Tenga cuidado cuando se administre a niños. La dosis debe ser menor de 5 ml dos veces al día en niños que pesan menos de 40 kg.
Si usted o su hijo es capaz de tragar comprimidos, Kaletra también se distribuye como 200 mg de lopinavir y 50 mg de ritonavir en comprimidos recubiertos y como 100 mg de lopinavir y 25 mg de ritonavir en comprimidos recubiertos.
Tome siempre este medicamento exactamente como le ha dicho su médico.Consulte a su médico o farmacéutico si tiene dudas sobre cómo tiene que tomar su medicamento.
Cómo y cuándo se debe tomar Kaletra
Para niños de 14 días y mayores y con peso de hasta 15 kg
- Su médico decidirá la dosis adecuada según la altura y el peso del niño.
- Es importante que todas las dosis de Kaletra solución oral se tomen con alimentos.
- Use la jeringa de dosificación oral de 2 mlproporcionada para medir la dosis.
Para niños con peso superior a 15 kg
- El médico decidirá la dosis correcta basándose en la estatura y el peso del niño.
- Es importante que todas las dosis de Kaletra solución oral se tomen con alimentos.
- Use, para medir la dosis, la jeringa de dosificación de 5 mlproporcionada.
Uso en adultos
- La dosis habitual en adultos es de 5 ml de solución oral dos veces al día, ej. cada 12 horas, en combinación con otros medicamentos contra el VIH. Su médico le recomendará la cantidad de Kaletra que debe tomar.
- Es importante que todas las dosis de Kaletra solución oral se tomen con alimentos.
- Use, para medir la dosis, la jeringa de dosificación de 5 mlproporcionada.
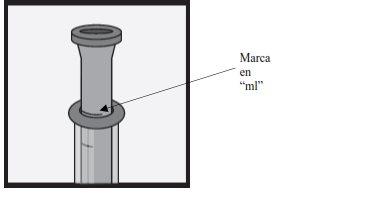
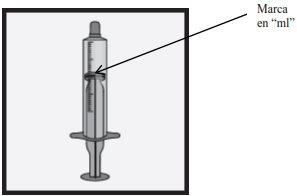
¿Cómo mido la dosis correcta?
- Si la dosis es hasta 2 ml – use la jeringa de dosificación oral de 2mlpara preparar una dosis.
- Si la dosis está entre 2 ml y 5 ml – use la jeringa de dosificación oral de 5mlpara preparar una dosis.
Compruebe con su farmacéutico que usted tiene el tamaño correcto de jeringa. Si usted no está seguro de cómo usar la jeringa de dosificación oral consulte a su médico, farmacéutico o enfermero. Ellos le dirán cómo usar la jeringa correctamente.
No agite el frasco – esto es porque pueden formarse burbujas de aire que afectarán a lo bien que pueda medir la dosis.
Abra la tapa, diseñada a prueba de niños, apretándola con la palma de la mano y girándola en el sentido contrario de las agujas del reloj o en la dirección de la flecha en la parte de arriba de la tapa. Si tiene problemas para abrir el frasco, consulte a su farmacéutico.
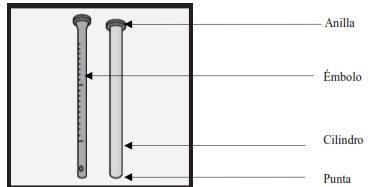
Usando la jeringa de dosificación oral de hasta 2 ml
La jeringa tiene dos partes principales, un 'émbolo' y un 'cilindro'. En esta imagen hemos sacado el émbolo para que pueda ver cada parte claramente. |
|
|
|
Vuelva a colocar la tapa del frasco después de cada dosis. |
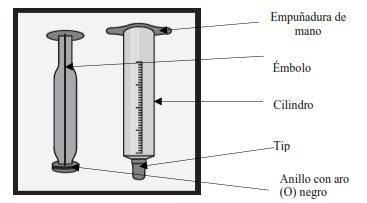
Usando la jeringa de dosificación oral de 5 ml para dosis superiores a 2 ml
La jeringa tiene dos partes principales, un 'émbolo' y un 'cilindro'. En esta imagen hemos sacado el émbolo para que pueda ver cada parteclaramente. |
|
|
|
|
Vuelva a colocar la tapa del frasco después de cada dosis.
Después de la administración de cada dosis de Kaletra, separar el émbolo del cuerpo de la jeringa. Lavar el émbolo y la jeringa con jabón lavavajillas y agua templada, tan pronto como pueda; puede dejarlos en remojo en agua jabonosa hasta 15 minutos. Aclarar la jeringa y el émbolo con agua limpia.
Poner el émbolo dentro de la jeringa y cargar y descargar varias veces con agua del grifo para aclararla. Dejar secar completamente la jeringa antes de usarla de nuevo.
No use las jeringas dosificadoras proporcionadas con Kaletra solución oral para administrar cualquier otro medicamento que usted o su hijo estén tomando.
Si usted o su hijo toman más Kaletra del que debieran
- Si se da cuenta que ha tomado más Kaletra de lo indicado, informe a su médico inmediatamente.
- Si no puede contactar con su médico, acuda al hospital.
Si usted o su hijo olvidaron tomar Kaletra
- Si se da cuenta de que ha olvidado tomar una dosis dentro de las 6 horas desde la hora habitual de su toma, tómela tan pronto como le sea posible y después continúe con la dosificación normal tomando la siguiente dosis a la hora que le corresponda tal y como le haya recetado su médico.
- Si han pasado más de 6 horas desde la hora habitual de su toma de dosis, no tome la dosis olvidada. Tome la siguiente dosis a su hora habitual. No tome una dosis doble para compensar las dosis olvidadas.
Si usted o su hijo dejan de tomar Kaletra
- No deje de tomar o cambie su dosis diaria de Kaletra sin consultar primero con su médico.
- Kaletra debe tomarse dos veces cada día para ayudar a controlar el VIH, independientemente de la mejoría que sienta.
- Tomar Kaletra como le han recomendado es la mejor manera de retrasar el desarrollo de resistencias al medicamento.
- Si una reacción adversa le impidiese tomar Kaletra como le han indicado dígaselo a su médico rápidamente.
- Tenga siempre una cantidad suficiente de Kaletra para no quedarse sin medicamento. Cuando viaje o necesite estar en el hospital asegúrese de que tiene la cantidad suficiente hasta que lo pueda obtener de nuevo.
Continúe tomando este medicamento hasta que su médico se lo indique.
4. Posibles efectos adversos
Al igual que todos los medicamentos, Kaletra puede producir efectos adversos, aunque no todas las personas los sufran. Es difícil distinguir entre los efectos adversos producidos por Kaletra y los de otros medicamentos que esté tomando al mismo tiempo o los derivados de las complicaciones de la infección por VIH.
Durante el tratamiento del VIH puede haber un aumento en el peso y en los niveles de glucosa y lípidos en la sangre. Esto puede estar en parte relacionado con la recuperación de la salud y con el estilo de vida y en el caso de los lípidos en la sangre, algunas veces a los medicamentos para el VIH por sí mismos. Su médico le controlará estos cambios.
Los siguientes efectos adversos han sido notificados por pacientes que tomaron este medicamento.Debe informar a su médico rápidamente sobre éstos o cualquier otro síntoma. Acuda al médico si persisten o empeoran.
Muy frecuentes:pueden afectar a más de 1 de cada 10 personas:
- diarrea;
- náuseas;
- infección del tracto respiratorio superior;
Frecuentes:pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 10 personas:
- inflamación del páncreas;
- vómitos, aumento de tamaño del abdomen, dolor en la zona superior e inferior del estómago, flatulencias pasajeras, indigestión, disminución del apetito, reflujo desde su estómago a su esófago que puede causar dolor;
- Informe a su médico si experimenta náuseas, vómitos o dolor abdominal, ya que pueden ser síntomas de pancreatitis (inflamación del páncreas).
- hinchazón o inflamación del estómago, intestino y colon;
- aumento de sus niveles de colesterol en sangre, aumento de sus niveles de triglicéridos (un tipo de grasa) en sangre, tensión alta;
- descenso de la capacidad del cuerpo para metabolizar azúcar como la diabetes mellitus, pérdida de peso;
- número bajo de góbulos rojos, número bajo de glóbulos blancos que suelen emplearse para combatir las infecciones;
- erupción, eczema, acumulación de escamas de piel grasa;
- mareo, ansiedad, dificultad para dormir;
- sensación de cansancio, pérdida de fuerzas y energía, dolor de cabeza incluyendo migraña;
- hemorroides;
- inflamación del hígado y aumento de las enzimas hepáticas;
- reacciones alérgicas incluyendo urticaria e inflamación en la boca;
- infección del tracto respiratorio inferior;
- aumento de los nódulos linfáticos;
- impotencia, flujo menstrual anormalmente fuerte o prolongado o falta de menstruación;
- problemas musculares como debilidad muscular y espasmos, dolor en las articulaciones, músculos y espalda;
- daño en los nervios del sistema nervioso periférico;
- sudores nocturnos, picores, sarpullido incluyendo bultos elevados en la piel, infección de la piel, inflamación de la piel o de los poros capilares, acumulación de fluído en las células y tejidos.
Poco frecuentes:pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 100 personas:
- sueños anormales;
- pérdida o cambio del sentido del gusto;
- pérdida de pelo;
- una alteración de su electrocardiograma (ECG ) llamada bloqueo auriculoventricular;
- acumulación de plaquetas en las arterias que puede llevar a un ataque cardíaco y accidente cerebrovascular;
- inflamación de los vasos y capilares sanguíneos;
- inflamación del conducto biliar;
- sacudidas incontrolables del cuerpo;
- estreñimiento;
- inflamación de las venas relacionada con un coágulo en la sangre;
- sequedad de boca;
- incapacidad para controlar los esfínteres;
- inflamación de la primera sección del intestino delgado justo después del estómago, herida o úlcera en el tracto digestivo, sangrado del tracto intestinal o recto;
- glóbulos rojos en la orina;
- amarilleamiento de la piel o del blanco de los ojos (ictericia);
- depósitos de grasa en el hígado, aumento del tamaño del hígado;
- falta de funcionalidad testicular;
- afloramiento repentino de los síntomas relacionados con una infección inactiva en su cuerpo (reconstitución inmune);
- aumento del apetito;
- aumento anormal del nivel de bilirrubina (un pigmento producido por la rotura de glóbulos rojos) en sangre;
- descenso del deseo sexual;
- inflamación del riñón;
- muerte de los huesos causada por un pobre suministro sanguíneo en la zona;
- llagas o úlceras bucales, inflamación del estómago y del intestino;
- fallo renal;
- rotura de las fibras musculares que ocasiona la liberación de los contenidos de dichas fibras (mioglobina) en el torrente sanguíneo;
- un sonido en un oído o en ambos oídos, como zumbidos, pitidos o silbidos;
- temblor;
- cierre anormal de una de las válvulas (válvula tricúspide del corazón);
- vértigo (sensación de girar);
- trastorno ocular, visión anormal;
- aumento de peso;
Raros:pueden afectar hasta 1 de cada 1.000 personas
- erupciones en la piel y ampollas graves o potencialmente mortales (síndrome de Stevens-Johnson y eritema multiforme)
Si considera que alguno de los efectos adversos que sufre es grave o si aprecia cualquier efecto adverso no mencionado en este prospecto, informe a su médico o farmacéutico.
Comunicación de efectos adversos
Si experimenta cualquier tipo de efecto adverso, consulte a su médico o farmacéutico, incluso si se trata de posibles efectos adversos que no aparecen en este prospecto. También puede comunicarlos directamente a través del Sistema Español de Farmacovigilancia de Medicamentos de Uso Humano: www.notificaRAM.es. Mediante la comunicación de efectos adversos usted puede contribuir a proporcionar más información sobre la seguridad de este medicamento.
5. Conservación de Kaletra
- Mantener este medicamento fuera de la vista y del alcance de los niños.
- No utilice este medicamento después de la fecha de caducidad que aparece en la caja después de CAD. La fecha de caducidad es el último día del mes que se indica.
¿Cómo debo conservar Kaletra y durante cuánto tiempo?
- Conservar en nevera (entre 2°C y 8°C).
- Conservación durante el uso: si se mantiene fuera de la nevera, no conservar a más de 25ºC y desechar el producto no utilizado después de 42 días (6 semanas). Se recomienda anotar en el envase la fecha en la que se ha sacado de la nevera.
- Conservar en el embalaje original y colocar la tapa del frasco despés de cada dosis. No transferir a ningún otro envase.
¿Cómo debo deshacerme del Kaletra no utilizado?
Los medicamentos no se deben tirar por los desagües ni a la basura. Pregunte a su farmacéutico cómo deshacerse de los envases y de los medicamentos que ya no necesita. De esta forma, ayudará a proteger el medio ambiente.
6. Contenido del envase e información adicional
Composición de Kaletra
Los principios activos son lopinavir y ritonavir.
Cada ml de Kaletra solución oral contiene 80 mg de lopinavir y 20 mg de ritonavir.
Los demás componentes son:
Etanol, jarabe de maíz con fructosa alta, propilenglicol, agua purificada, glicerol, povidona, saborizante Magnasweet-110 (mezcla de glicirrinato monoamónico y glicerol), sabor vainilla (contiene ácido p-hidroxibenzóico, p-hidroxibenzaldehido, ácido vainillínico, vainillina, heliotropina, etil vainillina), aceite de ricino polioxil 40 hidrogenado, saborizante caramelo de algodón (contiene etil maltol, etil vainillina, acetoína, dihidrocumarina, propilenglicol), acesulfame potásico, sacarina sódica, cloruro sódico, aceite de menta, citrato sódico, ácido cítrico, levomentol.
Aspecto del producto y contenido del envase
Kaletra solución oral se presenta en un frasco ámbar de 60 ml. Cada ml de Kaletra contiene 80 mg de lopinavir y 20 mg de ritonavir.
Están disponibles dos tamaños de envases de Kaletra solución oral:
- 120 ml (2 frascos x 60 ml) con 2 jeringas de 2 ml con graduaciones de 0.1 ml.
Para volúmenes de hasta 2 ml. Para volúmenes mayores está disponible un envase alternativo.
- 300 ml (5 frascos x 60 ml) con 5 jeringas de 5 ml con graduaciones de 0.1 ml.
Para volúmenes superiores a 2 ml. Para volúmenes más pequeños está disponible un envase alternativo.
Titular de la autorización de comercialización:
AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG, Knollstrasse, 67061 Ludwigshafen, Alemania
Responsable de la fabricación:
Aesica QueenboroughLtd, Queenborough, Kent ME11 5EL, Reino Unido
AbbVie Logistics B.V., Zuiderzeelaan 53, 8017 JV Zwolle, Países Bajos
AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG, Knollstrasse, 67061 Ludwigshafen, Germany
Pueden solicitar más información respecto a este medicamento dirigiéndose al representante local del titular de la autorización de comercialización.
België/Belgique/Belgien AbbVie SA Tél/Tel: +32 10 477811 | Lietuva AbbVie UAB Tel: +370 5 205 3023 |
???????? ???? ???? ???.: +359 2 90 30 430 | Luxembourg/Luxemburg AbbVie SA Belgique/Belgien Tél/Tel: +32 10 477811 |
Ceská republika AbbVie s.r.o. Tel: +420 233 098 111 | Magyarország AbbVie Kft. Tel.: +36 1 455 8600 |
Danmark AbbVie A/S Tlf: +45 72 30-20-28 | Malta V.J.Salomone Pharma Limited Tel: +356 22983201 |
Deutschland AbbVie Deutschland GmbH & Co. KG Tel: 00800 222843 33 (gebührenfrei) Tel: +49 (0) 611/1720-0 | Nederland AbbVie B.V. Tel: +31 (0)88 322 2843 |
Eesti AbbVie Biopharmaceuticals GmbH Eesti filiaal Tel: +372 6231011 | Norge AbbVie AS Tlf: +47 67 81 80 00 |
Ελλ?δα AbbVie ΦΑΡΜΑΚΕΥΤΙΚΗ Α.Ε. Τηλ: +30 214 4165 555 | Österreich AbbVie GmbH Tel: +43 1 20589-0 |
España AbbVie Spain, S.L.U. Tel: +34 91 384 09 10 | Polska AbbVie Polska Sp. z o.o. Tel.: +48 22 372 78 00 |
France AbbVie Tél: +33 (0)1 45 60 13 00 | Portugal AbbVie, Lda. Tel: +351 (0)21 1908400 |
Hrvatska AbbVie d.o.o. Tel: +385 (0)1 5625 501 | România AbbVie S.R.L. Tel: +40 21 529 30 35 |
Ireland AbbVie Limited Tel: +353 (0)1 4287900 | Slovenija AbbVie Biofarmacevtska družba d.o.o. Tel: +386 (1)32 08 060 |
Ísland Vistor hf. Tel: +354 535 7000 | Slovenská republika AbbVie s.r.o. Tel: +421 2 5050 0777 |
Italia AbbVie S.r.l. Tel: +39 06 928921 | Suomi/Finland AbbVie Oy Puh/Tel: +358 (0)10 2411 200 |
Κ?προς Lifepharma (Z.A.M.) Ltd Τηλ: +357 22 34 74 40 | Sverige AbbVie AB Tel: +46 (0)8 684 44 600 |
Latvija AbbVie SIA Tel: +371 67605000 | United Kingdom AbbVie Ltd Tel: +44 (0)1628 561090 |
Fecha de la última revisión de este prospecto:
La información detallada de este medicamento está disponible en la página web de la Agencia Europea de Medicamentos http://www.ema.europa.eu
- País de registro
- Principio activo
- Requiere recetaSí
- Fabricante
- Esta información es de carácter general y no sustituye la consulta con un profesional sanitario.
- Alternativas a KALETRA (80 MG + 20 MG)/ML SOLUCION ORALForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO, 100 mg / 25 mgPrincipio activo: lopinavir and ritonavirFabricante: Abbvie Deutschland Gmbh & Co. KgRequiere recetaForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO, 200 mg/ 50 mgPrincipio activo: lopinavir and ritonavirFabricante: Abbvie Deutschland Gmbh & Co. KgRequiere recetaForma farmacéutica: COMPRIMIDO, 100 mg/25 mgPrincipio activo: lopinavir and ritonavirFabricante: Viatris LimitedRequiere receta
Médicos online para KALETRA (80 MG + 20 MG)/ML SOLUCION ORAL
Comenta la dosis, los posibles efectos secundarios, interacciones, contraindicaciones o la revisión de receta de KALETRA (80 MG + 20 MG)/ML SOLUCION ORAL, sujeto a valoración médica y a la normativa local.
Preguntas frecuentes