
FENTANEST 0.05 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION


How to use FENTANEST 0.05 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Translated with AI
This page provides general information and does not replace a doctor’s consultation. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Seek urgent medical care if symptoms are severe.
Show originalContents of the leaflet
Introduction
Package Leaflet: Information for the Patient
Fentanest 0.05 mg/ml Solution for Injection
Fentanyl Citrate
Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information for you.
|
Contents of the pack:
- What is Fentanest and what is it used for
- What you need to know before you use Fentanest
- How to use Fentanest solution for injection
- Possible side effects
- Storage of Fentanest
- Contents of the pack and other information
1. What is Fentanest and what is it used for
Fentanest contains fentanyl as the active substance. It is a potent medicine for pain relief, belonging to the group of narcotic analgesics or opioids.
Fentanest is used:
- In general or local anesthesia, as a complementary narcotic analgesic.
- As premedication to help induce and maintain general and local anesthesia, when administered together with a neuroleptic medication (a medication that sedates the nervous system), such as droperidol.
- As an anesthetic with oxygen, in high-risk patients undergoing surgical interventions.
2. What you need to know before you use Fentanest
Do not use Fentanest
- If you are allergic to fentanyl or any of the other components of this medicine (listed in section 6).
- If you have known intolerance to this medicine or other morphine-like medications.
- If you have a head injury, increased intracranial pressure, or coma.
- If the patient is under 2 years of age.
Warnings and precautions
Consult your doctor, pharmacist, or nurse before starting to use Fentanest if:
You or a family member have ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription drugs, or illegal drugs ("addiction").
- You are a smoker.
- You have ever had mood problems (depression, anxiety, or personality disorder) or have been treated by a psychiatrist for another mental illness.
As with other potent opioids, respiratory depression(slow or weak breathing that cannot provide adequate ventilation and perfusion to the lungs) is dose-dependent and can be reversed with the use of a narcotic antagonist (such as naloxone). However, it may be necessary to administer additional doses of this antagonist, as respiratory depression can last longer than the action of the opioid antagonist. Deep analgesia is accompanied by marked respiratory depression that can persist or recur during the post-operative period. For this reason, patients must remain under adequate surveillance. Resuscitation equipment and narcotic antagonist medications must be available. Hyperventilation (faster and deeper breathing than normal) during anesthesia can alter the patient's response to carbon dioxide, affecting breathing in the post-operative period.
Muscle rigiditymay occur, including rigidity of the thoracic muscles, which can be prevented by taking the following measures: very slow intravenous injection (which is usually sufficient for low doses), premedication with benzodiazepines, and administration of muscle relaxants.
Non-epileptic myoclonic movements(sudden, involuntary movements) may occur.
If the patient does not receive sufficient amounts of an anticholinergic medication (medications that calm intestinal muscle spasms), or when fentanyl is associated with a non-vagolytic muscle relaxant, bradycardia(decrease in heart rate) may occur, and even cardiac arrest. Bradycardia can be treated with the administration of atropine.
Opioids can induce low blood pressure, especially in patients with a significant decrease in the normal amount of blood (hypovolemia). Appropriate measures must be taken to maintain stable blood pressure.
The use of rapid bolus injection of opioids should be avoided in patients with compromised cerebrovascular function; the transient decrease in mean arterial pressure has sometimes been accompanied by a transient reduction in cerebral perfusion in such patients.
If treatment is interrupted, withdrawal symptoms may appear. Inform your doctor or nurse if you think this is happening to you (see also section 4. Possible side effects).
Dependence and addiction
This medicine contains fentanyl, which is an opioid. It can cause dependence and/or addiction. |
Repeated use of opioid analgesics can make the medicine less effective (the person taking it gets used to it). It can also produce dependence and addiction, which can lead to potentially fatal overdose. It is essential that you consult your doctor if you are concerned about becoming dependent on Fentanest.
In particular, inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking:
- Certain pain medications for neuropathic pain (gabapentin and pregabalin).
Patients undergoing prolonged treatment with opioids or with a history of opioid dependence may require higher doses.
A dose reduction is recommended in elderly and debilitated patients. Careful dose adjustment of this medicine is necessary in patients with the following disorders: hypothyroidism (decreased levels of thyroid hormones), lung disease, respiratory depression, alcoholism, impaired renal or hepatic function. These patients also require prolonged post-operative monitoring.
In the simultaneous use of fentanyl and droperidol, the doctor should be aware of the characteristics of each medicine, especially the differences in the duration of action. The administration of these medicines at the same time increases the possibility of low blood pressure. Droperidol can cause uncontrolled body or face movements, which can be controlled with medications for Parkinson's disease.
Using Fentanest with other medicines
Tell your doctor or pharmacist that you are using or have recently used or may need to use any other medicines.
The simultaneous use of barbituric acid derivativeswith fentanyl should be avoided, as they can increase the depressant effect of fentanyl on respiration.
The simultaneous use of fentanyl with buprenorphine, nalbuphine, or pentazocine(medicines indicated for pain relief) is not recommended, as they can cause withdrawal symptoms in patients dependent on opioids.
The simultaneous use of Fentanest with medicines that slow down the activity of the central nervous system (other central nervous system depressants) can produce additive depressant effects, hypoventilation, and hypotension, and deep sedation or coma. Central nervous system depressants include:
- opioids,
- antipsychotics,
- hypnotics,
- general anesthetics,
- musculoskeletal relaxants,
- sedating antihistamines,
- alcoholic beverages.
Epinephrine should never be used as a vasoactive agent with fentanyl, as it can lead to low blood pressure.
Therefore, the simultaneous use of any of the aforementioned drugs and active substances requires patient monitoring.
It has been reported that MAO inhibitors(a certain group of antidepressant medications) increase the effect of narcotic analgesics, especially in patients with heart failure. Therefore, fentanyl should not be used during the 14 days following the interruption of treatment with this type of medication. It is generally recommended to suspend the administration of MAO inhibitors in the two weeks prior to any surgical intervention. However, several reports describe the use of fentanyl during surgical interventions in patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitors without any interactions occurring.
The simultaneous use of potent CYP3A4 inhibitors, e.g., ritonavir, ketoconazole, itraconazole, macrolide antibiotics, with fentanyl, could lead to an increase in fentanyl plasma concentrations, which could increase or prolong both therapeutic and adverse effects and could cause severe respiratory depression. In this situation, special care and patient observation are appropriate. The simultaneous use of ritonavir or other potent CYP3A4 inhibitors with fentanyl is not recommended, unless the patient is under constant monitoring.
The use of fentanyl in combination with sedative medicines such as benzodiazepines or related medicines increases the risk of drowsiness, breathing difficulties (respiratory depression), coma, and can be fatal. Therefore, concomitant use should only be considered when other treatment options are not possible.
However, if your doctor prescribes fentanyl together with sedative medicines, the dose and duration of concomitant treatment should be limited by your doctor.
Tell your doctor about all sedative medicines you are taking and follow your doctor's recommendations regarding the dose carefully. It may be useful to inform friends or family members so they are aware of the signs and symptoms mentioned above. Contact your doctor when you experience such symptoms.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding, and fertility
If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, or think you may be pregnant or are planning to have a baby, ask your doctor or pharmacist for advice before using this medicine.
The safety of using fentanyl during pregnancy has not been established. Fentanyl should not be used during pregnancy, unless clearly necessary. Prolonged use during pregnancy can cause withdrawal syndrome in the newborn.
Fentanyl should not be used during labor (including cesarean section) as it can cause respiratory depression in the newborn.
Fentanyl passes into breast milk and can cause sedation and respiratory depression in the newborn. Therefore, breastfeeding is not recommended during the 24 hours following administration of the medicine.
Driving and using machines
Do not drive or use tools or machines after receiving Fentanest, as this medicine can affect your ability to react. Your doctor will tell you how long you should wait before driving or using machines again.
Doping warnings
Athletes are informed that this medicine contains a component that can result in a positive doping test.
Fentanest contains sodium
This medicine contains less than 23 mg of sodium (1 mmol) per 2, 3, and 5 ml ampoule; i.e., it is essentially "sodium-free".
This medicine contains 35.4 mg of sodium (the main component of table salt) in each 10 ml ampoule. This is equivalent to 1.81% of the maximum recommended daily intake of sodium for an adult.
3. How to use Fentanest
Dosage
This medicine should be administered by a doctor or nurse. Your doctor will determine the most suitable dose for you based on your age, weight, general state of health, type of intervention, and use of other medicines.
Elderly and debilitated patients
The dose administered to elderly patients (65 years or older) or debilitated patients just before surgery is lower than that indicated for other adults. If the doctor considers it necessary, an additional dose can be administered later.
Children aged 2 years and older
The dose administered to children just before surgery depends on the child's weight. If the doctor considers it necessary, an additional dose can be administered later.
Adolescents from 12 to 17 years receive the same dose as adults.
Children under 2 years of age
There is no experience with the use of this medicine in children under 2 years of age. Therefore, it is not recommended to administer this medicine in this age group.
Patients with kidney problems
The doctor may decide to reduce the dose administered to patients with kidney problems.
Obese patients
The dose administered to obese patients just before surgery may be lower than that indicated for other adults. If the doctor considers it necessary, an additional dose can be administered later.
Method of administration
This medicine can be administered into a vein or into a muscle.
If you are given too much Fentanest
Since the administration of this medicine will be carried out in the hospital and will be performed by a doctor, it is unlikely that you will be given too much. However, consult your doctor or nurse if you think you have been given too much medicine or if you start to experience breathing difficulties, dizziness, or symptoms of low blood pressure or muscle rigidity. An overdose can also cause a brain disorder (known as toxic leukoencephalopathy).
If you have any further questions on the use of this medicine, ask your doctor or nurse.
4. Possible side effects
Like all medicines, this medicine can cause side effects, although not everybody gets them.
Very common(may affect more than 1 in 10 people):
- Drowsiness.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Nausea, vomiting, constipation.
- Sweating, itching.
Common(may affect up to 1 in 10 people):
- Sedation, nervousness, loss of appetite, depression.
- Dry mouth (xerostomia), discomfort in the upper abdomen (dyspepsia).
- Skin reactions at the application site.
Uncommon(may affect up to 1 in 100 people):
- Euphoria, amnesia, insomnia, hallucinations, agitation.
- Tremor, tingling sensation (paresthesia), speech disorders, muscle rigidity, myoclonus (involuntary, rapid, and irregular muscle movements).
- Tachycardia, bradycardia.
- Hypertension, hypotension.
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea), hypoventilation.
- Diarrhea.
- Acute skin rash (exanthema), skin redness (erythema).
- Urinary retention.
- Difficulty swallowing.
Rare(may affect up to 1 in 1,000 people):
- Arrhythmia.
- Vasodilation.
- Hiccup.
- Edema (swelling), feeling of cold.
Very rare(may affect up to 1 in 10,000 people):
- Severe allergic reaction (anaphylactic reaction).
- Delirium, excitement, asthenia, anxiety, confusion, sexual dysfunction, withdrawal symptoms.
- Clumsiness or loss of coordination (ataxia), convulsions (including clonic convulsions and grand mal convulsions).
- Decreased vision in one or both eyes (amblyopia).
- Respiratory depression, apnea.
- Flatulence with pain, intestinal obstruction.
- Pain in the urinary bladder (cystalgia), decreased urine production (oliguria).
Frequency not known(cannot be estimated from the available data):
- Development of tolerance and physical and psychological dependence with prolonged use of fentanyl.
- Delirium (symptoms may consist of a combination of agitation, restlessness, disorientation, confusion, fear, seeing or hearing things that do not really exist, sleep disturbances, nightmares).
- Withdrawal symptoms (may be manifested by the appearance of the following adverse effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, chills, tremor, and sweating).
Respiratory depression is the most serious effect of fentanyl.
Other side effects:
Laryngospasm.
After administration of fentanyl with another neuroleptic, such as droperidol, the following adverse reactions may occur: tremor, nervousness, post-operative hallucinatory experiences, and extrapyramidal symptoms.
Reporting of side effects
If you experience any side effects, talk to your doctor or pharmacist. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. You can also report side effects directly through the Spanish Pharmacovigilance System for Human Use Medicines: https://www.notificaram.es/. By reporting side effects, you can help provide more information on the safety of this medicine.
5. Storage of Fentanest
Keep out of the sight and reach of children.
No special storage conditions are required. Store in the original package to protect from light. Use immediately after opening.
Do not use this medicine after the expiry date stated on the package after "EXP". The expiry date is the last day of the month indicated.
Medicines should not be disposed of via wastewater or household waste. The disposal of unused medicine and all materials that have come into contact with it will be carried out in accordance with local regulations. This will help protect the environment.
6. Container Content and Additional Information
Fentanest Composition
- The active ingredient is fentanyl. Each ml of solution contains 0.0785 mg of fentanyl citrate, equivalent to 0.05 mg of fentanyl.
Each 2 ml ampoule contains 0.157 mg of fentanyl citrate, equivalent to 0.1 mg of fentanyl.
Each 3 ml ampoule contains 0.2355 mg of fentanyl citrate, equivalent to 0.15 mg of fentanyl.
Each 5 ml ampoule contains 0.3925 mg of fentanyl citrate, equivalent to 0.25 mg of fentanyl.
Each 10 ml ampoule contains 0.785 mg of fentanyl citrate, equivalent to 0.5 mg of fentanyl.
- The other components are sodium chloride and water for injection.
Product Appearance and Container Content
Boxes of 10 ampoules of 2 ml, 5 ampoules of 3 ml, 10 ampoules of 3 ml, 10 ampoules of 5 ml, or 10 ampoules of 10 ml.
Only some package sizes may be marketed.
The ampoules are transparent and contain a clear, colorless liquid.
Marketing Authorization Holder and Manufacturer
Kern Pharma, S.L.
Venus, 72 - Pol. Ind. Colón II
08228 Terrassa - Barcelona
Spain
Date of Last Revision of this Prospectus: March 2025
Detailed and updated information on this medication is available on the website of the Spanish Agency for Medicines and Health Products (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
This information is intended only for healthcare professionals:
Consult the Technical Data Sheet or summary of product characteristics for a complete description and other information.
Dosage and Administration
This medication should only be administered in an environment where respiratory function can be controlled and by professionals who can monitor respiratory function (see Technical Data Sheet section 4.4).
The dose of this medication should be determined individually based on age, body weight, physical condition, underlying pathological condition, use of other medications, and type of surgical intervention and anesthesia.
Adults
Pre-medication
As pre-medication (30 to 60 minutes before surgery), the usual dose is 0.7 to 1.4 μg/kg (0.014 to 0.028 mL/kg) of fentanest by intramuscular or slow intravenous route.
Use as analgesic supplement to local anesthesia
Fentanest injectable can be administered as a complementary analgesic to local anesthesia in doses of 0.35 to 1.4 μg/kg (0.007 to 0.028 mL/kg) by intramuscular or intravenous route.
Use as analgesic supplement to general anesthesia
Low doses: 2 μg/kg (0.04 mL/kg)
Fentanyl in low doses is very useful in "minor" but painful surgical interventions.
Moderate doses: 2-20 μg/kg (0.04-0.4 mL/kg)
When the surgical procedure is more complicated, it is necessary to administer a moderate dose.
The duration of action is dose-dependent.
High doses: 20-50 μg/kg (0.4-1 mL/kg)
During "major" surgical interventions where the procedure is more prolonged, the administration of doses 20-50 μg/kg (0.4-1 mL/kg) of fentanyl with nitrous oxide/oxygen has shown a buffering effect.
Your doctor will perform ventilation and postoperative observation.
Increments of 25-250 micrograms/kg (0.5-5 mL) can be administered based on what you need and the duration of the surgical intervention.
Use as anesthetic agent
When it is particularly important to reduce the response to surgical stimulus, doses of 50-100 μg/kg (1-2 mL/kg) can be administered by intramuscular or intravenous route with oxygen and a muscle relaxant. This technique provides anesthesia without the additional use of anesthetic agents.
In some cases, it may be necessary to administer doses up to 150 μg/kg (3 mL/kg) to achieve an anesthetic effect.
Fentanyl has been used in open-heart surgical procedures and certain major surgical interventions in patients for whom cardiac protection against excess oxygen is particularly indicated.
Use in Elderly and Debilitated Patients
As with other opioids, the dose administered in elderly or debilitated patients should be reduced.
Use in Children
For induction and maintenance of anesthesia in children from 2 to 12 years of age, it is recommended to reduce the dose to 2-3 μg/kg (0.04-0.06 mL/kg).
Use in Patients with Renal Insufficiency
Data obtained from a study in which fentanyl was administered intravenously in patients undergoing renal transplantation suggest that the elimination of fentanyl may be reduced in this patient population. If patients with renal impairment receive fentanyl, they should be closely monitored for signs of fentanyl toxicity and the dose reduced if necessary (see Dosage and Administration).
Obese Patients
In obese patients, there is a risk of overdose if the dose is calculated based on body weight. The dose for obese patients should be calculated based on lean body mass rather than just body weight.
Special Warnings and Precautions for Use
Like other potent opioids:
Respiratory depression is dose-related and can be reversed with the administration of a narcotic antagonist (naloxone), but it may be necessary to administer additional doses of this antagonist since respiratory depression could have a longer duration of action than opioid antagonists. Deep analgesia is accompanied by marked respiratory depression that can persist or reappear in the postoperative period. Therefore, patients should be subject to appropriate supervision. It is necessary to have resuscitation equipment and narcotic antagonists available.
Hyperventilation during anesthesia could modify the patient's response to CO2, affecting respiration during the postoperative period.
Muscle rigidity, including rigidity of the thoracic muscles, may occur, which can be avoided by taking the following measures: slow intravenous injection (which is usually sufficient for low doses), pre-medication with a benzodiazepine, and administration of muscle relaxants.
Non-epileptic (myo)clonic movements may occur.
Bradycardia and possibly asystole may occur if the patient receives insufficient anticholinergic medication or when Fentanest is combined with a non-vagolytic muscle relaxant. Bradycardia can be treated with atropine.
Opioids can cause hypotension, especially in patients with hypovolemia. Appropriate measures should be taken to maintain stable blood pressure.
Rapid bolus injection of opioids should be avoided in patients with altered cerebrovascular distensibility, as the transient reduction in mean arterial pressure has occasionally been accompanied by a transient reduction in cerebral blood flow in these patients.
Patients receiving prolonged treatment with opioids or with a history of opioid abuse may require higher doses.
If Fentanest is administered with droperidol, the physician should be aware of the properties of each medication, especially the difference in duration of action. The incidence of hypotension increases when this combination is administered. Droperidol may cause extrapyramidal symptoms that can be controlled with antiparkinsonian medications.
Pharmacological Dependence and Potential for Abuse
Tolerance, physical dependence, and psychological dependence can develop after repeated administration of opioids. The risks increase in patients with a personal history of substance abuse (including drug or alcohol abuse or addiction).
Withdrawal Syndrome
Repeated administration at short intervals over prolonged periods can lead to the development of a withdrawal syndrome after treatment is discontinued, which can manifest with the following adverse effects: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anxiety, chills, tremors, and sweating.
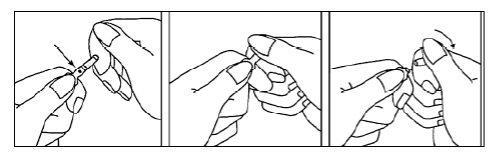
Instructions for Opening the Ampoules
- Hold the ampoule between the index and thumb fingers with the tip of the ampoule oriented upwards.
- Hold the tip of the ampoule by placing the index finger of the other hand against the neck of the ampoule. Place the thumb to cover the tip of the ampoule, as shown in the drawing.
- With the index fingers together, press on the tip to open the ampoule.
Incompatibilities
In the absence of compatibility studies, this medication should not be mixed with others.
Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity to the active ingredient or to any of the excipients included in section 6 of the technical data sheet, or to other opioids.
- Respiratory failure without mechanical ventilation, due to the specific respiratory depressant effect of morphine-like drugs.
- Country of registration
- Availability in pharmacies
Supply issue reported
Data from the Spanish Agency of Medicines (AEMPS) indicates a supply issue affecting this medicine.<br><br>Availability may be limited in some pharmacies.<br><br>For updates or alternatives, consult your pharmacist. - Active substance
- Prescription requiredYes
- Manufacturer
- This information is for reference only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a doctor before taking any medication. Oladoctor is not responsible for medical decisions based on this content.
- Alternatives to FENTANEST 0.05 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTIONDosage form: INJECTABLE, 50 microgramsActive substance: fentanylManufacturer: Laboratorios Basi Industria Farmaceutica S.A.Prescription requiredDosage form: INJECTABLE, 0.05 mg/mlActive substance: fentanylManufacturer: Kalceks AsPrescription requiredDosage form: SUBLINGUAL TABLET, 30 MICROGRAMSActive substance: sufentanilManufacturer: Laboratoire AguettantPrescription required
Online doctors for FENTANEST 0.05 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION
Discuss questions about FENTANEST 0.05 mg/ml INJECTABLE SOLUTION, including use, safety considerations and prescription review, subject to medical assessment and local regulations.
Frequently Asked Questions















