
OSMOHALE PÓ PARA INALAÇÃO (CÁPSULAS DURAS)
Pergunte a um médico sobre a prescrição de OSMOHALE PÓ PARA INALAÇÃO (CÁPSULAS DURAS)

Como usar OSMOHALE PÓ PARA INALAÇÃO (CÁPSULAS DURAS)
Introdução
Prospecto: informação para o utilizador
Osmohale pó para inalação (cápsulas duras)
manitol
Leia todo o prospecto atentamente antes de começar a tomar este medicamento, porque contém informações importantes para si.
- Conserva este prospecto, porque pode ter que voltar a lê-lo.
- Se tiver alguma dúvida, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
- Este medicamento foi prescrito apenas para si e não deve dá-lo a outras pessoas, mesmo que tenham os mesmos sintomas que si, porque pode prejudicá-las.
- Se experimentar efeitos adversos, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico, mesmo que se trate de efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Ver secção 4.
Conteúdo do prospecto
- O que é Osmohale e para que é utilizado
- O que precisa saber antes de começar a tomar Osmohale
- Como tomar Osmohale
- Possíveis efeitos adversos
- Conservação de Osmohale
- Conteúdo do envase e informações adicionais
1. O que é Osmohale e para que é utilizado
Osmohale é um testepara verificar se si tem sensibilidade nas vias respiratórias ou não.
Osmohale contém o princípio ativo manitol.
A sensibilidade nas vias respiratórias pode ser provocada por uma inflamação dessas, o que por vezes dificulta a respiração. As pessoas com sensibilidade nas vias respiratórias são frequentemente muito suscetíveis a factores ambientais, tais como o exercício, o pó, o fumo e outros factores irritantes.
O seu médico ou outro profissional de saúde especificamente treinado pedir-lhe-á que respire em Osmohale, utilizando um pequeno inhalador.
- Nas pessoas que efetivamentetêm sensibilidade nas vias respiratórias, estas estreitar-se-ão, e possivelmente lhes resultará mais difícil respirar.
- As pessoas que nãotêm sensibilidade nas vias respiratóriasnão experimentarão esse estreitamento delas ao respirar em Osmohale, e poderão continuar a respirar normalmente.
Como parte do teste, pedir-lhe-á que sople num tubo que medirá o efeito de Osmohale nos seus pulmões.
Este medicamento é utilizado exclusivamente para verificar se si tem sensibilidade nas vias respiratórias.
2. O que precisa saber antes de começar a tomar Osmohale
Não tome Osmohale
- se é alérgico(hipersensível) ao manitol ou a qualquer um dos outros componentes;
- se a sua capacidade pulmonarestá gravemente reduzida(isso será medido antes do teste);
- se atualmente tem ou teve um vaso sanguíneo distendido ou debilitado ao redor do coração ou do cérebro (aneurisma);
- se tem hipertensãoque não está controlada com medicação;
- se teve um infarto do miocárdionos últimos 6 meses;
- se teve um acidente vascular cerebralnos últimos 6 meses.
Advertências e precauções
Consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico antes de começar a tomar Osmohale.
- se a sua capacidade pulmonaré reduzida(isso será medido antes do teste);
- se anteriormente experimentou dificuldade para respirar,ou teve respiração sibilanteou tossedurante uma espirometria (estudo onde se sopla dentro de um instrumento de medição);
- se tosse com sangue;
- se tem ar no espaço pleural entre a parede torácica e os pulmões, o que provoca dor no peito e falta de ar (neumotórax);
- se recentemente foi submetido a cirurgia ocular, de estômagoou de tórax;
- se experimenta dor no peito (angina de peito);
- se tem problemas para realizar a espirometria(a pessoa que a realiza o informará);
- se teve uma infecçãonas vias respiratóriasnas últimas 2 semanas.
Se sofrer falta de ar, respiração sibilante e/ou tosse durante a espirometria, é possível que lhe seja administrado um medicamento para manter as suas vias respiratórias abertas, e o teste será interrompido.
Não faça exercícios vigorososno dia do teste, especialmente antes de realizá-lo, porque pode afetar os resultados.
Não fumedurante pelo menos 6 horas antes do teste, porque pode afetar os resultados.
Não tome Osmohale por conta própria. Osmohale apenas deve ser administrado num consultório ou laboratório adequado, por profissionais treinados e familiarizados com o uso de testes semelhantes e seus possíveis efeitos, sob a supervisão de um médico experiente.
Crianças e adolescentes
Não deve ser administrado Osmohale nem realizado o teste em crianças menores de 6 anos.
Não se recomenda Osmohale em pacientes de 6 a 18 anos de idade, devido à limitada informação disponível sobre o uso do medicamento nesta população.
Outros medicamentos e Osmohale
Informa ao seu médico ou farmacêutico se está a tomar, tomou recentemente ou possa ter que tomar qualquer outro medicamento.
Se está a utilizar outros medicamentos para o tratamento do asma ou alergias, é possível que tenha que suspender os mesmos antes do teste. Esses medicamentos podem afetar a reação do seu organismo a Osmohale. O seu médico indicar-lhe-á que medicamento(s) deve suspender, e por quanto tempo (em geral entre 6 horas e 4 dias antes do teste).
Uso de Osmohale com alimentos e bebidas
No dia do teste não beba café, chá nem bebidas cola, nem coma chocolate ou outros alimentos que contenham cafeína.
Gravidez, lactação e fertilidade
Não se submeta ao teste com Osmohale se está grávida.
Pode utilizar Osmohale durante a lactação.
Se está grávida ou em período de lactação, acredita que possa estar grávida ou tem intenção de engravidar, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico antes de utilizar este medicamento.
Condução e uso de máquinas
Não se observou qualquer efeito.
3. Como tomar Osmohale
Siga exatamente as instruções de administração deste medicamento indicadas pelo seu médico ou farmacêutico. Em caso de dúvida, consulte novamente o seu médico ou farmacêutico.
Adultos
Um médico ou outro profissional de saúde especialmente treinado administrará Osmohale mediante um inhalador e o acompanhará durante o desenvolvimento do teste. Não o deixará sozinho.
Não deve introduzir as cápsulas de Osmohale na boca nem engoli-las.
Realização do teste
- Ser-lhe-á pedido que se sente confortavelmente numa cadeira.
- Inicialmente ser-lhe-á pedido que sople com força num tubo (espirometria).
- A seguir ser-lhe-á colocada uma pinça nasal, de modo que apenas possa inspirar e expirar pela boca.
- Depois de expirar todo o ar, ser-lhe-á pedido que inspire profundamente o medicamento Osmohale, utilizando um inhalador especial.
- Ser-lhe-á indicado então que retenha a respiração durante cinco segundos antes de expirar.
- Ser-lhe-á retirada a pinça nasal, e ser-lhe-á pedido que respire normalmente.
- A seguir ser-lhe-á pedido que volte a soplar com força no tubo. Este teste mede o efeito de Osmohale nos seus pulmões.
- Os passos 3 a 7 podem ser repetidos um máximo de 9 vezes, com mais Osmohale dependendo do efeito nos seus pulmões (conforme medido no passo 7), até finalizar o teste.
- Uma vez finalizado o estudo, é possível que lhe seja administrado algum medicamento para ajudá-lo a respirar.
Se não tiver certeza sobre qualquer parte do teste, ou tiver alguma consulta sobre o medicamento, fale com o médico ou profissional de saúde especialmente treinado que realize o teste.
Se tomar mais Osmohale do que deve
Se pensar que talvez tenha sido administrada uma quantidade excessiva do medicamento, informe de imediato o médico ou profissional de saúde que está a realizar o teste. Se tomou demasiado Osmohale pode sentir que não consegue respirar, experimentar respiração sibilante ou tosse. O médico pode administrar-lhe oxigénio ou medicamentos para ajudá-lo a respirar.
4. Possíveis efeitos adversos
Como todos os medicamentos, este medicamento pode produzir efeitos adversos, embora nem todas as pessoas os sofram.
Lista de efeitos adversos
Frequentes(podem afetar 1 de cada 10 pessoas):
- Asma
- Falta de ar
- Opresão no peito
- Tosse
- Desejos de vomitar
- Cefaleia
- Dor de nariz e de garganta, molestias ao engolir
- Gotejo nasal
- Vómitos
Pouco frequentes(podem afetar 1 de cada 100 pessoas):
- Extremidades frias
- Diarréia
- Sensação de mareio
- Sensação de nervosismo
- Sensação de sede
- Sensação de cansaço
- Eritema e sudorese
- Ronquera
- Picazão e erupção cutânea
- Coceira nos olhos
- Redução de oxigénio no sangue
- Úlceras na boca
- Epistaxe (sangramento pelo nariz)
- Dor estomacal
- Dor muscular e articular
Comunicação de efeitos adversos
Se experimentar qualquer tipo de efeito adverso, consulte o seu médico ou farmacêutico, mesmo que se trate de possíveis efeitos adversos que não aparecem neste prospecto. Também pode comunicá-los directamente através do sistema nacional de notificação incluído no Apêndice V. Mediante a comunicação de efeitos adversos, pode contribuir para fornecer mais informações sobre a segurança deste medicamento.
5. Conservação de Osmohale
Mantenha este medicamento fora da vista e do alcance das crianças.
Não utilize este medicamento após a data de validade que aparece na caixa após CAD. A data de validade é o último dia do mês que se indica.
Não conserve a uma temperatura superior a 25°C.
Os medicamentos não devem ser jogados fora por meio dos esgotos nem pela lixeira. Deposite os envases e os medicamentos que não precisa no Ponto Sigre da farmácia. Em caso de dúvida, pergunte ao seu farmacêutico como se livrar dos envases e dos medicamentos que não precisa. Dessa forma, ajudará a proteger o meio ambiente.
6. Conteúdo do envase e informação adicional
Composição de Osmohale
O princípio ativo é manitol.
As cápsulas que são utilizadas para inalação contêm pó de manitol. Uma cápsula contém 0 mg, 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg ou 40 mg de manitol.
Aspecto do produto e conteúdo do envase
O pó é branco ou quase branco.
A cápsula vazia é transparente com duas bandas brancas impressas
A cápsula de 5 mg é metade branca e metade transparente, com a inscrição 5 mg.
A cápsula de 10 mg é metade amarela e metade transparente, com a inscrição 10 mg.
A cápsula de 20 mg é metade rosa e metade transparente, com a inscrição 20 mg.
As cápsulas de 40 mg são metade vermelhas e metade transparentes, com a inscrição 40 mg.
As cápsulas são apresentadas em blisters. Um equipamento para diagnóstico, embalado em uma caixa, consta de:
- 1 cápsula vazia
- 1 cápsula de 5 mg
- 1 cápsula de 10 mg
- 1 cápsula de 20 mg
- 15 cápsulas de 40 mg
- 1 inhalador
Titular da autorização de comercialização
Pharmaxis Europe Limited
108 Q House Furze Road,
Sandyford, Dublin 18,
D18AY29, Irlanda
Responsável pela fabricação
MIAS Pharma Limited
Suite 1 Stafford House
Strand Road, Portmarnock
Co. Dublin, D13 WC83
Irlanda
Arvato Supply Chain Solutions SE
Gottlieb-Daimler Straβe 1
33428 Harsewinkel
Renânia do Norte-Vestfália
Alemanha
Se tiver alguma consulta sobre este medicamento, dirija-se ao representante local do titular da autorização de comercialização:
Laboratório Aldo-União, S.L.
Baronesa de Maldá, 73
08950 Esplugues de LL.
Barcelona
Espanha
Tel: +34 93 372 71 11
Fax: +34 93 371 61 98
Este medicamento está autorizado nos estados membros do Espaço Económico Europeu com os seguintes nomes:
Aridol: Finlândia, Alemanha, Noruega, Suécia
Osmohale: Dinamarca, Irlanda, Países Baixos, Espanha, Reino Unido (Irlanda do Norte)
Data da última revisão deste prospecto:06/2022
A informação detalhada e atualizada deste medicamento está disponível no site da Agência Española del Medicamento y Productos Sanitarios (AEMPS) http://www.aemps.gob.es/
INFORMAÇÃO PARA MÉDICOS OU PROFISSIONAIS DE SAÚDE
Esta informação está destinada apenas a médicos ou profissionais do setor de saúde:
Contraindicações
Hipersensibilidade conhecida ao manitol ou a qualquer um dos componentes da cápsula.
Não deve ser administrado Osmohale a pacientes com limitação respiratória severa (FEV1 esperado <50% ou <1,0 l), ou afecções que possam ser comprometidas pela indução de broncoespasmos ou a repetição de manobras de soplado. Entre elas se incluem: aneurisma cerebral ou aórtico, hipertensão não controlada, infarto de miocárdio ou um acidente cerebrovascular nos seis meses anteriores.
Advertências e precauções especiais de emprego
Osmohale deve ser administrado exclusivamente por inalação. A inalação de manitol provoca broncoconstrição. A prova de inalação de Osmohale apenas deve ser realizada em clínicas ou laboratórios adequados, por um médico ou outro profissional de saúde devidamente capacitado para realizar provas de provocação bronquial e para manejar broncoespasmos agudos, e sob a supervisão de um médico experiente. O médico responsável, com a devida capacitação para tratar broncoespasmos agudos, o que inclui o uso apropriado do equipamento de reanimação, deve estar suficientemente perto para responder rapidamente a uma emergência. Deve-se contar com estetoscópio, esfigmomanómetro e oxímetro de pulso. Uma vez começada a administração de Osmohale, não deve deixar o paciente sem supervisão durante o procedimento.
Na área de realização da prova deve-se contar com medicamentos para o tratamento de broncoespasmos graves. Entre eles se incluem adrenalina para injeção subcutânea, e salbutamol ou outros agonistas beta em inhaladores com doses graduadas. Deve-se contar com oxigênio. Deve-se ter à disposição um nebulizador de pequeno volume para a administração de broncodilatadores.
Devem-se observar as precauções gerais para a realização de espirometrias e provas de provocação bronquial, incluídas precauções adicionais em pacientes com as seguintes condições: insuficiência respiratória (FEV1 basal inferior a 70% dos valores normais esperados ou um valor absoluto de 1,5 l ou menos em adultos), broncoconstrição induzida por espirometria, hemoptise de origem desconhecida, pneumotórax, cirurgia abdominal ou torácica recente, cirurgia intraocular recente, angina instável, incapacidade de realizar uma espirometria de qualidade aceitável ou infecção do trato respiratório inferior ou superior nas 2 semanas anteriores.
Se o paciente apresentar asma induzida pela espirometria, ou a queda do FEV1 for superior a 10% ante a administração contínua após a cápsula de 0 mg, deve-se aplicar uma dose padrão de broncodilatador e suspender a provocação com Osmohale.
Exercícios: O exercício físico vigoroso deve ser evitado por completo no dia da prova, pois pode afetar os resultados.
Fumar: Como fumar pode afetar os resultados da prova, recomenda-se que os pacientes se abstenham de fazê-lo durante um mínimo de 6 horas antes do estudo.
A prova de Osmohale não deve ser utilizada em pacientes menores de 6 anos de idade, devido à sua incapacidade de fornecer medições espirométricas reprodutíveis.
A informação sobre o uso de Osmohale em pacientes de 6 a 18 anos de idade é limitada; em consequência, não se recomenda o uso de Osmohale nesta população.
Não se investigaram os efeitos da repetição de provas com Osmohale em um período breve; em consequência, deve-se prestar especial consideração ao uso repetido de Osmohale.
Instruções para o dispositivo inhalador
Estas instruções mostram como utilizar o inhalador
- Retirada da tampa: Com ambas as mãos, segure o inhalador em posição vertical e retire a tampa.

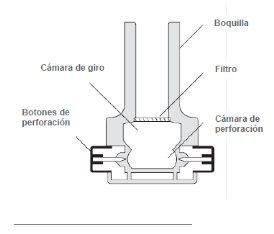
- Abertura: Segure firmemente a base do inhalador com uma mão, e abra o dispositivo girando a boquilla na direção da seta, tal como mostra a imagem.

- Carga: Certifique-se de ter as mãos secas; retire uma cápsula da caixa do inhalador e coloque-a no inhalador como mostra a ilustração.
Não tem importância de que lado se insere a cápsula na câmara.

- Fechamento: Mantendo o dispositivo em posição vertical, gire a boquilla para a posição de fechamento, até ouvir um “clic”.

- Perfuração da cápsula: Mantenha o inhalador em posição vertical e pressione simultaneamente a fundo os dois botões de perfuração localizados nos lados do dispositivo.
Faça-o apenas uma vez, pois perfurar a cápsula mais de uma vez poderia provocar que se rompa ou fragmente. A perfuração abre orifícios na cápsula, e permite que saia o pó durante a inalação.

- Preparação para a inalação: Incline o inhalador de modo que a boquilla fique ligeiramente para baixo em um ângulo de 45 graus, tal como mostra a figura seguinte, até que a cápsula caia dentro da câmara giratória. Mantenha o dispositivo inclinado desta forma e indique ao paciente que exhale completamente (fora do inhalador).

- Inalação: O paciente deve inclinar ligeiramente a cabeça para trás, e segurando o inhalador a 45 graus, leve-o à boca e ajuste os lábios à boquilla. Indique ao paciente que inspire rapidamente e profundamente para encher os pulmões. Em seguida, o paciente deve conter a respiração por cinco segundos.

Nota: Durante uma inalação correta, deve-se ouvir um som de “cascabel”, à medida que a cápsula gira dentro do inhalador.
- Exalação: Retire o inhalador da boca do paciente, e deixe que exhale e retome a respiração normal.

- Verificação: Para esvaziar, a cápsula de Osmohale deve girar dentro do inhalador. Se após a inalação a cápsula não se esvaziou, é possível que se requiera uma segunda inalação (com a mesma cápsula). Verifique a cápsula após cada inalação.

Tenha em conta:
O inhalador está projetado para UM SÓ USO (um dispositivo para cada prova de provocação), e não deve ser limpo durante a realização da prova.
Descarte o inhalador após cada provocação com Osmohale. O inhalador não deve ser esterilizado nem reutilizado, pois poderia comprometer a integridade dos resultados subsequentes da prova.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
LEIA O RESUMO DE CARACTERÍSTICAS DO PRODUTO COMPLETO ANTES DE REALIZAR ESTA PROVA DE PROVOCAÇÃO.
Para obter mais informações, comunique-se com:
Titular da autorização de comercialização:
Pharmaxis Europe Limited
108 Q House Furze Road,
Sandyford, Dublin 18,
D18AY29, Irlanda
Representante local:
Laboratório Aldo-União, S.L.
Baronesa de Maldá, 73
08950 Esplugues de LL.
Barcelona
Espanha
Tel: +34 93 372 71 11
Fax: +34 93 371 61 98
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
{Logo}
Instruções para a prova de provocação Osmohale
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Prova de provocação Osmohale
Inalador

Resultados da prova de provocação
Resultado positivo da prova de provocação com Osmohale
A resposta positiva com Osmohale é obtida de 2 formas:
uma queda ≥ 15% do FEV1 com respeito ao valor basal (usando o valor do FEV1 após a administração de 0 mg como comparador)
uma queda incremental ≥ 10% do FEV1 (entre doses consecutivas de Osmohale)
Resultado negativo da prova de provocação comOsmohale
Considera-se que a prova de provocação com Osmohale dá resultado negativo quando se administrou ao paciente uma dose acumulativa de 635 mg de Osmohale e seu FEV1 não diminuiu em um percentual ≥ 15% com respeito ao valor basal.
Equipamento
Equipamento de Osmohale(contém as cápsulas de Osmohale, o inhalador e o prospecto com instruções)
Espirômetro e boquilla
Pinça nasal
Temporizador(que possa ser configurado em 60 segundos)
Calculadora
Broncodilatador(por exemplo, salbutamol)
Deve-se contar com disponibilidade de oxigênio e demais equipamentos de emergência pertinentes, conforme os protocolos padrão para provas de provocação bronquial.
Pontos importantes para ter em conta
- O inhalador é para UM SÓ USO (um dispositivo para cada prova de provocação), e não deve ser limpo durante a realização da prova. Descarte o inhalador após cada provocação com Osmohale. O inhalador não deve ser esterilizado nem reutilizado, pois poderia comprometer a integridade dos resultados subsequentes da prova.
- Quando o paciente exhala durante a prova de provocação com Osmohale, certifique-se de que o faça LONGE do inhalador, para minimizar a umidade dentro do dispositivo.
- Ao perfurar a cápsula, faça-o apenas uma vez (pressionando totalmente ambos os botões em forma simultânea), pois uma nova perfuração poderia provocar a ruptura ou fragmentação da cápsula.
- O uso de luvas de borracha durante a administração da prova e a manipulação das cápsulas de Osmohale pode aumentar a estática e inibir o movimento das cápsulas dentro do inhalador.
- Se supõe que há um problema de estática, ou avisa que não se ouve o ruído da cápsula durante a inalação de Osmohale, dê um golpe firme sobre a base do inhalador com uma mão enquanto segura o inhalador com a outra (com a boquilla orientada para baixo em um ângulo de 45°). Isso garantirá que a cápsula se "desencaje" da câmara de perfuração e ingresse à câmara de giro.

- A inalação de Osmohale pode provocar tosse e/ou secura de garganta. Trata-se de um efeito adverso de rotina da prova de provocação bronquial.
Pode oferecer um copo de água ao paciente ao completar a prova.
- Nesta prova de provocação, o tempo é crucial, e requer que se estabeleça e mantenha um gradiente osmótico. Os intervalos prolongados entre as doses podem afetar a validade dos resultados, e devem ser evitados.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Directrizes para o procedimento
PASSO 1:Verifique que o paciente tenha suspendido os seguintes medicamentos (Veja a tabela seguinte).
Prazos recomendados para a suspensão de medicamentos.
A falta de suspensão dos medicamentos pode afetar os resultados da prova de provocação com Osmohale.
Os períodos recomendados para a suspensão dos medicamentos geralmente se baseiam na duração de sua ação.
Tempo de suspensão | Medicamento |
6-8 horas | AGENTES ANTIINFLAMATÓRIOS NÃO ESTEROIDES INALADOS por exemplo, cromoglicato de sódio, nedocromil sódico |
8 horas | AGONISTAS BETA2 DE AÇÃO RÁPIDA, por exemplo, salbutamol, terbutalina |
12 horas | CORTICOSTEROIDES INALADOS, por exemplo, beclometasona, budesonida, fluticasona |
12 horas | BROMURO DE IPRATROPIO |
24 horas | CORTICOSTEROIDES INALADOS MAIS AGONISTAS BETA2 DE EFEITO PROLONGADO por exemplo, fluticasona e salmeterol, budesonida e eformoterol |
24 horas | AGONISTAS BETA2 DE EFEITO PROLONGADO por exemplo, salmeterol, formoterol |
24 horas | TEOFILINA |
72 horas | BROMURO DE TIOTROPIO |
72 horas | ANTIHISTAMÍNICOS por exemplo, cetirizina, fexofenadina, loratadina |
4 dias | ANTAGONISTAS DOS RECEPTORES DE LEUCOTRIENOS por exemplo, montelukast |
Alimentos:A ingestão de quantidades significativas de café, chá, bebidas cola, chocolate ou outros alimentos que contenham cafeína pode diminuir a reatividade bronquial, e devem ser evitados por completo no dia do estudo.
Outros fatores que podem afetar os resultados:No dia da prova, não se deve fumar nem fazer exercícios físicos vigorosos, pois pode afetar os resultados.
PASSO 2:Para a prova, o paciente deve estar sentado. Explique o procedimento; inclua os requisitos para uma manobra de CVF e a medição do FEV1, e o tipo de fluxo inspiratório requerido para o inhalador. Faça uma demonstração, se necessário.
PASSO 3:Insira os dados do paciente no espirômetro (idade, altura, raça, data de nascimento, sexo, etc.).
PASSO 4:Determine o FEV1antes da prova de provocação. Peça ao paciente que execute uma manobra de CVF segundo as diretrizes da ATS/ERS, execute três manobras aceitáveis, das quais se reproduzam duas. Use o valor mais alto como FEV1 antes da prova. O FEV1 do paciente deve ser ≥ 70% do valor esperado.
Devem-se extremar precauções com os pacientes com um FEV1 de menos de 70% do valor esperado.
PASSO 5:Calcule o FEV1basal (0 mg)
- Retire a cápsula de 0 mg de Osmohale do blister, abra o inhalador (girando como indica a seta no dispositivo), insira a cápsula e feche o dispositivo.
- Perfure a cápsula apenas uma vez, pressionando os botões de cor a ambos os lados do inhalador.
- Peça ao paciente que se coloque a pinça nasal e respire pela boca.
- Incline o inhalador a 45° (com a boquilla para baixo). Verifique que a cápsula tenha passado da câmara de perfuração para a câmara de giro, mais próxima da boquilla.
Muitas vezes, pode-se ouvir como a cápsula cai para a frente, ou vê-la através dos orifícios a ambos os lados do dispositivo. Entregue o inhalador ao paciente, certificando-se de que o mantenha no mesmo ângulo.
- Verifique que o paciente esteja sentado em posição ereta. Peça ao paciente que exhale (fora do inhalador), que ajuste os lábios ao redor da boquilla do inhalador e que tome uma inspiração rápida e profunda até encher os pulmões. Durante uma inalação correta, deve-se ouvir um som de “cascabel”, à medida que a cápsula gira dentro do dispositivo.
- Ao final da inalação do paciente, inicie um temporizador de 60 segundos e peça ao paciente que contenha a respiração durante 5 segundos. Uma vez transcorridos os 5 segundos, indique ao paciente que exhale pela boca (longe do inhalador), se retire a pinça nasal e respire normalmente.
- Quando soar o temporizador aos 60 segundos, indique ao paciente de imediato que execute duas medições aceitáveis de FEV1. Estas medições devem estardentro de uma variabilidade de 0,15 l (150 ml). Se a variabilidade entre as leituras for superior a 0,15 l, indique ao paciente que execute outra medição do FEV1. Registre a leitura mais alta como o valor basal de FEV1. Se o valor mais alto do FEV1 for ≥ 10% inferior ao FEV1 anterior ao teste de provocação, não continue com ele.
- Calcule o FEV1 objetivo
Obtém-se um resultado positivo para o teste de provocação com Osmohale quando o FEV1 do paciente cai ≥ 15% em relação ao valor basal. Para calcular o FEV1 objetivo, multiplique o valor basal (a maior leitura obtida com 0 mg) obtido anteriormente por 0,85. Registre este valor.
PASO 6:Cápsula de 5 mg
- Insira a cápsula de 5 mg no inhalador e perfure-a como se indica no Passo 5.
- Repita os passos 5c – f precedentes.
- Após a inalação, retire a cápsula do inhalador e verifique se ela foi esvaziada por completo; caso contrário, deverá ser feita uma segunda inalação imediatamente.
- Carregue a cápsula de 10 mg como preparação para a próxima dose.
- Aos 60 segundos da inalação, imediatamente meça duas vezes o FEV1 do paciente (devem ser satisfeitos os critérios de aceitabilidade). Utilize o maior desses dois valores para calcular a variação do FEV1.
- Compare o valor do FEV1 com esta dose em relação ao FEV1 objetivo. Se o valor do FEV1 for inferior ou igual ao valor objetivo, ou se houve uma queda incremental ≥ 10% desde a dose anterior, o teste de provocação é positivo e está completo. Se não for, continue imediatamente com a próxima etapa de dosificação.
PASO 7:Cápsulas de 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg
Administre as doses de 10 mg, 20 mg e 40 mg conforme as instruções precedentes (no passo 6) para a dose de 5 mg.
PASO 8:Dose de 80 mg (2 cápsulas de 40 mg)
- Insira e perfure a primeira cápsula de 40 mg que compõe a dose de 80 mg.
- O paciente deverá inalar a dose da mesma forma que as anteriores, contendo a respiração durante 5 segundos e exalando.
- Retire a primeira cápsula de 40 mg do dispositivo e verifique se ela foi esvaziada por completo; caso contrário, deverá ser feita uma segunda inalação imediatamente. Faça isso após a administração de cada uma das cápsulas.
- Após a inalação, carregue a segunda cápsula de 40 mg e ofereça-a ao paciente imediatamente após a exalação.
- Indique ao paciente que inale a segunda cápsula imediatamente, para garantir que o efeito osmótico de Osmohale seja acumulativo.
- Ative o temporizador ao final da inalação da segunda cápsula.
- Indique ao paciente que contenha a respiração durante 5 segundos antes de exalar.
- Aos 60 segundos da inalação da segunda cápsula, imediatamente meça duas vezes o FEV1 do paciente (devem ser satisfeitos os critérios de aceitabilidade). Utilize o maior desses dois valores para calcular a variação do FEV1.
- Compare o valor do FEV1 com esta dose em relação ao FEV1 objetivo. Se o valor do FEV1 for inferior ou igual ao valor objetivo, ou se houve uma queda incremental ≥ 10%, o teste de provocação é positivo e está completo. Se não for, continue imediatamente com a próxima etapa de dosificação.
PASO 9:Primeira dose de 160 mg (4 cápsulas de 40 mg)
- Insira e perfure a primeira cápsula de 40 mg que compõe a dose de 160 mg.
- O paciente deverá inalar a dose da mesma forma que as anteriores, contendo a respiração durante 5 segundos e exalando.
- Retire a cápsula do dispositivo e verifique se ela foi esvaziada por completo; caso contrário, deverá ser feita uma segunda inalação imediatamente. Faça isso após a administração de cada uma das cápsulas.
- Após a inalação, carregue a segunda cápsula de 40 mg e ofereça-a ao paciente imediatamente após a exalação.
- O paciente deverá inalar o conteúdo da segunda cápsula, contendo a respiração durante 5 segundos e exalando.
5 segundos e exalar.
- Após a inalação, carregue a terceira cápsula de 40 mg e ofereça-a ao paciente imediatamente após a exalação.
- O paciente deverá inalar o conteúdo da terceira cápsula, contendo a respiração durante 5 segundos e exalando.
- Após a inalação, carregue a quarta cápsula de 40 mg e ofereça-a ao paciente imediatamente após a exalação.
- Indique ao paciente que inale a quarta cápsula imediatamente, para garantir que o efeito osmótico de Osmohale seja acumulativo.
- Ative o temporizador ao final da inalação da quarta cápsula.
- Indique ao paciente que contenha a respiração durante 5 segundos antes de exalar.
- Aos 60 segundos da inalação da quarta cápsula, imediatamente meça duas vezes o FEV1 do paciente (devem ser satisfeitos os critérios de aceitabilidade). Utilize o maior desses dois valores para calcular a variação do FEV1.
- Compare o valor do FEV1 com esta dose em relação ao FEV1 objetivo. Se o valor do FEV1 for inferior ou igual ao valor objetivo, ou se houve uma queda incremental ≥ 10% desde a dose anterior, o teste de provocação é positivo e está completo. Se não for, continue imediatamente com a próxima etapa de dosificação.
PASO 10:Segunda dose de 160 mg (4 cápsulas de 40 mg)
Administre a segunda dose de 160 mg conforme as instruções do passo 9 precedente.
PASO 11:Terceira dose de 160 mg (4 cápsulas de 40 mg)
Administre a terceira dose de 160 mg conforme as instruções do passo 9 precedente.
Ao finalizar esta dose, serão administrados 635 mg. Se não se obteve uma resposta positiva, o teste de provocação deverá ser considerado completo e com resultado negativo.
PASO 12:Após a finalização do teste de provocação, deverá ser administrado um broncodilatador ao paciente, e controlado durante 15 minutos para garantir que seu FEV1 tenha retornado a um valor compreendido em 5% do nível anterior ao teste. (Em caso de resultado negativo, a administração do broncodilatador é optativa).
- País de registo
- Disponibilidade em farmáciasProblema de disponibilidade reportado
- Substância ativa
- Requer receita médicaSim
- Fabricante
- Esta informação é apenas para referência e não constitui aconselhamento médico. Consulte sempre um médico antes de tomar qualquer medicamento. A Oladoctor não se responsabiliza por decisões médicas baseadas neste conteúdo.
- Alternativas a OSMOHALE PÓ PARA INALAÇÃO (CÁPSULAS DURAS)Forma farmacêutica: INJETÁVEL, 25 mg brometo de edrofônio/2 mlSubstância ativa: edrophoniumFabricante: Mana Pharma S.L.Requer receita médicaFabricante: Sociedad Española De Carburos Metalicos S.A.Requer receita médicaFabricante: Sociedad Española De Carburos Metalicos S.A.Requer receita médica
Médicos online para OSMOHALE PÓ PARA INALAÇÃO (CÁPSULAS DURAS)
Avaliação de posologia, efeitos secundários, interações, contraindicações e renovação da receita de OSMOHALE PÓ PARA INALAÇÃO (CÁPSULAS DURAS) – sujeita a avaliação médica e regras locais.














